G
| G | |
|---|---|
| G g | |
 | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Sound values | |
| InUnicode | U+0047, U+0067, U+0261 |
| Alphabetical position | 7 |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Time period | ~−300 to present |
| Descendants | |
| Sisters | |
| Transliterations | C |
| Other | |
| Associated graphs | gh,g(x) |
| Writing direction | Left-to-right |
| ISO basic Latin Alpha bet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |
G,org,is the seventhletterof theLatin Alpha bet,used in themodern English Alpha bet,the Alpha bets of other western European languages, and others worldwide. Its name in English isgee(pronounced/ˈdʒiː/), pluralgees.[1]
Thelowercaseversion can be written in two forms: the single-storey (sometimes "opentail" )![]() and the double-storey (sometimes "looptail" )
and the double-storey (sometimes "looptail" )![]() .The former is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children.
.The former is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children.
History
| Egyptian | Phoenician gaml |
Western Greek Gamma |
Etruscan C |
Old Latin C |
Latin G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The evolution of the Latin Alpha bet's G can be traced back to the Latin Alpha bet's predecessor, theGreek Alpha bet.The voiced velar stop was represented by the third letter of the Greek Alpha bet,gamma (Γ),which was later adopted by theEtruscan language.Latin then borrowed this "rounded form" of gamma, C, to represent the same sound in words such asrecei,which was likely an early dative form ofrex,meaning "king", as found in an "early Latin inscription."[2]Over time, however, the letter C shifted to represent theunvoiced velarstop, leading to the displacement of the letter K. Scholars believe that this change can be attributed to the influence of the Etruscan language on Latin.[2]
Afterwards, the letter 'G' was introduced in theOld Latin periodas a variant of 'C' to distinguish voiced/ɡ/from voiceless/k/,and G was used to represent a voiced velar from this point on and C "stood for the unvoiced velar only".[2]
The recorded originator of 'G' isfreedmanSpurius Carvilius Ruga,who added letter G to the teaching of theRoman Alpha betduring the 3rd century BC:[3]he was the first Roman to open a fee-paying school, around 230BC.At this time, 'K' had fallen out of favor, and 'C', which had formerly represented both/ɡ/and/k/before open vowels, had come to express/k/in all environments.
Ruga's positioning of 'G' shows thatAlpha betic orderrelated to the letters' values asGreek numeralswas a concern even in the 3rd century BC. According to some records, the original seventh letter, 'Z', had been purged from the Latin Alpha bet somewhat earlier in the 3rd century BC by theRoman censorAppius Claudius,who found it distasteful and foreign.[4]Sampson (1985) suggests that: "Evidently the order of the Alpha bet was felt to be such a concrete thing that a new letter could be added in the middle only if a 'space' was created by the dropping of an old letter."[5]
George Hempl proposed in 1899 that there never was such a "space" in the Alpha bet and that in fact 'G' was a direct descendant ofzeta.Zeta took shapes like ⊏ in some of theOld Italic scripts;the development of themonumentalform 'G' from this shape would be exactly parallel to the development of 'C' fromgamma.He suggests that the pronunciation/k/>/ɡ/was due to contamination from the also similar-looking 'K'.[6]
Eventually, bothvelar consonants/k/and/ɡ/developedpalatalizedallophonesbefore front vowels; consequently in today'sRomance languages,⟨c⟩and⟨g⟩have different sound values depending on context (known ashard and soft Candhard and soft G). Because ofFrenchinfluence,English language orthographyshares this feature.
