Bilboes
| Part ofa serieson |
| Forced labourandslavery |
|---|
 |
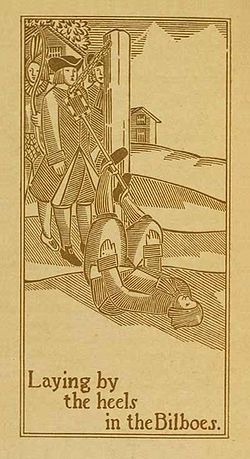
Bilboes(plurale tantum) are iron restraints normally placed on a person's ankles. They have commonly been used asleg shacklesto restrain prisoners for different purposes until the modern ages. Bilboes were also used on slave ships, such as theHenrietta Marie. According to legend, the device was invented inBilbaoand was imported into England by the ships of theSpanish Armadafor use on prospective English prisoners. However, theOxford English Dictionarynotes that the term was used in English well before then.
Description
[edit]Bilboes consist of a pair of U-shaped iron bars (shackles) with holes in the ends, through which an iron rod is inserted. The rod mostly has a large knob on one end, and a slot in the other end into which a wedge or a padlock is driven to secure the assembly. Bilboes occur in different sizes, ranging from regular large ones to smaller sizes particularly fitting women's ankles and even sizes to restrain the wrists. The rod can also be fastened to a wall or a rigid trestle as it was mostly used in prisons. This way the person is restrained to stay put, while only allowing movement of the feet sideways inside the limited range the rod allows for.[1]
History
[edit]Bilboes used as public punishment in former times combined physical discomfort withpublic humiliation.The person was often restrainedbarefoot,which added to the humiliation. They were popular inEnglandand America in the colonial and early revolutionary periods (such as in theMassachusetts Bay Colony). They were used in England to "punyssche transgressours ageynste ye Kinges Maiesties lawes". Bilboes appear occasionally in literature, includingHamlet(Act V, Scene 2: "Methought I lay worse than the mutinies in the bilboes" ) and the journals ofCaptain Cook.[2]
A notable case of excessive use is documented fromTrinidadunder British administration by governorThomas Pictonduring the criminal procedure against eighteen-year-old Louisa Calderon in 1801. The former maid of governor Picton was accused oftheftfrom his household and interrogated. She was also subjected to thepickettorture, which first led to an extorted confession. Subsequently, she was left restrained in bilboes over the continuous period of eight months while the legal inquest was in progress. The shackles were rigidly fastened to the wall of her confinement cell, so she was forced to remain in one place for the entire duration of her imprisonment. The charges were eventually dropped, so Louisa Calderon was released from her incarceration and the bilboes were taken off after months of being incessantly restrained. This excessive form of incarceration along with the preceding torture was later assessed asinhumanein a juridic reappraisal.[3]
Use in slavery
[edit]Bilboes were used to restrain slaves onslave ships.Components forming more than eighty bilboes have been recovered from theHenrietta Marie,an English slave ship that waswreckedin theFlorida Keysin 1700 after delivering slaves toJamaica.Bilboes were also found in theMolasses Reef Wreck,a Spanish wreck in theTurks and Caicos Islandsfrom very early in the 16th century, which may have been a slave ship huntingLucayansinthe Bahamas.Bilboes were used to fasten two slaves together, so that the eighty-plus bilboes found on the Henrietta Marie would have restrained up to 160 slaves. Bilboes were usually not placed on every slave transported, nor were they left on for all of a voyage. Only the slaves that were strongest and presumably most likely to revolt or escape were kept in bilboes for all of a voyage.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^abMalcom, Corey (October 1998)."The Iron Bilboes of theHenrietta Marie"(PDF).The Navigator: Newsletter of the Mel Fisher Maritime Heritage Society.13(10). Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 18 December 2015.Retrieved28 May2012.
- ^Earle, Alice Morse (1896).Curious Punishments of Bygone Days.at Project Gutenberg
- ^"THOMAS PICTON, ESQ".The Newgate Calendar.Retrieved2014-02-22.
