Aerodynamics

Aerodynamics(Ancient Greek:ἀήρaero(air) +Ancient Greek:δυναμική(dynamics)) is the study of the motion ofair,particularly when affected by asolidobject, such as anairplanewing.[1]It involves topics covered in the field offluid dynamicsand its subfield ofgas dynamics,and is an important domain of study inaeronautics.The termaerodynamicsis often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such asaerodynamic dragwere recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achievingheavier-than-air flight,which was first demonstrated byOtto Lilienthalin 1891.[2]Since then, the use of aerodynamics throughmathematicalanalysis, empirical approximations,wind tunnelexperimentation, andcomputer simulationshas formed a rational basis for the development of heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related tocompressible flow,turbulence,andboundary layersand has become increasinglycomputationalin nature.
History[edit]
Modern aerodynamics only dates back to the seventeenth century, but aerodynamic forces have been harnessed by humans for thousands of years in sailboats and windmills,[3]and images and stories of flight appear throughout recorded history,[4]such as theAncient Greeklegend ofIcarusandDaedalus.[5]Fundamental concepts ofcontinuum,drag,andpressure gradientsappear in the work ofAristotleandArchimedes.[6]
In1726,Sir Isaac Newtonbecame the first person to develop a theory of air resistance,[7]making him one of the first aerodynamicists.Dutch-SwissmathematicianDaniel Bernoullifollowed in 1738 withHydrodynamicain which he described a fundamental relationship between pressure, density, and flow velocity for incompressible flow known today asBernoulli's principle,which provides one method for calculating aerodynamic lift.[8]In 1757,Leonhard Eulerpublished the more generalEuler equationswhich could be applied to both compressible and incompressible flows. The Euler equations were extended to incorporate the effects of viscosity in the first half of the 1800s, resulting in theNavier–Stokes equations.[9][10]The Navier–Stokes equations are the most general governing equations of fluid flow but are difficult to solve for the flow around all but the simplest of shapes.

In 1799,Sir George Cayleybecame the first person to identify the four aerodynamic forces of flight (weight,lift,drag,andthrust), as well as the relationships between them,[11][12]and in doing so outlined the path toward achieving heavier-than-air flight for the next century. In 1871,Francis Herbert Wenhamconstructed the firstwind tunnel,allowing precise measurements of aerodynamic forces. Drag theories were developed byJean le Rond d'Alembert,[13]Gustav Kirchhoff,[14]andLord Rayleigh.[15]In 1889,Charles Renard,a French aeronautical engineer, became the first person to reasonably predict the power needed for sustained flight.[16]Otto Lilienthal,the first person to become highly successful with glider flights, was also the first to propose thin, curvedairfoilsthat would produce high lift and low drag. Building on these developments as well as research carried out in their own wind tunnel, theWright brothersflew the first powered airplane on December 17, 1903.
During the time of the first flights,Frederick W. Lanchester,[17]Martin Kutta,andNikolai Zhukovskyindependently created theories that connectedcirculationof a fluid flow to lift. Kutta and Zhukovsky went on to develop a two-dimensional wing theory. Expanding upon the work of Lanchester,Ludwig Prandtlis credited with developing the mathematics[18]behind thin-airfoil and lifting-line theories as well as work withboundary layers.

As aircraft speed increased designers began to encounter challenges associated with aircompressibilityat speeds near the speed of sound. The differences in airflow under such conditions lead to problems in aircraft control, increased drag due toshock waves,and the threat of structural failure due toaeroelastic flutter.The ratio of the flow speed to the speed of sound was named theMach numberafterErnst Machwho was one of the first to investigate the properties of thesupersonicflow.Macquorn RankineandPierre Henri Hugoniotindependently developed the theory for flow properties before and after ashock wave,whileJakob Ackeretled the initial work of calculating the lift and drag of supersonic airfoils.[19]Theodore von KármánandHugh Latimer Drydenintroduced the termtransonicto describe flow speeds between thecritical Mach numberand Mach 1 where drag increases rapidly. This rapid increase in drag led aerodynamicists and aviators to disagree on whether supersonic flight was achievable until thesound barrierwas broken in 1947 using theBell X-1aircraft.
