Stroke ratio
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(August 2009) |
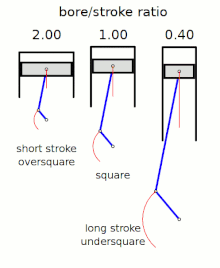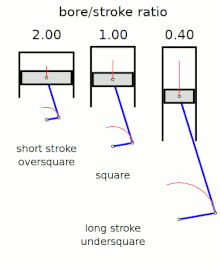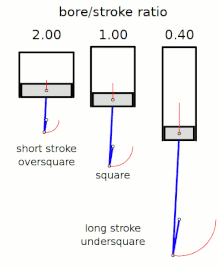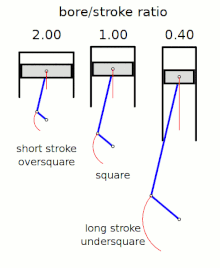
Stroke ratio,today universally defined asbore/stroke ratio,is a term to describe the ratio betweencylinder borediameter andpistonstrokelength in areciprocating piston engine.This can be used for either aninternal combustion engine,where the fuel is burned within the cylinders of the engine, orexternal combustion engine,such as asteam engine,where the combustion of the fuel takes placeoutsidethe working cylinders of the engine.
Conventions
[edit]The contemporary convention for describing thestroke ratioof apiston engine‘scylindersis itsbore/strokeratio.[1]
Stroke/boreratio is an obsolete expression dating to the early era of reciprocating engine development.[2]
Bore/stroke ratio
[edit]The diameter of thecylinder boreis divided by the length of thepistonstroketo give the ratio.
Square, oversquare and undersquare engines
[edit]The following terms describe the naming conventions for the configurations of the various bore/stroke ratio:
Square
[edit]Asquare enginehas equal boreandstroke dimensions, giving a bore/stroke value of exactly 1:1.
Square engine examples
[edit]This this section has too many examples. Notability of some exemplars needs to be established, and the list trimmed down substantially of its chaff.may containexcessiveorirrelevantexamples.(November 2023) |
1953 –Ferrari 250 EuropahadLampredi V12with 68.0 mm × 68.0 mm (2.7 in × 2.7 in) bore and stroke.
1967 – FIAT 125, 124Sport engine 125A000, 125B000, 125BC000, 1608 ccm, DOHC, 80.0 mm × 80.0 mm (3.15 in × 3.15 in) bore and stroke.
1970 – Ford400had a 101.6 mm × 101.6 mm (4.00 in × 4.00 in) bore and stroke.
1973 –Kawasaki Z1and KZ(Z)900 had a 66.0 mm × 66.0 mm (2.60 in × 2.60 in) bore and stroke.[3]
1982 -Honda Nighthawk 250andHonda CMX250CRebel have a 53.0 mm × 53.0 mm (2.09 in × 2.09 in) bore and stroke.[4]
1983 –MazdaFE 2.0Linline four-cylinder engine with a 86.0 mm × 86.0 mm (3.4 in × 3.4 in) bore and stroke.
1987 – The Opel/Vauxhall 2.0 LGM Family II enginesare square at 86.0 mm × 86.0 mm (3.39 in × 3.39 in) bore and stroke; example as C20XE C20NE C20LET X20A X20XEV X20XER Z20LET Z20LEH Z20LER A20NHT A20NFT.
1989 –Nissan'sSR20DEis a square engine, with an 86.0 mm × 86.0 mm (3.39 in × 3.39 in) bore and stroke.
1990–2010Saab B234/B235is a square engine, with a 90.0 mm × 90.0 mm (3.54 in × 3.54 in) bore and stroke.
1991 –Ford's 4.6V8 OHC engine has a 90.2 mm × 90.0 mm (3.552 in × 3.543 in) bore and stroke.
1995 – TheBMWM52engine with a displacement of 2793 cubic centimeters is an example of a perfect square engine with an 84.0 mm × 84.0 mm (3.31 in × 3.31 in) bore and stroke.
1996 – Jaguar'sAJ-V8engine in 4.0-litre form has an 86.0 mm bore and stroke.
2000 –Mercedes-Benz4.0-litre (3996 cc; 243.9 cu in)OM628V8 diesel engine is an example of a square engine – with an 86.0 mm × 86.0 mm (3.39 in × 3.39 in) bore and stroke.
Oversquare
[edit]An engine is described asoversquareorshort-strokeif its cylinders have a greater bore diameter than its stroke length, giving a bore/stroke ratio greater than 1:1.
An oversquare engine allows for more and larger valves in the head of the cylinder, higher possible rpm by lowering maximum piston speed, and lower crank stress due to the lower peak piston acceleration for the same engine (rotational) speed. Because these characteristics favor higher engine speeds, oversquare engines are often tuned to develop peak torque at a relatively high speed.
