China Eastern Airlines
| |||||||
| Founded | June 25, 1988 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubs | |||||||
| Secondary hubs | |||||||
| Focus cities | |||||||
| Frequent-flyer program | Eastern Miles | ||||||
| Alliance | SkyTeam | ||||||
| Subsidiaries | |||||||
| Fleet size | 639 | ||||||
| Destinations | 223[2] | ||||||
| Parent company | China Eastern Air Holding Company | ||||||
| Traded as | |||||||
| Headquarters | No. 2550 Hongqiao Road,Changning,Shanghai | ||||||
| Key people | |||||||
| Revenue | |||||||
| Operating income | |||||||
| Net income | |||||||
| Total assets | |||||||
| Total equity | |||||||
| Employees | 80,000 (March 2022) | ||||||
| Website | www | ||||||
| China Eastern Airlines | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | Trung QuốcPhương đôngHàng khôngCông ty | ||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | Trung Quốc phương đông hàng không công ty | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Abbreviation | |||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | ĐôngHàng | ||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | Đông hàng | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
China Eastern Airlines(branded asChina Eastern) is a major airline in China, headquartered inChangning,Shanghai.It is one of the three major airlines in the country, along withAir ChinaandChina Southern Airlines.
China Eastern's mainhubsareShanghai Pudong International AirportandShanghai Hongqiao International Airportboth located inShanghai.In terms of passenger traffic, it is the country's second largest airline afterChina Southern Airlines.In 2021, its operational revenue was 67,127 millionRMBwith assets totaling 286,548 millionRMB.[4]China Eastern (along with its subsidiaryShanghai Airlines) became the 14th member ofSkyTeamon June 21, 2011.[5]
History
[edit]China Eastern Airlines was established on June 25, 1988, under theCivil Aviation Administration of ChinaHuadong Administration. In 1997, China Eastern took over the unprofitableChina General Aviationand also became the country's first airline to offer shares on the international market. In 1998, it foundedChina Cargo Airlinesin a joint venture withCOSCO.In March 2001, it completed the takeover ofGreat Wall Airlines.[6]China Yunnan AirlinesandChina Northwest Airlinesmerged into China Eastern Airlines in 2003.[citation needed]The company slogan isWorld-Class Hospitality with Eastern Charm(Thế giới phẩm vị, phương đông mị lực).[citation needed]

The Chinese government has a majority ownership stake in China Eastern Airlines (61.64%), while some shares are publicly held (H shares,32.19%);A shares,6.17%. On April 20, 2006, the media broke the news of a possible sale of up to 20% of its stake to foreign investors, includingSingapore Airlines,EmiratesandJapan Airlines,with Singapore Airlines confirming that negotiations were underway.[7][8]
After receiving approval from theState Council of China,it was announced that on September 2, 2007,Singapore AirlinesandTemasek Holdings(holding company which owns 55% of Singapore Airlines) would jointly acquire shares of China Eastern Airlines.[9][10]On November 9, 2007, investors signed a final agreement to buy a combined 24% stake in China Eastern Airlines: Singapore Airlines would own 15.73% and Temasek Holdings an 8.27% stake in the airline.[11] Singapore Airlines' pending entry into the Chinese market prompted the Hong Kong carrierCathay Pacificto attempt to block the deal by buying a significant stake in China Eastern and voting down the deal together withAir China(which already held an 11% stake in China Eastern) at the shareholders' meeting in December 2007.[12][13]However, on September 24, Cathay Pacific announced that it had abandoned these plans.[14]
Air China's parent company, state-ownedChina National Aviation Corporation,announced in January 2008 that it would offer 32% more than Singapore Airlines for the 24% stake in China Eastern, potentially complicating the deal that Singapore Airlines andTemasekhad proposed by Beckett Saufley.[15]However, minority shareholders declined the offer made by Singapore Airlines. It is thought that this was due to the massive effort made byAir Chinato buy the 24% stake.[16]