By the time the sound barrier was broken, aerodynamicists' understanding of the subsonic and low supersonic flow had matured. TheCold Warprompted the design of an ever-evolving line of high-performance aircraft.Computational fluid dynamicsbegan as an effort to solve for flow properties around complex objects and has rapidly grown to the point where entire aircraft can be designed using computer software, with wind-tunnel tests followed by flight tests to confirm the computer predictions. Understanding ofsupersonicandhypersonicaerodynamics has matured since the 1960s, and the goals of aerodynamicists have shifted from the behaviour of fluid flow to the engineering of a vehicle such that it interacts predictably with the fluid flow. Designing aircraft for supersonic and hypersonic conditions, as well as the desire to improve the aerodynamic efficiency of current aircraft and propulsion systems, continues to motivate new research in aerodynamics, while work continues to be done on important problems in basic aerodynamic theory related to flow turbulence and the existence and uniqueness of analytical solutions to the Navier–Stokes equations.
Fundamental concepts[edit]
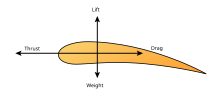
Understanding the motion of air around an object (often called a flow field) enables the calculation of forces andmomentsacting on the object. In many aerodynamics problems, the forces of interest are the fundamental forces of flight:lift,drag,thrust,andweight.Of these, lift and drag are aerodynamic forces, i.e. forces due to air flow over a solid body. Calculation of these quantities is often founded upon the assumption that the flow field behaves as a continuum. Continuum flow fields are characterized by properties such asflow velocity,pressure,density,andtemperature,which may be functions of position and time. These properties may be directly or indirectly measured in aerodynamics experiments or calculated starting with the equations for conservation of mass,momentum,and energy in air flows. Density, flow velocity, and an additional property,viscosity,are used to classify flow fields.
Flow classification[edit]
Flow velocity is used to classify flows according to speed regime. Subsonic flows are flow fields in which the air speed field is always below the local speed of sound. Transonic flows include both regions of subsonic flow and regions in which the local flow speed is greater than the local speed of sound. Supersonic flows are defined to be flows in which the flow speed is greater than the speed of sound everywhere. A fourth classification, hypersonic flow, refers to flows where the flow speed is much greater than the speed of sound. Aerodynamicists disagree on the precise definition of hypersonic flow.
Compressible flowaccounts for varying density within the flow. Subsonic flows are often idealized as incompressible, i.e. the density is assumed to be constant. Transonic and supersonic flows are compressible, and calculations that neglect the changes of density in these flow fields will yield inaccurate results.
Viscosity is associated with the frictional forces in a flow. In some flow fields, viscous effects are very small, and approximate solutions may safely neglect viscous effects. These approximations are called inviscid flows. Flows for which viscosity is not neglected are called viscous flows. Finally, aerodynamic problems may also be classified by the flow environment. External aerodynamics is the study of flow around solid objects of various shapes (e.g. around an airplane wing), while internal aerodynamics is the study of flow through passages inside solid objects (e.g. through a jet engine).
Continuum assumption[edit]
Unlike liquids and solids, gases are composed of discretemoleculeswhich occupy only a small fraction of the volume filled by the gas. On a molecular level, flow fields are made up of the collisions of many individual of gas molecules between themselves and with solid surfaces. However, in most aerodynamics applications, the discrete molecular nature of gases is ignored, and the flow field is assumed to behave as acontinuum.This assumption allows fluid properties such as density and flow velocity to be defined everywhere within the flow.
The validity of thecontinuum assumptionis dependent on the density of the gas and the application in question. For the continuum assumption to be valid, themean free pathlength must be much smaller than the length scale of the application in question. For example, many aerodynamics applications deal with aircraft flying in atmospheric conditions, where the mean free path length is on the order of micrometers and where the body is orders of magnitude larger. In these cases, the length scale of the aircraft ranges from a few meters to a few tens of meters, which is much larger than the mean free path length. For such applications, the continuum assumption is reasonable. The continuum assumption is less valid for extremely low-density flows, such as those encountered by vehicles at very high altitudes (e.g. 300,000 ft/90 km)[6]or satellites inLow Earth orbit.In those cases,statistical mechanicsis a more accurate method of solving the problem than is continuum aerodynamics. TheKnudsen numbercan be used to guide the choice between statistical mechanics and the continuous formulation of aerodynamics.
