Pregnancy
| Pregnancy | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Gestation |
 | |
| A woman in the third trimester of pregnancy | |
| Specialty | Obstetrics,midwifery |
| Symptoms | Missed periods, tender breasts,nausea and vomiting,hunger, frequent urination[1] |
| Complications | Miscarriage,high blood pressure of pregnancy,gestational diabetes,iron-deficiency anemia,severe nausea and vomiting[2][3] |
| Duration | ~40 weeks from thelast menstrual period(38 weeks after conception)[4][5] |
| Causes | Sexual intercourse,assisted reproductive technology[6] |
| Diagnostic method | Pregnancy test[7] |
| Prevention | Birth control(includingemergency contraception)[8] |
| Treatment | Prenatal care,[9]abortion[8] |
| Medication | Folic acid,iron supplements[9][10] |
| Frequency | 213 million (2012)[11] |
| Deaths | |
Pregnancyis the time during which one or moreoffspringdevelops (gestates) inside awoman'suterus(womb).[4][13]Amultiple pregnancyinvolves more than one offspring, such as withtwins.[14]
Pregnancy usually occurs bysexual intercourse,but can also occur throughassisted reproductive technologyprocedures.[6]A pregnancy may end in alive birth,amiscarriage,aninduced abortion,or astillbirth.Childbirthtypically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of thelast menstrual period(LMP), a span known as thegestational age.[4][5]This is just over nine months. Counting byfertilization age,the length is about 38 weeks.[5][13]Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus";implantationoccurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization.[15]Anembryois the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the termfetusis used until birth.[5]
Signs and symptoms of early pregnancymay includemissed periods,tender breasts,morning sickness(nausea and vomiting), hunger,implantation bleeding,and frequent urination.[1]Pregnancy may be confirmed with apregnancy test.[7]Methods ofbirth control—or, more accurately,contraception—are used to avoid pregnancy.
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters of approximately three months each. Thefirst trimesterincludes conception, which is when the sperm fertilizes the egg. Thefertilized eggthen travels down thefallopian tubeand attaches to the inside of theuterus,where it begins to form theembryoandplacenta.During the first trimester, the possibility of miscarriage (natural death of embryo or fetus) is at its highest. Around the middle of the second trimester, movement of the fetus may be felt. At 28 weeks, more than 90% of babies cansurvive outside of the uterusifprovided with high-quality medical care,though babies born at this time will likely experience serious health complications such as heart and respiratory problems and long-term intellectual and developmental disabilities.
Prenatal careimproves pregnancy outcomes.[9]Nutritionduring pregnancy is important to ensure healthy growth of the fetus.[16]Prenatal care may also include avoidingrecreational drugs(includingtobaccoandalcohol), taking regular exercise, havingblood tests,and regularphysical examinations.[9]Complications of pregnancymay includedisorders of high blood pressure,gestational diabetes,iron-deficiency anemia,andsevere nausea and vomiting.[3]In the ideal childbirth, labor begins on its own "at term".[17]Babies born before 37 weeks are "preterm"and at higher risk of health problems such ascerebral palsy.[4]Babies born between weeks 37 and 39 are considered "early term" while those born between weeks 39 and 41 are considered "full term".[4]Babies born between weeks 41 and 42 weeks are considered "late-term" while after 42 weeks they are considered "post-term".[4]Deliverybefore 39 weeks bylabor inductionorcaesarean sectionis not recommended unless required for other medical reasons.[18]
Terminology

Associated terms for pregnancy aregravidandparous.Gravidusandgravidcome from theLatinword meaning "heavy" and a pregnant female is sometimes referred to as agravida.[19]Gravidityrefers to the number of times that a female has been pregnant. Similarly, the termparityis used for the number of times that a female carries a pregnancy to aviable stage.[20]Twinsand other multiple births are counted as one pregnancy and birth.
A woman who has never been pregnant is referred to as anulligravida.A woman who is (or has been only) pregnant for the first time is referred to as aprimigravida,[21]and a woman in subsequent pregnancies as amultigravidaor asmultiparous.[19][22]Therefore, during a second pregnancy a woman would be described asgravida 2, para 1and upon live delivery asgravida 2, para 2.In-progress pregnancies,abortions,miscarriagesand/orstillbirthsaccount for parity values being less than the gravida number. Women who have never carried a pregnancy more than 20 weeks are referred to asnulliparous.[23]
A pregnancy is consideredtermat 37 weeks of gestation. It ispretermif less than 37 weeks andposttermat or beyond 42 weeks of gestation. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists have recommended further division withearly term37 weeks up to 39 weeks,full term39 weeks up to 41 weeks, andlate term41 weeks up to 42 weeks.[24]The termspretermandposttermhave largely replaced earlier terms ofprematureandpostmature.Pretermandposttermare defined above, whereasprematureandpostmaturehave historical meaning and relate more to the infant's size and state of development rather than to the stage of pregnancy.[25][26]
Demographics and statistics
About 213 million pregnancies occurred in 2012, of which, 190 million (89%) were in thedeveloping worldand 23 million (11%) were in the developed world.[11]The number of pregnancies in women aged between 15 and 44 is 133 per 1,000 women.[11]About 10% to 15% of recognized pregnancies end inmiscarriage.[2]In 2016,complications of pregnancyresulted in 230,600maternal deaths,down from 377,000 deaths in 1990.[12]Common causes includebleeding,infections,hypertensive diseases of pregnancy,obstructed labor,miscarriage, abortion, orectopic pregnancy.[12]Globally, 44% of pregnancies areunplanned.[27]Over half (56%) of unplanned pregnancies are aborted.[27]Among unintended pregnancies in the United States, 60% of the women usedbirth controlto some extent during the month pregnancy began.[28]
Signs and symptoms
The usualsigns and symptoms of pregnancydo not significantly interfere withactivities of daily livingor pose a health-threat to themotheror baby. However,pregnancy complicationscan cause other more severe symptoms, such as those associated withanemia.
Common signs and symptoms of pregnancy include:
- Tiredness
- Morning sickness
- Constipation
- Pelvic girdle pain
- Back pain
- Braxton Hicks contractions.Occasional, irregular, and often painless contractions that occur several times per day.
- Peripheral edemaswelling of the lower limbs. Common complaint in advancing pregnancy. Can be caused byinferior vena cava syndromeresulting from compression of theinferior vena cavaand pelvic veins by theuterusleading to increasedhydrostatic pressurein lower extremities.
- Low blood pressureoften caused by compression of both the inferior vena cava and theabdominal aorta(aortocaval compression syndrome).
- Increased urinary frequency.A common complaint, caused by increased intravascular volume, elevatedglomerular filtration rate,and compression of thebladderby the expanding uterus.
- Urinary tract infection[29]
- Varicose veins.Common complaint caused by relaxation of the venoussmooth muscleand increased intravascular pressure.
- Hemorrhoids(piles). Swollenveins at or inside the anal area.Caused by impaired venous return, straining associated with constipation, or increased intra-abdominal pressure in later pregnancy.[30]
- Regurgitation,heartburn,andnausea.
- Stretch marks
- Breast tendernessis common during the first trimester, and is more common in women who are pregnant at a young age.[31]
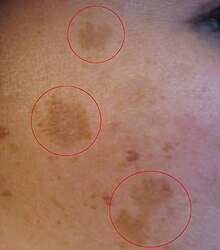
- Melasma,also known as the mask of pregnancy, is a discoloration, most often of the face. It usually begins to fade several months after giving birth.
Timeline
| Event | Gestational age
(from the start of thelast menstrual period) |
Fertilization age | Implantation age |
|---|---|---|---|
| Menstrual periodbegins | Day 1 of pregnancy | Not pregnant | Not pregnant |
| Hassexandovulates | 2 weeks pregnant | Not pregnant | Not pregnant |
| Fertilization;cleavage stagebegins[32] | Day 15[32] | Day 1[32][33] | Not pregnant |
| Implantationofblastocystbegins | Day 20 | Day 6[32][33] | Day 0 |
| Implantation finished | Day 26 | Day 12[32][33] | Day 6 (orDay 0) |
| Embryostage begins; also, firstmissed period | 4 weeks | Day 15[32] | Day 9 |
| Primitive heart functioncan bedetected | 5 weeks, 5 days[32] | Day 26[32] | Day 20 |
| Fetal stagebegins | 10 weeks, 1 day[32] | 8 weeks, 1 day[32] | 7 weeks, 2 days |
| First trimester ends | 13 weeks | 11 weeks | 10 weeks |
| Second trimester ends | 26 weeks | 24 weeks | 23 weeks |
| Childbirth | 39–40 weeks | 37–38 weeks[33]: 108 | 36–37 weeks |
Thechronologyof pregnancy is, unless otherwise specified, generally given asgestational age,where the starting point is the beginning of the woman'slast menstrual period(LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. This model means that the woman is counted as being "pregnant" two weeks beforeconceptionand three weeks beforeimplantation.Sometimes, timing may also use thefertilization age,which is the age of the embryo since conception.
Start of gestational age
TheAmerican Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologistsrecommends the following methods to calculate gestational age:[34]
- Directly calculating the days since the beginning of thelast menstrual period.
- Earlyobstetric ultrasound,comparing the size of anembryoorfetusto that of areference groupof pregnancies of known gestational age (such as calculated from last menstrual periods), and using the mean gestational age of other embryos or fetuses of the same size. If the gestational age as calculated from an early ultrasound is contradictory to the one calculated directly from the last menstrual period, it is still the one from the early ultrasound that is used for the rest of the pregnancy.[34]
- In case ofin vitro fertilization,calculating days sinceoocyte retrievalorco-incubationand adding 14 days.[35]
Trimesters
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters, each lasting for approximately three months.[4]The exact length of each trimester can vary between sources.
- Thefirst trimesterbegins with the start of gestational age as described above, that is, the beginning of week 1, or 0 weeks + 0 days of gestational age (GA). It ends at week 12 (11 weeks + 6 days of GA)[4]or end of week 14 (13 weeks + 6 days of GA).[36]
- Thesecond trimesteris defined as starting, between the beginning of week 13 (12 weeks +0 days of GA)[4]and beginning of week 15 (14 weeks + 0 days of GA).[36]It ends at the end of week 27 (26 weeks + 6 days of GA)[36]or end of week 28 (27 weeks + 6 days of GA).[4]
- Thethird trimesteris defined as starting, between the beginning of week 28 (27 weeks + 0 days of GA)[36]or beginning of week 29 (28 weeks + 0 days of GA).[4]It lasts untilchildbirth.

Estimation of due date

Due date estimationbasically follows two steps:
- Determination of which time point is to be used asoriginforgestational age,as described in the section above.
- Adding the estimated gestational age at childbirth to the above time point. Childbirth on average occurs at a gestational age of 280 days (40 weeks), which is therefore often used as a standard estimation for individual pregnancies.[38]However, alternative durations as well as more individualized methods have also been suggested.
