BBC English Regions
| TV transmitters | Terrestrial, cable andBBC UK regional TV on satellite |
|---|---|
| Radio stations | BBC Local Radio |
| Headquarters | The Mailbox,Birmingham |
| Nation | |
| Regions | |
Key people | Helen Thomas, Director of BBC England (2018–present)[1] |
Official website | bbc.co.uk/england |
| BBC |
|---|
BBC English Regionsis the division of theBBCresponsible for local and regional television, radio,web,andteletextservices inEngland,theIsle of Man,and theChannel Islands.It is one of the BBC's four "nations" – the others beingBBC Cymru Wales,BBC Northern Ireland,andBBC Scotland.[2]
The division is made up of 12 regions. Many of the names of these regions are similar to those of the official governmentRegions of England,but the areas covered are often significantly different, being determined byterrestrialtransmission coverage rather than administrative boundaries.[3]
BBC English Regions has its headquarters atThe MailboxinBirmingham(West Midlands) and additional regional television centres inNorwich,Nottingham,Broadcasting House(London),Newcastle,MediaCityUK(Salford),Southampton,Tunbridge Wells,Plymouth,Bristol,Leeds,andKingston upon Hullas well as local radio stations based at 43 locations across England.[4]
Overall, the division produces over 70% of the BBC's domestic television and radio output hours, for about 7% of thelicencefee.[5]
Since April 2009, the English Regions division has been aligned with theBBC Newsdepartment to "maximise co-operation in the BBC's news operations".[6]
History
[edit]The four regions
[edit]The current BBC English Regions division was the product of the controversialBroadcasting in the Seventiesreport – a radical review of the BBC's network radio and non-metropolitan broadcasting structure – published on 10 July 1969.[7]
Before this the structure of regional broadcasting in England had remained virtually unchanged since the late 1920s, when the establishment of four regional radio transmission stations covering England had led to a regional structure on similar lines.BBC Northwas based inManchesterand covered the area fromCheshireandSheffieldnorthwards,BBC Midlands and East Angliawas based inBirminghamcovering a swathe of central England fromthe PotteriestoNorfolk,andBBC South and Westwas based inBristolcovering the area south and west of a line fromGloucestertoBrighton.The London area, though it had regional transmission infrastructure of its own, produced only national programming and wasn't considered to be a region as it acted as the sustaining service for the other regions.
These regions (alongside the national regionsBBC Scotland,BBC WalesandBBC Northern Irelandthat performed a similar role outside England) were well-suited to delivering the pre-warBBC Regional Programmeand the post-warBBC Home Servicethat replaced it. By the 1960s, though, the growth of television, the birth of the more locally basedITVfranchises in 1955 and the development of smallerBBC Local Radiostations (made possible by the development ofFM radio) were making the structure look increasingly anachronistic.
Broadcasting in the Seventies
[edit]
The effect ofBroadcasting in the Seventieswas to separate the two different roles of regional BBC offices into different organisations:[8][9]
- The two major television channelsBBC1andBBC2were to remain primarily national operations. To prevent this leading to total domination by London, three largeNetwork Production Centres(NPC), each one having its own medium-size colour TV studio –BBC Bristol,BBC BirminghamandBBC Manchester– were established in the headquarters of the former regions, to produce programming for national broadcast across the entire United Kingdom.[10]
Each of the production centres also had network radio studios (BBC Birmingham,for instance, producingThe Archers) plus a small television news studio, the latter to enable local (opt out) programming.
- BBC English Regions was created to take on this other role of the former regions – the production of specifically local programming (mainly from smallisland sites) – through a new tier of eight much smaller regions described on page eight of the report as"the basic unit of English broadcasting outside London"and controlled from headquarters in the newly builtPebble Mill studiosin Birmingham.[11]
As a result of the latter,Plymouth-basedBBC South WestandSouthampton-basedBBC Southwere split fromBBC Westin Bristol;Norwich-basedBBC Eastseparated fromBBC Midlandsin Birmingham; a new smallerBBC North Westwas created from the existingManchester-based region, with the oldBBC Northname being taken by the newly created region based inLeeds;[12]and the existingNewcastle-basedBBC North Eastseparated from the old BBC North Region in this process.
In addition, London and the surrounding area was finally recognised as a region with the creation ofBBC South Eastalthough the region was not to get a dedicated regional programme of its own until 1982 and regional news bulletins for the area did not launch until September 1985.
These new regions produced local news programmes andopt-outson television, but regional radio programming on theBBC Home Servicewas to be replaced byBBC Local Radio.[13]The report stated that the local radio experiment, started in 1967"has proved that there is a demand for local radio"and that the BBC should"put forward to thePostmaster Generala provisional scheme for expanding our local network to about forty stations ".
Current structure
[edit]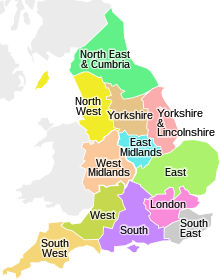
This structure has largely survived since the 1970s. Local news services were developed onCeefaxfrom 1997 and were extended onto thewebin 1999. The decreasing costs of television production and improving technology also enabled the gradual development of even smaller regions. In 1991,BBC East Midlandswas finally created inNottingham,[14]BBC London(separated from BBC South East) became a region in 2001[15]andBBC Northwas split intoBBC YorkshireandBBC Yorkshire and Lincolnshirein 2004[16]– with the new millennium seeing several BBC regions moving into new premises. In the East, South and South West regions, sub-regional opt-outs during local news programmes have also been created (similar to those onITVregional news programmes), based respectively in Cambridge, Oxford and Jersey. In total, the BBC has produced the regional news bulletins forLondon,theEast,South East,South,South West,West,theWestandEast Midlands,and theNorth Westregions of England, with theLook Northbranding forYorkshire,East Yorkshire and Lincolnshireandthe North East and Cumbria,with national bulletins forScotland,WalesandNorthern Ireland.All follow the national UK-wideBBC Newsbulletins.