Conservation laws[edit]
The assumption of afluid continuumallows problems in aerodynamics to be solved usingfluid dynamics conservation laws.Three conservation principles are used:
- Conservation of mass
- Conservation of mass requires that mass is neither created nor destroyed within a flow; the mathematical formulation of this principle is known as themass continuity equation.
- Conservation of momentum
- The mathematical formulation of this principle can be considered an application ofNewton's Second Law.Momentum within a flow is only changed by external forces, which may include bothsurface forces,such as viscous (frictional) forces, andbody forces,such asweight.The momentum conservation principle may be expressed as either avectorequation or separated into a set of threescalarequations (x,y,z components).
- Conservation of energy
- The energy conservation equation states that energy is neither created nor destroyed within a flow, and that any addition or subtraction of energy to a volume in the flow is caused byheat transfer,or byworkinto and out of the region of interest.
Together, these equations are known as theNavier–Stokes equations,although some authors define the term to only include the momentum equation(s). The Navier–Stokes equations have no known analytical solution and are solved in modern aerodynamics usingcomputational techniques.Because computational methods using high speed computers were not historically available and the high computational cost of solving these complex equations now that they are available, simplifications of the Navier–Stokes equations have been and continue to be employed. TheEuler equationsare a set of similar conservation equations which neglect viscosity and may be used in cases where the effect of viscosity is expected to be small. Further simplifications lead toLaplace's equationandpotential flowtheory. Additionally,Bernoulli's equationis a solution in one dimension to both the momentum and energy conservation equations.
Theideal gas lawor another suchequation of stateis often used in conjunction with these equations to form a determined system that allows the solution for the unknown variables.[20]
Branches of aerodynamics[edit]

Aerodynamic problems are classified by the flow environment or properties of the flow, includingflow speed,compressibility,andviscosity.Externalaerodynamics is the study of flow around solid objects of various shapes. Evaluating theliftanddragon anairplaneor theshock wavesthat form in front of the nose of arocketare examples of external aerodynamics.Internalaerodynamics is the study of flow through passages in solid objects. For instance, internal aerodynamics encompasses the study of the airflow through ajet engineor through anair conditioningpipe.
Aerodynamic problems can also be classified according to whether theflow speedis below, near or above thespeed of sound.A problem is called subsonic if all the speeds in the problem are less than the speed of sound,transonicif speeds both below and above the speed of sound are present (normally when the characteristic speed is approximately the speed of sound),supersonicwhen the characteristic flow speed is greater than the speed of sound, andhypersonicwhen the flow speed is much greater than the speed of sound. Aerodynamicists disagree over the precise definition of hypersonic flow; a rough definition considers flows withMach numbersabove 5 to be hypersonic.[6]
The influence ofviscosityon the flow dictates a third classification. Some problems may encounter only very small viscous effects, in which case viscosity can be considered to be negligible. The approximations to these problems are calledinviscid flows.Flows for which viscosity cannot be neglected are called viscous flows.
Incompressible aerodynamics[edit]
An incompressible flow is a flow in which density is constant in both time and space. Although all real fluids are compressible, a flow is often approximated as incompressible if the effect of the density changes cause only small changes to the calculated results. This is more likely to be true when the flow speeds are significantly lower than the speed of sound. Effects of compressibility are more significant at speeds close to or above the speed of sound. TheMach numberis used to evaluate whether the incompressibility can be assumed, otherwise the effects of compressibility must be included.