TheAmerican College of Obstetricians and Gynecologistsdivides full term into three divisions:[39]
- Early-term: 37 weeks and 0 days through 38 weeks and 6 days
- Full-term: 39 weeks and 0 days through 40 weeks and 6 days
- Late-term: 41 weeks and 0 days through 41 weeks and 6 days
- Post-term: greater than or equal to 42 weeks and 0 days
Naegele's ruleis a standard way of calculating the due date for a pregnancy when assuming a gestational age of 280 days at childbirth. The rule estimates the expected date of delivery (EDD) by adding a year, subtracting three months, and adding seven days to the origin of gestational age. Alternatively there aremobile apps,which essentially always give consistent estimations compared to each other and correct forleap year,while pregnancy wheels made of paper can differ from each other by 7 days and generally do not correct for leap year.[40]
Furthermore, actual childbirth has only a certain probability of occurring within the limits of the estimated due date. A study of singleton live births came to the result that childbirth has astandard deviationof 14 days when gestational age is estimated by first trimesterultrasound,and 16 days when estimated directly by last menstrual period.[37]
Physiology
Capacity
Fertilityandfecundityare the respective capacities tofertilizeand establish a clinical pregnancy and have a live birth.Infertilityis an impaired ability to establish a clinical pregnancy andsterilityis the permanent inability to establish a clinical pregnancy.[41]
The capacity for pregnancy depends on thereproductive system,its developmentandits variation,as well as on the condition of a person. Womenas well asintersexandtransgenderpeople who have a functioningfemale reproductive systemare capable of pregnancy. In some cases, someone might be able to produce fertilizable eggs, but might not have a womb or none that can sufficiently gestate, in which case they might findsurrogacy.[42]
Initiation
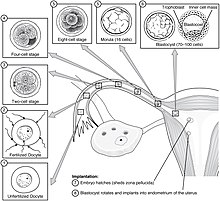
Through an interplay of hormones that includesfollicle stimulating hormonethat stimulatesfolliculogenesisandoogenesiscreates a matureegg cell,the femalegamete.Fertilizationis the event where the egg cell fuses with the male gamete,spermatozoon.After the point of fertilization, the fused product of the female and male gamete is referred to as azygoteor fertilized egg. The fusion of female and male gametes usually occurs following the act ofsexual intercourse.Pregnancy rates for sexual intercourseare highest during themenstrual cycletime from some 5 days before until 1 to 2 days after ovulation.[43]Fertilization can also occur byassisted reproductive technologysuch asartificial inseminationandin vitro fertilisation.
Fertilization (conception) is sometimes used as the initiation of pregnancy, with the derived age being termedfertilization age.Fertilization usually occurs about two weeks before thenextexpected menstrual period.
A third point in time is also considered by some people to be the true beginning of a pregnancy: This is time of implantation, when the future fetus attaches to the lining of the uterus. This is about a week to ten days after fertilization.[44]
Development of embryo and fetus
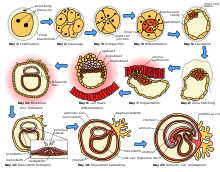
The sperm and the egg cell, which has been released from one of the female's twoovaries,unite in one of the twofallopian tubes.The fertilized egg, known as azygote,then moves toward the uterus, a journey that can take up to a week to complete. Cell division begins approximately 24 to 36 hours after the female and male cells unite. Cell division continues at a rapid rate and the cells then develop into what is known as ablastocyst.The blastocyst arrives at the uterus and attaches to the uterine wall, a process known asimplantation.
The development of the mass of cells that will become the infant is calledembryogenesisduring the first approximately ten weeks of gestation. During this time, cells begin to differentiate into the various body systems. The basic outlines of the organ, body, and nervous systems are established. By the end of the embryonic stage, the beginnings of features such as fingers, eyes, mouth, and ears become visible. Also during this time, there is development of structures important to the support of the embryo, including theplacentaandumbilical cord.The placenta connects the developing embryo to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. The umbilical cord is the connecting cord from the embryo or fetus to the placenta.
After about ten weeks of gestational age—which is the same as eight weeks after conception—the embryo becomes known as afetus.[45]At the beginning of the fetal stage, the risk of miscarriage decreases sharply.[46]At this stage, a fetus is about 30 mm (1.2 inches) in length, the heartbeat is seen via ultrasound, and the fetus makes involuntary motions.[47]During continued fetal development, the early body systems, and structures that were established in the embryonic stage continue to develop. Sex organs begin to appear during the third month of gestation. The fetus continues to grow in both weight and length, although the majority of the physical growth occurs in the last weeks of pregnancy.
Electricalbrain activityis first detected at the end of week 5 of gestation, but as inbrain-deadpatients, it is primitive neural activity rather than the beginning of conscious brain activity. Synapses do not begin to form until week 17.[48]Neural connections between thesensory cortexandthalamusdevelop as early as 24 weeks' gestational age, but the first evidence of their function does not occur until around 30 weeks, when minimalconsciousness,dreaming,and the ability to feel pain emerges.[49]
Although the fetus begins to move during the first trimester, it is not until the second trimester that movement, known asquickening,can be felt. This typically happens in the fourth month, more specifically in the 20th to 21st week, or by the 19th week if the woman has been pregnant before. It is common for some women not to feel the fetus move until much later. During the second trimester, when the body size changes,maternity clothesmay be worn.
-
Embryo at 4 weeks after fertilization (gestational age of 6 weeks)
-
Fetus at 8 weeks after fertilization (gestational age of 10 weeks)
-
Fetus at 18 weeks after fertilization (gestational age of 20 weeks)
-
Fetus at 38 weeks after fertilization (gestational age of 40 weeks)
-
Relative size in 1st month (simplified illustration)
-
Relative size in 3rd month (simplified illustration)
-
Relative size in 5th month (simplified illustration)
-
Relative size in 9th month (simplified illustration)
Maternal changes


During pregnancy, a woman undergoes many normalphysiologicalchanges, includingbehavioral,cardiovascular,hematologic,metabolic,renal,andrespiratorychanges. Increases inblood sugar,breathing,andcardiac outputare all required. Levels ofprogesteroneandestrogensrise continually throughout pregnancy, suppressing thehypothalamic axisand therefore themenstrual cycle.A full-term pregnancy at an early age (less than 25 years) reduces the risk ofbreast,ovarian,andendometrial cancer,and the risk declines further with each additional full-term pregnancy.[50][51]

The fetus isgeneticallydifferent from its mother and can therefore be viewed as an unusually successfulallograft.[52]The main reason for this success is increasedimmune toleranceduring pregnancy,[53]which prevents the mother's body from mounting animmune system responseagainst certain triggers.[52]
During the first trimester,minute ventilationincreases by 40 percent.[54]The womb will grow to the size of alemonby eight weeks. Manysymptoms and discomforts of pregnancy,such as nausea andtender breasts,appear in the first trimester.[55]
During the second trimester, most women feel more energized and put on weight as the symptoms ofmorning sicknesssubside. They begin to feel regularfetal movements,which can become strong and even disruptive.[citation needed]
Braxton Hicks contractionsare sporadicuterine contractionsthat may start around six weeks into a pregnancy; however, they are usually not felt until the second or third trimester.[56]
Final weight gain takes place during the third trimester; this is the most weight gain throughout the pregnancy. The woman's abdomen will transform in shape as the fetus turns in a downward position ready for birth. The woman'snavelwill sometimes become convex, "popping" out, due to the expandingabdomen.The uterus, the muscular organ that holds the developing fetus, can expand up to 20 times its normal size during pregnancy.
Head engagement,also called "lightening" or "dropping", occurs as the fetal head descends into acephalic presentation.While it relieves pressure on the upper abdomen and gives a renewed ease in breathing, it also severely reduces bladder capacity, resulting in a need tovoid more frequently,and increases pressure on the pelvic floor and the rectum. It is not possible to predict when lightening will occur. In a first pregnancy it may happen a few weeks before the due date, though it may happen later or even not until labor begins, as is typical with subsequent pregnancies.[57]
It is during the third trimester that maternal activity and sleep positions may affectfetal developmentdue to restrictedblood flow.For instance, the enlarged uterus may impede blood flow by compressing thevena cavawhen lying flat, a condition that can be relieved by lying on the left side.[58]
Childbirth
Childbirth, referred to as labor and delivery in the medical field, is the process whereby an infant is born.[59]
A woman is considered to be in labor when she begins experiencing regular uterine contractions, accompanied by changes of her cervix—primarily effacement and dilation. While childbirth is widely experienced as painful, some women do report painless labors, while others find that concentrating on the birth helps to quicken labor and lessen the sensations. Most births are successful vaginal births, but sometimes complications arise and a woman may undergo acesarean section.
