Cherry angioma
| Cherry angioma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A cherry angioma on a person's arm | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
Cherry angioma,also called cherry hemangioma[1]or Campbell de Morgan Spot,[2]is a smallbright reddome-shapedbumpon the skin.[3]It ranges between 0.5 – 6 mm in diameter and usually several are present, typically on the chest and arms, and increasing in number with age.[3][4]If scratched, they may bleed.[5]
They are a harmless benign tumour, containing an abnormal proliferation of blood vessels, and have no relationship to cancer. They are the most common kind ofangioma,and increase with age, occurring in nearly all adults over 30 years. They were first described by the nineteenth-century British surgeon,Campbell de Morgan.
Signs and symptoms
[edit]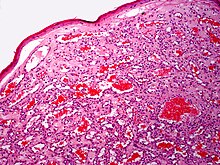
Cherry angiomas are made up of clusters ofcapillariesat the surface of theskin,[5]forming a small round dome ( "papule"),[5]which may be flat topped[citation needed].They range incolourfrom brightredtopurple.When they first develop, they may be only a tenth of a millimeter in diameter and almost flat, appearing as small red dots. However, they then usually grow to about one or two millimeters across, and sometimes to a centimeter or more in diameter[citation needed].As they grow larger, they tend to expand in thickness, and may take on the raised and rounded shape of adome.Multiple adjoining angiomas form apolypoid angioma.[5]Because theblood vesselscomprising an angioma are so close to the skin's surface, cherry angiomas maybleedprofusely if they are injured.[5]
One study found that the majority of capillaries in cherry hemangiomas arefenestratedand stain forcarbonic anhydraseactivity.[6]
Cause
[edit]Cherry angiomas appear spontaneously in many people in middle age but can also, less commonly, occur in young people. They can also occur in an aggressive eruptive manner in any age. The underlying cause for the development of cherry angiomas is not understood.
Cherry angioma may occur through two different mechanisms:angiogenesis(the formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels), andvasculogenesis(the formation of totally new vessels, which usually occurs during embryonic and fetal development).[7]
One study published in 2010 found that a regulatory nucleic acid suppresses protein growth factors that cause vascular growth. This regulatory nucleic acid was lower in tissue samples of hemangiomas, and the growth factors were elevated, which suggests that the elevated growth factors may cause hemangiomas.[8]The study found that the level ofmicroRNA424 is significantly reduced in senile hemangiomas compared to normal skin resulting in increased protein expression ofMEK1andcyclin E1.By inhibiting mir-424 in normalendothelial cellsthey could observe the same increased protein expression of MEK1 and cyclin E1 which, important for the development of senile hemangioma, induced cell proliferation of theendothelial cells.They also found that targeting MEK1 and cyclin E1 withsmall interfering RNAdecreased the number of endothelial cells.
A study published in 2019 identified that somatic mutations inGNAQandGNA11genes[9]are present in many cherry angiomas. These specific missense mutations found in hemangiomas are also associated withport-wine stainsanduveal melanoma.As--the mostly juvenile--Waterhouse Friedrichsen Syndrome is caused by adrenal bleeding from bacterial infections, the 'senile' cherry angiomas may have to be researched for a viral and fungal pathology of the adrenals themselves or of the meninges affecting the adrenals with less dramatic bleeding compared to Waterhouse Friedrichsen's.
Chemicals and compounds that have been seen to cause cherry angiomas aremustard gas,[10][11][12][13]2-butoxyethanol,[14]bromides,[15]andcyclosporine.[16]
A significant increase in the density ofmast cellshas been seen in cherry hemangiomas compared with normal skin.[17]

Diagnosis
[edit]The diagnosis is based on the clinical appearance of the lesions. Examination with adermatoscopeshows characteristic red, purple, or blue-blacklagoons.
