Temporal fascia
| Temporal fascia | |
|---|---|
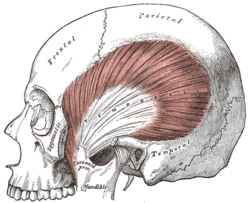 | |
 Muscles of the head, face, and neck. (Temporal fascia labeled at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fascia temporalis |
| TA98 | A04.1.04.013 |
| TA2 | 2138 |
| FMA | 76863 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Thetemporal fascia(ordeep temporal fascia[1]: 357 ) is afasciaof the head that covers thetemporalis muscleand structures situated superior to thezygomatic arch.[2]
The fascia is attached superiorly at thesuperior temporal line;inferiorly, it splits into two layers at the superior border of thezygomatic arch- the superficial layer then attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior border of the arch, and the deep layer to its medial aspect.[1]: 357
The space between the two layers is occupied byadipose tissueand contains a branch of thesuperficial temporal artery,and thezygomaticotemporal nerve.[1]: 357
Anatomy
[edit]The temporal fascia t is a strong fibrous investment.[citation needed]
Structure
[edit]Superiorly, it is a single layer, attached to the entire extent of thesuperior temporal line.[citation needed]
Inferiorly, where it is fixed to thezygomatic arch,it consists of two layers, one of which is inserted into the lateral, and the other into the medial border of the arch.[citation needed]
Contents
[edit]A small quantity of fat, the orbital branch of thesuperficial temporal artery,and a filament from thezygomatic branchof themaxillary nerve,are contained between the two layers created by the inferior split of the fascia.[citation needed]
Attachments
[edit]The superficial fibers of thetemporalis muscleattach onto the deep surface of the temporal fascia.[citation needed]
Relations
[edit]Superficial to the temporal fascia are theauricularis anterior muscleandsuperior auricular muscle,thegalea aponeurotica,and (part of) theorbicularis oculi muscle.[citation needed]
The superficial temporal vessels and theauriculotemporal nervecross it inferoposteriorly.[citation needed]
Theparotid fasciaproceeds to the temporal fascia.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^abcSinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011).Last's Anatomy(12th ed.).ISBN978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^Fehrenbach, Margaret J.; Herring, Susan W. (2017).Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck(5th ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier. p. 266.ISBN978-0-323-39634-9.
![]() This article incorporates text in thepublic domainfrompage 386of the 20th edition ofGray's Anatomy(1918)
This article incorporates text in thepublic domainfrompage 386of the 20th edition ofGray's Anatomy(1918)