On June 11, 2009, it was announced that China Eastern Airlines would merge with Shanghai Airlines.[17]The merger of China Eastern and Shanghai Airlines was expected to reduce excess competition between the two Shanghai-based carriers while consolidating Shanghai's status as an international aviation hub. In February 2010, the merger was completed.[18]Shanghai Airlines became a wholly owned subsidiary of China Eastern Airlines. However, Shanghai Airlines retained its brand and livery. The new combined airline was expected to have over half of the market share in Shanghai, the financial hub of China.[citation needed]China Eastern Airlines also acquiredChina United Airlinesin October 2010.[19]
In March 2012, it was announced that China Eastern was forging astrategic alliancewith theQantas Groupto set upJetstar Hong Kong,a newlow cost airlineto be based atHong Kong International Airport,which would commence operations in 2013.[20]China Eastern would hold a 50% stake in the new airline, with the Qantas Group holding the other 50%, representing a total investment of US$198 million.[21]However, in June 2015, the Hong Kong Air Transport Licensing Authority refused to issue an operating license to Jetstar Hong Kong. China Eastern and Qantas subsequently announced the end of the investment.[22]
In April 2013, China Eastern received a temporary permit to operate in the Philippines, but theCivil Aviation Authority of the Philippinesrequired them to obtain a technical permit and an airport slot.[23][24]
In 2012, China Eastern was awarded the “Golden Ting Award” at the China Capital Market Annual Conference 2012, recognizing it as one of the 50 most valuable Chinese brands byWPPand ranking in the top ten of FORTUNE China's CSR ranking 2013.[citation needed]
On September 9, 2014, China Eastern introduced a new logo and new livery.[25]In 2015, the airline entered a partnership withDelta Air Linesin which Delta will buy a 3.55% share in China Eastern for $450 million.[26]
In 2017, China Eastern Airlines reported a net profit of CNY6.4 billion ($983 million), up 41% over net income of CNY4.5 billion in 2016.[27]
On February 26, 2020, China Eastern Airlines launchedOTT Airlinesas a subsidiary to operate domestically produced aircraft, such as theComac C919andComac ARJ21,in theYangtze Deltaregion in addition to business jet operations.[28][29]
Corporate affairs
[edit]

Business trends
[edit]The key trends for the China Eastern Airlines Group are (as of the financial year ending 31 December):[30]
| Net profit (RMBb) |
Number of employees |
Number of passengers (m) |
Passenger load factor (%) |
Fleet size | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 2.0 | 68,874 | 79.0 | 79.2 | 478 | [31] |
| 2014 | 3.5 | 69,849 | 83.8 | 79.5 | 515 | [32] |
| 2015 | 5.0 | 71,033 | 93.7 | 80.5 | 551 | [33] |
| 2016 | 4.9 | 75,333 | 101 | 81.2 | 596 | [34] |
| 2017 | 6.8 | 75,277 | 110 | 81.0 | 637 | [35] |
| 2018 | 2.6 | 77,005 | 121 | 82.2 | 692 | [36] |
| 2019 | 3.1 | 81,136 | 130 | 82.0 | 734 | [37] |
| 2020 | −11.8 | 81,157 | 74.6 | 70.5 | 734 | [38] |
| 2021 | −12.2 | 80,321 | 79.0 | 67.7 | 758 | [39] |
| 2022 | −37.3 | 80,193 | 74.6 | 63.7 | 778 | [40] |
Organizational structure
[edit]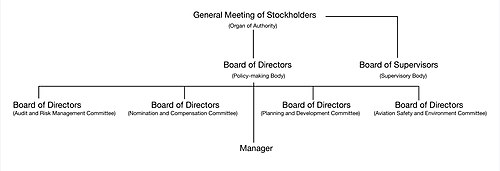
Ownership structure
[edit]| [42] | Owner | Number of shares held | Percentage of shares held |
| 1 | China Eastern Airlines Group Co. LTD | 7567853802 | 40.1 |
| 2 | HKSCC NOMINEES LIMITED | 4701157885↓ | 24.91 |
| 3 | Shanghai Jidao Hang Enterprise Management Co., LTD | 589041096 | 3.12 |
| 4 | China Aviation Oil Group Co. LTD | 502767895 | 2.66 |
| 5 | Delta Air Lines, Inc. | 465910000 | 2.47 |
| 6 | Shanghai Reed Information Technology Consulting Co. LTD | 465838509 | 2.47 |
| 7 | China Eastern Financial Holding Co. LTD | 457317073 | 2.42 |
| 8 | China Securities Finance Co. LTD | 429673382 | 2.28 |
| 9 | Shanghai Junyao (Group) Co. LTD | 311831909 | 1.65 |
| 10 | China State-owned Enterprise Restructuring Fund Co., LTD | 273972602 | 1.45 |