During the time immediately after birth, both the mother and thebabyare hormonally cued to bond, the mother through the release ofoxytocin,a hormone also released duringbreastfeeding.Studies show that skin-to-skin contact between a mother and her newborn immediately after birth is beneficial for both the mother and baby. A review done by theWorld Health Organizationfound that skin-to-skin contact between mothers and babies after birth reduces crying, improves mother–infant interaction, and helps mothers to breastfeed successfully. They recommend thatneonatesbe allowed to bond with the mother during their first two hours after birth, the period that they tend to be more alert than in the following hours of early life.[60]
Childbirth maturity stages
| stage | starts | ends |
|---|---|---|
| Preterm[61] | - | at 37 weeks |
| Early term[62] | 37 weeks | 39 weeks |
| Full term[62] | 39 weeks | 41 weeks |
| Late term[62] | 41 weeks | 42 weeks |
| Postterm[62] | 42 weeks | - |
In the idealchildbirth,labor begins on its own when a woman is "at term".[17] Events before completion of 37 weeks are considered preterm.[61]Preterm birthis associated with a range of complications and should be avoided if possible.[63]
Sometimes if a woman'swater breaksor she hascontractionsbefore 39 weeks, birth is unavoidable.[62]However, spontaneous birth after 37 weeks is considered term and is not associated with the same risks of a preterm birth.[59]Planned birth before 39 weeks bycaesarean sectionorlabor induction,although "at term", results in an increased risk of complications.[64]This is from factors includingunderdeveloped lungs of newborns,infection due to underdeveloped immune system, feeding problems due to underdeveloped brain, andjaundicefrom underdeveloped liver.[65]
Babies born between 39 and 41 weeks' gestation have better outcomes than babies born either before or after this range.[62]This special time period is called "full term".[62]Whenever possible, waiting for labor to begin on its own in this time period is best for the health of the mother and baby.[17]The decision to perform an induction must be made after weighing the risks and benefits, but is safer after 39 weeks.[17]
Events after 42 weeks are consideredpostterm.[62]When a pregnancy exceeds 42 weeks, the risk of complications for both the woman and the fetus increases significantly.[66][67]Therefore, in an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy, obstetricians usually prefer to induce labor at some stage between 41 and 42 weeks.[68]
Postnatal period
Thepostpartum periodalso referred to as thepuerperium,is the postnatal period that begins immediately after delivery and extends for about six weeks.[59]During this period, the mother's body begins the return to pre-pregnancy conditions that includes changes in hormone levels and uterus size.[59]
Diagnosis
The beginning of pregnancy may be detected either based on symptoms by the woman herself, or by usingpregnancy tests.However, an important condition with serious health implications that is quite common is thedenial of pregnancyby the pregnant woman. About 1 in 475 denials will last until around the 20th week of pregnancy. The proportion of cases of denial, persisting until delivery is about 1 in 2500.[69]Conversely, some non-pregnant women have a very strong belief that they are pregnant along with some of the physical changes. This condition is known as afalse pregnancy.[70]
Physical signs

Most pregnant women experience a number of symptoms,[71]which can signify pregnancy. A number of earlymedical signsare associated with pregnancy.[72][73]These signs include:
- the presence ofhuman chorionic gonadotropin(hCG) in the blood and urine
- missedmenstrual period
- implantation bleedingthat occurs atimplantationof the embryo in the uterus during the third or fourth week after last menstrual period
- increasedbasal body temperaturesustained for over two weeks afterovulation
- Chadwick's sign(bluish discolouration of thecervix,vagina,andvulva)
- Goodell's sign(softening of the vaginal portion of the cervix)
- Hegar's sign(softening of theuterine isthmus)
- Pigmentationof thelinea alba,calledlinea nigra(darkening of the skin in a midline of theabdomen,resulting from hormonal changes, usually appearing around the middle of pregnancy).[72][73]
- Darkening of the nipples and areolas due to an increase in hormones.[74]
Biomarkers
Pregnancy detection can be accomplished using one or more variouspregnancy tests,[75]which detect hormones generated by the newly formedplacenta,serving asbiomarkersof pregnancy.[76]Blood and urine tests can detect pregnancy by 11 and 14 days, respectively, after fertilization.[77][78]Blood pregnancy tests are moresensitivethan urine tests (giving fewer false negatives).[79]Home pregnancy tests are urine tests, and normally detect a pregnancy 12 to 15 days after fertilization.[80]A quantitative blood test can determine approximately the date the embryo was fertilized becausehCGlevels double every 36 to 72 hours before 8 weeks' gestation.[59][78]A single test ofprogesteronelevels can also help determine how likely a fetus will survive in those with athreatened miscarriage(bleeding in early pregnancy), but only if the ultrasound result was inconclusive.[81]
Ultrasound
Obstetric ultrasonographycan detectfetal abnormalities,detectmultiple pregnancies,and improve gestational dating at 24 weeks.[82]The resultant estimatedgestational ageand due date of the fetus are slightly more accurate than methods based on last menstrual period.[83]Ultrasound is used to measure thenuchal foldin order to screen forDown syndrome.[84]
Management
Prenatal care
Pre-conception counselingis care that is provided to a woman or couple to discuss conception, pregnancy, current health issues and recommendations for the period before pregnancy.[87]
Prenatal medical careis the medical and nursing care recommended for women during pregnancy, time intervals and exact goals of each visit differ by country.[88]Women who are high risk have better outcomes if they are seen regularly and frequently by a medical professional than women who are low risk.[89]A woman can be labeled as high risk for different reasons including previous complications in pregnancy, complications in the current pregnancy, current medical diseases, or social issues.[90][91]
The aim of good prenatal care is prevention, early identification, and treatment of any medical complications.[92]A basic prenatal visit consists of measurement of blood pressure,fundal height,weight and fetal heart rate, checking for symptoms of labor, and guidance for what to expect next.[87]
Nutrition
Nutritionduring pregnancy is important to ensure healthy growth of the fetus.[16]Nutrition during pregnancy is different from the non-pregnant state.[16]There are increased energy requirements and specific micronutrient requirements.[16]Women benefit from education to encourage a balanced energy and protein intake during pregnancy.[93]Some women may need professional medical advice if their diet is affected by medical conditions, food allergies, or specific religious/ ethical beliefs.[94]Further studies are needed to access the effect of dietary advice to preventgestational diabetes,although low quality evidence suggests some benefit.[95]Adequate periconceptional (time before and right after conception)folic acid(also called folate or Vitamin B9) intake has been shown to decrease the risk of fetal neural tube defects, such asspina bifida.[96]The neural tube develops during the first 28 days of pregnancy, a urine pregnancy test is not usually positive until 14 days post-conception, explaining the necessity to guarantee adequate folate intake before conception.[80][97]Folate is abundant ingreen leafy vegetables,legumes,andcitrus.[98]In the United States and Canada, most wheat products (flour, noodles) are fortified with folic acid.[99]
Weight gain

The amount of healthy weight gain during a pregnancy varies.[100]Weight gain is related to the weight of the baby, the placenta, extra circulatory fluid, larger tissues, and fat and protein stores.[16]Most needed weight gain occurs later in pregnancy.[101]
TheInstitute of Medicinerecommends an overall pregnancy weight gain for those of normal weight (body mass indexof 18.5–24.9), of 11.3–15.9 kg (25–35 pounds) having a singleton pregnancy.[102]Women who are underweight (BMI of less than 18.5), should gain between 12.7 and 18 kg (28–40 lb), while those who areoverweight(BMI of 25–29.9) are advised to gain between 6.8 and 11.3 kg (15–25 lb) and those who areobese(BMI ≥ 30) should gain between 5–9 kg (11–20 lb).[103]These values reference the expectations for a term pregnancy.
During pregnancy, insufficient or excessive weight gain can compromise the health of the mother and fetus.[101]The most effective intervention for weight gain in underweight women is not clear.[101]Being or becoming overweight in pregnancy increases the risk of complications for mother and fetus, includingcesarean section,gestational hypertension,pre-eclampsia,macrosomiaandshoulder dystocia.[100]Excessive weight gain can make losing weight after the pregnancy difficult.[100][104]Some of these complications are risk factors forstroke.[105]
Around 50% of women of childbearing age in developed countries like the United Kingdom are overweight or obese before pregnancy.[104]Diet modification is the most effective way to reduce weight gain and associated risks in pregnancy.[104]
Medication
Drugs used during pregnancy can have temporary or permanent effects on the fetus.[106]Anything (including drugs) that can cause permanent deformities in the fetus are labeled asteratogens.[107]In the U.S., drugs were classified into categories A, B, C, D and X based on theFood and Drug Administration(FDA) rating system to provide therapeutic guidance based on potential benefits and fetal risks.[108]Drugs, including somemultivitamins,that have demonstrated no fetal risks after controlled studies in humans are classified as Category A.[106]On the other hand, drugs likethalidomidewith proven fetal risks that outweigh all benefits are classified as Category X.[106]
Recreational drugs
The use ofrecreational drugsin pregnancy can cause variouspregnancy complications.[59]
- Alcoholic drinksconsumed during pregnancy can cause one or morefetal alcohol spectrum disorders.[59]According to theCDC,there is no known safe amount of alcohol during pregnancy and no safe time to drink during pregnancy, including before a woman knows that she is pregnant.[109]
- Tobacco smoking during pregnancycan cause a wide range of behavioral, neurological, and physical difficulties.[110]Smoking during pregnancy causes twice the risk ofpremature rupture of membranes,placental abruptionandplacenta previa.[111]Smoking is associated with 30% higher odds of preterm birth.[112]
- Prenatal cocaine exposureis associated withpremature birth,birth defectsandattention deficit disorder.[59]
- Prenatal methamphetamine exposurecan cause premature birth andcongenital abnormalities.[113]Short-term neonatal outcomes inmethamphetamine babiesshow small deficits in infant neurobehavioral function and growth restriction.[114]Long-term effects in terms of impaired brain development may also be caused bymethamphetamineuse.[113]
- Cannabis in pregnancyhas been shown to beteratogenicin large doses in animals, but has not shown any teratogenic effects in humans.[59]
Exposure to toxins
Intrauterine exposure toenvironmental toxins in pregnancyhas the potential to cause adverse effects onprenatal development,and to causepregnancy complications.[59]Air pollution has been associated with low birth weight infants.[115]Conditions of particular severity in pregnancy includemercury poisoningandlead poisoning.[59]To minimize exposure to environmental toxins, the American College of Nurse-Midwives recommends: checking whether the home haslead paint,washing all freshfruitsandvegetablesthoroughly and buyingorganicproduce, and avoiding cleaning products labeled "toxic" or any product with a warning on the label.[116]
Pregnant women can also be exposed totoxins in the workplace,including airborne particles. The effects of wearing anN95 filtering facepiece respiratorare similar for pregnant women as for non-pregnant women, and wearing a respirator for one hour does not affect the fetal heart rate.[117]
Death by violence
Pregnant women or those who have recently given birth in the U.S. aremore likely to be murderedthan to die from obstetric causes. These homicides are a combination of intimate partner violence and firearms. Health authorities have called the violence "a health emergency for pregnant women", but say that pregnancy-related homicides are preventable if healthcare providers identify those women at risk and offer assistance to them.[118][119][120]
Sexual activity
Most women can continue to engage in sexual activity, includingsexual intercourse,throughout pregnancy.[121]Research suggests that during pregnancy both sexual desire and frequency of sexual relations decrease during the first and third trimester, with a rise during the second trimester.[122][123][124][125]Sex during pregnancy is a low-risk behavior except when the healthcare provider advises that sexual intercourse be avoided for particular medical reasons.[121]For a healthy pregnant woman, there is no singlesafeorrightway to have sex during pregnancy.[121]
Exercise

Regularaerobic exerciseduring pregnancy appears to improve (or maintain) physical fitness.[126]Physical exerciseduring pregnancy appears to decrease the need forC-section,[127]and even vigorous exercise carries no significant risks to babies[128]and provides significant health benefits to the mother.[129]Bed rest,outside of research studies, is not recommended as there is no evidence of benefit and potential harm.[130]
The Clinical Practice Obstetrics Committee of Canada recommends that "All women without contraindications should be encouraged to participate in aerobic and strength-conditioning exercises as part of a healthy lifestyle during their pregnancy".[131]Although an upper level of safe exercise intensity has not been established, women who were regular exercisers before pregnancy and who have uncomplicated pregnancies should be able to engage in high intensity exercise programs, without a higher risk of prematurity, lower birth weight, or gestational weight gain.[128]In general, participation in a wide range of recreational activities appears to be safe, with the avoidance of those with a high risk of falling such as horseback riding or skiing or those that carry a risk of abdominal trauma, such as soccer or hockey.[132]