Thedifferential diagnosisincludesnodular basal cell carcinoma,amelanotic melanoma,andangiokeratoma.[1]
Treatment
[edit]These lesions generally do not require treatment. If they are cosmetically unappealing or are subject to bleeding angiomas may be removed byelectrocautery,a process of destroying the tissue by use of a small probe with an electric current running through it.[18]Removal may cause scarring. More recentlypulsed dye laserorintense pulsed light(IPL) treatment has also been used.[19][20]
Future treatment based on a locally acting inhibitor ofMEK1andCyclin E1could possibly be an option. A natural MEK1 inhibitor ismyricetin.[21][22]
Prognosis
[edit]In most patients, the number and size of cherry angiomas increases with advancing age. They are harmless, having no relation to cancer at all.[23] Eruptive cherry hemangiomatosis has been rarely reported as a heralding sign of multicentricCastleman disease(MCD),multiple myeloma,and otherlymphoproliferativediseases.[24][25]
Epidemiology
[edit]Cherry angiomas occur in all races, ethnic backgrounds, and sexes.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^abWaldman, Reid A.; Grant-Kels, Jane M. (2021).Dermatology for the Primary Care Provider.Elsevier. p. 230.ISBN9780323712378.
- ^"Campbell de Morgan Spots (Causes, Symptoms and Treatment)".patient.info.2022-01-18.Retrieved2024-02-13.
- ^abJames, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020)."28. Dermal and subcutaneous tumors".Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology(13th ed.). Elsevier. pp. 593–594.ISBN978-0-323-54753-6.
- ^Johnstone, Ronald B. (2017). "38. Vascular tumors".Weedon's Skin Pathology Essentials(2nd ed.). Elsevier. p. 690.ISBN978-0-7020-6830-0.
- ^abcdeStockman, David L. (2016)."Cherry angioma".Diagnostic pathology. Vascular.Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. pp. 3.4–3.5.ISBN978-0-323-37674-7.
- ^Eichhorn, M; Jungkunz, W; Wörl, J; Marsch, WC (1994)."Carbonic anhydrase is abundant in fenestrated capillaries of cherry hemangioma".Acta Dermato-Venereologica.74(1): 51–3.doi:10.2340/00015555745456.PMID7908484.S2CID6716433.
- ^Kishimoto, Saburo; Hideya Takenaka; Hideya Takenaka; Hideya Takenaka; Hirokazu Yasuno (2000). "Glomeruloid hemangioma in POEMS syndrome shows two different immunophenotypic endothelial cells".Cutaneous Pathology.27(2): 87–92.doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2000.027002087.x.PMID10678704.S2CID25150654.
- ^Nakashima, T; Jinnin, M; Etoh, T; Fukushima, S; Masuguchi, S; Maruo, K; Inoue, Y; Ishihara, T; Ihn, H (2010). Egles, Christophe (ed.)."Down-regulation of mir-424 contributes to the abnormal angiogenesis via MEK1 and cyclin E1 in senile hemangioma: its implications to therapy".PLOS ONE.5(12): e14334.Bibcode:2010PLoSO...514334N.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014334.PMC3001869.PMID21179471.
- ^Klebanov, Nikolai; Lin, William M.; Artomov, Mykyta; Shaughnessy, Michael; Njauw, Ching-Ni; Bloom, Romi; Eterovic, Agda Karina; Chen, Ken; Kim, Tae-Beom (2019-01-02)."Use of Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing to Identify Activating Hot Spot Mutations in Cherry Angiomas".JAMA Dermatology.155(2): 211–215.doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4231.ISSN2168-6084.PMC6440195.PMID30601876.
- ^Firooz, Alireza; Komeili, Ali; Dowlati, Yahya (1999). "Eruptive melanocytic nevi and cherry angiomas secondary to exposureto sulfur mustard gas".Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.40(4): 646–7.doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70460-3.PMID10188695.
- ^Hefazi, Mehrdad; Maleki, Masoud; Mahmoudi, Mahmoud; Tabatabaee, Abbas; Balali-Mood, Mahdi (2006). "Delayed complications of sulfur mustard poisoning in the skin and the immune system of Iranian veterans 16–20 years after exposure".International Journal of Dermatology.45(9): 1025–31.doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.03020.x.PMID16961503.S2CID38801029.
- ^Ma, Hui-Jun; Zhao, Guang; Shi, Fei; Wang, Yi-Xia (2006). "Eruptive cherry angiomas associated with vitiligo: Provoked by topical nitrogen mustard?".The Journal of Dermatology.33(12): 877–9.doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2006.00200.x.PMID17169094.S2CID6811229.
- ^Emadi, Seyed Naser; Hosseini-Khalili, Alireza; Soroush, Mohammad Reza; Davoodi, Seyed Masoud; Aghamiri, Seyed Samad (2008). "Mustard gas scarring with specific pigmentary, trophic and vascular characteristics (case report, 16-year post-exposure)".Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.69(3): 574–6.doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.01.003.PMID17382390.
