Central Region, Portugal
Central Region
Região do Centro | |
|---|---|
From top left to right: The village ofMonsanto,theFesta dos Tabuleiros,theSerra da Estrela,theCastle of Almourol,the town ofNazaréand the city ofCoimbra. | |
| Etymology:centro,Portugueseforcentre | |
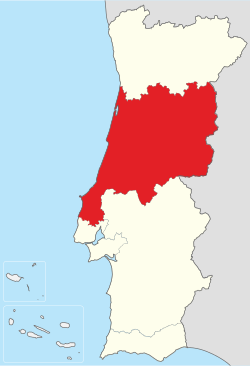 Location of the Central Region in context of the national borders | |
| Country | |
| Region | Central |
| Provinces | Beiras,RibatejoandEstremadura |
| Capital | Coimbra |
| Area | |
| • Total | 28,462 km2(10,989 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 2,327,026 (3rd) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | €45.029 billion (2022) |
| • Per capita | €20,161 (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC+0(WET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1(WEST) |
| HDI(2021) | 0.857[3] very high·2nd |
| NUTS | PT16 |
| Website | centerofportugal |
| Statistics fromINE(2005); geographic detail from Instituto Geográfico Português (2010) | |
TheCentral Region(Portuguese:Região do Centro,IPA:[ʁɨʒiˈɐ̃wduˈsẽtɾu]) orCentral Portugalis one of thestatistical regionsofPortugal.The cities with major administrative status inside this region areCoimbra,Aveiro,Viseu,Caldas da Rainha,Leiria,Castelo Branco,Torres Vedras,Tomar,andGuarda.It is one of the sevenRegions of Portugal(NUTSII subdivisions). It is also one of the regions of Europe, as given by theEuropean Unionfor statistical andgeographicalpurposes. Its area totals 28,462 km2(10,989 sq mi). As of 2011, its population totalled 2,327,026 inhabitants,[4]with a population density of 82 inhabitants per square kilometre.
History[edit]

Inhabited by theLusitanians,anIndo-European peopleliving in the westernIberian Peninsula,theRomanssettled in the region and colonized it as a part of the Roman Province ofLusitânia.The Roman town ofConímbriga,nearCoimbra,is among the most noted and well-preserved remains of that period. After thefall of the Western Roman Empire,Visigothswere the main rulers and colonizers from the 5th to the 8th century.
In the 8th century, theMuslim conquest of Iberiaturned the region a Muslim-dominated territory.
In the earliest years of the ChristianReconquista,just before the rise of a Portuguese national identity, the region was a battle place between Christiancrusadersand Muslim Moors. Once theChristianregained control, kings and landlords made the region a county, called theCounty of Coimbra.It was integrated into the newly createdCondado Portucalensis,the early precursor of the modern nation ofPortugal.
The modern region matches up roughly with the boundaries of the historicalBeira Province,as well as theOestein formerEstremaduraandMédio Tejoin formerRibatejo.Beirawas an historical province of Portugal and its name was used by the heirs to thePortuguese throneduring the monarchy period, before 1910. The princes were known as thePrinces of Beira.

Historic villages[edit]
Along the region's mountainous border withSpainare a series offortressesandcastlesthat once protected the country from its many invaders. Over the centuries, Moors,Christians,SpaniardsandPortuguesehave all tried to take thesevillages,but their higher elevations usually gave them a distinct advantage. On that border, the more than one dozen fortified frontier villages beckon today's visitors to come explore a 900-year history — full of the heroism, epic battles and romance upon whichPortugalstruggled to become a nation. Today, Portugal boasts the longest-standing border in all ofEurope.

In these rural bordervillages,ancient rituals and religious festivals remain popular. Visitors can sample them and partake in the traditional foods of that area, such as cheese, sausages, and mountain honey.
In the fortress town ofAlmeida,a walk through the narrow cobbled streets can lead a visitor to the ruins of a once mighty 12-pointed fortress. One of Portugal's manyPousadas— an historic property turned into an inn— is located in Almeida.
In the town of Castelo Rodrigo, a memorial stone marks the place of a fierce battle in 1664, and visitors can view the remains of the castle and itskeep,as well as a palace. The town also has a smallGothic church.Near Castelo Mendo stands an intricate stone bridge built by theRomans.
Frontier castles[edit]
Most of the castles in this border region of Central are classified asnational monuments.These stone fortresses date back to the 11th, 12th and 13th centuries. Castles, or parts of castles, still stand at Alfaiates, Sortelha,Vilar Maior,Sabugal,Castelo Mendo,Castelo Bom,Castelo Rodrigo, Penamacor, Monsanto, Pinhel and Almeida. A 20-castle route has been delineated by the Portugal government (seevisitportugal), of which Sortelha, Castelo Mendo, Castelo Rodrigo and the fortified town ofAlmeidaare considered gems among them all.
Geography[edit]