Typographic variants
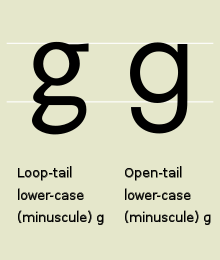
The modernlowercaseghas two typographic variants: the single-storey (sometimes "opentail" )![]() and the double-storey (sometimes "looptail" )
and the double-storey (sometimes "looptail" )![]() .The single-storey form derives from the majuscule (uppercase) form by raising theserifthat distinguishes it from 'c' to the top of the loop (thus closing the loop), and extending the vertical stroke downward and to the left. The double-storey form(
.The single-storey form derives from the majuscule (uppercase) form by raising theserifthat distinguishes it from 'c' to the top of the loop (thus closing the loop), and extending the vertical stroke downward and to the left. The double-storey form(![]() )had developed similarly, except that some ornate forms then extended the tail back to the right, and to the left again, forming a closedbowlor loop. The initial extension to the left was absorbed into the upper closed bowl. The double-storey version became popular when printing switched fromBlacklettertype toRoman type,because the tail was effectively shorter, making it possible to put more lines on a page. In the double-storey version, a small top stroke in the upper-right, often terminating in an orb shape, is called an "ear".
)had developed similarly, except that some ornate forms then extended the tail back to the right, and to the left again, forming a closedbowlor loop. The initial extension to the left was absorbed into the upper closed bowl. The double-storey version became popular when printing switched fromBlacklettertype toRoman type,because the tail was effectively shorter, making it possible to put more lines on a page. In the double-storey version, a small top stroke in the upper-right, often terminating in an orb shape, is called an "ear".
Generally, the two forms are complementary and interchangeable; the form displayed is atypefaceselection choice. InUnicode,the two appearances are generally treated as glyph variants with nosemanticdifference. Mostseriftypefaces use the looptail form (for example,g) and mostsans-seriftypefaces use the opentail form (for example,g) but thecode pointin both cases is U+0067. For applications where the single-storey variant must be distinguished (such as strictIPAin a typeface where the usual g character is double-storey), the characterU+0261ɡLATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT Gis available, as well as an upper case version,U+A7ACꞬLATIN CAPITAL LETTER SCRIPT G.
Occasionally the difference has been exploited to provide contrast. In theInternational Phonetic Alphabet,opentail⟨![]() ⟩has always represented avoiced velar plosive,while looptail⟨
⟩has always represented avoiced velar plosive,while looptail⟨![]() ⟩represented avoiced velar fricativefrom 1895 to 1900.[7][8]In 1948, the Council of theInternational Phonetic Associationrecognized ⟨ɡ⟩ and⟨
⟩represented avoiced velar fricativefrom 1895 to 1900.[7][8]In 1948, the Council of theInternational Phonetic Associationrecognized ⟨ɡ⟩ and⟨![]() ⟩as typographic equivalents,[9]and this decision was reaffirmed in 1993.[10]While the 1949Principles of the International Phonetic Associationrecommended the use of⟨
⟩as typographic equivalents,[9]and this decision was reaffirmed in 1993.[10]While the 1949Principles of the International Phonetic Associationrecommended the use of⟨![]() ⟩for a velar plosive and ⟨ɡ⟩ for an advanced one for languages where it is preferable to distinguish the two, such as Russian,[11]this practice never caught on.[12]The 1999Handbook of the International Phonetic Association,the successor to thePrinciples,abandoned the recommendation and acknowledged both shapes as acceptable variants.[13]
⟩for a velar plosive and ⟨ɡ⟩ for an advanced one for languages where it is preferable to distinguish the two, such as Russian,[11]this practice never caught on.[12]The 1999Handbook of the International Phonetic Association,the successor to thePrinciples,abandoned the recommendation and acknowledged both shapes as acceptable variants.[13]
