Amphenicol
Appearance
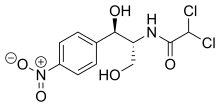

Amphenicolsare a class ofantibioticswith aphenylpropanoidstructure. They function by blocking the enzymepeptidyl transferaseon the50Sribosomesubunit ofbacteria.[1]
Examples of amphenicols includechloramphenicol,thiamphenicol,azidamfenicol,andflorfenicol.The first-in-class compound was chloramphenicol, introduced in 1949. Chloramphenicol was initially discovered as a natural product and isolated from the soil bacteriaSteptomyces venezuelae;[2]however, all amphenicols are now made by chemical synthesis.[3]
References
[edit]- ^"APVMA: Florfenicol".Archived fromthe originalon 2007-09-07.Retrieved2007-07-22.
- ^Scholar, Eric (2007). "Chloramphenicol".X Pharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference.pp. 1–7.doi:10.1016/B978-008055232-3.61439-4.ISBN9780080552323.
- ^Berendsen, Bjorn; Stolker, Linda; De Jong, Jacob; Nielen, Michel; Tserendorj, Enkhtuya; Sodnomdarjaa, Ruuragchas; Cannavan, Andrew; Elliott, Christopher (2010)."Evidence of natural occurrence of the banned antibiotic chloramphenicol in herbs and grass".Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.397(5): 1955–1963.doi:10.1007/s00216-010-3724-6.PMC2886120.PMID20431869.
