AquaMaps
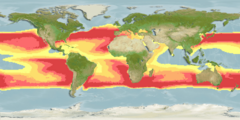
AquaMapsis a collaborative project with the aim of producing computer-generated (and ultimately, expert reviewed) predicted global distribution maps formarine specieson a 0.5 x 0.5 degreegridof theoceansbased on data available through online species databases such asFishBaseandSeaLifeBaseand species occurrence records fromOBISorGBIFand using an environmental envelope model (seeniche modelling) in conjunction with expert input.[1][2]The underlying model represents a modified version of the relative environmental suitability (RES) model developed by Kristin Kaschner to generate global predictions of marine mammal occurrences.[3]
According to the AquaMaps website in August 2013, the project held standardized distribution maps for over 17,300 species offishes,marine mammalsandinvertebrates. The project is also expanding to incorporatefreshwaterspecies,[4]with more than 600 biodiversity maps for freshwater fishes of the Americas available as at November 2009. AquaMaps predictions have been validated successfully for a number of species using independent data sets and the model was shown to perform equally well or better than other standard species distribution models, when faced with the currently existing suboptimal input data sets.[5]
In addition to displaying individual maps per species, AquaMaps provides tools to generate species richness maps by higher taxon, plus a spatial search for all species overlapping a specified grid square. There is also the facility to create custom maps for any species via the web by modifying the input parameters and re-running the map generating algorithm in real time, and a variety of other tools including the investigation of effects of climate change on species distributions (see relevant section of theAquaMaps search page).
Coordination
[edit]The project is coordinated by DrRainer FroeseofIFM-GEOMARand involves contributions from other research institutes including theEvolutionary Biology and Ecology Lab, Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg,University of British Columbia(UBC), theSwedish Museum of Natural History(NRM - Naturhistoriska Riksmuseet), theWorldFish Centerin Malaysia, andCSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Researchin Australia. The creation of AquaMaps is supported byMARA,Pew Fellows Program in Marine Conservation,INCOFISH,Sea Around Us Project,Biogeoinformatics of Hexacorals,FishBaseandSeaLifeBase.
Research use
[edit]A multi-author study by E. Salaet al.utilizing Aquamaps modelled data for marine fishes and invertebrates, entitled "Protecting the global ocean for biodiversity, food and climate", was published in the prestigious journalNaturein 2021.[6]
See also
[edit]- Environmental niche modelling
- Biogeography
- Biodiversity informatics
- Marine biology
- C-squares- global grid system utilized by AquaMaps for data storage and map creation
References
[edit]- ^"AquaMaps Official Website".
- ^Kesner-Reyes, K.; K. Kaschner; S. Kullander; C. Garilao; J. Barile & R. Froese (2012). Froese, R. & D. Pauly (eds.)."AquaMaps: algorithm and data sources for aquatic organisms"(PDF).FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. fishbase.org, version (04/2012). Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2013-07-29.Retrieved2013-12-04.
- ^Kaschner, K.; R. Watson; A.W. Trites & D. Pauly (2006)."Mapping worldwide distributions of marine mammals using a Relative Environmental Suitability (RES) model"(PDF).model. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 316:285-310. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2011-07-16.
- ^"Freshwater Biodiversity AquaMaps".
- ^Ready, J.; K. Kaschner; A.B. South; P.D. Eastwood; T. Rees; J. Rius; E. Agbayani; S. Kullander & R. Froese (2010). "Predicting the distributions of marine organisms at the global scale".Ecological Modelling.221(3): 467–478.doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.10.025.
- ^Sala, E.; J. Mayorga; D. Bradley; et al. (2010). "Protecting the global ocean for biodiversity, food and climate".Nature.592:397–402.doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03371-z.
Further reading
[edit]- Candela L.; Castelli D.; Coro G.; Pagano P.; Sinibaldi F. (2013)."Species distribution modeling in the cloud".Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience.28(4): 1056–1079.doi:10.1002/cpe.3030.
