2 41polytope
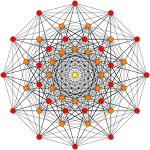 421 |
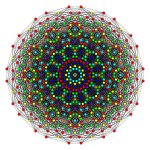 142 |
 241 |
 Rectified 421 |
 Rectified 142 |
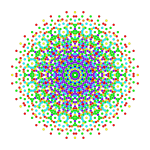 Rectified 241 |
 Birectified 421 |
 Trirectified 421 | |
| Orthogonal projectionsin E6Coxeter plane | ||
|---|---|---|
In 8-dimensionalgeometry,the241is auniform 8-polytope,constructed within the symmetry of theE8group.
ItsCoxeter symbolis241,describing its bifurcatingCoxeter-Dynkin diagram,with a single ring on the end of the 2-node sequences.
Therectified 241is constructed by points at the mid-edges of the241.Thebirectified 241is constructed by points at the triangle face centers of the241,and is the same as therectified 142.
These polytopes are part of a family of 255 (28− 1) convexuniform polytopesin 8-dimensions, made ofuniform polytopefacets, defined by all permutations of rings in thisCoxeter-Dynkin diagram:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
241polytope
[edit]| 241polytope | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform8-polytope |
| Family | 2k1polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,3,34,1} |
| Coxeter symbol | 241 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| 7-faces | 17520: 240231 17280{36} |
| 6-faces | 144960: 6720221 138240{35} |
| 5-faces | 544320: 60480211 483840{34} |
| 4-faces | 1209600: 241920{201 967680{33} |
| Cells | 1209600{32} |
| Faces | 483840{3} |
| Edges | 69120 |
| Vertices | 2160 |
| Vertex figure | 141 |
| Petrie polygon | 30-gon |
| Coxeter group | E8,[34,2,1] |
| Properties | convex |
The241is composed of 17,520facets(240231polytopes and 17,2807-simplices), 144,9606-faces(6,720221polytopes and 138,2406-simplices), 544,320 5-faces (60,480211and 483,8405-simplices), 1,209,6004-faces(4-simplices), 1,209,600 cells (tetrahedra), 483,840faces(triangles), 69,120edges,and 2160vertices.Itsvertex figureis a7-demicube.
This polytope is a facet in theuniform tessellation, 251withCoxeter-Dynkin diagram:
Alternate names
[edit]- E. L. Eltenamed it V2160(for its 2160 vertices) in his 1912 listing of semiregular polytopes.[1]
- It is named241byCoxeterfor its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of the 2-node sequence.
- Diacositetracont-myriaheptachiliadiacosioctaconta-zetton(Acronym Bay) - 240-17280 facetted polyzetton (Jonathan Bowers)[2]
Coordinates
[edit]The 2160 vertices can be defined as follows:
- 16 permutations of (±4,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) of (8-orthoplex)
- 1120 permutations of (±2,±2,±2,±2,0,0,0,0) of (trirectified 8-orthoplex)
- 1024 permutations of (±3,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1)with an odd number of minus-signs
Construction
[edit]It is created by aWythoff constructionupon a set of 8hyperplanemirrors in 8-dimensional space.