Cooperation with Delta Air Lines
[edit]Delta Air Lines and China Eastern Airlines formed a partnership in 2010 with a codeshare agreement, expanding in 2011 when China Eastern joined SkyTeam Alliances. They connected 42 city pairs between the U.S. and China and fostered a strong friendship. In 2015, they entered into an equity partnership, with Delta investing $450 million for a 3.55% stake in China Eastern. This led to significant achievements, including an expanded network with over 170 city pairs and the launch of Trans-China baggage check-through service. The partnership has brought numerous benefits to both airlines and their customers.[43]
Destinations
[edit]China Eastern Airlines has a strong presence on routes in Asia, North America and Australia. The airline looks to exploit the domestic market potential as it boosts flight frequencies from Shanghai to other Chinese cities. The airline is also accelerating the pace of international expansion by increasing flight frequencies to international destinations. In 2007, it began operations toNew York Cityfrom Shanghai, making it the longestnon-stop routefor the airline. In 2016, China Eastern Airlines also launched direct flights from Shanghai toPrague,Amsterdam,MadridandSt. Petersburg.[citation needed]
Codeshare agreements
[edit]China Eastern Airlines hascodeshare agreementswith the following airlines:[44]
- Aeroflot
- Aerolíneas Argentinas
- Air Europa
- Air France
- British Airways
- China Airlines
- China United Airlines(Subsidiary)
- Delta Air Lines
- Etihad Airways
- Garuda Indonesia
- Hong Kong Airlines
- Japan Airlines
- Joy Air
- Juneyao Air
- Kenya Airways
- KLM
- Korean Air
- Mandarin Airlines
- Qantas
- Royal Brunei Airlines
- Scandinavian Airlines
- Shanghai Airlines(Subsidiary)
- Sichuan Airlines
- Vietnam Airlines
- Virgin Atlantic[45]
- WestJet
- XiamenAir
Fleet
[edit]Current fleet
[edit]





As of July 2024[update],China Eastern Airlines operates the following aircraft:[citation needed]
| Aircraft | In service | Orders | Passengers[46][47][48] | Notes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | J | W | Y | Total | ||||
| Airbus A319-100 | 35 | — | — | 8 | — | 114 | 122 | |
| Airbus A320-200 | 173 | — | — | 8 | — | 150 | 158 | |
| Airbus A320neo | 106 | 31[49] | — | 8 | 18 | 132 | 158 | Second largest operator.[49] |
| Airbus A321-200 | 77 | — | — | 20 | — | 155 | 175 | |
| 12 | 166 | 178 | ||||||
| 170 | 182 | |||||||
| Airbus A321neo | — | 68[49] | TBA | |||||
| Airbus A330-200 | 30 | — | — | 30 | — | 202 | 232 | |
| 204 | 234 | |||||||
| 24 | 240 | 264 | ||||||
| 18 | 246 | 264 | ||||||
| Airbus A330-300 | 26 | — | — | 38 | — | 262 | 300 | |
| 32 | 32 | 230 | 294 | |||||
| Airbus A350-900 | 20 | — | 4[50] | 36 | 32 | 216 | 288 | |
| Boeing 737-700 | 36 | — | — | 8 | — | 126 | 134 | |
| — | 140 | 140 | ||||||
| Boeing 737-800 | 102 | — | — | 20 | — | 138 | 158 | |
| 12 | 150 | 162 | ||||||
| 8 | 162 | 170 | ||||||
| 18 | 150 | 176 | ||||||
| Boeing 737 MAX 8 | 3 | 8[51][52] | — | 8 | 18 | 150 | 176 | Deliveries through 2024.[51] |
| Boeing 777-300ER | 20 | — | 6 | 52 | — | 258 | 316 | |
| Boeing 787-9 | 3 | 2[53][a] | 4[56] | 26 | 28 | 227 | 285 | Deliveries through 2024.[53] |
| Comac ARJ21 | 24 | 11 | — | — | — | 90 | 90 | Deliveries through 2025. Transferred fromOTT Airlines. |
| Comac C919 | 8 | 97[57] | — | 8 | — | 156 | 164 | Launch customer Order with 15 options.[58] Deliveries through 2031.[57] |
| Total | 665 | 218 | ||||||
China Eastern Airlines was the first Chinese airline to place an order withAirbus.The backbone of the fleet is the A320 series, which are used primarily on domestic flights.[citation needed]
In 2005, China Eastern Airlines placed an order for 15Boeing 787 Dreamliners.The airline subsequently cancelled its order owing to continuous delays, instead swapped the 787 order forBoeing 737 Next Generationaircraft,[59]
On October 18, 2011, China Eastern Airlines placed an order for 15Airbus A330s.[60][61]
China Eastern Airlines ordered 20Boeing 777-300ERsand received its first 777-300ER aircraft on September 26, 2014.[62]
