Al-Jawf offensive
| Al Jawf offensive | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of theYemeni Civil War (2014–present),Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen,and theMa'rib Campaign | |||||||||
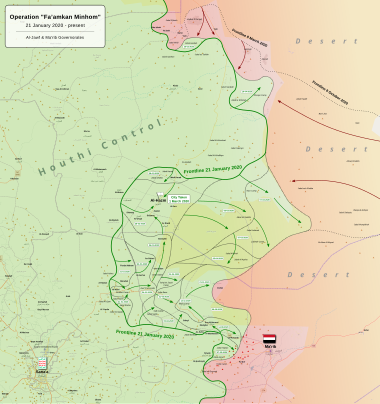 Map of the offensive Pro-Houthi Government control Pro-Hadi Government control | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
(Minister of Defense) (Chief of Staff 6th military Region)[11] |
(Chief of Staff)[12] (Governor of Al-Jawf)[13][14] (Commander)[14] (Chief-of-operations in Kofal military camp)[15] (72nd Brgd. Commander)[15] (310th Brgd. Commander)[15] (122nd Brigade)[16] (Commander)[17] | ||||||||
| Units involved | |||||||||
|
Houthi fighters Popular Committees |
Islah militias[18] Saudi Armed Forces | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| unknown |
6Brigades 3Battalions | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| unknown | 1,200 casualties(Acc. to Houthis)[19] | ||||||||
TheAl Jawf offensivewas a Houthi offensive that began in February 2020 with clashes in theAl Jawf Governorateduring theSecond Yemeni Civil War.Houthi forces were able to decisively capture the town ofAl Hazmon 1 March 2020 from theHadi government.[20][21][22]On 27 April, the first phase of the offensive ended with the Houthis capturing 3,500 square kilometers of territory inAl Jawf Governorate.[23]After reinforcing, the Houthis launched the second phase of their offensive on 27 May, making further advances toward the city ofMariband capturing the Maas military base on 20 November, 2020.[10]The Houthis halted the offensive on 5 February 2021, in order to account for changes in theSaudi-led coalitionandSouthern Transitional Council.[2]After reinforcing once more, the Houthis launched a new offensive towards Marib city on 7 February.[24]
First phase[edit]

After weeks of clashes, Houthi fighters stormed the city of Al Hazm, the capital of Al Jawf province, from different directions on 1 March 2020. A Hadi Government official toldXinhua News Agencythat the Hadi forces had failed to repulse the Houthi fighters storming Al Hazm from the western and northwestern sides. The Houthi forces were deployed in different parts of the city whilst all pro-Hadi government military withdrew toMa'ribcity. The fighting left dozens of soldiers killed.[3]
The Houthi movement spokesperson said that the group controlled most of the Al Jawf District with the exception of some areas close to Saudi Arabia; the areas captured by the group comprised the Khub wal Shaaf and Yatma districts. The Houthi forces then turned the offensive on the Ma'rib Governorate with the aim of attacking Ma'rib city.[20][25]
On 18 March, local sources reported that the Houthi forces had expelled the Saudi-backed forces from the Atias mountain, a base at the Kufil mountain, and the Ghabira mountain, with reported clashes taking place near Talaat al-Hamra.[9]
On 28 March, according to the Houthi media wing, Houthi fighters seized the Kofal Camp.[26]Two days later, local sources informed that Houthi fighters captured the military base of Labnah in Labnah mountains from Saudi led coalition forces.[6]the capture of the military base allowed the Houthi forces to arm their alignedPopular Committees,the aim of the offensive was to encircle theal-Islahstronghold in oil-rich Ma'rib Province.[18]Ongoing battles were reported in the Kofal Camp.[18]
On 4 April, Yemeni government forces issued a statement saying that government forces supported by Saudi-led coalition airstrikes launched an attack on the Houthi militants in theSirwah District,Ma'rib Governorate. According to Hadi Government forces, the fighting claimed 25 Houthi militants killed and several vehicles were destroyed. On the same day, pro-Houthi media reported that the clashes resulted in the death of a senior commander and several soldiers of the government forces.[27][28]According to Houthi media 80 Pro Hadi government forces were killed and wounded. The 310th Brigade Commander Gen Mohamed Kamil al-Thaifani; the Chief of operations Gen Hameed al-Maswari and the 72nd Brigade's commander Gen Khalid al-Joma'ei were confirmed dead in the fighting.[15]
On 8 April, Saudi-led coalition spokesmanTurki Al-Malikiannounced a two-week ceasefire, in part to avoid repercussions from theCOVID-19 pandemic.Saudi vice defence minister PrinceKhalid bin Salmantweetedthat Saudi Arabia would contribute $500 million to theU.N.humanitarian response plan for Yemen in 2020 and another $25 million to help combat the spread of thecoronavirus.[29]
On 10 April, Houthis announced the capture of the military base of Khanjar from Saudi led coalition Forces after several attacks.[8]
