Buton
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(August 2009) |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 5°3′S122°53′E/ 5.050°S 122.883°E |
| Area | 4,727.07 km2(1,825.13 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,100 m (3600 ft) |
| Highest point | Unnamed |
| Administration | |
| Province | |
| Largest settlement | Baubau(pop. 159,248) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 414,899 (2020 Census) |
| Pop. density | 87.8/km2(227.4/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Butonese people |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone |
|
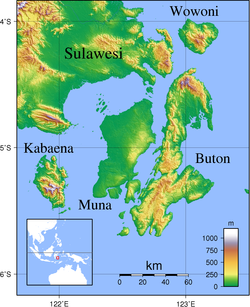
Buton(alsoButung,BoetonorButton) is anislandinIndonesialocated off the southeast peninsula ofSulawesi.It covers roughly 4,727 square kilometers in area, or about the size ofMadura;it is the 129thlargest island in the worldand Indonesia's 19th largest in area.
History[edit]

In the precolonial era, the island, then usually known as Butung, was within the sphere of influence ofTernate.Especially in the sixteenth century, Buton served as an important secondary regional center within the Ternaten empire, controlling regional trade and collecting tribute to be sent to Ternate.
TheSultanate of Butonruled over the island from the 14th until the 20th century.[1]
Sultan Murhum, the first Islamic monarch on the island, is remembered in the name of the island's major harbor, Murhum Harbor, in Baubau.
Geography[edit]
Its largest town isBaubau,where theWolioandCia-Cialanguages are spoken. Major nearby islands includeWawonii(to the north),MunaandKabaena(to the west) and Siumpu (to the southwest). TheTukangbesi Islandslie just to the east whereTukang Besiis spoken, and is separated by theGulf of Kolowana Watabo(Teluk Kolowana Watabo).
BatuatasIsland is to the south. Also theBouton Passage(as it was known in the pre-Independence era) was an important inter-island navigational location of the northernFlores Sea.[2]
Ecology[edit]
The island is largely covered byrainforestand is known for its wildlife. It is one of only two habitats of theanoa,a type ofbuffalo.
People[edit]

The languages spoken on Buton includeWolio,Cia-Cia,various dialects ofMuna,Tukang Besi,Kumbewaha,Lasalimu,Kamaru,Pancana,Busoa,Taloki,KulisusuandKioko.[3][4]TheIndonesian language,the national language of Indonesia, is also widely used and taught in schools.
In 2009, theCia-Ciatribe in Baubau city began to use the KoreanHangulAlpha bet for their language, based on textbooks created by theHunminjeongeum Society,a linguistic society in Seoul.,[5]but in 2012 it was reported that adoption ultimately failed and has been abandoned.[6]
Economy[edit]
The island has a massive reserve of naturalasphaltand several other minerals. Asphalt from Buton can be utilized as bitumen modifiers[7]as well as a substitute for petroleum asphalt. As a result, natural asphalt can be used to reduce dependency on conventional fossil based resources.
Administration[edit]
Buton Island is administratively divided into five second level administrative divisions (Daerah Tingkat II):BaubauCity,Buton Regency,(part of)South Buton Regency(which includes several smaller islands to the west and south of Buton),North Buton Regencyand (part of)Muna Regency.
| Kabupaten | Area in km2 |
Pop'n Census 2010[8] |
Pop'n Census 2020[9] |
comprising |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Buton Regency | 1,923.03 | 54,736 | 66,653 | all districts |
| Muna Regency (part) | 400.78 | 19,488 | 22,534 | Pasih Putih, Pasi Kolaga, Wakorumba Selatan, Batukara and Maligano districts |
| Buton Regency | 1,648.04 | 94,388 | 115,207 | all districts |
| Baubau city | 295.07 | 136,991 | 159,248 | all districts |
| South Buton Regency (part) | 460.15 | 41,886 | 51,257 | Sampolawa, Lapandewa and Batauga districts |
| Totals | 4,727.07 | 347,489 | 414,899 |
However, the eponymous archipelago is administered under an additional four regencies: the rest ofMuna RegencyandSouth Buton Regency,together withWest Muna Regency,Wakatobi Regency,Central Buton Regency(which does not include any portion of Buton Island), and (part of)Bombana Regency.
Notes[edit]
- ^Purwanto, Muhammad Roy (October 2017)."SISTEM PEMERINTAHAN ISLAM DAN UNDANG-UNDANG KESULTANAN BUTON DI SULAWESI TENGGARA".Kecamatan Galang Dalam Angka.ISSN0852-7504.
- ^Goodall, George (Editor)(1943)Philips' International AtlasLondon, George Philip and Son map 'East Indies' pp.91-92
- ^van den Berg, Rene (1991). "Preliminary Notes on the Cia-Cia language (South Buton)".Excursies in Celebes.p. 305.ISBN90-6718-032-7.
- ^"Ethnologue".Retrieved2009-10-11.
- ^"Cia-Cia adopts Hangul to preserve spoken language".7 August 2009.
- ^"Adoption of Hangeul by Indonesian Tribe Hits Snag",The chosunibo
- ^"Buton Asphalt Indonesia".
- ^Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.