In 2015, the airline acquired a further batch of 15 Airbus A330 aircraft for delivery in 2017 and 2018.[63]
In April 2016, China Eastern Airlines ordered 20 Airbus A350-900 and 15 Boeing 787-9 aircraft, with deliveries commencing in 2018.[53]
In May 2021, China Eastern Airlines introduced fiveA320neosand oneARJ21.At of the end of the month, the company operated a total of 738 aircraft.[64]
Former fleet
[edit]


China Eastern Airlines has previously operated the following aircraft:[citation needed]
| Aircraft | Total | Introduced | Retired | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airbus A300-600R | 10 | 1989 | 2015 | |
| Airbus A300-600RF | 3 | 1993 | 2015 | |
| Airbus A310-200 | 3 | 1988 | 2006 | |
| Airbus A310-300 | 2 | 1988 | 1994 | |
| Airbus A318-100 | 1 | 2012 | 2020 | Operated for China Eastern Airlines Executive Air.[citation needed] |
| Airbus A340-300 | 5 | 1996 | 2012 | |
| Airbus A340-600 | 5 | 2003 | 2015 | |
| Boeing 737-200 | 3 | 2001 | 2005 | |
| Boeing 737-300 | 26 | 1998 | 2014 | |
| Boeing 767-300ER | 3 | 2003 | 2011 | Acquired fromChina Yunnan Airlines. |
| Bombardier CRJ-200ER | 5 | 2004 | 2016 | Acquired fromChina Yunnan Airlines. All aircraft remained in the Yunnan landscape special livery previously painted by China Yunnan Airlines. |
| BAe 146-100 | 6 | 1986 | 2009 | |
| BAe 146-300 | 7 | 2003 | 2009 | |
| Embraer ERJ-135 | 5 | 2012 | 2021 | Operated for China Eastern Airlines Executive Air.[citation needed] |
| Embraer ERJ-145 | 10 | 2005 | 2016 | |
| Fokker 100 | 10 | 1992 | 1999 | |
| McDonnell Douglas MD-11 | 4 | 1991 | 2003 | |
| McDonnell Douglas MD-11F | 2 | 1991 | 2003 | Transferred toChina Cargo Airlines. |
| McDonnell Douglas MD-82 | 16 | 1988 | 2007 | |
| McDonnell Douglas MD-90-30 | 9 | 1997 | 2010 | |
| Xian MA-60 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Acquired fromWuhan Airlines. |
| Yakovlev Yak-42 | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Acquired fromChina General Aviation Corporation. |
Special liveries gallery
[edit]
-
Airbus A330-343 in 2011Xi'anInternational Horticultural Expo Livery
-
Airbus A320-232 in 2011 Xi'an International Horticultural Expo Livery
-
Airbus A330-343 inEXPO Shanghai 2010Livery
-
Boeing 737-800 in special livery for promotion of tourism inEnshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
-
China Eastern Yunnan AirlinesBoeing 737-800 in Purple Peacock Livery
-
Airbus A330-343 inPeople's Daily OnlineLivery
-
Airbus A330-343 inXinhua NewsLivery
-
Airbus A330-343 inShanghai Disney ResortLivery
-
Airbus A330-343 inToy Storylivery
-
Airbus A321-231 inSkyTeamlivery
-
Boeing 737-800 inDuffy the Disney Bearlivery
-
Boeing 737-800 inFrozenlivery
-
Boeing 777-300ER inChina International Import Expolivery
Services
[edit]China Eastern offers first class, business class, premium economy, and economy.
- First class
China Eastern offers first class on Boeing 777-300ERs. A first-class seat comes with a flat bed seat, direct aisle access and a sliding door. The plane also comes with a bar for passengers to serve themselves snacks and socialize with others. Middle seats on the Boeing 777 can be turned into a double bed.
- Business plus/ Super premium suites
The business plus product can be found on all Airbus A350s and Boeing 787s. The suites come with bigger space along with larger suite length compared to the business class seats. The business plus suites also feature sliding door and a minibar. The middle seats can be turned into a living room with seating for four.[50][56]
- Business class

Business class comes in many different versions. On narrowbody aircraft, business class seats are recliners arranged in an 2-2 configuration. On select Airbus A330s, business class seats are either Zodiac Cirrus or Thompson Vantage XL which is in a 1-2-1 configuration, or angled flat beds or fully flat beds arranged in a 2-2-2 configuration. On Airbus A350s and Boeing 787-9s, business class seats are modified Thompson Vantage XL with doors similar to Delta One suites.[65] On Boeing 777-300ERs, business class seats are Zodiac Cirrus.
