Altamura
Altamura
Ialtamùre(Neapolitan) | |
|---|---|
| Comune di Altamura | |
 | |
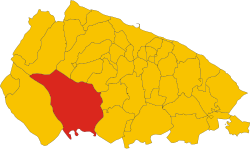 Altamura within the Province of Bari | |
| Coordinates:40°49′N16°33′E/ 40.817°N 16.550°E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Apulia |
| Metropolitan city | Bari(BA) |
| Frazioni | Casal Sabini,Fornello, Madonna del Buon Cammino, Marinella, Masseria Franchini, Pescariello, Sanuca |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Francesco Rinaldi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 427 km2(165 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 450 m (1,480 ft) |
| Population (31 July 2017)[2] | |
| • Total | 70,539 |
| • Density | 170/km2(430/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Altamuran |
| Time zone | UTC+1(CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2(CEST) |
| Postal code | 70022 |
| Dialing code | 080 |
| Patron saint | Saint Irene of Lecce |
| Saint day | May 5 |
| Website | Official website |



Altamura(/ˌæltəˈmʊərə/,Italian:[ˌaltaˈmuːra];Barese:Ialtamùre) is a town andcomuneofApulia,in southern Italy. It is located on one of the hills of theMurgeplateau in theMetropolitan City of Bari,45 kilometres (28 miles) southwest ofBari,close to the border withBasilicata.As of 2017[update],its population amounts to 70,595 inhabitants.[3]
The city is known for its particular quality ofbreadcalledPane di Altamura,which is sold in numerous other Italian cities. The 130,000-year-old calcifiedAltamura Manwas discovered in 1993 in the nearby limestone cave calledgrotta di Lamalunga.
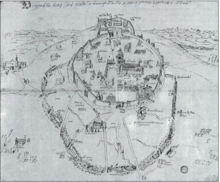
History
[edit]
The area of modern Altamura was densely inhabited in theBronze Age(La Croce settlement and necropolis). The region contains some fiftytumuli.Between the 6th and the 3rd century BC a massive line of megalithic walls was erected, traces of which are still visible in some areas of the city.
Ancient city
[edit]The city was inhabited until around the tenth century AD. Then it was reportedly looted bySaracens.There are no reliable sources confirming what the original name of Altamura was. Inside theTabula Peutingeriana,onlySublupatiaoccurs, which may refer either toSanteramo in Colle,Altamura or to a small region nearby namedJesce.Sublupatiaimplies that a city whose name wasLupatiawas also present, even though there is no mention ofLupatiaeither inTabula Peutingerianaor theAntonine Itinerary.NeverthelessLupatiaoccurs inRavenna Cosmography(Byzantine period)[5]and inGuido of Pisa's workGeographica(Middle Ages).[6][7]
According to an ancient legend, appearing for the first time in the 13th century AD, Altamura's former name wasAltilia,fromAlter Ilium,the "otherTroy".According to a legend, it was founded by a friend ofAeneas,Antellus, also a fugitive from the Asian city destroyed by the Greeks. Another legend attributes the foundation to Althea, queen of theMyrmidons.Ottavio Serena,as early as in 1880, rejected the above legends as well as the belief that the ancient name of Altamura was Altilia, as it lacked reliable sources. Serena suggested that this name may have originated with an unknownHigh Middle Agesscholar who tried to provide an explanation of the ruins found in that place.[8]
During the 15th and 16th centuries AD, Altamura was also mistaken for the ancient city ofPetilia.The belief that Petilia was the ancient name of Altamura at that time was so strong that on some Italian translations ofPtolemy'sGeography,"Petilia" was translated as "Petilia, now Altamura", despite the coordinates given byPtolemyunequivocally pointed toward today'sCalabria.[9][10][11] The hypothesis that Altamura was the ancient city of Petilia probably originated withRaffaello Maffei,as he was the first known author that suggested it.[12]Leandro Alberti,instead, was the first scholar who dismissed that Altamura was Petilia in his workDescrittione [sic] di tutta Italia(1550).[12] According to modern scholars, Petilia probably refers to the archeological remains found onMonte Stella.[13]
The new city
[edit]A couple of centuries[vague]after Altamura was reportedly looted by theSaracens[when?],it started to be inhabited again as emperorFrederick IIrefounded the city (1232) and ordered the construction of the largeAltamura Cathedral,which became one of the most venerated sanctuaries in Apulia. In 1248, under pressure from Frederick,Pope Innocent IVdeclared Altamura exempt from the jurisdiction of thebishop of Bari,making it a "palatine church", that is the equivalent of apalacechapel.