In 2018, a study found that native English speakers have little conscious awareness of the looptail form(![]() ).The authors write: "Despite being questioned repeatedly, and despite being informed directly that G has two lowercase print forms, nearly half of the participants failed to reveal any knowledge of the looptail 'g', and only 1 of the 38 participants was able to write looptail 'g' correctly".[14][15]
).The authors write: "Despite being questioned repeatedly, and despite being informed directly that G has two lowercase print forms, nearly half of the participants failed to reveal any knowledge of the looptail 'g', and only 1 of the 38 participants was able to write looptail 'g' correctly".[14][15]
Use in writing systems
| Orthography | Phonemes | Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Afrikaans | /x/ | |
| Arabic romanization | /ɡ/ | |
| Azeri | /ɟ/ | |
| Catalan | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i |
| /(d)ʒ/ | Before e, i | |
| Standard Chinese(Pinyin) | /k/ | |
| Danish | /k/ | Except word-initially |
| /ɡ/ | Word-initially | |
| Dutch | /ɣ/or/χ/ | |
| English | /ɡ/ | Any |
| /dʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i in more recent loanwords from French | |
| silent | Some words, initial <gn>, and word-finally before a consonant | |
| Esperanto | /ɡ/ | |
| Faroese | /j/ | soft, lenited; seeFaroese phonology |
| /k/ | hard | |
| /tʃ/ | soft | |
| /v/ | after a, æ, á, e, o, ø and before u | |
| /w/ | after ó, u, ú and before a, i, or u | |
| silent | after a, æ, á, e, o, ø and before a | |
| Fi gian | /ŋ/ | |
| French | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |
| Galician | /ɡ/~/ħ/ | Except before e, i, seeGheadafor consonant variation |
| /ʃ/ | Before e, i, obsolete, replaced by⟨x⟩ | |
| Greek romanization | /ɡ/ | Except before ai, e, i, oi, y |
| /ɟ/ | Before ai, e, i, oi, y | |
| Icelandic | /c/ | soft |
| /k/ | hard | |
| /ɣ/ | hard, lenited; seeIcelandic phonology | |
| /j/ | soft, lenited | |
| Irish | /ɡ/ | Except after i or before e, i |
| /ɟ/ | After i or before e, i | |
| Italian | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i |
| /dʒ/ | Before e, i | |
| Malay | /g/ | |
| Norman | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i |
| /dʒ/ | Before e, i | |
| Norwegian | /ɡ/ | Except before ei, i, j, øy, y |
| /j/ | Before ei, i, j, øy, y | |
| Portuguese | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /ʒ/ | Before e, i, y | |
| Romanian | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i |
| /dʒ/ | Before e, i | |
| Romansh | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i |
| /dʑ/ | Before e, i | |
| Samoan | /ŋ/ | |
| Scottish Gaelic | /k/ | Except after i or before e, i |
| /kʲ/ | After i or before e, i | |
| Spanish | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i, y |
| /x/~/h/ | Before e, i, y | |
| Swedish | /ɡ/ | Except before ä, e, i, ö, y |
| /j/ | Before ä, e, i, ö, y | |
| Turkish | /ɡ/ | Except before e, i, ö, ü |
| /ɟ/ | Before e, i, ö, ü | |
| Vietnamese | /ɣ/ | |
| /z/ ~ /j/ | Before i |
English
In English, the letter appears either alone or in somedigraphs.Alone, it represents
- avoiced velar plosive(/ɡ/or "hard"⟨g⟩), as ingoose,gargoyle,andgame;
- avoiced palato-alveolar affricate(/d͡ʒ/or "soft"⟨g⟩), predominates before⟨i⟩or⟨e⟩,as ingiant,ginger,andgeology;or
- avoiced palato-alveolar sibilant(/ʒ/) in post-medieval loanwords from French, such asrouge,beige,genre(often), andmargarine(rarely)
⟨g⟩is predominantly soft before⟨e⟩(including the digraphs⟨ae⟩and⟨oe⟩),⟨i⟩,or⟨y⟩,and hard otherwise. It is hard in those derivations fromγυνή(gynḗ)meaning woman where initial-worded as such. Soft⟨g⟩is also used in many words that came into English from medieval church/academic use, French, Spanish, Italian or Portuguese – these tend to, in other ways in English, closely align to their Ancient Latin and Greek roots (such asfragile,logicormagic). There remain widely used a few English words of non-Romance origin where⟨g⟩is hard followed by⟨e⟩or⟨i⟩(get,give,gift), and very few in which⟨g⟩is soft though followed by⟨a⟩such asgaol,which since the 20th century is almost always written as "jail".
The double consonant⟨gg⟩has the value/ɡ/(hard⟨g⟩) as innugget,with very few exceptions:/d͡ʒ/inexaggerateandveggiesand dialectally/ɡd͡ʒ/insuggest.