On 21 April, Houthi fighters captured the al-Jufra base from Saudi led coalition forces.[7]Later Houthi forces concentrated their forces attacking the Mass military base and Wadi Mass.[30]The same day Houthi media displayed a 15 min video of the capture of anAQAPbase in the Khasaf region in Al-Jawf. The footage showed a prison, explosive belts, ammunition and Al-Qaeda operational documents.[31]
By 28 April, Houthi forces said that they managed to capture eleven of the twelve districts and 95% of the Al-Jawf province with only the eastern district ofKhab and al-Shaafstill being in Saudi-led coalition control. They controlled all ofNorth Yemenexcept for Marib Governorate.[4][5]
Second phase[edit]
On 27 May, Houthi fighters launched two ballistic missiles on the Saudi backed forces of the Hadi government in Marib province. One missile targeted an army headquarters and another a military camp. The attack left 7 officers dead, including the Chief of Staff, Lieutenant General Sagheer bin Aziz's son and nephew, both officers. Bin Aziz survived the attack.[32]
On 30 May, regional media reported the departure of American and Saudi servicemen from Marib province. One of the alleged reasons was to avoid Houthi attacks and missile strikes.[33]
On 3 June, anexplosive devicekilled 9 Hadi Government soldiers and high-ranking officers, including the 81st Infantry Brigade Chief of Operations, Brigadier General Abdullah Ahmad Al Abdi and the Commander of the 2nd Battalion, Colonel Ali Omar Murad. Another Colonel was killed by another IED after going to the region to investigate. In the last weeks a total of 13 officers were killed in IED style of ambushes near the Seventh Military Region in Marib.[34]
On 24 June 2020, media sources close to the Houthis reported the deaths of prominent commanders on Hadi Government forces including Lt. Col. Saleh Abdo Hashem al-Jamali, two Captains; Ibrahim al Akki and Adam Jarban, the Chief from the 4th Battalion, 141st Brigade. Several other soldiers were reported killed amid news of hospitals in Shabwa and Marib collapsing from battle casualties.[35]
On 17 August 2020, forces loyal to al-Hadi launched an ill-fated counter offensive to recapture Al Jawf. The attack left 8 servicemen killed, including General Mohammed Ali-Roqn of the Army 122nd Brigade.[16]
On 22 August 2020, Houthi affiliated media said Houthi forces captured the Mas military camp in Northwest Marib, after defeating Hadi government forces and Islah party militias.[36]The Mas military camp was twice unsuccessfully attacked by Houthi fighters on 4 April and 16 July, it is reportedly the main military base of Saudi Arabia-led forces in west Marib and overlooks the Saana Marib highway.[37]
On 7 September 2020, Houthi forces made further advances on Marib Province closing into the city itself, Mohamed al-Bokhaiti a member of the Houthi movement informed in social media.[38]
On 13 September 2020, pro-Hadi forces said that it had taken a Houthi command center in the northern province of Al-Jawf.[39]
On 10 October 2020, pro-Hadi forces said they recaptured the strategic Al-Khanjar military camp.[40]
On 20 November 2020, Houthi forces captured the Mas military camp[10]after three previous unsuccessful attacks.[36][37]The capture could allow the Houthis to take over the Raghwan and Midghal districts.[41]
On 5 February 2021, the Houthis reportedly halted their offensive on Marib and al-Jawf in order to account for changes in the Saudi-led coalition and Southern separatists.[2]
On 7 February 2021, the Houthis renewed their offensive from al-Jawf toMarib governorate.[24]
Aftermath[edit]
On 24 March 2021, Houthi-led forces captured swathes of desert areas inal-Jawfbordering Saudi Arabia.[42]Regional source reported by December 2021 Houthi forces controlled all areas between Al-Jawf province and the Saudi border, including Hadi Government held Khub Washa’af district.[43]
Analysis[edit]
The capture of Al Hazm was considered by the head of the Sanaa Centre think tank as a "game-changer" for the Houthis, and could totally change the "course of the war".[21]The United Nations Ambassador to YemenMartin Griffithslabeled the offensive as the "most alarming military escalation" in the war.[44]
References[edit]
- ^"Map: Ansar Allah operation end in al-Jawf province".IWN.
- ^abc"Latest Updates on Al Jawf, 5 February 2021".
- ^ab"Roundup: Houthis make new military progress in NE Yemen".Xinhua News Agency.2 March 2020. Archived fromthe originalon 1 March 2020.Retrieved27 March2020.
- ^abc"Audience Question: Did Ansar Allah Liberated 95% of al-Jawf?".Islamic World News.30 April 2020.Retrieved30 April2020.
- ^abc"Yemen: Houthi army spokesman declares end of Jawf operation, holds 'key to Marib'".Middle East Monitor.Retrieved1 May2020.
- ^ab"Roundup:Yemenis Edge Closer to Ma'rib Liberation as Infighting Rocks Saudi-Led Coalition".Tasnim News Agency.30 March 2020.Retrieved1 April2020.