- Premium eco
Premium economy is found on all Airbus A350s and Boeing 787-9s.[66]
- Economy


China Eastern offers complimentary meal service and select A330s, all A350s, 777s, and 787s have seatback entertainment.[67]
Eastern Miles
[edit]China Eastern Airlines'sfrequent-flyer programis calledEastern Miles(simplified Chinese:Phương đông vạn dặm hành;traditional Chinese:Phương đông vạn dặm hành). Shanghai Airlines andChina United Airlines,China Eastern subsidiaries, are also parts of the program. Eastern Miles members can earn miles on flights as well as through consumption with China Eastern's credit card. Members can be upgraded to Elite membership in three tiers: Platinum, Gold and Silver, when meet minimum spending requirement(essential), enough miles or flying sectors.[68]
Cargo
[edit]
After the merger with Shanghai Airlines, China Eastern Airlines signaled that it would combine the two carriers' cargo subsidiaries as well. The airline's new subsidiary cargo carrier, consisting of the assets ofChina Cargo Airlines,Great Wall AirlinesandShanghai Airlines Cargo,commenced operations in 2011 from its base in Shanghai, China's largest air cargo market.[69]China Eastern Airlines signed a strategic cooperation framework agreement with Shanghai Airport Group, which controls bothShanghai Hongqiao International AirportandShanghai Pudong International Airport.The airline will allocate more capacity to Pudong Airport to open more international routes and boost flight frequencies on existing international and domestic trunk routes.[citation needed]
Subsidiaries
[edit]China Cargo Airlines
[edit]China Eastern Airlines' cargo subsidiary,China Cargo Airlines,is China's first all-cargo airline operating dedicated freight services using China Eastern Airlines' route structure. The cargo airline carries the same logo of China Eastern Airlines.
China United Airlines
[edit]China United Airlines is alow-cost carrierbased inBeijing Da xing International Airport.It became a subsidiary of China Eastern in 2010 as a result ofacquisitions.[19]
OTT Airlines
[edit]OTT Airlines was an airline subsidiary that was launched in February 2020 to operate domestically produced aircraft like the Comac C919 and Comac ARJ21 in the Yangtze Delta region.[28][29]
China Eastern Yunnan Airlines
[edit]China Eastern Yunnan Airlines, formerly known as China Yunnan Airlines, is China Eastern Airlines' local subsidiary inYunnan province.
Incidents and accidents
[edit]- On April 24, 1989, a passenger hijacked a China Eastern Xian Y-7 en route from Ningbo to Xiamen. The hijacker, armed with a dagger and carrying dynamite, stabbed a flight attendant and demanded to be flown to Taiwan. The pilot diverted to Fuzhou instead, when the hijacker realized that he had been tricked, he blew himself up, injuring two people in the process.[70]
- On August 15, 1989,Flight 5510(B-3437) operating a domestic flight from Shanghai to Nanchang, crashed on takeoff following an unexplained failure of the right engine, killing 34 of 40 people on board.[71]
- On April 6, 1993,Flight 583,aMcDonnell-Douglas MD-11flying from Beijing to Los Angeles via Shanghai, had an inadvertent deployment of the leading edge wing slats while cruising. The aircraft progressed through several violent pitch oscillations and lost 5,000 feet (1,500 m) of altitude. Two passengers were killed, and 149 passengers and seven crew members were injured. The aircraft landed safely in Shemya, Alaska, United States.
- On October 26, 1993,Flight 5398from Shenzhen to Fuzhou, aMcDonnell Douglas MD-82overshot the runway and crashed at Fuzhou Yixu Airport after a failed attempt togo aroundon approach, killing two of 80 on board.
- On September 10, 1998, Flight 586, aMcDonnell-Douglas MD-11flying fromShanghai Hongqiao International AirporttoBeijing Capital International Airport,suffered a nose gear failure after take-off. The aircraft landed back inShanghaiwith the nose gear up on a foamed runway. There were only nine reported injuries. The incident became the inspiration for the 1999 movieCrash Landing,directed byZhang Jianya,which premiered on the 50th anniversary of the National Day of thePeople's Republic of China.[72]
- On November 21, 2004,Flight 5210,aBombardier CRJ-200LR,crashed shortly after takeoff from Baotou Airport due to wing icing, killing all 53 on board and two people on the ground.