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologistsreports that in the past, the main concerns of exercise in pregnancy were focused on the fetus and any potential maternal benefit was thought to be offset by potential risks to the fetus. However, they write that more recent information suggests that in the uncomplicated pregnancy, fetal injuries are highly unlikely.[132]They do, however, list several circumstances when a woman should contact her healthcare provider before continuing with an exercise program: vaginal bleeding,dyspneabefore exertion, dizziness, headache, chest pain, muscle weakness, preterm labor, decreased fetal movement, amniotic fluid leakage, and calf pain or swelling (to rule outthrombophlebitis).[132]
Sleep
It has been suggested thatshift workand exposure to bright light at night should be avoided at least during the last trimester of pregnancy to decrease the risk of psychological and behavioral problems in the newborn.[133]
Stress
The children of women who had high stress levels during pregnancy are slightly more likely to haveexternalizing behavioral problemssuch as impulsivity.[134]The behavioral effect was most pronounced during early childhood.[134]
Dental care
The increased levels ofprogesteroneandestrogenduring pregnancy makegingivitismore likely; thegumsbecome edematous, red in colour, and tend to bleed.[135]Also apyogenic granulomaor "pregnancy tumor", is commonly seen on the labial surface of the papilla. Lesions can be treated by local debridement or deep incision depending on their size, and by following adequateoral hygienemeasures.[136]There have been suggestions that severeperiodontitismay increase the risk of havingpreterm birthandlow birth weight;however, a Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine ifperiodontitiscan develop adverse birth outcomes.[137]
Flying
In low risk pregnancies, most health care providers approve flying until about 36 weeks of gestational age.[138]Most airlines allow pregnant women to fly short distances at less than 36 weeks, and long distances at less than 32 weeks.[139]Many airlines require a doctor's note that approves flying, especially at over 28 weeks.[139]During flights, the risk ofdeep vein thrombosisis decreased by getting up and walking occasionally, as well as by avoiding dehydration. The exposure to cosmic radiation is negligible for most travelers. For pregnant women, even the longest intercontinental fight would expose them less than 15% of both theNCRPMandICRPlimit.[140][139]Full body scannersdo not use ionizing radiation, and are safe in pregnancy.[141]
Pregnancy classes and birth plan
To prepare for the birth of the baby, health care providers recommend that parents attend antenatal classes during the third trimester of pregnancy. Classes include information about the process of labor and birth and the various kinds of births, including both vaginal andcaesarean delivery,the use of forceps, and other interventions that may be needed to safely deliver the infant. Types of pain relief, including relaxation techniques, are discussed. Partners or others who may plan to support a woman during her labor and delivery learn how to assist in the birth.[citation needed]
It is also suggested that a birth plan be written at this time. A birth plan is a written statement that outlines the desires of the mother during labor and delivery of the baby. Discussing the birth plan with the midwife or other care provider gives parents a chance to ask questions and learn more about the process of labour.[142]
In 1991 theWHOlaunched theBaby-Friendly Hospital Initiative,a global program that recognizes birthing centers and hospitals that offer optimal levels of care for giving birth. Facilities that have been certified as "Baby Friendly" accept visits from expecting parents to familiarize them with the facility and the staff.[143]
Complications
Each year, ill health as a result of pregnancy is experienced (sometimes permanently) by more than 20 million women around the world.[144]In 2016, complications of pregnancy resulted in 230,600 deaths down from 377,000 deaths in 1990.[12]Common causes includebleeding(72,000),infections(20,000),hypertensive diseases of pregnancy(32,000),obstructed labor(10,000), andpregnancy with abortive outcome(20,000), which includesmiscarriage,abortion,andectopic pregnancy.[12]
The following are some examples of pregnancy complications:
- Pregnancy induced hypertension
- Anemia[145]
- Postpartum depression,a common but solvable complication following childbirth that may result from decreased hormonal levels.[146]
- Postpartum psychosis
- Thromboembolic disorders,with an increased risk due tohypercoagulability in pregnancy.These are the leading cause of death in pregnant women in the US.[147][148]
- Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy(PUPPP), a skin disease that develops around the 32nd week. Signs are red plaques, papules, and itchiness around the belly button that then spreads all over the body except for the inside of hands and face.
- Ectopic pregnancy,includingabdominal pregnancy,implantation of the embryo outside the uterus
- Hyperemesis gravidarum,excessive nausea and vomiting that is more severe than normal morning sickness.
- Pulmonary embolism,a blood clot that forms in the legs and migrates to the lungs.[148]
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancyis a rare complication thought to be brought about by a disruption in the metabolism of fatty acids bymitochondria.
There is also an increasedsusceptibility and severity of certain infections in pregnancy.
Miscarriage and stillbirth
Miscarriage is the most common complication of early pregnancy. It is defined as the loss of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. The most common symptom of miscarriage is vaginal bleeding with or without pain. The miscarriage may be evidenced by a clot-like material passing through and out of the vagina.[149]About 80% of miscarriages occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. The underlying cause in about half of cases involves chromosomal abnormalities.[150]
Stillbirth is defined as fetal death after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. Each year about 21,000 babies are stillborn in the U.S.[151]Sadness, anxiety, and guilt may occur after a miscarriage or a stillbirth. Emotional support may help with processing the loss.[152]Fathers may experience grief over the loss as well. A large study found that there is a need to increase the accessibility of support services available for fathers.[153]
Diseases in pregnancy
A pregnant woman may have apre-existing disease,which is not directly caused by the pregnancy, but may causecomplicationsto develop that include a potential risk to the pregnancy; or a disease may develop during pregnancy.
- Diabetes mellitus and pregnancydeals with the interactions ofdiabetes mellitus(not restricted togestational diabetes) and pregnancy. Risks for the child include miscarriage, growth restriction, growth acceleration,large for gestational age(macrosomia),polyhydramnios(too muchamniotic fluid), and birth defects.
- Thyroid disease in pregnancycan, if uncorrected, cause adverse effects on fetal and maternal well-being. The deleterious effects of thyroid dysfunction can also extend beyond pregnancy and delivery to affectneurointellectual developmentin the early life of the child. Demand for thyroid hormones is increased during pregnancy, which may cause a previously unnoticed thyroid disorder to worsen.
- Untreatedceliac diseasecan cause amiscarriage,intrauterine growth restriction,small for gestational age,low birthweightandpreterm birth.Oftenreproductive disordersare the only manifestation of undiagnosed celiac disease and most cases are not recognized. Complications or failures of pregnancy cannot be explained simply bymalabsorption,but by theautoimmune responseelicited by the exposure togluten,which causes damage to theplacenta.Thegluten-free dietavoids or reduces the risk of developing reproductive disorders in pregnant women with celiac disease.[154][155]Also, pregnancy can be a trigger for the development of celiac disease ingenetically susceptiblewomen who are consuming gluten.[156]
- Lupus in pregnancyconfers an increased rate of fetal deathin utero,miscarriage, and ofneonatal lupus.
- Hypercoagulability in pregnancyis the propensity of pregnant women to developthrombosis(blood clots). Pregnancy itself is a factor ofhypercoagulability(pregnancy-induced hypercoagulability), as a physiologically adaptive mechanism to preventpostpartum bleeding.[157]However, in combination with an underlying hypercoagulable state, the risk of thrombosis or embolism may become substantial.[157]
Abortion
An abortion is the termination of an embryo or fetus via medical method. It is usually done within the first trimester, sometimes in the second, and rarely in the third. Reasons forpregnancies being undesiredare broad,[158]rapebeing the most legally accepted.[159]
Birth control and education
Family planning,as well as the availability and use ofcontraception,along with increasedcomprehensive sex education,has enabled many to prevent pregnancies when they are not desired. Schemes and funding to support education and the means to prevent pregnancies when they are not intended have been instrumental and are part of the third of theSustainable Development Goals(SDGs) advanced by theUnited Nations.[160]
Technologies and science
Assisted reproductive technology
Modern reproductive medicine offers many forms of assisted reproductive technology for couples who stay childless against their will, such asfertility medication,artificial insemination,in vitrofertilizationandsurrogacy.
Medical imaging


Medical imagingmay beindicatedin pregnancy because ofpregnancy complications,disease, or routineprenatal care.Medical ultrasonographyincludingobstetric ultrasonography,andmagnetic resonance imaging (MRI)withoutcontrast agentsare not associated with any risk for the mother or the fetus, and are the imaging techniques of choice for pregnant women.[161]Projectional radiography,CT scanandnuclear medicine imagingresult in some degree ofionizing radiationexposure, but in most cases theabsorbed dosesare not associated with harm to the baby.[161]At higher dosages or frequency, effects can includemiscarriage,birth defectsandintellectual disability.[161]
Epidemiology
About 213 million pregnancies occurred in 2012 of which 190 million were in thedeveloping worldand 23 million were in the developed world.[11]This is about 133 pregnancies per 1,000 women aged 15 to 44.[11]About 10% to 15% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage.[2]Globally, 44% of pregnancies areunplanned.Over half (56%) of unplanned pregnancies are aborted. In countries whereabortion is prohibited,or only carried out in circumstances where the mother's life is at risk, 48% of unplanned pregnancies areaborted illegally.Compared to the rate in countries where abortion is legal, at 69%.[27]
Of pregnancies in 2012, 120 million occurred in Asia, 54 million in Africa, 19 million in Europe, 18 million in Latin America and the Caribbean, 7 million in North America, and 1 million inOceania.[11]Pregnancy rates are 140 per 1000 women of childbearing age in the developing world and 94 per 1000 in the developed world.[11]
The rate of pregnancy, as well as the ages at which it occurs, differ by country and region. It is influenced by a number of factors, such as cultural, social and religious norms; access to contraception; and rates of education. Thetotal fertility rate(TFR) in 2013 was estimated to be highest inNiger(7.03 children/woman) and lowest inSingapore(0.79 children/woman).[162]
In Europe, the average childbearing age has been rising continuously for some time. In Western, Northern, and Southern Europe, first-time mothers are on average 26 to 29 years old, up from 23 to 25 years at the start of the 1970s. In a number of European countries (Spain), the mean age of women at first childbirth has crossed the 30-year threshold.
This process is not restricted to Europe. Asia, Japan and the United States are all seeing average age at first birth on the rise, and increasingly the process is spreading to countries in the developing world like China, Turkey and Iran. In the US, the average age of first childbirth was 25.4 in 2010.[163]
In the United States and United Kingdom, 40% of pregnancies areunplanned,and between a quarter and half of those unplanned pregnancies wereunwanted pregnancies.[164][165]
In the US, a woman's educational attainment and her marital status are correlated with childbearing: the percentage of women unmarried at the time of first birth drops with increasing educational level. In other words: among uneducated women, a large fraction (~80%) have their first child while they are unmarried. By contrast, few women with a bachelor's degree or higher (~25%) have their first child while unmarried. However, this phenomenon also has a strong generational component: in 1996, about 50% of women without a university degree had their first child being unmarried while that number increased to ~85% in 2018. Similarly, in 1996, only 4% of women with a BA degree or similar had their first child being unmarried. In 2018, that fraction increased to ~25%.[166]
Legal and social aspects
Legal protection
Many countries have various legal regulations in place to protect pregnant women and their children. Many countries have laws againstpregnancy discrimination.[167]
Maternity Protection Conventionensures that pregnant women are exempt from activities such as night shifts or carrying heavy stocks.Maternity leavetypically provides paid leave from work during roughly the last trimester of pregnancy and for some time after birth. Notable extreme cases include Norway (8 months with full pay) and the United States (no paid leave at all except in some states).