Subsonic flow[edit]
Subsonic (or low-speed) aerodynamics describes fluid motion in flows which are much lower than the speed of sound everywhere in the flow. There are several branches of subsonic flow but one special case arises when the flow isinviscid,incompressibleandirrotational.This case is calledpotential flowand allows thedifferential equationsthat describe the flow to be a simplified version of the equations offluid dynamics,thus making available to the aerodynamicist a range of quick and easy solutions.[21]
In solving a subsonic problem, one decision to be made by the aerodynamicist is whether to incorporate the effects of compressibility. Compressibility is a description of the amount of change ofdensityin the flow. When the effects of compressibility on the solution are small, the assumption that density is constant may be made. The problem is then an incompressible low-speed aerodynamics problem. When the density is allowed to vary, the flow is called compressible. In air, compressibility effects are usually ignored when theMach numberin the flow does not exceed 0.3 (about 335 feet (102 m) per second or 228 miles (366 km) per hour at 60 °F (16 °C)). Above Mach 0.3, the problem flow should be described using compressible aerodynamics.
Compressible aerodynamics[edit]
According to the theory of aerodynamics, a flow is considered to be compressible if thedensitychanges along astreamline.This means that – unlike incompressible flow – changes in density are considered. In general, this is the case where theMach numberin part or all of the flow exceeds 0.3. The Mach 0.3 value is rather arbitrary, but it is used because gas flows with a Mach number below that value demonstrate changes in density of less than 5%. Furthermore, that maximum 5% density change occurs at thestagnation point(the point on the object where flow speed is zero), while the density changes around the rest of the object will be significantly lower. Transonic, supersonic, and hypersonic flows are all compressible flows.
Transonic flow[edit]
The term Transonic refers to a range of flow velocities just below and above the localspeed of sound(generally taken asMach0.8–1.2). It is defined as the range of speeds between thecritical Mach number,when some parts of the airflow over an aircraft becomesupersonic,and a higher speed, typically nearMach 1.2,when all of the airflow is supersonic. Between these speeds, some of the airflow is supersonic, while some of the airflow is not supersonic.
Supersonic flow[edit]
Supersonic aerodynamic problems are those involving flow speeds greater than the speed of sound. Calculating the lift on theConcordeduring cruise can be an example of a supersonic aerodynamic problem.
Supersonic flow behaves very differently from subsonic flow. Fluids react to differences in pressure; pressure changes are how a fluid is "told" to respond to its environment. Therefore, sincesoundis, in fact, an infinitesimal pressure difference propagating through a fluid, thespeed of soundin that fluid can be considered the fastest speed that "information" can travel in the flow. This difference most obviously manifests itself in the case of a fluid striking an object. In front of that object, the fluid builds up astagnation pressureas impact with the object brings the moving fluid to rest. In fluid traveling at subsonic speed, this pressure disturbance can propagate upstream, changing the flow pattern ahead of the object and giving the impression that the fluid "knows" the object is there by seemingly adjusting its movement and is flowing around it. In a supersonic flow, however, the pressure disturbance cannot propagate upstream. Thus, when the fluid finally reaches the object it strikes it and the fluid is forced to change its properties –temperature,density,pressure,andMach number—in an extremely violent andirreversiblefashion called ashock wave.The presence of shock waves, along with the compressibility effects of high-flow velocity (seeReynolds number) fluids, is the central difference between the supersonic and subsonic aerodynamics regimes.
Hypersonic flow[edit]
In aerodynamics, hypersonic speeds are speeds that are highly supersonic. In the 1970s, the term generally came to refer to speeds of Mach 5 (5 times the speed of sound) and above. The hypersonic regime is a subset of the supersonic regime. Hypersonic flow is characterized by high temperature flow behind a shock wave, viscous interaction, and chemical dissociation of gas.
Associated terminology[edit]

The incompressible and compressible flow regimes produce many associated phenomena, such as boundary layers and turbulence.
Boundary layers[edit]
The concept of aboundary layeris important in many problems in aerodynamics. The viscosity and fluid friction in the air is approximated as being significant only in this thin layer. This assumption makes the description of such aerodynamics much more tractable mathematically.
Turbulence[edit]
In aerodynamics, turbulence is characterized by chaotic property changes in the flow. These include low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time. Flow that is not turbulent is calledlaminar flow.