The digraph⟨dg⟩has the value/d͡ʒ/(soft⟨g⟩), as inbadger.Non-digraph⟨dg⟩can also occur, in compounds likefloodgateandheadgear.
The digraph⟨ng⟩may represent:
- avelar nasal(/ŋ/) as inlength,singer
- the latter followed by hard⟨g⟩(/ŋɡ/) as injungle,finger,longest
Non-digraph⟨ng⟩also occurs, with possible values
- /nɡ/as inengulf,ungainly
- /nd͡ʒ/as insponge,angel
- /nʒ/as inmelange
The digraph⟨gh⟩(in many cases a replacement for the obsolete letteryogh,which took various values including/ɡ/,/ɣ/,/x/and/j/) may represent:
- /ɡ/as inghost,aghast,burgher,spaghetti
- /f/as incough,laugh,roughage
- ∅ (no sound) as inthrough,neighbor,night
- /x/inugh
- (rarely)/p/inhiccough
- (rarely)/k/ins'ghetti
Non-digraph⟨gh⟩also occurs, in compounds likefoghorn,pigheaded.
The digraph⟨gn⟩may represent:
- /n/as ingnostic,deign,foreigner,signage
- /nj/in loanwords likechampignon,lasagna
Non-digraph⟨gn⟩also occurs, as insignature,agnostic.
The trigraph⟨ngh⟩has the value/ŋ/as inginghamordinghy.Non-trigraph⟨ngh⟩also occurs, in compounds likestrongholdanddunghill.
G is thetenth least frequently used letterin the English language (afterY,P,B,V,K,J,X,Q,andZ), with a frequency of about 2.02% in words.
Other languages
MostRomance languagesand someNordic languagesalso have two main pronunciations for⟨g⟩,hard and soft. While the soft value of⟨g⟩varies in different Romance languages (/ʒ/inFrenchandPortuguese,[(d)ʒ]inCatalan,/d͡ʒ/inItalianandRomanian,and/x/in most dialects ofSpanish), in all except Romanian and Italian, soft⟨g⟩has the same pronunciation as the⟨j⟩.
In Italian and Romanian,⟨gh⟩is used to represent/ɡ/before front vowels where⟨g⟩would otherwise represent a soft value. In Italian and French,⟨gn⟩is used to represent thepalatal nasal/ɲ/,a sound somewhat similar to the⟨ny⟩in Englishcanyon.In Italian, thetrigraph⟨gli⟩,when appearing before a vowel or as the article and pronoungli,represents thepalatal lateral approximant/ʎ/.Other languages typically use⟨g⟩to represent/ɡ/,regardless of position.
Amongst European languages,Czech,Dutch,EstonianandFinnishare exceptions, as they do not have/ɡ/in their native words. InDutch,⟨g⟩represents avoiced velar fricative/ɣ/instead, a sound that does not occur in modern English, but there is a dialectal variation: many Netherlandic dialects use a voiceless fricative ([x]or[χ]) instead, and in southern dialects it may be palatal[ʝ].Nevertheless, word-finally, it is always voiceless in all dialects, including the standard Dutch of Belgium and the Netherlands. On the other hand, some dialects (likeAmelands) may have a phonemic/ɡ/.
Faroeseuses⟨g⟩to represent/dʒ/,in addition to/ɡ/,and also uses it to indicate aglide.
InMāori,⟨g⟩is used in the digraph⟨ng⟩which represents thevelar nasal/ŋ/and is pronounced like the⟨ng⟩insinger.
TheSamoanandFi gianlanguages use the letter⟨g⟩by itself for/ŋ/.
In olderCzechandSlovakorthographies,⟨g⟩was used to represent/j/,while/ɡ/was written as⟨ǧ⟩(⟨g⟩withcaron).
TheAzerbaijaniLatin Alpha bet uses⟨g⟩exclusively for the "soft" sound, namely/ɟ/.The sound/ɡ/is written as⟨q⟩.This leads to unusual spellings of loanwords:qram'gram',qrup'group',qaraj'garage',qallium'gallium'.