In the United States, some actions that result in miscarriage or stillbirth, such as beating a pregnant woman, are considered crimes. One law that does so is the federalUnborn Victims of Violence Act.In 2014, the American state ofTennesseepassed a law which allows prosecutors to charge a woman with criminal assault if she uses illegal drugs during her pregnancy and her fetus or newborn is harmed as a result.[168]
However, protections are not universal. InSingapore,theEmployment of Foreign Manpower Actforbids current and formerwork permitholders from becoming pregnant or giving birth in Singapore without prior permission.[169][170]Violation of the Act is punishable by a fine of up toS$10,000 (US$7300) anddeportation,[169][171]and until 2010, their employers would lose their $5,000 security bond.[172]
Teenage pregnancy
Teenage pregnancyis also known asadolescentpregnancy.[173]TheWHOdefines adolescence as the period between the ages of 10 and 19 years.[174]Adolescents face higher health risks than women who give birth at age 20 to 24 and their infants are at a higher risk for preterm birth, low birth weight, and other severe neonatal conditions. Their children continue to face greater challenges, both behavioral and physical, throughout their lives. Teenage pregnancies are also related to social issues, including social stigma, lower educational levels, and poverty.[175][173]Studies show that female adolescents are often in abusive relationships at the time of their conceiving.[176]
Nurse-Family Partnership(NFP) is a non-profit organization operating in the United States and the UK designed to serve the needs of low income young mothers who may have special needs in their first pregnancy. Each mother served is partnered with a registered nurse early in her pregnancy and receives ongoing nurse home visits that continue through her child's second birthday. NFP intervention has been associated with improvements in maternal health, child health, and economic security.[177][178]
Racial disparities
There are significant racial imbalances in pregnancy and neonatal care systems.[179]Midwifery guidance, treatment, and care have been related to better birth outcomes. Diminishing racial inequities in health is an increasingly large public health challenge in the United States. Despite the fact that average rates have decreased, data on neonatal mortality demonstrates that racial disparities have persisted and grown. The death rate for African American babies is nearly double that of white neonates. According to studies,congenital defects,SIDS,preterm birth,andlow birth weightare all more common among African American babies.[180]
Midwifery care has been linked to better birth and postpartum outcomes for both mother and child. It caters to the needs of the woman and provides competent, sympathetic care, and is essential for maternal health improvement. The presence of adoula,or birth assistant, during labor and delivery, has also been associated with improved levels of satisfaction with medical birth care. Providers recognized their profession from a historical standpoint, a link to African origins, the diaspora, and prevailing African American struggles. Providers participated in both direct clinical experience and activist involvement. Advocacy efforts aimed to enhance the number of minority birth attendants and to promote the benefits of woman-centered birth care to neglected areas.[180]
Transgender people
Transgender people have experienced significant advances in societal acceptance in recent years leaving many health professionals unprepared to provide quality care. A 2015 report suggests that "numbers of transgender individuals who are seeking family planning, fertility, and pregnancy services could certainly be quite large". Regardless of prior hormone replacement therapy treatments, the progression of pregnancy and birthing procedures fortransgender people who carry pregnanciesare typically the same as those ofcisgenderwomen[181]however, they may be subjected to discrimination, which can include a variety of negative social, emotional, and medical experiences, as pregnancy is regarded as an exclusively female activity. According to a study by theAmerican College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,there is a lack of awareness, services, and medical assistance available to pregnant trans men.[182]
Culture

In most cultures, pregnant women have a special status in society and receive particularly gentle care.[183]At the same time, they are subject to expectations that may exert great psychological pressure, such as having to produce a son and heir. In many traditional societies, pregnancy must be preceded by marriage, on pain of ostracism of mother and(illegitimate) child.
Overall, pregnancy is accompanied by numerous customs that are often subject to ethnological research, often rooted intraditional medicineor religion. Thebaby showeris an example of a modern custom. Contrary tocommon misconception,women historically in theUnited Stateswere not expected to seclude themselves during pregnancy, as was popularized byGone With the Wind.[184][185]
Pregnancy is an important topic insociology of the family.The prospective child may preliminarily be placed into numeroussocial roles.The parents' relationship and the relation between parents and their surroundings are also affected.
Abelly castmay be made during pregnancy as a keepsake.
Arts
Images of pregnant women, especially smallfigurines,were made in traditional cultures in many places and periods, though it is rarely one of the most common types of image. These include ceramic figures from somePre-Columbiancultures, and a few figures from most of the ancient Mediterranean cultures. Many of these seem to be connected withfertility.Identifying whether such figures are actually meant to show pregnancy is often a problem, as well as understanding their role in the culture concerned.
Among the oldest surviving examples of the depiction of pregnancy are prehistoric figurines found across much ofEurasiaand collectively known asVenus figurines.Some of these appear to be pregnant.
Due to the important role of theMother of GodinChristianity,the Western visual arts have a long tradition of depictions of pregnancy, especially in the biblical scene of theVisitation,and devotional images called aMadonna del Parto.[186]
The unhappy scene usually calledDiana and Callisto,showing the moment of discovery ofCallisto's forbidden pregnancy, is sometimes painted from the Renaissance onwards. Gradually, portraits of pregnant women began to appear, with a particular fashion for "pregnancy portraits" in elite portraiture of the years around 1600.
Pregnancy, and especially pregnancy of unmarried women, is also an important motif in literature. Notable examples includeThomas Hardy's 1891 novelTess of the d'Urbervillesand Goethe's 1808 playFaust.
See also
References
- ^ab"What are some common signs of pregnancy?".Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.12 July 2013.Archivedfrom the original on 19 March 2015.Retrieved14 March2015.
- ^abcThe Johns Hopkins Manual of Gynecology and Obstetrics(4 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2012. p. 438.ISBN978-1-4511-4801-5.Archivedfrom the original on 10 September 2017.
- ^ab"What are some common complications of pregnancy?".Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.12 July 2013.Archivedfrom the original on 26 February 2015.Retrieved14 March2015.
- ^abcdefghijk"Pregnancy: Condition Information".Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.19 December 2013.Archivedfrom the original on 19 March 2015.Retrieved14 March2015.
- ^abcdAbman SH (2011).Fetal and neonatal physiology(4th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders. pp. 46–47.ISBN978-1-4160-3479-7.
- ^abShehan CL (2016).The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Family Studies, 4 Volume Set.John Wiley & Sons. p. 406.ISBN978-0-470-65845-1.Archivedfrom the original on 10 September 2017.
- ^ab"How do I know if I'm pregnant?".Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.30 November 2012.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2015.Retrieved14 March2015.
- ^abTaylor D, James EA (2011)."An evidence-based guideline for unintended pregnancy prevention".Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, and Neonatal Nursing.40(6): 782–793.doi:10.1111/j.1552-6909.2011.01296.x.ISSN0090-0311.PMC3266470.PMID22092349.
- ^abcd"What is prenatal care and why is it important?".Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.12 July 2013.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2015.Retrieved14 March2015.
- ^Keats EC, Haider BA, Tam E, Bhutta ZA (March 2019)."Multiple-micronutrient supplementation for women during pregnancy".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.3(3): CD004905.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub6.PMC6418471.PMID30873598.
- ^abcdefgSedgh G, Singh S, Hussain R (September 2014)."Intended and unintended pregnancies worldwide in 2012 and recent trends".Studies in Family Planning.45(3): 301–314.doi:10.1111/j.1728-4465.2014.00393.x.PMC4727534.PMID25207494.
- ^abcdeNaghavi M, Abajobir AA, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, Abera SF, et al. (GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators) (September 2017)."Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016".Lancet.390(10100): 1151–1210.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9.PMC5605883.PMID28919116.
- ^abMosby (2009).Mosby's Pocket Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing & Health Professions - E-Book.Elsevier Health Sciences.p. 1078.ISBN978-0-323-06604-4.
- ^Wylie L (2005).Essential anatomy and physiology in maternity care(Second ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. p. 172.ISBN978-0-443-10041-3.Archivedfrom the original on 10 September 2017.
- ^Massachusetts General Laws c.112 § 12K: Definitions applicable to Secs. 12L to 12U,Commonwealth of Massachusetts, 2022
- ^abcdeLammi-Keefe CJ, Couch SC, Philipson EH, eds. (2008).Handbook of Nutrition and Pregnancy.Nutrition and health. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. p. 28.doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-112-3.ISBN978-1-59745-112-3.
- ^abcdAmerican Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists(February 2013),"Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question",Choosing Wisely:an initiative of theABIM Foundation,American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,archivedfrom the original on 1 September 2013,retrieved1 August2013
- ^World Health Organization (November 2014)."Preterm birth Fact sheet N°363".who.int.Archivedfrom the original on 7 March 2015.Retrieved6 March2015.
- ^ab"definition of gravida".The Free Dictionary.Retrieved17 January2008.
- ^"Gravidity and Parity Definitions (Implications in Risk Assessment)".patient.info.Archivedfrom the original on 12 December 2016.
- ^Robinson, Victor, ed. (1939). "Primipara".The Modern Home Physician, A New Encyclopedia of Medical Knowledge.WM. H. Wise & Company (New York).,page 596.
- ^"Definition of nulligravida".Merriam-Webster, Incorporated.Archived fromthe originalon 8 September 2008.Retrieved9 March2012.
- ^"Nulliparous definition".MedicineNet, Inc. 18 November 2000.Archivedfrom the original on 9 July 2009.
- ^"Definition of Term Pregnancy – ACOG".acog.org.Retrieved27 September2019.
- ^"Definition of Premature birth".Medicine.net.Archivedfrom the original on 9 July 2009.Retrieved16 January2008.
- ^Lama Rimawi, MD (22 September 2006)."Premature Infant".Disease & Conditions Encyclopedia.Discovery Communications, LLC.Archivedfrom the original on 19 January 2008.Retrieved16 January2008.
- ^abcBearak J, Popinchalk A, Alkema L, Sedgh G (April 2018)."Global, regional, and subregional trends in unintended pregnancy and its outcomes from 1990 to 2014: estimates from a Bayesian hierarchical model".The Lancet. Global Health.6(4): e380–e389.doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30029-9.PMC6055480.PMID29519649.
- ^Hurt KJ, Guile MW, Bienstock JL, Fox HE, Wallach EE (28 March 2012).The Johns Hopkins manual of gynecology and obstetrics(4th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health / Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 382.ISBN978-1-60547-433-5.
- ^Merck."Urinary tract infections during pregnancy".Merck Manual Home Health Handbook.Archivedfrom the original on 10 November 2011.
- ^Vazquez JC (August 2010)."Constipation, haemorrhoids, and heartburn in pregnancy".BMJ Clinical Evidence.2010:1411.PMC3217736.PMID21418682.