Altamura was ruled by various feudal families, including theOrsini del Balzoand theFarnese(1538–1734), the latter responsible of the construction of numerous palaces and churches. In the past, Altamura also had a largecastle,whose construction dated back to the 11th-13th century, which has been completely demolished and is not visible anymore. In 1748Charles VII of Napleshad a university built in the city.
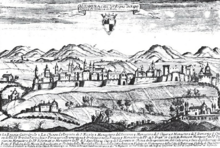
In 1799, an important event in the history of Altamura, commonly labelled asAltamuran Revolution,took place. In February 1799, the city joined theParthenopean Republic,after the king had fled toPalermofearing for his safety. From 8 February 1799 to 9 May 1799, the city was self-governed and it joined the ideals spread by theFrench Revolution.On 9 May,Sanfedistireached Altamura, and after a battle on the city walls, the rule of theKingdom of Napleswas restored in Altamura too. During theRisorgimento(19th century), Altamura was the seat of the Insurrection Bari Committee and, after the unification, the provisional capital of Apulia.
DuringWorld War II,the transit camp known as P.G. 51 was located at Villa Serena in Altamura.[14]
Geography
[edit]The city is located in the south-west area of theMetropolitan City of Bari,near the borders with theProvince of Matera,inBasilicata.The bordering municipalities areBitonto,Cassano delle Murge,Gravina in Puglia,Grumo Appula,Matera,Ruvo di Puglia,Santeramo in ColleandToritto.
Some 12,660 hectares (31,300 acres) of the communal territory are included in theAlta Murgia National Park.
Main sights
[edit]Altamura's main landmark is theRomanesquecathedral,begun in 1232 by Frederick II and restored in 1330 and 1521–47. It is one of the four Palatine churches of Apulia,[15]the others being the cathedral ofAcquaviva delle Fonti,theBasilica of San NicolainBariand the church ofMonte Sant'Angelo sul Gargano.The construction is influenced by that of Bari, but also with strong Gothic influences typical of the time of Frederick II. The orientation of the construction was probably changed during the 14th century restoration, to which also belongs the northern portal opening on the square; a second bell tower, the altar area and the sacristy are instead from the 16th century. Externally, the main features are therose window,with 15 small columns radially intermingling, and the Gothic portal, set into the entrance portico standing on two stone lions. On the arch of portals are sculpted 22 panels with scenes from Jesus' life. The interior, with a nave and two aisles, has stonepresepeby Altobello Persio (1587).
The medieval walls, erected by Frederick II, rest upon the megalithic walls of an ancient city of unknown name. These early walls are of rough blocks of stone without mortar.[15]
Ancient tombs with fragments of vases and terracottas have also been found, of which there is a collection at the Museo Archeologico Statale di Altamura. There are caves which have been used as primitive tombs or dwellings, and a group of some fiftytumulinear Altamura.[15]
Some thirty thousanddinosaur footprintswere discovered in 1999 in Altamura's territory named "contrada Pontrelli", making it a major site for the study of dinosaurs.
Events
[edit]A three-daymedieval faircalledFedericusis held every year in the city, usually on the last weekend of April.
Economy
[edit]Banca Popolare di Puglia e Basilicata,a cooperative bank of southern Italy, is based in Altamura. The bank is a successor of Banca Popolare della Murgia.