Due to the increased piston and head surface area, the heat loss increases as the bore/stroke ratio is increased. Thus an excessively high ratio can lead to a decreasedthermal efficiencycompared to other engine geometries. The large size/width of the combustion chamber at ignition can cause increased inhomogeneity in the air/fuel mixture during combustion, resulting in higher emissions.
The reduced stroke length allows for a shorter cylinder and sometimes a shorter connecting rod, generally making oversquare engines less tall but wider than undersquare engines of similarengine displacement.
Oversquare engine examples
[edit]Oversquare engines (a.k.a. "short stroke engines" ) are very common, as they allow higherrpm(and thus more power), without excessive piston speed.
Examples include both Chevrolet and Ford small-block V8s; theGMC 478V6 has a bore/stroke ratio of 1.33. The 1.6 litre version of theBMW N45gasoline engine has a bore/stroke ratio of 1.167.
Horizontally opposed, also known as "Boxer" or "flat", enginestypically feature oversquare designs since any increase in stroke length would result in twice the increase in overall engine width. This is particularly so inSubaru’s front-engine layout, where the steering angle of the front wheels is constrained by the width of the engine. TheSubaru EJ181 enginedevelops peak torque at speeds as low as 3200 rpm.
Nissan's RB, VQ, VK, VH and VR38DETT engines are all oversquare. Additionally,SR16VEengine found inNissan PulsarVZ-R and VZ-R N1 is an oversquare engine with 86 millimetres (3.39 in) bore and 68.7 millimetres (2.70 in) stroke, giving it 175–200 horsepower (130–150 kW) but relatively small torque of 119–134 pound-feet (161–182 N⋅m; 16.5–18.5 kg⋅m)
Extreme oversquare engines are found inFormula Oneracing cars, where strict rules limit displacement, thereby necessitating that power be achieved through high engine speeds. Stroke ratios approaching 2.5:1 are allowed,[a]enabling engine speeds of 18,000 rpm while remaining reliable for multiple races.[5]
TheDucati Panigalemotorcycle engineis extremely oversquare with a bore/stroke ratio of 1.84:1. It was given the name "SuperQuadro" byDucati,roughly translated as "super-square" from Italian.[6]
Theside-valveBelgianD-Motor LF26aero-enginehas a bore/stroke ratio of 1.4:1.[7]
EarlyMercedes-Benz M116 engineshad a 92 millimetres (3.62 in) bore and a 65.6 millimetres (2.58 in) stroke for a 3.5 litre V8.[8]
Undersquare
[edit]An engine is described asundersquareorlong-strokeif its cylinders have a smaller bore (width, diameter) than its stroke (length of piston travel) - giving a ratio value of less than 1:1.
At a given engine speed, a longer stroke increases engine friction and increases stress on the crankshaft due to the higher peak piston acceleration. The smaller bore also reduces the area available for valves in the cylinder head, requiring them to be smaller or fewer in number.
Undersquare engines often exhibit peak torque at lower rpm than an oversquare engine due to their smaller valves and high piston speed limiting their potential to rev higher.
Undersquare engines have become more common lately, as manufacturers push for more and more efficient engines and higher fuel economy.[clarify][9]
Undersquare engine examples
[edit]Many inline engines, particularly those mounted transversely in front-wheel-drive cars, utilize an undersquare design. The smaller bore allows for a shorter engine that increases room available for the front wheels to steer. Examples of this include manyVolkswagen,Nissan,Honda,andMazdaengines. The1KR-FE-engine used in theToyota Aygo,Citroën C1andPeugeot 107amongst others is an example of a modern long-stroke engine widely used inFF layoutcars. This engine has a bore and stroke of 71 mm × 84 mm (2.8 in × 3.3 in) stroke giving it a bore/stroke ratio of 0.845:1. Some rear-wheel-drive cars that borrow engines from front-wheel-drive cars (such as theMazda MX-5) use an undersquare design.
BMW's acclaimedS54B32M54 engine was undersquare with a bore and stroke of 87 mm × 91 mm (3.4 in × 3.6 in)), offering a world record torque-per-litre figure (114 N⋅m/L, 1.38 lb⋅ft/cu in) for normally-aspirated production engines at the time; this record stood until Ferrari unveiled the458 Italia.
ManyBritishautomobile companies used undersquare designs until the 1950s, largely because of a motor tax system thattaxed cars by their cylinder bore.This includes theBMC A-Series engine,and manyNissanderivatives. TheTrojan Carused an undersquare,split piston,two stroke,two-cylinder inline engine; this was partly for this tax advantage and partly because its proportions allowed flexing V-shaped connecting rods for the two pistons of each U-shaped cylinder, which was cheaper and simpler than two connecting rods joined with an additional bearing.
Their French and German competitors at the time also used undersquare designs even in absence of the tax reasoning, e. g.Renault Billancourt engineandOpel straight-6 engine.