- ^MedlinePlus > Breast painArchived5 August 2012 atarchive.todayUpdate Date: 31 December 2008. Updated by: David C. Dugdale, Susan Storck. Also reviewed by David Zieve.
- ^abcdefghijNair M, Kumar B (7 April 2016)."Embryology for fetal medicine".In Kumar B, Alfirevic Z (eds.).Fetal Medicine.Cambridge University Press. pp. 54–59.ISBN978-1-107-06434-8.
- ^abcdMishra S, ed. (7 August 2019).Langman's Medical Embryology.Wolters kluwer india Pvt Ltd. p. 48.ISBN978-93-88696-53-1.
- ^abObstetric Data Definitions Issues and Rationale for Change – Gestational Age & TermArchived6 November 2013 at theWayback Machinefrom Patient Safety and Quality Improvement atAmerican Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.Created November 2012.
- ^Tunón K, Eik-Nes SH, Grøttum P, Von Düring V, Kahn JA (January 2000)."Gestational age in pregnancies conceived after in vitro fertilization: a comparison between age assessed from oocyte retrieval, crown-rump length and biparietal diameter".Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology.15(1): 41–46.doi:10.1046/j.1469-0705.2000.00004.x.PMID10776011.S2CID20029116.
- ^abcd"Pregnancy – the three trimesters".University of California San Francisco.Retrieved30 November2019.
- ^abHoffman CS, Messer LC, Mendola P, Savitz DA,Herring AH,Hartmann KE (November 2008). "Comparison of gestational age at birth based on last menstrual period and ultrasound during the first trimester".Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology.22(6): 587–596.doi:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2008.00965.x.PMID19000297.
- ^"Pregnancy week by week".Mayo Clinic. 3 June 2022.Retrieved8 July2023.
- ^"ement Health IT and Clinical Informatics reVITALize: Obstetrics Data Definitions reVITALize: Obstetrics Data Definitions".ACOG.Retrieved27 November2022.
- ^Chambliss LR, Clark SL (February 2014). "Paper gestational age wheels are generally inaccurate".American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.210(2): 145.e1–145.e4.doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2013.09.013.PMID24036402.
- ^Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, Dyer S, Racowsky C, de Mouzon J, Sokol R, et al. (September 2017)."The International Glossary on Infertility and Fertility Care, 2017".Fertility and Sterility.108(3). Elsevier BV: 393–406.doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.06.005.PMID28760517.S2CID3640374.
- ^"Differences in sex development".nhs.uk.18 November 2021.Retrieved29 June2022.
- ^Weschler T (2002).Taking Charge of Your Fertility(Revised ed.). New York: HarperCollins. pp.242,374.ISBN978-0-06-093764-5.
- ^Berger KS (2011).The Developing Person Through the Life Span.Macmillan. p. 90.ISBN978-1-4292-3205-0.Archivedfrom the original on 25 April 2016.
- ^"Stages of Development of the Fetus – Women's Health Issues".MSD Manual Consumer Version.Retrieved10 July2020.
- ^
- Lennart Nilsson,A Child is Born91 (1990): at eight weeks, "the danger of a miscarriage... diminishes sharply."
- "Women's Health InformationArchived30 April 2007 at theWayback Machine",Hearthstone Communications Limited:" The risk of miscarriage decreases dramatically after the 8th week as the weeks go by. "Retrieved 2007-04-22.
- ^Kalverboer AF, Gramsbergen AA (1 January 2001).Handbook of Brain and Behaviour in Human Development.Springer. p. 1.ISBN978-0-7923-6943-1.Archivedfrom the original on 19 September 2015.
- ^Illes J, ed. (2008).Neuroethics: defining the issues in theory, practice, and policy(Repr. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 142.ISBN978-0-19-856721-9.Archivedfrom the original on 19 September 2015.
- ^
- Harley TA (2021).The Science of Consciousness: Waking, Sleeping and Dreaming.Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. p. 245.ISBN978-1-107-12528-5.Retrieved3 May2022.
- Cleeremans A, Wilken P, Bayne T, eds. (2009).The Oxford Companion to Consciousness.New York, NY: Oxford University Press. p. 229.ISBN978-0-19-856951-0.Retrieved3 May2022.
- Thompson E, Moscovitch M, Zelazo PD, eds. (2007).The Cambridge Handbook of Consciousness.Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. pp. 415–417.ISBN978-1-139-46406-2.Retrieved3 May2022.
- ^"Abortion & Pregnancy Risks".Louisiana Department of Health.Retrieved22 August2019.
- ^"Reproductive History and Cancer Risk".National Cancer Institute.30 November 2016.Retrieved23 August2019.
- ^abMor G, ed. (2006).Immunology of pregnancy.Medical intelligence unit. Georgetown, Tex.: New York: Landes Bioscience/Eurekah; Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 1–4.doi:10.1007/0-387-34944-8.ISBN978-0-387-34944-2.
- ^Williams Z (September 2012)."Inducing tolerance to pregnancy".The New England Journal of Medicine.367(12): 1159–1161.doi:10.1056/NEJMcibr1207279.PMC3644969.PMID22992082.
- ^Campbell LA, Klocke RA (April 2001). "Implications for the pregnant patient".American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.163(5): 1051–1054.doi:10.1164/ajrccm.163.5.16353.PMID11316633.
- ^"Your baby at 0–8 weeks pregnancy – Pregnancy and baby guide – NHS Choices".nhs.uk.20 December 2017.Archivedfrom the original on 20 November 2013.
- ^Hennen L, Murray L, Scott J (2005).The BabyCenter Essential Guide to Pregnancy and Birth: Expert Advice and Real-World Wisdom from THE tip Top Pregnancy and Parenting Resource.Emmaus, Penn.: Rodale Books.ISBN1-59486-211-7.
- ^"Pregnancy: Dropping (Lightening)".University of Michigan.Retrieved9 June2021.
- ^Stacey T, Thompson JM, Mitchell EA, Ekeroma AJ, Zuccollo JM, McCowan LM (June 2011)."Association between maternal sleep practices and risk of late stillbirth: a case-control study".BMJ.342:d3403.doi:10.1136/bmj.d3403.PMC3114953.PMID21673002.
- ^abcdefghijkCunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Spong CY, Dashe JS, Hoffman BL, Casey BM, Sheffield JS, eds. (2014)."Chapter 12. Teratology, Teratogens, and Fetotoxic Agents".William's Obstetrics.McGraw-Hill Education.ISBN978-0-07-179893-8.Archived fromthe originalon 31 December 2018.Retrieved9 November2015.
- ^"RHL".apps.who.int.Archived fromthe originalon 27 December 2011.
- ^abWorld Health Organization (November 2013)."Preterm birth".who.int.Archivedfrom the original on 7 September 2014.Retrieved19 September2014.
- ^abcdefghAmerican Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine(22 October 2013)."Ob-Gyns Redefine Meaning of 'Term Pregnancy'".acog.org.Archived fromthe originalon 15 September 2014.Retrieved19 September2014.
- ^Saigal S, Doyle LW (January 2008). "An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood".Lancet.371(9608): 261–269.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60136-1.PMID18207020.S2CID17256481.
- ^American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists(February 2013),"Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question",Choosing Wisely:an initiative of theABIM Foundation,American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists,archivedfrom the original on 1 September 2013,retrieved1 August2013,which cites
- Main E, Oshiro B, Chagolla B, Bingham D, Dang-Kilduff L, Kowalewski L,Elimination of Non-medically Indicated (Elective) Deliveries Before 39 Weeks Gestational Age(PDF),March of Dimes;California Maternal Quality Care Collaborative; Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health Division; Center for Family Health;California Department of Public Health,archived fromthe original(PDF)on 10 November 2012,retrieved1 August2013
- ^Michele Norris(18 July 2011)."Doctors To Pregnant Women: Wait at Least 39 Weeks".All Things Considered.Archivedfrom the original on 23 July 2011.Retrieved20 August2011.
- ^Norwitz ER."Postterm Pregnancy (Beyond the Basics)".UpToDate, Inc.Archivedfrom the original on 7 October 2012.Retrieved24 August2012.
- ^The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (April 2006)."What To Expect After Your Due Date".Medem.Medem, Inc. Archived fromthe originalon 29 April 2003.Retrieved16 January2008.
- ^"Induction of labour – Evidence-based Clinical Guideline Number 9"(PDF).Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. 2001. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 30 December 2006.Retrieved18 January2008.
- ^Jenkins A, Millar S, Robins J (July 2011)."Denial of pregnancy: a literature review and discussion of ethical and legal issues".Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine.104(7): 286–291.doi:10.1258/jrsm.2011.100376.PMC3128877.PMID21725094.
- ^Gabbe S (1 January 2012).Obstetrics: normal and problem pregnancies(6th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders. p.1184.ISBN978-1-4377-1935-2.
- ^"Pregnancy Symptoms".National Health Service (NHS).11 March 2010.Archivedfrom the original on 28 February 2010.Retrieved11 March2010.
- ^ab"Early symptoms of pregnancy: What happens right away".Mayo Clinic.22 February 2007.Archivedfrom the original on 14 September 2007.Retrieved22 August2007.
- ^ab"Pregnancy Symptoms – Early Signs of Pregnancy: American Pregnancy Association".Archivedfrom the original on 15 January 2008.Retrieved16 January2008.
- ^"Pregnancy video".Channel 4. 2008.Archivedfrom the original on 23 January 2009.Retrieved22 January2009.
- ^"NHS Pregnancy Planner".National Health Service (NHS).19 March 2010. Archived fromthe originalon 29 August 2021.Retrieved19 March2010.
- ^Cole LA, Butler SA, eds. (2015).Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)(2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier.ISBN978-0-12-800821-8.Archived fromthe originalon 26 January 2021.Retrieved10 November2015.
- ^Qasim SM, Callan C, Choe JK (October 1996). "The predictive value of an initial serum beta human chorionic gonadotropin level for pregnancy outcome following in vitro fertilization".Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics.13(9): 705–708.doi:10.1007/BF02066422.PMID8947817.S2CID36218409.
- ^ab"What is HCG?".American Pregnancy Association.18 October 2021.Retrieved23 July2023.
- ^"BestBets: Serum or Urine beta-hCG?".Archivedfrom the original on 31 December 2008.
- ^abCole LA, Khanlian SA, Sutton JM, Davies S, Rayburn WF (January 2004). "Accuracy of home pregnancy tests at the time of missed menses".American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.190(1): 100–105.doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2003.08.043.PMID14749643.
- ^Verhaegen J, Gallos ID, van Mello NM, Abdel-Aziz M, Takwoingi Y, Harb H, et al. (September 2012)."Accuracy of single progesterone test to predict early pregnancy outcome in women with pain or bleeding: meta-analysis of cohort studies".BMJ.345:e6077.doi:10.1136/bmj.e6077.PMC3460254.PMID23045257.