Aerodynamics in other fields[edit]
This sectionneeds additional citations forverification.(March 2018) |
Engineering design[edit]
Aerodynamics is a significant element ofvehicle design,includingroad carsandtruckswhere the main goal is to reduce the vehicledrag coefficient,andracing cars,where in addition to reducing drag the goal is also to increase the overall level ofdownforce.[21]Aerodynamics is also important in the prediction of forces and moments acting onsailing vessels.It is used in the design of mechanical components such ashard driveheads.Structural engineersresort to aerodynamics, and particularlyaeroelasticity,when calculatingwindloads in the design of large buildings,bridges,andwind turbines.
The aerodynamics of internal passages is important inheating/ventilation,gas piping,and inautomotive engineswhere detailed flow patterns strongly affect the performance of the engine.
Environmental design[edit]
Urban aerodynamics are studied bytown plannersand designers seeking to improveamenityin outdoor spaces, or in creating urban microclimates to reduce the effects of urban pollution. The field of environmental aerodynamics describes ways in whichatmospheric circulationand flight mechanics affect ecosystems.
Aerodynamic equations are used innumerical weather prediction.
Ball-control in sports[edit]
Sports in which aerodynamics are of crucial importance includesoccer,table tennis,cricket,baseball,andgolf,in which most players can control the trajectory of the ball using the "Magnus effect".
See also[edit]
- Aeronautics
- Aerostatics
- Aviation
- Insect flight– how bugs fly
- List of aerospace engineering topics
- List of engineering topics
- Nose cone design
- Fluid dynamics
- Computational fluid dynamics
References[edit]
- ^Wragg, David W. (1974).A Dictionary of Aviation(1st American ed.). New York: Frederick Fell, Inc. p. 8.ISBN0-85045-163-9.
- ^"How the Stork Inspired Human Flight".flyingmag.[permanent dead link]
- ^"Wind Power's Beginnings (1000 BC – 1300 AD) Illustrated History of Wind Power Development".Telosnet. Archived fromthe originalon 2010-12-02.Retrieved2011-08-24.
- ^Berliner, Don (1997).Aviation: Reaching for the Sky.The Oliver Press, Inc. p. 128.ISBN1-881508-33-1.
- ^Ovid; Gregory, H. (2001).The Metamorphoses.Signet Classics.ISBN0-451-52793-3.OCLC45393471.
- ^abcAnderson, John David (1997).A History of Aerodynamics and its Impact on Flying Machines.New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.ISBN0-521-45435-2.
- ^Newton, I. (1726).Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, Book II.
- ^"Hydrodynamica".Britannica Online Encyclopedia.Retrieved2008-10-30.
- ^Navier, C. L. M. H. (1827). "Memoire Sur les Lois du Mouvement des fluides".Mémoires de l'Académie des Sciences.6:389–440.
- ^Stokes, G. (1845)."On the Theories of the Internal Friction of Fluids in Motion".Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society.8:287–305.
- ^"U.S Centennial of Flight Commission – Sir George Cayley".Archived fromthe originalon 20 September 2008.Retrieved2008-09-10.
Sir George Cayley, born in 1773, is sometimes called the Father of Aviation. A pioneer in his field, he was the first to identify the four aerodynamic forces of flight – weight, lift, drag, and thrust and their relationship. He was also the first to build a successful human-carrying glider. Cayley described many of the concepts and elements of the modern airplane and was the first to understand and explain in engineering terms the concepts of lift and thrust.
- ^d'Alembert, J. (1752).Essai d'une nouvelle theorie de la resistance des fluides.
- ^Kirchhoff, G. (1869)."Zur Theorie freier Flussigkeitsstrahlen".Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik.1869(70): 289–298.doi:10.1515/crll.1869.70.289.S2CID120541431.
- ^Rayleigh, Lord (1876)."On the Resistance of Fluids".Philosophical Magazine.2(13): 430–441.doi:10.1080/14786447608639132.
- ^Renard, C. (1889). "Nouvelles experiences sur la resistance de l'air".L'Aéronaute.22:73–81.