- ^Raymond, Lawrence W.; Williford, Linda S.; Burke, William A. (1998). "Eruptive Cherry Angiomas and Irritant Symptoms After One Acute Exposure to the Glycol Ether Solvent 2-Butoxyethanol".Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.40(12): 1059–64.doi:10.1097/00043764-199812000-00005.PMID9871882.
- ^Cohen, Arnon D.; Cagnano, Emanuela; Vardy, Daniel A. (2001). "Cherry Angiomas Associated with Exposure to Bromides".Dermatology.202(1): 52–3.doi:10.1159/000051587.PMID11244231.S2CID45485034.
- ^De Felipe, I.; Redondo, P (1998). "Eruptive Angiomas After Treatment With Cyclosporine in a Patient With Psoriasis".Archives of Dermatology.134(11): 1487–8.doi:10.1001/archderm.134.11.1487.PMID9828895.
- ^Hagiwara, K; Khaskhely, NM; Uezato, H; Nonaka, S (1999). "Mast cell" densities "in vascular proliferations: a preliminary study of pyogenic granuloma, portwine stain, cavernous hemangioma, cherry angioma, Kaposi's sarcoma, and malignant hemangioendothelioma".The Journal of Dermatology.26(9): 577–86.doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.1999.tb02052.x.PMID10535252.S2CID40976538.
- ^Aversa, AJ; Miller Of, 3rd (1983). "Cryo-curettage of cherry angiomas".The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology.9(11): 930–1.doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.1983.tb01042.x.PMID6630708.
{{cite journal}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^Dawn, G.; Gupta, G. (2003). "Comparison of potassium titanyl phosphate vascular laser and hyfrecator in the treatment of vascular spiders and cherry angiomas".Clinical and Experimental Dermatology.28(6): 581–3.doi:10.1046/j.1365-2230.2003.01352.x.PMID14616818.S2CID13497344.
- ^Fodor, Lucian; Ramon, Ytzhack; Fodor, Adriana; Carmi, Nurit; Peled, Isaac J.; Ullmann, Yehuda (2006). "A Side-by-Side Prospective Study of Intense Pulsed Light and Nd:YAG Laser Treatment for Vascular Lesions".Annals of Plastic Surgery.56(2): 164–70.doi:10.1097/01.sap.0000196579.14954.d6.PMID16432325.S2CID43324812.
- ^Lee, KW; Kang, NJ; Rogozin, EA; Kim, HG; Cho, YY; Bode, AM; Lee, HJ; Surh, YJ; et al. (2007)."Myricetin is a novel natural inhibitor of neoplastic cell transformation and MEK1".Carcinogenesis.28(9): 1918–27.doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm110.PMID17693661.
- ^Kim, JE; Kwon, JY; Lee, DE; Kang, NJ; Heo, YS; Lee, KW; Lee, HJ (2009). "MKK4 is a novel target for the inhibition of tumor necrosis factor- Alpha -induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression by myricetin".Biochemical Pharmacology.77(3): 412–21.doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.10.027.PMID19026990.
- ^Perkins, Sharon."Cherry Angioma & Skin Cancer".livestrong.Retrieved10 April2018.
- ^Fajgenbaum, David C.; Rosenbach, Misha; van Rhee, Frits; Nasir, Adnan; Reutter, Jason (2013-02-01)."Eruptive Cherry Hemangiomatosis Associated With Multicentric Castleman Disease: A Case Report and Diagnostic Clue".JAMA Dermatology.149(2): 204–208.doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.1552.ISSN2168-6068.PMID23426475.
- ^Lim, Eun-Hwa; Kim, Hyeong-rae; Im, Myung; Seo, Young-Joon; Lee, Jeung-Hoon; Lee, Young (2013-04-01)."Eruptive cherry hemangioma–like lesions developing in a patient with multiple myeloma".Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.68(4): e137–e138.doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.09.045.ISSN0190-9622.PMID23522425.
External links
[edit]- eMedicine with picture showing small red dots
- Pereira, José Marcos (2004)."Hemangioma rubi no couro cabeludo".Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia.79:83–89.doi:10.1590/S0365-05962004000100010.