- ^ab"Latest Updates on Yemen, 21 April 2020".IWN.
- ^ab"Map: Latest updates on al Jawf front, 10 April 2020".IWN.
- ^ab"Latest Updates on Marib Battles, 18 March 2020".IWN.
- ^abc"Weekly report on Marib fronts, Feb 23 to March 2 Map Update".Islamic World News.2 March 2021.
- ^ab"Houthi senior officers killed in Jawf north Yemen".24 August 2020.
- ^"Prominent Foe of Houthis Appointed Yemen Chief of Staff".Asharq AL-awsat.
- ^"In dramatic counterattack, Houthis take Yemen's Al-Jawf and eye Marib".Middle East Eye.
- ^ab"Heavy blow to the body of Mansour Hadi forces in Al Yatmah".Retrieved6 April2020.
- ^abcd"105 Yemeni troops, Houthis reportedly killed, injured in Marib".Debriefer.4 May 2020.Retrieved6 April2020.
- ^ab"Eleven Yemeni government troops killed in Houthi attacks".17 August 2020.
- ^"Map: Latest Updates on Yemen, 24 April 2020".IWN.
- ^abcKareem, Kareem (31 March 2020)."Yemeni forces and Popular Committees retake military base as they surround Marib".
- ^"Details of the" Fa'amkon Minhom "operation by the spokesman of Yemeni Armed Forces".IWN.
- ^abCaleb, Weiss (17 March 2020)."Houthis report capture of province bordering Saudi Arabia".The Long War Journal.Retrieved27 March2020.
- ^ab"Yemen Houthis seize strategic city bordering Saudi Arabia".Middle East Monitor.2 March 2020.Retrieved27 March2020.
- ^"Officials say Yemen's rebels seize strategic northern city".aljazeera.
- ^"Map: Ansar Allah operation end in al-Jawf province".
- ^ab"Yemen's Houthis renew offensive to capture government stronghold Marib".Middle East Eye.
- ^"Ansarallah forces announce the capture of Al-Jawf province".17 March 2020. Archived fromthe originalon 20 December 2021.Retrieved28 March2020.
- ^"Ansarallah forces capture important military camp in northern Yemen".28 March 2020. Archived fromthe originalon 2 November 2020.Retrieved1 April2020.
- ^"Yemen's gov't forces claim killing 25 Houthi fighters in ambush - Xinhua | English.news.cn".xinhuanet.Archived fromthe originalon 7 April 2020.Retrieved6 April2020.
- ^"Cũng môn chính phủ quân đánh chết 25 danh hồ tắc võ trang nhân viên".mbd.baidu.Retrieved5 April2020.
- ^El Yaakoubi, Aziz; Kalin, Stephen (8 April 2020)."Saudi-led coalition announces ceasefire in five-year Yemen war".Reuters.Retrieved9 April2020.
- ^"Map: Ansar Allah heavy attacks on Maas base".IWN.
- ^Caleb, Weiss (21 April 2020)."Houthis capture Al Qaeda base in northern Yemen".The Long War Journal.Retrieved23 April2020.
- ^"Missile attack on Yemen army command in Marib kills at least 7".Aljazeera.27 May 2020.Retrieved27 May2020.
- ^"Saudi Forces, US Experts Left Marib Secretly".Daily Yemen.Archived fromthe originalon 25 December 2020.Retrieved2 September2020.
- ^"13 high-ranking officers were killed... mysterious liquidations in the Army legitimacy in Marib".Marib News Yemen.
- ^"Military commanders loyal to coalition killed in Sewah front of Marib".Retrieved24 June2020.
- ^ab"Ansarallah forces score major victory as they close in on key Yemeni city".Al Masdar.Archived fromthe originalon 5 May 2021.Retrieved2 September2020.
- ^ab"Ansar Allah heavy attack to Maas base in Marib province".Islamic World News.
- ^"Bokhaiti confirms Houthi military advance towards Marib".Debriefer.7 September 2020.
- ^Hamdi, Yildiz (12 September 2020)."Yemeni army takes control of Houthi command center in Al-Jawf".Anadolu Agency.Retrieved15 September2020.
- ^"Recapturing Al-Khanjar camp a turning point in battles against Houthis in Jawf, says government officer".debriefer.net.8 October 2020.Retrieved8 April2021.
- ^"Ansarallah forces achieve major victory as they approach de facto gov't capital in northern Yemen".Almasdar News.13 November 2020. Archived fromthe originalon 14 May 2021.Retrieved14 November2020.
- ^"Army takes over strategic desert areas in Jawf | Yemen Press Agency".24 March 2021.Retrieved24 March2021.
- ^"Yemeni forces establish full control over areas linking Jawf province with Saudi border | Yemen Press Agency".24 December 2021.
- ^"UN blasts 'new and irresponsible' offensive in northern Yemen".The National (Abu Dhabi).12 March 2020.Retrieved27 March2020.