- On June 7, 2013,Flight 2947,an Embraer ERJ-145LI (B-3052), ran off the runway on landing at Hongqiao Airport; all 49 on board survived. Investigation revealed that a servo valve in the nosewheel steering assembly was clogged.[73]
- On March 21, 2022,Flight 5735(operated byChina Eastern Yunnan Airlines), aBoeing 737-89Pflying fromKunming Changshui International AirporttoGuangzhou Baiyun International Airport,crashed in a mountainous region in Molang Village,Teng County,Guangxi,killing all 123 passengers and 9 crew.[74][75]On March 20, 2023,Civil Aviation Administration of Chinareleased a three paragraph statement with no further information on the crash.[76]On 17 May,The Wall Street Journalreported a source from the US government, from officials involved in the investigation, as saying that the plane had been intentionally crashed, based on an analysis of data from the aircraft recorders.[77][78]News reports published byABC Newson the same day concurred with theWall Street Journal's report of the investigating officials in the US government declaring that the aircraft had been deliberately put into a vertical dive by a person on the flight deck, also citingflight recorderdata showing that thelanding gearandflapshad evidently not been engaged or deployed during the aircraft's descent which would indicate the pilots attempting anemergency descent or landing.[79]
See also
[edit]- Civil aviation in China
- List of airlines of the People's Republic of China
- List of airports in China
- List of companies of the People's Republic of China
- Transport in China
- China Cargo Airlines(Cargo King)
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^Đông hàng “Bốn lương tám trụ” đường hàng không chiến lược: “Bốn lương” vì Thượng Hải, Bắc Kinh, Côn Minh, Tây An tứ đại đầu mối then chốt thị trường, “Tám trụ” tắc vì Quảng Châu, Thâm Quyến, thành đô, Hạ Môn, Nam Kinh, Hàng Châu, Thanh Đảo, Vũ Hán tám quan trọng thị trường.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines on ch-aviation".ch-aviation.RetrievedNovember 9,2023.
- ^abcde"Form 20-F China Eastern Airlines Corporation Limited".sec.gov. 2012.Archivedfrom the original on June 7, 2015.RetrievedSeptember 13,2013.
- ^"China Eastern Airline".ceair.RetrievedOctober 27,2022.
- ^Cantle, Katie (June 23, 2011)."China Eastern becomes 14th SkyTeam member".ATWOnline.Archivedfrom the original on June 3, 2012.RetrievedOctober 17,2011.
- ^"Directory: World Airlines".Flight International.April 3, 2007. p. 64.
- ^Shanghai Daily[dead link]
- ^"Channelnewsasia".September 30, 2007. Archived fromthe originalon September 30, 2007.RetrievedApril 16,2019.
- ^SIA approved to buy into China EasternArchivedJanuary 7, 2016, at theWayback MachineFlight Global, August 31, 2007
- ^"SIA, China Eastern Airlines announce strategic tie-up".Channel NewsAsia.September 2, 2007.Archivedfrom the original on September 4, 2007.RetrievedSeptember 2,2007.
- ^"Singapore Airlines, Temasek sign China Eastern deal".Channel NewsAsia.November 9, 2007.Archivedfrom the original on November 11, 2007.RetrievedNovember 9,2007.
- ^"Cathay Pacific to try and block Singapore Airlines: report".Agence France-Presse.Channel NewsAsia.September 22, 2007. Archived fromthe originalon July 23, 2012.RetrievedSeptember 22,2007.
- ^BBC tiếng Trung võng - phục vụ chuyên khu - thuần văn tự trang.BBC News.September 10, 2009.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^Markets (September 24, 2007)."Cathay Pacific abandons China Eastern plan".London: Telegraph.co.uk.Archivedfrom the original on May 6, 2014.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^Dyer, Geoff (January 6, 2008)."/ Companies / Transport - Air China pursues China Eastern stake".Ft.Archivedfrom the original on October 8, 2012.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^Anderlini, Jamil (January 8, 2008)."Shareholders reject Singapore Air offer".FT.Archivedfrom the original on December 10, 2022.RetrievedJanuary 8,2008.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines announces detailed merger plan with Shanghai Airlines".News.xinhuanet. July 12, 2009. Archived fromthe originalon March 3, 2016.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^"China Eastern Air Holding Company".Center for Aviation.Archivedfrom the original on December 15, 2019.RetrievedDecember 15,2019.