The facet information can be extracted from itsCoxeter-Dynkin diagram:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the node on the short branch leaves the7-simplex:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .There are 17280 of these facets
.There are 17280 of these facets
Removing the node on the end of the 4-length branch leaves the231,![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .There are 240 of these facets. They are centered at the positions of the 240 vertices in the421polytope.
.There are 240 of these facets. They are centered at the positions of the 240 vertices in the421polytope.
Thevertex figureis determined by removing the ringed node and ringing the neighboring node. This makes the7-demicube,141,![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Seen in aconfiguration matrix,the element counts can be derived by mirror removal and ratios ofCoxeter grouporders.[3]
| Configuration matrix | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E8 | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | f7 | k-figure | notes | |||||
| D7 | ( ) | f0 | 2160 | 64 | 672 | 2240 | 560 | 2240 | 280 | 1344 | 84 | 448 | 14 | 64 | h{4,3,3,3,3,3} | E8/D7= 192*10!/64/7! = 2160 | |
| A6A1 | { } | f1 | 2 | 69120 | 21 | 105 | 35 | 140 | 35 | 105 | 21 | 42 | 7 | 7 | r{3,3,3,3,3} | E8/A6A1= 192*10!/7!/2 = 69120 | |
| A4A2A1 | {3} | f2 | 3 | 3 | 483840 | 10 | 5 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 2 | {}x{3,3,3} | E8/A4A2A1= 192*10!/5!/3!/2 = 483840 | |
| A3A3 | {3,3} | f3 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1209600 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 1 | {3,3}V( ) | E8/A3A3= 192*10!/4!/4! = 1209600 | |
| A4A3 | {3,3,3} | f4 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 241920 | * | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 0 | {3,3} | E8/A4A3= 192*10!/5!/4! = 241920 | |
| A4A2 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | * | 967680 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | {3}V( ) | E8/A4A2= 192*10!/5!/3! = 967680 | |||
| D5A2 | {3,3,31,1} | f5 | 10 | 40 | 80 | 80 | 16 | 16 | 60480 | * | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | {3} | E8/D5A2= 192*10!/16/5!/2 = 40480 | |
| A5A1 | {3,3,3,3} | 6 | 15 | 20 | 15 | 0 | 6 | * | 483840 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | { }V( ) | E8/A5A1= 192*10!/6!/2 = 483840 | ||
| E6A1 | {3,3,32,1} | f6 | 27 | 216 | 720 | 1080 | 216 | 432 | 27 | 72 | 6720 | * | 2 | 0 | { } | E8/E6A1= 192*10!/72/6! = 6720 | |
| A6 | {3,3,3,3,3} | 7 | 21 | 35 | 35 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 7 | * | 138240 | 1 | 1 | E8/A6= 192*10!/7! = 138240 | |||
| E7 | {3,3,33,1} | f7 | 126 | 2016 | 10080 | 20160 | 4032 | 12096 | 756 | 4032 | 56 | 576 | 240 | * | ( ) | E8/E7= 192*10!/72!/8! = 240 | |
| A7 | {3,3,3,3,3,3} | 8 | 28 | 56 | 70 | 0 | 56 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 8 | * | 17280 | E8/A7= 192*10!/8! = 17280 | |||
Visualizations
[edit]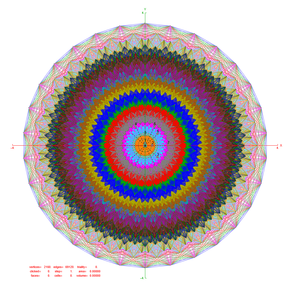