- ^Lanchester, F. W. (1907).Aerodynamics.
- ^Prandtl, L. (1919).Tragflügeltheorie.Göttinger Nachrichten, mathematischphysikalische Klasse, 451–477.
- ^Ackeret, J. (1925). "Luftkrafte auf Flugel, die mit der grosser also Schallgeschwindigkeit bewegt werden".Zeitschrift für Flugtechnik und Motorluftschiffahrt.16:72–74.
- ^"Understanding Aerodynamics: Arguing from the Real Physics" Doug McLean John Wiley & Sons, 2012 Chapter 3.2 "The main relationships comprising the NS equations are the basic conservation laws for mass, momentum, and energy. To have a complete equation set we also need an equation of state relating temperature, pressure, and density..."https://play.google /books/reader?id=_DJuEgpmdr8C&printsec=frontcover&pg=GBS.PA191.w.0.0.0.151
- ^abKatz, Joseph (1991).Low-speed aerodynamics: From wing theory to panel methods.McGraw-Hill series in aeronautical and aerospace engineering. New York: McGraw-Hill.ISBN0-07-050446-6.OCLC21593499.
Further reading[edit]
General aerodynamics
- Anderson, John D.(2007).Fundamentals of Aerodynamics(4th ed.). McGraw-Hill.ISBN978-0-07-125408-3.OCLC60589123.
- Bertin, J. J.; Smith, M. L. (2001).Aerodynamics for Engineers(4th ed.). Prentice Hall.ISBN0-13-064633-4.OCLC47297603.
- Smith, Hubert C. (1991).Illustrated Guide to Aerodynamics(2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.ISBN0-8306-3901-2.OCLC24319048.
- Craig, Gale (2003).Introduction to Aerodynamics.Regenerative Press.ISBN0-9646806-3-7.OCLC53083897.
Subsonic aerodynamics
- Katz, Joseph; Plotkin, Allen (2001).Low-Speed Aerodynamics(2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.ISBN0-521-66552-3.OCLC43970751.
- Obert, Ed (2009).Aerodynamic Design of Transport AircraftatGoogle Books.Delft; About practical aerodynamics in industry and the effects on design of aircraft.ISBN978-1-58603-970-7.
Transonic aerodynamics
- Moulden, Trevor H. (1990).Fundamentals of Transonic Flow.Krieger Publishing Company.ISBN0-89464-441-6.OCLC20594163.
- Cole, Julian D;Cook, L. Pamela(1986).Transonic Aerodynamics.North-Holland.ISBN0-444-87958-7.OCLC13094084.
Supersonic aerodynamics
- Ferri, Antonio(2005).Elements of Aerodynamics of Supersonic Flows(Phoenix ed.). Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-44280-2.OCLC58043501.
- Shapiro, Ascher H.(1953).The Dynamics and Thermodynamics of Compressible Fluid Flow, Volume 1.Ronald Press.ISBN978-0-471-06691-0.OCLC11404735.
- Anderson, John D.(2004).Modern Compressible Flow.McGraw-Hill.ISBN0-07-124136-1.OCLC71626491.
- Liepmann, H. W.;Roshko, A.(2002).Elements of Gasdynamics.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-41963-0.OCLC47838319.
- von Mises, Richard(2004).Mathematical Theory of Compressible Fluid Flow.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-43941-0.OCLC56033096.
- Hodge, B. K.; Koenig K. (1995).Compressible Fluid Dynamics with Personal Computer Applications.Prentice Hall.ISBN0-13-308552-X.OCLC31662199.
Hypersonic aerodynamics
- Anderson, John D.(2006).Hypersonic and High Temperature Gas Dynamics(2nd ed.). AIAA.ISBN1-56347-780-7.OCLC68262944.
- Hayes, Wallace D.;Probstein, Ronald F.(2004).Hypersonic Inviscid Flow.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-43281-5.OCLC53021584.
History of aerodynamics
- Chanute, Octave(1997).Progress in Flying Machines.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-29981-3.OCLC37782926.