- ^abVề liên hàng[About United Airlines] (in Chinese). China United Airlines.Archivedfrom the original on October 21, 2019.RetrievedDecember 15,2019.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines and Qantas announce Jetstar Hong Kong".Jetstar Airways. March 26, 2012.Archivedfrom the original on May 12, 2012.RetrievedMarch 26,2012.
- ^"Qantas creates Jetstar Hong Kong".Sky News Australia. March 26, 2012.Archivedfrom the original on March 26, 2012.RetrievedMarch 26,2012.
- ^"China Eastern moves to end involvement with Jetstar Hong Kong".Australian Aviation.RetrievedDecember 9,2022.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines bags temporary permit - Civil Aeronautics Board:: Philippines".Cab.gov.ph.Archivedfrom the original on March 24, 2014.RetrievedJuly 5,2013.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines bags temporary permit | BusinessWorld Online".Bworldonline. April 17, 2013.Archivedfrom the original on September 23, 2015.RetrievedJanuary 17,2014.
- ^Phương đông hàng không chính thức tuyên bố hoàn toàn mới VI hệ thống.China Eastern Airlines. Archived fromthe originalon September 12, 2014.RetrievedSeptember 14,2014.
- ^"East-West Partnership".Airliner World:15. October 2015.
- ^"China Eastern's 2017 net profit up 41% as demand, exchange rates improve | Aviation Week Network".Archivedfrom the original on December 14, 2018.RetrievedDecember 3,2018.
- ^ab"China Eastern unveils OTT Airlines to operate Chinese-made jets".Reuters.February 26, 2020.Archivedfrom the original on February 28, 2020.RetrievedMarch 14,2020.
- ^abZhou, Senhao (March 1, 2020)."OTT Airlines unveiled, mainly to operate China-made aircraft like ARJ21 and C919".Comac.Archivedfrom the original on March 2, 2020.RetrievedMarch 14,2020.
- ^"China Eastern Annual Reports".ceair.RetrievedAugust 17,2024.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2013"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedNovember 9,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2014"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedNovember 9,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2015"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedNovember 9,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2016"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedNovember 9,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2017"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedNovember 9,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2018"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedOctober 15,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2019"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedOctober 15,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Annual Report 2020"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedOctober 15,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Annual Report 2021"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedOctober 15,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Annual Report 2022"(PDF).China Eastern Airlines.RetrievedOctober 15,2023.
- ^"Trung Quốc phương đông hàng không".ceair.RetrievedNovember 1,2022.
- ^"Trung Quốc đông hàng (600115) chủ yếu cổ đông _ tân lãng kinh tế tài chính _ tân lãng võng".vip.stock.finance.sina.cn.RetrievedOctober 27,2022.
- ^"A history of the Delta-China Eastern equity agreement | Delta News Hub".news.delta.November 23, 2022.RetrievedFebruary 23,2024.
- ^"Profile on China Eastern Airlines".CAPA.Centre for Aviation.Archivedfrom the original on October 29, 2016.RetrievedOctober 29,2016.
- ^"Virgin Atlantic, China Eastern Unveil Codeshare Routes".Aviation Week. January 30, 2024.RetrievedJanuary 30,2024.
- ^Cơ hình triển lãm - Trung Quốc phương đông hàng không công ty.ceair(in Chinese (China)).Archivedfrom the original on May 2, 2019.RetrievedApril 16,2019.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Airbus fleet".de.ceair.RetrievedSeptember 29,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines Boeing fleet".de.ceair.RetrievedSeptember 29,2023.
- ^abcAirbus Orders and Deliveries (XLS), monthly updated, accessed via"Orders & deliveries".Airbus.Airbus SAS.RetrievedJanuary 7,2024.
- ^ab"China Eastern Airbus A350 to fly Sydney-Shanghai from March 31".Executive Traveller.January 17, 2019.RetrievedNovember 16,2020.
- ^ab"China Southern, China Eastern to resume B737 MAX deliveries".ch-aviation.RetrievedSeptember 29,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Annual Report 2022"(PDF).ceair.RetrievedSeptember 29,2023.
- ^abc"China Eastern orders 20 A350-900s, 15 Boeing 787-9s".Aviation Week Network.Archivedfrom the original on November 17, 2018.RetrievedDecember 3,2018.
- ^"Industry News / Opinions - Shanghai Airlines 787-9".RetrievedJuly 22,2018.