TheCentrois a region of diversified landscapes. The interior is mountainous with some plateaus, dominated by theSerra da Estrelamountain. The region is plentiful ofpineandchestnuttrees forests. The green, rugged landscape of this region is crisscrossed by rivers. Several river valleys at the foot of the mountains have a full bodied charm that draw one to outdoor activities like hiking, fishing, tennis and canoeing. In the Winter season, skiing onSerra da Estrelais a popular activity, but in some places, like near the town ofSeia,skiing before the Winter season is possible due to artificial snow infrastructures. The coastal plain has several beaches, like the ones ofMira,Figueira da Foz,Ílhavo,Nazaré,PenicheandSão Martinho do Porto.Natural landmarks in this region are theSerra da Estrelamountain range (the biggest and highest inmainland Portugal), with itsSerra da Estrela Natural Park,theMondego river(the longest river located exclusively in Portuguese territory), theAveiro Lagoon(Ria de Aveiro)and the coastal beaches.
The largest urban centres includeCoimbra,Aveiro,Viseu,Leiria,Covilhã,Castelo Branco,Figueira da Foz,Guarda,Pombal,Tomar,Torres Vedras,Torres Novas,ÁguedaandCaldas da Rainha.
Subregions[edit]
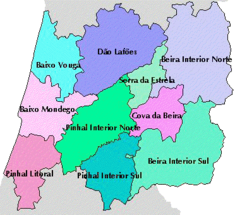
The region is divided in eight sub-regions:
- Beira Baixa
- Beiras e Serra da Estrela
- Médio Tejo
- Oeste
- Região de Aveiro
- Região de Coimbra
- Região de Leiria
- Viseu Dão Lafões
Economy[edit]
TheGross domestic product(GDP) of the region was 38.2 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 18.8% of Portugal's economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 20,100 euros or 67% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 68% of the EU average.[5]
One of Portugal's richest regions by the abundance of natural streams of water, forests, arable land and its long coast line, the Central region has some of the most economically dynamic and densely populated municipalities of the country. Excellent transportation links with theLisbon metropolitan areato the south and thePorto Metropolitan Areato the north, making ocean, rail and motorway access possible via containers, have all contributed to making manufacturing the principal industry, found mainly in the littoral strip, which is one of the largest industrialized areas in Portugal. Important products such asmotor vehicles,food,electrical appliances,machinery,chemicals,andpaperare produced there.Higher education,research and development,healthcare,information technologies,biotechnology,forestry,agriculture,fishing,andtourismindustries are all major industries in the region. Thewineregions ofDão DOCandBairrada DOCare among the most reputed inPortugal.The major industrial, commerce, and service centres are located in and aroundCoimbra,Aveiro,Viseu,Leiria,Covilhã,Castelo Branco,andFigueira da Foz.Important light industry and agriculture is also based in and aroundGuarda,Torres Novas,Torres VedrasandCaldas da Rainha.
Education[edit]
The Central region has threepublic universities:theUniversity of Coimbra,the oldest Portuguese university and the largest in the region; theAveiro University;and theUniversity of Beira Interior.There are also five state-runpolytechnicalinstitutes:Castelo Branco Polytechnical Institute;Coimbra Polytechnical Institute;Guarda Polytechnical Institute;Leiria Polytechnical Institute;Tomar Polytechnical Institute andViseu Polytechnical Institute.In addition, there are a large number of publicnursing schoolsandprivate higher educationinstitutions across the region.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^"Produto interno bruto (B.1*g) a preços correntes (Base 2016 - €) por Localização geográfica (NUTS - 2013); Anual".ine.pt.Retrieved3 September2023.
- ^"Produto interno bruto (B.1*g) por habitante a preços correntes (Base 2016 - €) por Localização geográfica (NUTS - 2013); Anual".ine.pt.Retrieved3 September2023.
- ^"Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab".hdi.globaldatalab.org.Retrieved31 July2023.
- ^"Censos 2011 Resultados Preliminares 2011".INE.
- ^"Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018".Eurostat.
External links[edit]
- Center of Portugal(Official Center Tourism site)
- Fatima Tourism(Official Fatima Tourism site)






