Artemis 5
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(February 2022) |
 Summary of the Artemis 5 mission plan | |
| Mission type | Crewed lunar landing, Gateway Assembly |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Orion Gateway Space Station Blue Moon Lander |
| Manufacturer | |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | March 2030 (planned)[1] |
| Rocket | SLS Block 1B(Orion) |
| Launch site | Kennedy Space Center,LC-39B |
| End of mission | |
| Landing site | Pacific Ocean(planned) |
| Moonlander | |
| Landing site | South polar region |
Artemis 5(officiallyArtemis V) is the fifth planned mission ofNASA'sArtemis programand the first crewed flight of theBlue Moonlander.[2]The mission will launch four astronauts on aSpace Launch Systemrocket and anOrionto theLunar Gatewayand will be the third lunar landing of the Artemis program. In addition, Artemis V will also deliver two new elements to the Gateway Space Station.[3]
Overview[edit]
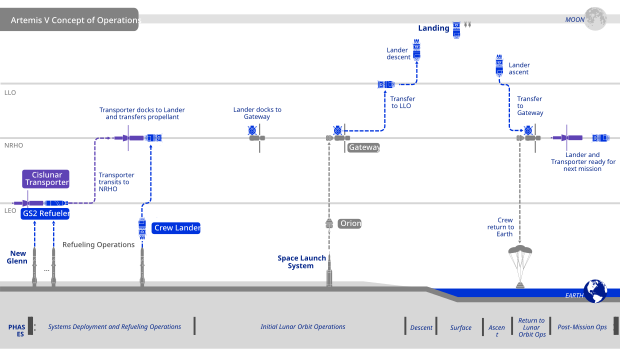
Artemis V will launch four astronauts to the Gateway Space Station. The mission will deliver theEuropean Space Agency'sESPRITrefueling and communications module and a Canadian-built robotic arm system for the Gateway. Also delivered will be NASA'sLunar Terrain Vehicle.
After docking to the Gateway, two astronauts will board theBlue Moonlunar lander and fly it down to theLunar south poleto land near the Lunar Terrain Vehicle. This will be the first lunar landing sinceApollo 17to use an unpressurized lunar rover. It is planned to have the two astronauts on the surface of theMoonfor about one week where they will conduct science and exploration activities.[4]
As of March 2024[update],Artemis V is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 2030.[1]
Spacecraft[edit]

Space Launch System[edit]
The Space Launch System is a super-heavy-lift launcher used to launch the Orion spacecraft from Earth to a trans-lunar orbit.
Orion[edit]
Orion is the crew transport vehicle used by all Artemis missions. It will transport the crew from Earth to the Gateway orbit, and return them to Earth.
Gateway[edit]
Gateway is a small modular space station to be established inNear-rectilinear halo orbit(NRHO) in late 2024. The first two Gateway elements will launch together aboard aSpaceXFalcon Heavyrocket in late 2024.[5]The I-Hab habitat module will be delivered byArtemis 4.
Blue Origin's Blue Moon lander[edit]
The Blue Moon lander will transfer astronauts from the Gateway to the Lunar surface and back. Blue Origin will be the second provider to deliver Artemis astronauts to the lunar surface. NASA previously contracted SpaceX to develop and demonstrate theStarship Human Landing System.
Blue Origin will design, develop, test, and verify its Blue Moon lander to meet NASA's human landing system requirements for recurring astronaut expeditions to the lunar surface. In addition to design and development work, the contract includes one uncrewed demonstration mission to the lunar surface and the crewed demo in 2029. The total award value of the contract is $3.4 billion.[6]
Lunar Terrain Vehicle[edit]
The Lunar Terrain Vehicle is an unenclosed rover being developed by NASA that astronauts will drive on the Moon while wearing spacesuits.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ab"NASA Budget FY2025"(PDF).11 March 2024.Retrieved11 March2024.
- ^O’Shea, Claire (19 May 2023)."NASA Selects Blue Origin as Second Artemis Lunar Lander Provider".NASA.Retrieved19 May2023.
- ^Foust, Jeff (20 January 2022)."NASA foresees gap in lunar landings after Artemis 3".SpaceNews.Retrieved2 February2022.
- ^O’Shea, Claire (19 May 2023)."NASA Selects Blue Origin as Second Artemis Lunar Lander Provider".NASA.Retrieved19 May2023.
- ^Foust, Jeff (10 February 2021)."NASA selects Falcon Heavy to launch first Gateway elements".SpaceNews.Retrieved2 February2022.
- ^O’Shea, Claire (19 May 2023)."NASA Selects Blue Origin as Second Artemis Lunar Lander Provider".NASA.Retrieved19 May2023.
External links[edit]
- Orion websiteat nasa.gov
- Space Launch System websiteat nasa.gov


