V1073 Scorpii
| Observation data EpochJ2000.0EquinoxJ2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Right ascension | 17h04m49.35254s[1] |
| Declination | −34° 07′ 22.5483″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude(V) | +4.87[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B0.7 Ia[3] |
| U−Bcolor index | −0.69[2] |
| B−Vcolor index | +0.26[2] |
| Variable type | α Cyg[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity(Rv) | 7.00[5]km/s |
| Proper motion(μ) | RA:+0.600[1]mas/yr Dec.:−2.015[1]mas/yr |
| Parallax(π) | 1.1161 ± 0.2097mas[1] |
| Distance | approx. 2,900ly (approx. 900pc) |
| Absolute magnitude(MV) | −6.8[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 28[7] 19.7±1.0[8] 27.11±8.39[9]M☉ |
| Radius | 36.0[6][3]R☉ |
| Luminosity | 302,000[6]L☉ |
| Surface gravity(logg) | 2.70[7] 2.65[3]cgs |
| Temperature | 20,800[9] 22,500[3]K |
| Rotational velocity(vsini) | 47[7]km/s |
| Age | 4.2±0.3[8]Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
V1073 Scorpiiis avariable starin theconstellationScorpius.It has a non-GreekBayer designationof k Scorpii. The star has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with anapparent visual magnitudethat fluctuates around +4.87.[2]Parallaxmeasurements yield a distance estimate of approximately 2,920ly(896pc) from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with aradial velocityof +7 km/s.[5]It has anabsolute magnitudeof −6.8[6]
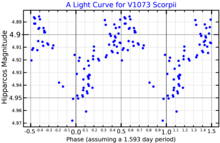
This object is a massivesupergiant starwith astellar classificationof B0.7 Ia.[3]It is anα Cygni variable;[12]a supergiant that pulsates erratically on a timescale of days to weeks with an amplitude of less than a tenth of a magnitude. A simplistic fitting of Hipparcos data suggests a periodicity of 1.6 days.[13][11]The star is around 4.2[8]million years old and is a member of the Upper Scorpius subgroup of the Sco OB2 association.[14]V1073 Scorpii is considered a "runaway" star, showing apeculiar velocityof more than 37 km/s relative to its neighbourhood.[8]No bow shock has been detected from its motion through interstellar space.[15]
V1073 Sco has a 14th magnitude visual companion,[16]which is an unrelated background object according to itsGaia Data Release 2parallax.[17]
References
[edit]- ^abcdeBrown, A. G. A.;et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018)."GaiaData Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties ".Astronomy & Astrophysics.616.A1.arXiv:1804.09365.Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G.doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051.Gaia DR2 record for this sourceatVizieR.
- ^abcdDucati, J. R. (2002). "Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system".CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues.2237.Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- ^abcdeKraus, M.; et al. (2009)."Parameters of galactic early B supergiants. The influence of the wind on the interstellar extinction determination".Astronomy and Astrophysics.499(1): 291.Bibcode:2009A&A...499..291K.doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810319.
- ^Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)".VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S.1.Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ^abKharchenko, N. V.; et al. (2007). "Astrophysical supplements to the ASCC-2.5: Ia. Radial velocities of ˜55000 stars and mean radial velocities of 516 Galactic open clusters and associations".Astronomische Nachrichten.328(9): 889.arXiv:0705.0878.Bibcode:2007AN....328..889K.doi:10.1002/asna.200710776.S2CID119323941.
- ^abcdCrowther, P. A.; et al. (2006). "Physical parameters and wind properties of galactic early B supergiants".Astronomy and Astrophysics.446(1): 279–293.arXiv:astro-ph/0509436.Bibcode:2006A&A...446..279C.doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053685.S2CID18815761.
- ^abcFraser, M.; et al. (2010)."Atmospheric parameters and rotational velocities for a sample of Galactic B-type supergiants".Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.404(3): 1306.arXiv:1001.3337.Bibcode:2010MNRAS.404.1306F.doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.16392.x.S2CID118674151.
- ^abcdTetzlaff, N.; et al. (2011)."A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun".Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.410(1): 190–200.arXiv:1007.4883.Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T.doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x.S2CID118629873.
- ^abHohle, M. M.; et al. (April 2010), "Masses and luminosities of O- and B-type stars and red supergiants",Astronomische Nachrichten,331(4): 349,arXiv:1003.2335,Bibcode:2010AN....331..349H,doi:10.1002/asna.200911355,S2CID111387483
- ^"9 Cet".SIMBAD.Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.Retrieved2020-12-02.
- ^abLefèvre, L.; et al. (2009)."A systematic study of variability among OB-stars based on HIPPARCOS photometry"(PDF).Astronomy and Astrophysics.507(2): 1141.Bibcode:2009A&A...507.1141L.doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200912304.
- ^Kazarovets, E. V.; et al. (1999). "The 74th Special Name-list of Variable Stars".Information Bulletin on Variable Stars.4659:1.Bibcode:1999IBVS.4659....1K.
- ^Koen, Chris; Eyer, Laurent (2002)."New periodic variables from the Hipparcos epoch photometry".Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.331(1): 45–59.arXiv:astro-ph/0112194.Bibcode:2002MNRAS.331...45K.doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05150.x.S2CID10505995.
- ^Brown, A.G.A.; Verschueren, W. (1997). "High S/N Echelle spectroscopy in young stellar groups. II. Rotational velocities of early-type stars in SCO OB2".Astronomy and Astrophysics.319:811.arXiv:astro-ph/9608089.Bibcode:1997A&A...319..811B.
- ^Peri, C. S.; et al. (2012). "E-BOSS: An Extensive stellar BOw Shock Survey. I. Methods and first catalogue".Astronomy & Astrophysics.538:A108.arXiv:1109.3689.Bibcode:2012A&A...538A.108P.doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201118116.S2CID62840857.
- ^Mason, Brian D.; et al. (2001)."The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog".The Astronomical Journal.122(6): 3466.Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M.doi:10.1086/323920.
- ^Brown, A. G. A.;et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018)."GaiaData Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties ".Astronomy & Astrophysics.616.A1.arXiv:1804.09365.Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G.doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051.Gaia DR2 record for this sourceatVizieR.