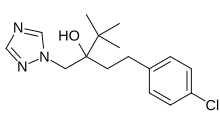
Tebuconazole
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(RS)- 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)- 4,4-dimethyl-3-(1H, 1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)pentan- 3-ol
| |
| Other names
(±)-1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-3-(1H, 1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)pentan-3-ol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.100.535 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H22ClN3O | |
| Molar mass | 307.82 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.249 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 102.4 °C (216.3 °F; 375.5 K) |
| 0.032 g/L at 20 °C | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tebuconazole is a triazole fungicide used agriculturally to treat plant pathogenic fungi.
Environmental Hazards
[edit]Though the U.S. Food and Drug Administration considers this fungicide to be safe for humans, it may still pose a risk. It is listed as a possible carcinogen in the United States Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pesticide Programs carcinogen list with a rating of C (possible carcinogen). Its acute toxicity is moderate.[2] According to the World Health Organization toxicity classification, it is listed as III, which means slightly hazardous.[citation needed]
Due to the potential for endocrine-disrupting effects, tebuconazole was assessed by the Swedish Chemicals Agency[3] as being potentially removed from the market by EU regulation 1107/2009.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Tebuconazole, - Archived 2011-04-29 at the Wayback Machine Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- ^ EPA regulation on Tebuconazole Archived 2006-04-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Interpretation of criteria for approval of active substances in the proposed EU plant protection regulation". Swedish Chemicals Agency (KemI). 2008-09-23. Archived from the original on 2009-01-01. Retrieved 2009-01-14.
- ^ "European regulation 1107/2009". 2009-10-21. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