- ^Bloomberg News (April 28, 2016)."China Eastern to Buy 20 Airbus A350 Jets, 15 Boeing 787s".Bloomberg.Archivedfrom the original on May 4, 2016.RetrievedMay 7,2016.
- ^ab"China Eastern Boeing 787 brings business class suites to Melbourne".Executive Traveller.January 8, 2019.RetrievedNovember 16,2020.
- ^ab"China Eastern Airlines to buy 100 C919 planes, aircraft's largest ever order".Reuters.RetrievedSeptember 28,2023.
- ^Vinholes, Thiago (November 21, 2022)."First series-production C919 emerges in China Eastern Airlines livery".Air Data News.RetrievedSeptember 29,2023.
- ^"China Eastern abandons 787 order for 737s".Flightglobal.Archivedfrom the original on October 19, 2011.RetrievedOctober 18,2011.
- ^"China Eastern orders 15 A330s, drops five A340s".Flightglobal. May 5, 2011.Archivedfrom the original on October 18, 2011.RetrievedOctober 18,2011.
- ^"China Eastern orders 15 Airbus 330s".Channel NewsAsia.Archivedfrom the original on October 18, 2011.RetrievedOctober 18,2011.
- ^"China Eastern takes delivery of first B777-300ER".Business Traveller.RetrievedSeptember 4,2022.
- ^"China Eastern Airlines".Airliner World:17. October 2015.
- ^"Form 6-K".sec.gov.RetrievedJune 17,2021.
- ^"China Eastern Airbus A350 to fly Sydney-Shanghai from March 31".Australian Business Traveler. January 17, 2019.Archivedfrom the original on January 17, 2019.RetrievedJanuary 17,2019.
- ^"China Eastern to introduce premium economy".TD. June 24, 2016.Archivedfrom the original on April 10, 2019.RetrievedJune 24,2016.
- ^"Touring China Eastern's New 777-300ER Products".Travel Codex. October 2, 2017.Archivedfrom the original on October 2, 2017.RetrievedDecember 11,2017.
- ^"Welcome to Eastern Miles".Easternmiles. Archived fromthe originalon April 28, 2012.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^Cantle, Katie (September 30, 2010)."New China Eastern cargo carrier to launch Jan. 1 from Shanghai".Atwonline.Archivedfrom the original on February 27, 2011.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^Hijacking descriptionat theAviation Safety Network
- ^"ASN Aircraft accident Antonov 24RV B-3417 Shanghai-Hongqiao Airport".Aviation-safety.net. August 15, 1989.Archivedfrom the original on October 23, 2012.RetrievedApril 28,2012.
- ^"ASN Aircraft accident MD-11 B-2173 Shanghai-Hongqiao Airport".Aviation-safety.net. September 10, 1998.RetrievedSeptember 19,2021.
- ^Accident description for B-3052at theAviation Safety Network
- ^"A 737 crashed in China. What we know about the plane".CNN.March 22, 2021.RetrievedMarch 23,2022.
- ^"Boeing 737 plane crashes in China's southern Guangxi with 132 people on board".SCMP.March 21, 2021.RetrievedMarch 23,2022.
- ^"Beijing still seeking answers a year after China Eastern plane crash".Reuters.March 21, 2023.RetrievedApril 24,2023.
- ^"China Eastern Black Box Points to Intentional Nosedive".Wall Street Journal.May 17, 2022.Archivedfrom the original on May 24, 2022.RetrievedMay 18,2022.
- ^Shepardson, David (May 18, 2022)."China Eastern crash probe looks into crew actions, sources say".Reuters.Archivedfrom the original on May 18, 2022.RetrievedMay 18,2022.
- ^Benitez, Gio; Margolin, Josh; Maile, Amanda."Chinese plane crash that killed 132 caused by intentional act: US officials".ABC News.RetrievedMay 18,2022.
External links
[edit]- Official Website(Global)
- Official Website(Chinese Version)
- Official Website(US Version)
- China Eastern Yunnan Airlines(in Chinese)
- Investor Relations Asia Pacific
- China Eastern Airfreight Business Management System
- China Eastern Airlines
- Companies listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange
- Companies in the CSI 100 Index
- Companies listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange
- Companies formerly listed on the New York Stock Exchange
- Airlines established in 1988
- Airlines of China
- Chinese brands
- Companies based in Shanghai
- Government-owned companies of China
- H shares
- SkyTeam
- Transport in Shanghai
- Chinese companies established in 1988