- ^Whitworth M, Bricker L, Mullan C (July 2015)."Ultrasound for fetal assessment in early pregnancy".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2015(7): CD007058.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007058.pub3.PMC4084925.PMID26171896.
- ^Nguyen TH, Larsen T, Engholm G, Møller H (July 1999)."Evaluation of ultrasound-estimated date of delivery in 17,450 spontaneous singleton births: do we need to modify Naegele's rule?".Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology.14(1): 23–28.doi:10.1046/j.1469-0705.1999.14010023.x.PMID10461334.S2CID30749264.
- ^Pyeritz RE (2014).Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2015.McGraw-Hill.
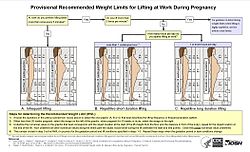
- ^Waters TR, MacDonald LA, Hudock SD, Goddard DE (February 2014)."Provisional recommended weight limits for manual lifting during pregnancy".Human Factors.56(1): 203–214.doi:10.1177/0018720813502223.PMC4606868.PMID24669554.Archivedfrom the original on 1 April 2017.
- ^MacDonald LA, Waters TR, Napolitano PG, Goddard DE, Ryan MA, Nielsen P, et al. (August 2013)."Clinical guidelines for occupational lifting in pregnancy: evidence summary and provisional recommendations".American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.209(2): 80–88.doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2013.02.047.PMC4552317.PMID23467051.
- ^abLyons P (2015).Obstetrics in family medicine: a practical guide.Current clinical practice (2nd ed.). Cham, Switzerland: Humana Press. pp. 19–28.ISBN978-3-319-20077-4.Archived fromthe originalon 26 January 2021.Retrieved11 November2015.
- ^"WHO | Antenatal care".who.int.Archived fromthe originalon 20 November 2015.Retrieved10 November2015.
- ^Dowswell T, Carroli G, Duley L, Gates S, Gülmezoglu AM, Khan-Neelofur D, et al. (American College of Obstetricians Gynecologists Committee on Health Care for Undeserved Women) (July 2015)."Alternative versus standard packages of antenatal care for low-risk pregnancy".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2015(7): CD000934.doi:10.1002/14651858.cd000934.pub3.PMC7061257.PMID26184394.
- ^American College of Obstetricians Gynecologists Committee on Health Care for Undeserved Women (August 2006)."ACOG Committee Opinion No. 343: psychosocial risk factors: perinatal screening and intervention".Obstetrics and Gynecology.108(2): 469–477.doi:10.1097/00006250-200608000-00046.PMID16880322.
- ^Hurt JK, ed. (2011).The Johns Hopkins manual of gynecology and obstetrics(4th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.ISBN978-1-4511-0913-9.
- ^McCormick MC, Siegel JE, eds. (1999).Prenatal care: effectiveness and implementation.Cambridge, UK; New York: Cambridge University Press.ISBN978-0-521-66196-6.Archived fromthe originalon 6 November 2018.Retrieved10 November2015.
- ^Ota E, Hori H, Mori R, Tobe-Gai R, Farrar D (June 2015). "Antenatal dietary education and supplementation to increase energy and protein intake".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2015(6): CD000032.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000032.pub3.PMID26031211.
- ^"| Choose MyPlate".Choose MyPlate.29 April 2015.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2015.Retrieved15 November2015.
- ^Tieu J, Shepherd E, Middleton P, Crowther CA (January 2017)."Dietary advice interventions in pregnancy for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.1(1): CD006674.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006674.pub3.PMC6464792.PMID28046205.
- ^Klusmann A, Heinrich B, Stöpler H, Gärtner J, Mayatepek E, Von Kries R (November 2005). "A decreasing rate of neural tube defects following the recommendations for periconceptional folic acid supplementation".Acta Paediatrica.94(11): 1538–1542.doi:10.1080/08035250500340396.PMID16303691.S2CID13506877.
- ^Stevenson RE, Allen WP, Pai GS, Best R, Seaver LH, Dean J, et al. (October 2000). "Decline in prevalence of neural tube defects in a high-risk region of the United States".Pediatrics.106(4): 677–683.doi:10.1542/peds.106.4.677.PMID11015508.S2CID39696556.
- ^"Folic acid in diet: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia".nlm.nih.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2015.Retrieved15 November2015.
- ^Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) (January 2008). "Use of supplements containing folic acid among women of childbearing age--United States, 2007".MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.57(1): 5–8.PMID18185493.
- ^abcViswanathan M, Siega-Riz AM, Moos MK, et al. (May 2008)."Outcomes of Maternal Weight Gain".Evidence Report/Technology Assessment.Evidence Reports/Technology Assessments, No. 168 (168). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: 1–223.PMC4781425.PMID18620471.Archivedfrom the original on 28 May 2013.Retrieved23 June2013.
- ^abcInstitute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care."Weight gain in pregnancy".Fact sheet.Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care.Archivedfrom the original on 14 December 2013.Retrieved23 June2013.
- ^"Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexaminging the Guidelines, Report Brief".Institute of Medicine.Archived fromthe originalon 10 August 2010.Retrieved29 July2010.
- ^American College of Obstetricians Gynecologists (January 2013)."ACOG Committee opinion no. 548: weight gain during pregnancy".Obstetrics and Gynecology.121(1): 210–212.doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000425668.87506.4c.PMID23262962.
- ^abcThangaratinam S, Rogozińska E, Jolly K, Glinkowski S, Duda W, Borowiack E, et al. (July 2012)."Interventions to reduce or prevent obesity in pregnant women: a systematic review".Health Technology Assessment.16(31).National Institute for Health and Care Research:iii–iv, 1–191.doi:10.3310/hta16310.PMC4781281.PMID22814301.
- ^Bushnell C, McCullough LD, Awad IA, Chireau MV, Fedder WN, Furie KL, et al. (May 2014)."Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in women: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association".Stroke.45(5): 1545–1588.doi:10.1161/01.str.0000442009.06663.48.PMC10152977.PMID24503673.S2CID6297484.
- ^abcBriggs GG, Freeman RK (2015).Drugs in pregnancy and lactation: A Reference Guide to Fetal and Neonatal Risk(Tenth ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. p. Appendix.ISBN978-1-4511-9082-3.Archived fromthe originalon 25 February 2021.Retrieved16 November2015.
- ^Genetic Alliance, The New England Public Health Genetics Education Collaborative (17 February 2010)."Appendix A: Teratogens/Prenatal Substance Abuse".Understanding Genetics: A New England Guide for Patients and Health Professionals.Genetic Alliance.
- ^"Press Announcements – FDA issues final rule on changes to pregnancy and lactation labeling information for prescription drug and biological products".fda.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2015.Retrieved16 November2015.
- ^"Basics about FASDs".CDC.Retrieved25 July2018.
- ^Hackshaw A, Rodeck C, Boniface S (September–October 2011)."Maternal smoking in pregnancy and birth defects: a systematic review based on 173 687 malformed cases and 11.7 million controls".Human Reproduction Update.17(5): 589–604.doi:10.1093/humupd/dmr022.PMC3156888.PMID21747128.
- ^Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2007.Preventing Smoking and Exposure to Secondhand Smoke Before, During, and After PregnancyArchived11 September 2011 at theWayback Machine.
- ^"Tobacco Use and Pregnancy – Reproductive Health".cdc.gov.16 January 2019.Archivedfrom the original on 29 July 2017.
- ^ab"New Mother Fact Sheet: Methamphetamine Use During Pregnancy".North Dakota Department of Health.Archived fromthe originalon 10 September 2011.Retrieved7 October2011.
- ^Della Grotta S, LaGasse LL, Arria AM, Derauf C, Grant P, Smith LM, et al. (July 2010)."Patterns of methamphetamine use during pregnancy: results from the Infant Development, Environment, and Lifestyle (IDEAL) Study".Maternal and Child Health Journal.14(4): 519–527.doi:10.1007/s10995-009-0491-0.PMC2895902.PMID19565330.
- ^Martin R, Dombrowski SC (2008). "12. Air and Water Pollution".Prenatal exposures: psychological and educational consequences for children.New York: Springer.doi:10.1007/978-0-387-74398-1.ISBN978-0-387-74398-1.
- ^Byrne CC (2006). "Environmental hazards during pregnancy".Journal of Midwifery and Women's Health.1(51): 57–58.doi:10.1016/j.jmwh.2005.09.008.PMID16402445.
- ^"N95 Respirator Use During Pregnancy – Findings from Recent NIOSH Research | NIOSH Science Blog | Blogs | CDC".blogs.cdc.gov.18 June 2015.Archivedfrom the original on 16 November 2016.Retrieved16 November2016.
- ^"Homicide leading cause of death for pregnant women in U.S."News.Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. 21 October 2022.Retrieved8 November2022.
- ^"With homicide a leading cause of maternal death, doctors urged to screen pregnant women for domestic violence".CNN Health.20 October 2022.Retrieved8 November2022.
- ^Wallace ME (September 2022)."Trends in Pregnancy-Associated Homicide, United States, 2020".American Journal of Public Health.112(9): 1333–1336.doi:10.2105/AJPH.2022.306937.PMC9382166.PMID35797500.
- ^abcCunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Spong CY, Dashe JS, Hoffman BL, Casey BM, Sheffield JS, eds. (2014)."Chapter 9: Prenatal Care".Williams Obstetrics(24th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education.ISBN978-0-07-179893-8.Archived fromthe originalon 31 December 2018.Retrieved9 November2015.
- ^Bermudez MP, Sanchez AI, Buela-Casal G (2001)."Influence of the Gestation Period on Sexual Desire".Psychology in Spain.5(1): 14–16.Archivedfrom the original on 9 February 2012.
- ^Fok WY, Chan LY, Yuen PM (October 2005)."Sexual behavior and activity in Chinese pregnant women".Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica.84(10): 934–938.doi:10.1111/j.0001-6349.2005.00743.x.PMID16167907.S2CID23075166.
- ^Reamy K, White SE, Daniell WC, Le Vine ES (June 1982). "Sexuality and pregnancy. A prospective study".The Journal of Reproductive Medicine.27(6): 321–327.PMID7120209.
- ^Malarewicz A, Szymkiewicz J, Rogala J (September 2006). "[Sexuality of pregnant women]".Ginekologia Polska(in Polish).77(9): 733–739.PMID17219804.
- ^Kramer MS, McDonald SW (July 2006). Kramer MS (ed.)."Aerobic exercise for women during pregnancy".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.3(3): CD000180.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000180.pub2.PMC7043271.PMID16855953.
- ^Domenjoz I, Kayser B, Boulvain M (October 2014). "Effect of physical activity during pregnancy on mode of delivery".American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.211(4): 401.e1–401.11.doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2014.03.030.PMID24631706.
- ^abBeetham KS, Giles C, Noetel M, Clifton V, Jones JC, Naughton G (August 2019)."The effects of vigorous intensity exercise in the third trimester of pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis".BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.19(1): 281.doi:10.1186/s12884-019-2441-1.PMC6686535.PMID31391016.