- von Karman, Theodore(2004).Aerodynamics: Selected Topics in the Light of Their Historical Development.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-43485-0.OCLC53900531.
- Anderson, John D.(1997).A History of Aerodynamics: And Its Impact on Flying Machines.Cambridge University Press.ISBN0-521-45435-2.OCLC228667184.
Aerodynamics related to engineering
Ground vehicles
- Katz, Joseph (1995).Race Car Aerodynamics: Designing for Speed.Bentley Publishers.ISBN0-8376-0142-8.OCLC181644146.
- Barnard, R. H. (2001).Road Vehicle Aerodynamic Design(2nd ed.). Mechaero Publishing.ISBN0-9540734-0-1.OCLC47868546.
Fixed-wing aircraft
- Ashley, Holt; Landahl, Marten (1985).Aerodynamics of Wings and Bodies(2nd ed.). Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-64899-0.OCLC12021729.
- Abbott, Ira H.; von Doenhoff, A. E. (1959).Theory of Wing Sections: Including a Summary of Airfoil Data.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-60586-8.OCLC171142119.
- Clancy, L.J.(1975).Aerodynamics.Pitman Publishing Limited.ISBN0-273-01120-0.OCLC16420565.
Helicopters
- Leishman, J. Gordon (2006).Principles of Helicopter Aerodynamics(2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.ISBN0-521-85860-7.OCLC224565656.
- Prouty, Raymond W. (2001).Helicopter Performance, Stability, and Control.Krieger Publishing Company Press.ISBN1-57524-209-5.OCLC212379050.
- Seddon, J.; Newman, Simon (2001).Basic Helicopter Aerodynamics: An Account of First Principles in the Fluid Mechanics and Flight Dynamics of the Single Rotor Helicopter.AIAA.ISBN1-56347-510-3.OCLC47623950.
Missiles
- Nielson, Jack N. (1988).Missile Aerodynamics.AIAA.ISBN0-9620629-0-1.OCLC17981448.
Model aircraft
- Simons, Martin (1999).Model Aircraft Aerodynamics(4th ed.). Trans-Atlantic Publications, Inc.ISBN1-85486-190-5.OCLC43634314.
Related branches of aerodynamics
Aerothermodynamics
- Hirschel, Ernst H. (2004).Basics of Aerothermodynamics.Springer.ISBN3-540-22132-8.OCLC228383296.
- Bertin, John J. (1993).Hypersonic Aerothermodynamics.AIAA.ISBN1-56347-036-5.OCLC28422796.
Aeroelasticity
- Bisplinghoff, Raymond L.; Ashley, Holt; Halfman, Robert L. (1996).Aeroelasticity.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-69189-6.OCLC34284560.
- Fung, Y. C. (2002).An Introduction to the Theory of Aeroelasticity(Phoenix ed.). Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-49505-1.OCLC55087733.
Boundary layers
- Young, A. D. (1989).Boundary Layers.AIAA.ISBN0-930403-57-6.OCLC19981526.
- Rosenhead, L. (1988).Laminar Boundary Layers.Dover Publications.ISBN0-486-65646-2.OCLC17619090.
Turbulence
- Tennekes, H.;Lumley, J. L.(1972).A First Course in Turbulence.The MIT Press.ISBN0-262-20019-8.OCLC281992.
- Pope, Stephen B. (2000).Turbulent Flows.Cambridge University Press.ISBN0-521-59886-9.OCLC174790280.
External links[edit]
- NASA's Guide to AerodynamicsArchived2012-07-15 at theWayback Machine
- Aerodynamics for Students
- Aerodynamics for Pilots
- Aerodynamics and Race Car Tuning
- Aerodynamic Related ProjectsArchived2018-12-13 at theWayback Machine
- eFluids Bicycle AerodynamicsArchived2009-12-15 at theWayback Machine
- Application of Aerodynamics in Formula One (F1)
- Aerodynamics in Car RacingArchived2009-12-06 at theWayback Machine
- Aerodynamics of BirdsArchived2010-03-24 at theWayback Machine
- NASA Aerodynamics Index