- u = (1,φ,0, −1,φ,0,0,0)
- v = (φ,0, 1,φ,0, −1,0,0)
- w = (0, 1,φ,0, −1,φ,0,0)

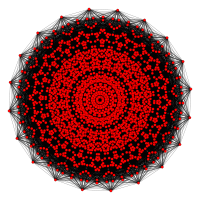
| E8 [30] |
[20] | [24] |
|---|---|---|
 (1) |
|

|
| E7 [18] |
E6 [12] |
[6] |

|
 (1,8,24,32) |

|
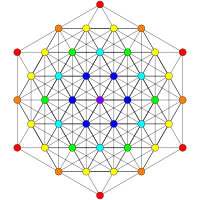
Petrie polygonprojections are 12, 18, or 30-sided based on the E6, E7, and E8 symmetries (respectively). The 2160 vertices are all displayed, but lower symmetry forms have projected positions overlapping, shown as different colored vertices. For comparison, a B6 coxeter group is also shown.
| D3 / B2 / A3 [4] |
D4 / B3 / A2 [6] |
D5 / B4 [8] |
|---|---|---|

|

|

|
| D6 / B5 / A4 [10] |
D7 / B6 [12] |
D8 / B7 / A6 [14] |

|
 (1,3,9,12,18,21,36) |

|
| B8 [16/2] |
A5 [6] |
A7 [8] |

|
|

|
Related polytopes and honeycombs
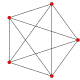
[edit]| 2k1figuresinndimensions | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space | Finite | Euclidean | Hyperbolic | ||||||||
| n | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |||
| Coxeter group |
E3=A2A1 | E4=A4 | E5=D5 | E6 | E7 | E8 | E9== E8+ | E10== E8++ | |||
| Coxeter diagram |
|||||||||||
| Symmetry | [3−1,2,1] | [30,2,1] | [[31,2,1]] | [32,2,1] | [33,2,1] | [34,2,1] | [35,2,1] | [36,2,1] | |||
| Order | 12 | 120 | 384 | 51,840 | 2,903,040 | 696,729,600 | ∞ | ||||
| Graph | 
|
|

|

|

|

|
- | - | |||
| Name | 2−1,1 | 201 | 211 | 221 | 231 | 241 | 251 | 261 | |||
Rectified 2_41 polytope
[edit]| Rectified 241polytope | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform8-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | t1{3,3,34,1} |
| Coxeter symbol | t1(241) |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| 7-faces | 19680 total: |
| 6-faces | 313440 |
| 5-faces | 1693440 |
| 4-faces | 4717440 |
| Cells | 7257600 |
| Faces | 5322240 |
| Edges | 19680 |
| Vertices | 69120 |
| Vertex figure | rectified 6-simplexprism |
| Petrie polygon | 30-gon |
| Coxeter group | E8,[34,2,1] |
| Properties | convex |
Therectified 241is arectificationof the 241polytope, with vertices positioned at the mid-edges of the 241.
Alternate names
[edit]- Rectified Diacositetracont-myriaheptachiliadiacosioctaconta-zetton for rectified 240-17280 facetted polyzetton (known as robay for short)[4][5]
Construction
[edit]It is created by aWythoff constructionupon a set of 8hyperplanemirrors in 8-dimensional space, defined by root vectors of theE8Coxeter group.
The facet information can be extracted from itsCoxeter-Dynkin diagram:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the node on the short branch leaves therectified 7-simplex:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the node on the end of the 4-length branch leaves therectified 231,![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the node on the end of the 2-length branch leaves the7-demicube,141![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Thevertex figureis determined by removing the ringed node and ringing the neighboring node. This makes therectified 6-simplexprism,![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Visualizations
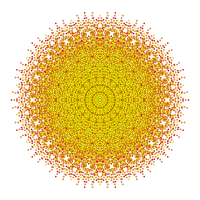
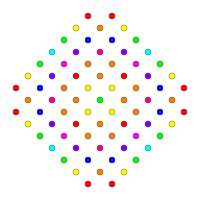
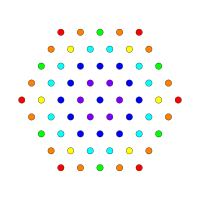
[edit]Petrie polygonprojections are 12, 18, or 30-sided based on the E6, E7, and E8 symmetries (respectively). The 2160 vertices are all displayed, but lower symmetry forms have projected positions overlapping, shown as different colored vertices. For comparison, a B6 coxeter group is also shown.
| E8 [30] |
[20] | [24] |
|---|---|---|
 (1) |

|

|
| E7 [18] |
E6 [12] |
[6] |
|
 (1,8,24,32) |

|
| D3 / B2 / A3 [4] |
D4 / B3 / A2 [6] |
D5 / B4 [8] |
|---|---|---|
|
|

|
| D6 / B5 / A4 [10] |
D7 / B6 [12] |
D8 / B7 / A6 [14] |

|
 (1,3,9,12,18,21,36) |

|
| B8 [16/2] |
A5 [6] |
A7 [8] |
|

|

|
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- Elte, E. L. (1912),The Semiregular Polytopes of the Hyperspaces,Groningen: University of Groningen
- H. S. M. Coxeter,Regular Polytopes,3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter,edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995,ISBN978-0-471-01003-6[1]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter,Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III,[Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- Klitzing, Richard."8D Uniform polyzetta".x3o3o3o *c3o3o3o3o - bay, o3x3o3o *c3o3o3o3o - robay