- ^Di Mascio D, Magro-Malosso ER, Saccone G, Marhefka GD, Berghella V (November 2016). "Exercise during pregnancy in normal-weight women and risk of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials".American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.215(5): 561–571.doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2016.06.014.hdl:11573/1110770.PMID27319364.S2CID32419788.
- ^McCall CA, Grimes DA, Lyerly AD (June 2013). ""Therapeutic" bed rest in pregnancy: unethical and unsupported by data ".Obstetrics and Gynecology.121(6): 1305–1308.doi:10.1097/aog.0b013e318293f12f.PMID23812466.
- ^Davies GA, Wolfe LA, Mottola MF, MacKinnon C, Arsenault MY, Bartellas E, et al. (June 2003). "Exercise in pregnancy and the postpartum period".Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada.25(6): 516–529.doi:10.1016/s1701-2163(16)30313-9.PMID12806453.
- ^abcArtal R, O'Toole M (February 2003)."Guidelines of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists for exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period".British Journal of Sports Medicine.37(1): 6–12, discussion 12.doi:10.1136/bjsm.37.1.6.PMC1724598.PMID12547738.
- ^Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Korkmaz A, Rosales-Corral SA (2014)."Melatonin and stable circadian rhythms optimize maternal, placental and fetal physiology".Human Reproduction Update.20(2): 293–307.doi:10.1093/humupd/dmt054.PMID24132226.
- ^abTung I, Hipwell AE, Grosse P, Battaglia L, Cannova E, English G, et al. (November 2023). "Prenatal stress and externalizing behaviors in childhood and adolescence: A systematic review and meta-analysis".Psychological Bulletin.150(2): 107–131.doi:10.1037/bul0000407.PMC10932904.PMID37971856.S2CID265272043.
- ^"Oral health care during pregnancy: A strategies and considerations"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 22 August 2018.Retrieved2 June2018.
- ^Jafarzadeh H, Sanatkhani M, Mohtasham N (December 2006)."Oral pyogenic granuloma: a review".Journal of Oral Science.48(4): 167–175.doi:10.2334/josnusd.48.167.PMID17220613.
- ^Iheozor-Ejiofor Z, Middleton P, Esposito M, Glenny AM (June 2017)."Treating periodontal disease for preventing adverse birth outcomes in pregnant women".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2017(6): CD005297.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005297.pub3.PMC6481493.PMID28605006.
- ^Howland G (2017).The Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and Childbirth.Simon and Schuster. p. 173.ISBN978-1-5011-4668-8.
- ^abcJarvis S, Stone J, Eddleman K, Duenwald M (2011).Pregnancy For Dummies.John Wiley & Sons. p. 157.ISBN978-1-119-99706-1.
- ^"Air Travel During Pregnancy".acog.org.Retrieved22 December2023.
- ^"TSA Travel Tips for Pregnant Passengers".Transportation Security Administration.22 July 2014. Archived fromthe originalon 6 August 2020.Retrieved27 February2019.
- ^"Antenatal classes".NHS.December 2020.Retrieved16 November2022.
- ^"Promoting baby-friendly hospitals".World Health Organization.Retrieved16 November2022.
- ^"Reproductive Health and Research Publications: Making Pregnancy Safer".World Health Organization Regional Office for South-East Asia. 2009. Archived fromthe originalon 15 December 2009.Retrieved7 December2009.
- ^"Pregnancy complicated by disease".Merck Manual, Home Health Handbook.Merck Sharp & Dohme.
- ^Stewart DE, Vigod S (December 2016). "Postpartum Depression".The New England Journal of Medicine.375(22): 2177–2186.doi:10.1056/nejmcp1607649.PMID27959754.
- ^Lara A Friel."Thromboembolic Disorders During Pregnancy".Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
- ^abLeveno K (2013). "52".Williams Manual of Pregnancy Complications.New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 323–334.ISBN978-0-07-176562-6.
- ^"What are the symptoms of pregnancy loss (before 20 weeks of pregnancy)?".NIH.September 2017.Retrieved4 October2022.
- ^"Miscarriage Causes".WebMD.Retrieved6 October2022.
- ^"What Is Stillborn".CDC.29 September 2022.Retrieved6 October2022.
- ^"Miscarriage".NHS.9 March 2022.
- ^Obst KL, Due C, Oxlad M, Middleton P (January 2020)."Men's grief following pregnancy loss and neonatal loss: a systematic review and emerging theoretical model".BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.20(1): 11.doi:10.1186/s12884-019-2677-9.PMC6953275.PMID31918681.
- ^Tersigni C, Castellani R, de Waure C, Fattorossi A, De Spirito M, Gasbarrini A, et al. (2014)."Celiac disease and reproductive disorders: meta-analysis of epidemiologic associations and potential pathogenic mechanisms".Human Reproduction Update.20(4): 582–593.doi:10.1093/humupd/dmu007.hdl:10807/56796.PMID24619876.
- ^Saccone G, Berghella V, Sarno L, Maruotti GM, Cetin I, Greco L, et al. (February 2016). "Celiac disease and obstetric complications: a systematic review and metaanalysis".American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.214(2): 225–234.doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.09.080.hdl:11369/330101.PMID26432464.
- ^"The Gluten Connection".Health Canada. May 2009.Archivedfrom the original on 5 July 2017.Retrieved1 October2013.
- ^abPage 264 in:Gresele, Paolo (2008).Platelets in hematologic and cardiovascular disorders: a clinical handbook.Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.ISBN978-0-521-88115-9.
- ^Zdanowicz C (21 May 2019)."Women have abortions for many reasons aside from rape and incest. Here are some of them".CNN.Retrieved2 July2022.
- ^"Law and Policy Guide: Rape and Incest Exceptions".Center for Reproductive Rights.18 January 2022.Retrieved2 July2022.
- ^"SDG Indicator 3.7.1 on Contraceptive Use".Population Division.Retrieved3 July2022.
- ^abc"Guidelines for Diagnostic Imaging During Pregnancy and Lactation".American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.Archivedfrom the original on 30 July 2017.February 2016
- ^"The World Factbook".cia.gov.Archived fromthe originalon 28 October 2009.
- ^National Vital Statistics ReportsArchived20 July 2017 at theWayback MachinefromCenters for Disease Control and PreventionNational Center for Health Statistics. Volume 61, Number 1 August 28, 2012: Births: Final Data for 2010
- ^"40% of pregnancies 'unplanned'".BBC News.16 March 2004.Archivedfrom the original on 30 July 2012.
- ^Jayson S (20 May 2011)."Unplanned pregnancies in U.S. at 40 percent".PhysOrg.Archivedfrom the original on 5 January 2012.
- ^Cherlin AJ (September 2021)."Rising nonmarital first childbearing among college-educated women: Evidence from three national studies".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.118(37): e2109016118.Bibcode:2021PNAS..11809016C.doi:10.1073/pnas.2109016118.PMC8449381.PMID34493673.
- ^"Maternity and paternity at work: Law and practice across the world".International Labour Organization.Retrieved3 September2022.
- ^Katie Mcdonough (30 April 2014)."Tennessee just became the first state that will jail women for their pregnancy outcomes".Salon.Archivedfrom the original on 5 May 2014.Retrieved5 May2014.
- ^ab"NONFICTION: When Pregnancy is a Crime".17 June 2021.
- ^"Employment of Foreign Manpower (Work Passes) Regulations 2012 - Singapore Statutes Online".
- ^"Employment of Foreign Manpower Act - Singapore Statutes Online".
- ^"Employers will not lose security bond if FDW gets pregnant – MOM".twc2.org.sg.1 July 2011.Retrieved15 December2021.
- ^ab"Adolescent pregnancy".World Health Organization.Retrieved26 October2022.
- ^"Adolescent health".who.int.
- ^"The Adverse Effects of Teen Pregnancy".youth.gov.Retrieved26 October2022.
- ^Bekaert S, SmithBattle L (2016)."Teen Mothers' Experience of Intimate Partner Violence: A Metasynthesis".ANS. Advances in Nursing Science.39(3): 272–290.doi:10.1097/ANS.0000000000000129.PMID27490882.S2CID10471475.
- ^"Nurse-Family Partnership".Social Programs that Work.Retrieved4 December2022.
- ^Miller CC (25 July 2017)."How Home Visits by Nurses Help Mothers and Children, Especially Boys".The New York Times.Retrieved6 December2022.
- ^Pereira GM, Pimentel VM, Surita FG, Silva AD, Brito LG (2022)."Perceived racism or racial discrimination and the risk of adverse obstetric outcomes: a systematic review".Sao Paulo Med J.140(5): 705–718.doi:10.1590/1516-3180.2021.0505.R1.07042022.PMC9514866.PMID36043663.
- ^abGuerra-Reyes L, Hamilton LJ (February 2017). "Racial disparities in birth care: Exploring the perceived role of African-American women providing midwifery care and birth support in the United States".Women and Birth.30(1): e9–e16.doi:10.1016/j.wombi.2016.06.004.PMID27364419.
- ^Obedin-Maliver J, Makadon HJ (March 2016)."Transgender men and pregnancy".Obstetric Medicine.9(1): 4–8.doi:10.1177/1753495X15612658.PMC4790470.PMID27030799.
- ^Light AD, Obedin-Maliver J, Sevelius JM, Kerns JL (December 2014)."Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning".Obstetrics and Gynecology.124(6): 1120–1127.doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.PMID25415163.S2CID36023275.
- ^Womack M (2010).The anthropology of health and healing.Plymouth: AltaMira Press. p. 133.ISBN978-0-7591-1044-1.
- ^Baumgarten L (2002).What Clothes Reveal: The Language of Clothing in Colonial and Federal America.Williamsburg, Virginia:Colonial Williamsburg.p. 148.ISBN0879352167.
- ^Chrisman-Campbell K (12 July 2013)."Dressing for Two".Slate.Retrieved26 June2024.
- ^Rossi TV (2005).Mary in western art.New York: In Association with Hudson Hills Press. p. 106.ISBN978-0-9712981-9-4.
Further reading
- "Nutrition for the First Trimester of Pregnancy".IDEA Health & Fitness Association.Retrieved9 December2013.
- Bothwell TH (July 2000)."Iron requirements in pregnancy and strategies to meet them".The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.72(1 Suppl): 257S–264S.doi:10.1093/ajcn/72.1.257S.PMID10871591.
- Stevens J (June 2005). "Pregnancy envy and the politics of compensatory masculinities".Politics & Gender.1(2): 265–296.CiteSeerX10.1.1.485.5791.doi:10.1017/S1743923X05050087.S2CID39231847.
External links
- PregnancyatCurlie
- Merck Manual Home Health Handbook– further details on the diseases, disorders, etc., which may complicate pregnancy.
- Pregnancy care– NHS guide to having a baby including preconception, pregnancy, labor, and birth.