Museums
[edit]- Archivio Biblioteca Museo Civico
- National Archaeological Museum of Altamura[16]
- Museum of TypographyPortoghese
- Alta Murgia Ethnographic Museum[17]
- Altamura Diocesan Museum Matroneum(MUDIMA), located insideAltamura Cathedral'smatroneum[18]
Transport
[edit]The city is crossed by the SS7 "Via Appia"national road.
Altamura railway station,operated by the national companyFSand byFAL,is located on the regional linesRocchetta Sant'Antonio-Altamura-Gioia del Colle(FS),Bari-Altamura-Matera(FAL) and
Altamura-Avigliano-Potenza(FAL). Also the municipal localities of Casal Sabini, Marinella and Pescariello have their own stations. The one of Sanuca was closed in the late 1990s.
Twin towns — sister cities
[edit]Altamura istwinnedwith:
 Lucera,Italy
Lucera,Italy Modica,Italy
Modica,Italy Castellana Sicula,Italy
Castellana Sicula,Italy
People
[edit]- Giovanni Antonio Del Balzo Orsini(1386 or 1393–1463), prince of Taranto
- Giacomo Tritto(1733–1824), composer
- Giuseppe Ciccimarra(1790–1836), opera singer
- Saverio Mercadante(1795–1870), opera composer
- Domenico Tranaso(1796–1854), notary
- Giacomo Bellacchi(1838–1924), mathematician
- Giuseppe Oronzo Giannuzzi(1838–76), physiologist
- Ottavio Serena(1837-1914), Italian politician and historian
- Nicola Serena di Lapigio(1875–1938), writer and journalist
- Donato Squicciarini(1927–2006), Catholic archbishop
- Romeo Sacchetti(born 1953), former basketball player
- Francesco Caputo(born 1987), football player
- Mary Valastro Pinto (néeTubito), former employee ofCarlo's Bake Shopand character of the TLC network programCake Boss,as well as mother ofBuddy Valastro[19]
Military
[edit]The 31st tank regiment of theItalian Armyis stationed at Altamura.
Sources
[edit]- Berloco, Tommaso (1985).Storie inedite della città di Altamura.ATA - Associazione Turistica Altamurana Pro Loco.[permanent dead link]
- Pupillo, Giuseppe (2017).Altamura, immagini e descrizioni storiche(PDF).Matera: Antezza Tipografi.ISBN9788889313282.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2018-10-21.Retrieved2018-10-22.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^"Superficie di Comuni Province e Regioni italiane al 9 ottobre 2011".Italian National Institute of Statistics.Retrieved16 March2019.
- ^"Population data from ISTAT - National Institute of Statistics (Italy)".
- ^(in Italian)Source:Archived2014-02-02 at theWayback MachineComune di Altamura 12-31-2013
- ^pupillo-immaini, pag. 19
- ^Celia, Ecetium, Norbae, Veneris, Lupicia, Sublupacia, Blera, Silitum, Benusia, Ponti Aufidi, Aquilonia, Submurula
- ^Esetium, Norbe, Veneris, Lupicia, Sublupicia, Blera, Silitum, Venusium, Serica, quae nunc Asculus, Aquilonia, Subromula. Item civitas quae dicitur Pissandas
- ^pupillo-jesce, pag. 11
- ^Berloco 1985.p. 171.
- ^Berloco 1985.p. 134
- ^"Geography".1478.
- ^"Ptolemy's World Map".
- ^abBerloco 1985.p. 177-178
- ^"Strabo, Geography, BOOK VI., CHAPTER I".
- ^List of World War II prisoner-of-war camps in Italy
- ^abcOne or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in thepublic domain:Chisholm, Hugh,ed. (1911). "Altamura".Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 759.
- ^"Musei".
- ^https://museoetnograficodellaltamurgia.wordpress /[user-generated source]
- ^Official website
- ^Infos at gpo.gov
External links
[edit]- Official website(in Italian)
- Richard Stillwell, ed.Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites,1976:"Altamura, Apulia, Italy"
- "The Altamura prehistorical man"
- Museo Archeologico Statale di Altamura(in Italian)
- Catholic Encyclopedia:"Altamura and Aquaviva"
- Altamura bread, discussion and photos