The 225 cu in (3.7litre)Chrysler Slant-6 engineis undersquare, with a bore and stroke of 86 mm × 105 mm (3.4 in × 4.1 in) stroke (bore/stroke ratio = 0.819:1).
The Ford5.4L Modular Enginefeatures a bore and stroke of 90.1 mm × 105.8 mm (3.55 in × 4.17 in), which makes a bore/stroke ratio of 0.852:1. Since the stroke is significantly longer than the bore, the SOHC 16V (2-valve per cylinder) version of this engine is able to generate a peak torque of 350 lb·ft as low as 2501 rpm.
The Willys JeepL134andF134engines were undersquare, with a bore and stroke of 79.4 mm × 111.1 mm (3.13 in × 4.37 in) stroke (bore/stroke ratio = 0.714:1).
TheDodge Power Wagonused astraight-sixChrysler Flathead engineof 230 cu in (3.8 L) with a bore and stroke of 83 mm × 117 mm (3.3 in × 4.6 in), yielding a substantially undersquare bore/stroke ratio of 0.709:1.
The 4-litreBarra Inline 6andIntechengines from the AustralianFord Falcon,uses a bore and stroke of 92.21 mm × 99.31 mm (3.63 in × 3.91 in) stroke, which equates to a 0.929:1 bore-stroke ratio.
The 292 Chevrolet I6 is also undersquare, with a bore and stroke of 98.4 mm × 104.8 mm (3.875 in × 4.125 in) in (bore/stroke ratio = 0.939:1).
Mitsubishi's 4G63T engine found primarily in many generations ofMitsubishi Lancer Evolutionis an undersquare engine with a bore and stroke of 85 mm × 88 mm (3.3 in × 3.5 in).
TheJaguar XK6 engine,used in all 6-cylinder Jaguars from 1949 to 1987 was undersquare. For example, the 4.2 litre engine had a bore and stroke of 92.08 mm × 106 mm (3.63 in × 4.17 in), providing a bore/stroke ratio of 0.869:1.
Virtually all piston engines used in military aircraft were long-stroke engines. The PW R-2800, Wright R-3350,Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major,Rolls-Royce Merlin (1650), Allison V-1710, and Hispano-Suiza 12Y-Z are only a few of more than a hundred examples.
All diesel-powered ships have massively undersquare marine engines, usually usingcrossheads.AWärtsilätwo-stroke marine diesel enginehas a bore and stroke of 960 mm × 2,500 mm (37.8 in × 98.4 in), (bore/stroke ratio = 0.384:1).
While most modernmotorcycle enginesare square or oversquare, some are undersquare. TheKawasaki Z1300'sstraight-six enginewas made undersquare to minimise engine width, more recently, a newstraight-twin enginefor theHonda NC700 seriesused an undersquare design to achieve bettercombustion efficiencyin order to reduce fuel consumption.[10][11]
Notes
[edit]- ^There is no actual restriction on bore:stroke ratio, but cylinder bores are limited to 98 millimetres or 3.86 inches and capacity to 2,400 cubic centimetres (150 cu in).
References
[edit]- ^Bore/strokeis the more commonly used term, with usage inNorth America,Europe,United Kingdom,Asia,andAustralia.[citation needed]
- ^Ingram, Edward (April 1916)."As to the Matter of Stroke".Horseless Age.37(6 & 7): 275, 325.Retrieved12 November2015.
- ^"Kawasaki 900 Super Four".240 Landmarks of Japanese Automotive Technology.Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.Retrieved6 November2013.
Journalists and riders called it the king of motorcycles, and it gained a reputation as a super sport model all over the world. The Super Four boasted high performance and quality. This best-selling motorcycle won many prizes around the world within only six months of its release.
- ^"2013 Honda Rebel Specifications".Honda Media Newsroom.American Honda Motor Co. 4 September 2012.Retrieved25 March2014.
- ^"2011F1 Technical Regulations"(PDF).FIA.Retrieved21 July2011.
- ^"Ducati 1199 Panigale - Ducati".www.1199panigale.ducati.com.Retrieved9 April2018.
- ^"Price".Netherlands: D-Motor. Archived fromthe originalon 25 April 2012.
- ^"Mercedes Benz 350SL Technical Specifications".Archived fromthe originalon 31 August 2007.
- ^"2.0-liter Dynamic Force Engine, a New 2.0-liter Direct-injection, Inline 4-cylinder Gasoline Engine"(Press release). Japan: Toyota. 26 February 2018.Retrieved11 June2018.
- ^"Global 700cc Engine for Next-Generation: Technical details".Honda Worldwide.Honda Motor Co. 8 March 2012. p. 5.Retrieved25 March2014.
- ^Garrett, Jerry (14 September 2012)."Reality Check From Honda, in Touch With Economics".New York Times.Retrieved25 March2014.