In May 2022 the BBC announced the cessation of the Cambridge and Oxford sub-regional television news bulletins as part of plans to move to a digital-first BBC. The last bulletins aired at 18:30 on the 16th December 2022.[17]
Programmes
[edit]Programmes made for BBC English Regions includeWalking with...andWinter Walks,[18]two series produced byCy Chadwick,where presenters take solitary walks along scenic paths, filming themselves and their surroundings with a360-degree cameraon aselfie stick.All the episodes from a series get a regional slot on BBC One where they are broadcast at all the same time, before the whole series gets a national repeat on eitherBBC TwoorBBC Four.
We Are England
[edit]
In 2022, a new regional documentary strand titledWe Are Englandwas launched,[19][20]as a replacement for the current affairs showInside Out.A notable change is that episodes represent large, new, combinations of English regions, based in six main bases (Birmingham, Bristol, Leeds, London, Newcastle and Norwich); each week is themed around a different subtitle, with the first beingMental Health.[21]
Aisling O'Connor, the head of TV Commissioning for BBC England, commissioned 120 episodes to be broadcast in 2022, with the first being shown on 26 January 2022 at 7:30pm.[22][23][24][25][26]In-addition to being shown onBBC One,select episodes are also repeated onBBC News[27]and onBBC Three.[28][29]
In May 2022, the BBC announced a raft of closures, restructures and cost-cutting measures and one of these was the decision not to renewWe Are Englandfor a third series.[30]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^"Helen Thomas".
- ^"BBC Nations & Regions".BBC Press Office. August 2004.Retrieved20 April2007.
- ^"BBC English Regions".BBC Commissioning. Archived fromthe originalon 30 June 2007.Retrieved20 April2007.
- ^"English Regions".BBC Press Office. Archived fromthe originalon 29 March 2007.Retrieved20 April2007.
- ^"Information About BBC English Regions".BBC English Regions.Archivedfrom the original on 20 March 2007.Retrieved13 April2007.
- ^"BBC promotes role of national and regional broadcasting in leadership restructuring".BBC Press Office. 7 October 2008.Retrieved7 June2012.
- ^The BBC Story – 1960s(page 6) BBC
- ^Broadcasting in the Seventies.British Broadcasting Corporation. 1969.ISBN0-563-08562-2.
- ^"Broadcasting in the Seventies".Retrieved11 January2016.
- ^"House of Lords – BBC Charter Review – Minutes of Evidence".UK Parliament. 22 November 2005.Retrieved13 April2007.
- ^"The future of Pebble Mill".BECTU. 7 May 1999.Retrieved20 April2007.
- ^"Look North is 35!".BBC Bradford and West Yorkshire. 25 March 2003.
- ^"Frequency Finder UK – History of radio transmission".Archived fromthe originalon 30 April 2007.Retrieved13 April2007.
- ^Broadcasting in the Seventieswas a document concerned mainly with radio reorganisation and funding – having only one and one half pages devoted to television and the regions (on pages 7 and 8) – where it had stated, back in 1969, that"in the longer term, as money permits, we would hope to set up further centres, with the one in the East Midlands as a first priority".
- ^"BBC South East – News".TV Ark. Archived fromthe originalon 18 January 2016.Retrieved5 April2009.
- ^"BBC – BBC buildings".Archivedfrom the original on 22 March 2007.Retrieved20 April2007.
- ^"Regional BBC shows in Oxford and Cambridge end - BBC News".BBC News.Retrieved11 February2022.
- ^"BBC Four - Winter Walks, Series 1, Simon Armitage".BBC.
- ^"BBC One - We Are England - Available now".
- ^"BBC One - We Are England".
- ^"BBC One - We Are England, Mental Health, Unfiltered - Cambridge".
- ^"BBC commissions 120 We Are England documentaries".6 January 2022.
- ^"We Are England replaces Inside Out on BBC One".7 January 2022.
- ^"BBC England launches new current affairs programme as platform for underserved audiences".10 January 2022.
- ^"We Are England to redraw BBC TV regions".25 January 2022.
- ^"BBC announces new regional current affairs strand for England".6 January 2022.
- ^"BBC One - We Are England, Mental Health, Cold Swim - Tynemouth".
- ^"We Are England - My Hometown: Jayde Adams: Coming Home".
- ^"BBC iPlayer - BBC Three Guide - Mon Jul 11 2022".BBC Iplayer.
- ^"BBC to move CBBC and BBC Four online".BBC News.26 May 2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Briggs, Asa(1961–1995).The History of Broadcasting in the United Kingdom (Volumes I-V).Oxford University Press.
- British Broadcasting Corporation(1969).Broadcasting in the Seventies: The B.B.C.'s plan for network radio and non-metropolitan broadcasting.BBC. p. 14pp.ISBN0-563-08562-2.