Other systems
In theInternational Phonetic Alphabet,⟨ɡ⟩represents thevoiced velar plosive.Thesmall caps⟨ɢ⟩represents thevoiced uvular plosive.
Other uses
- Unit prefixG, meaning 1,000,000,000 times.
Related characters
Ancestors, descendants and siblings
- 𐤂:SemiticletterGimel,from which the following symbols originally derive
- C c: Latin letterC,from which G derives
- Γ γ:GreekletterGamma,from which C derives in turn
- ɡ: Latin letterscript small G
- ᶢ:Modifier letter small script g is used for phonetic transcription[16]
- 𝼁: Latin small letter reversed script g, anextension to IPAfor disordered speech (extIPA)[17][18]
- ᵷ:Turned g
- 𝼂: Latin letter small capital turned g, anextension to IPAfor disordered speech (extIPA)[17][18]
- Г г:CyrillicletterGe
- Ȝ ȝ: Latin letterYogh
- Ɣ ɣ: Latin letterGamma
- Ᵹ ᵹ:Insular g
- ᫌ: Combining insular g, used in theOrmulum[19]
- Ꝿ ꝿ: Turned insular g
- Ꟑ ꟑ: Closed insular g, used in theOrmulum[19]
- ɢ: Latin letter small capital G, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent avoiced uvular stop
- 𐞒: Modifier letter small capital G, used as asuperscript IPA letter[20]
- ʛ: Latin letter small capital G with hook, used in the International Phonetic Alphabet to represent avoiced uvular implosive
- 𐞔: Modifier letter small capital G with hook, used as asuperscript IPA letter[20]
- 𐞓: Modifier letter small g with hook, used as asuperscript IPA letter[20]
- ᴳ ᵍ: Modifier letters are used in theUralic Phonetic Alphabet[21]
- ꬶ: Used for theTeuthonistaphonetic transcription system[22]
- G withdiacritics:Ǵ ǵǤ ǥĜ ĝǦ ǧĞ ğĢ ģƓ ɠĠ ġḠ ḡꞠ ꞡᶃ
- ց: Armenian Alpha betTso
Ligatures and abbreviations
- ₲-Paraguayan guaraní
- ㎏- thekilogramsymbol as a single character in theCJK Compatibilityblock
Other representations
Computing
| Preview | G | g | Ɡ | ɡ | G | g | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER G | LATIN SMALL LETTER G | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER SCRIPT G | LATIN SMALL LETTER SCRIPT G | FULLWIDTH LATIN CAPITAL LETTER G | FULLWIDTH LATIN SMALL LETTER G | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71 | U+0047 | 103 | U+0067 | 42924 | U+A7AC | 609 | U+0261 | 65319 | U+FF27 | 65351 | U+FF47 |
| UTF-8 | 71 | 47 | 103 | 67 | 234 158 172 | EA 9E AC | 201 161 | C9 A1 | 239 188 167 | EF BC A7 | 239 189 135 | EF BD 87 |
| Numeric character reference | G |
G |
g |
g |
Ɡ |
Ɡ |
ɡ |
ɡ |
G |
G |
g |
g |
| EBCDICfamily | 199 | C7 | 135 | 87 | ||||||||
| ASCII[a] | 71 | 47 | 103 | 67 | ||||||||
Other
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Golf |
|

|

| ||
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | American manual Alpha bet(ASLfingerspelling) | British manual Alpha bet(BSLfingerspelling) | Braille dots-1245 Unified English Braille |
See also
Notes
- ^Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
References
- ^The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language.1976.
- ^abcRay, Michael; Gaur, Aakanksha (2022-04-27)."G".Encyclopedia Britannica.Retrieved2023-05-08.
- ^Gnanadesikan, Amalia E. (2011-09-13).The Writing Revolution: Cuneiform to the Internet.John Wiley & Sons.ISBN9781444359855.
- ^Encyclopaedia Romana
- ^Everson, Michael; Sigurðsson, Baldur; Málstöð, Íslensk."Sorting the letter ÞORN".Evertype.ISO CEN/TC304. Archived fromthe originalon 2018-09-24.Retrieved2018-11-01.
- ^Hempl, George (1899). "The Origin of the Latin Letters G and Z".Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association.30.The Johns Hopkins University Press:24–41.doi:10.2307/282560.JSTOR282560.
- ^Association phonétique internationale (January 1895). "vɔt syr l alfabɛ" [Votes sur l' Alpha bet].Le Maître Phonétique.10(1): 16–17.JSTOR44707535.
- ^Association phonétique internationale (February–March 1900). "akt ɔfisjɛl" [Acte officiel].Le Maître Phonétique.15(2/3): 20.JSTOR44701257.
- ^Jones, Daniel (July–December 1948). "desizjɔ̃ ofisjɛl" [Décisions officielles].Le Maître Phonétique.26 (63) (90): 28–30.JSTOR44705217.
- ^International Phonetic Association (1993). "Council actions on revisions of the IPA".Journal of the International Phonetic Association.23(1): 32–34.doi:10.1017/S002510030000476X.S2CID249420050.
- ^International Phonetic Association (1949).The Principles of the International Phonetic Association.Department of Phonetics,University College, London.Supplement toLe Maître Phonétique91, January–June 1949.JSTORi40200179.
- Reprinted inJournal of the International Phonetic Association40 (3), December 2010, pp. 299–358,doi:10.1017/S0025100311000089.
- ^Wells, John C. (6 November 2006)."Scenes from IPA history".John Wells's phonetic blog.Department of Phonetics and Linguistics, University College London.Archivedfrom the original on 13 June 2018.Retrieved29 March2018.
- ^International Phonetic Association (1999).Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A Guide to the Use of the International Phonetic Alphabet.Cambridge:Cambridge University Press.p. 19.ISBN0-521-63751-1.
- ^Wong, Kimberly; Wadee, Frempongma; Ellenblum, Gali; McCloskey, Michael (2 April 2018). "The Devil's in the g-tails: Deficient letter-shape knowledge and awareness despite massive visual experience".Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance.44(9): 1324–1335.doi:10.1037/xhp0000532.PMID29608074.S2CID4571477.
- ^Dean, Signe (4 April 2018)."Most People Don't Know What Lowercase 'G' Looks Like And We're Not Even Kidding".Science Alert.Archivedfrom the original on 8 April 2018.Retrieved7 April2018.
- ^Constable, Peter (2004-04-19)."L2/04-132 Proposal to add additional phonetic characters to the UCS"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2017-10-11.Retrieved2018-03-24.
- ^abMiller, Kirk; Ball, Martin (2020-07-11)."L2/20-116R: Expansion of the extIPA and VoQS"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2020-10-24.
- ^abAnderson, Deborah (2020-12-07)."L2/21-021: Reference doc numbers for L2/20-266R" Consolidated code chart of proposed phonetic characters "and IPA etc. code point and name changes"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2021-01-08.
- ^abEverson, Michael; West, Andrew (2020-10-05)."L2/20-268: Revised proposal to add ten characters for Middle English to the UCS"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2020-10-24.
- ^abcMiller, Kirk; Ashby, Michael (2020-11-08)."L2/20-252R: Unicode request for IPA modifier-letters (a), pulmonic"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2021-07-30.
- ^Everson, Michael;et al. (2002-03-20)."L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2018-02-19.Retrieved2018-03-24.
- ^Everson, Michael; Dicklberger, Alois; Pentzlin, Karl; Wandl-Vogt, Eveline (2011-06-02)."L2/11-202: Revised proposal to encode" Teuthonista "phonetic characters in the UCS"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2017-10-11.Retrieved2018-03-24.
External links
 Media related toGat Wikimedia Commons
Media related toGat Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition ofGat Wiktionary
The dictionary definition ofGat Wiktionary The dictionary definition ofgat Wiktionary
The dictionary definition ofgat Wiktionary- Lewis and ShortLatin Dictionary:G