EA-3990
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
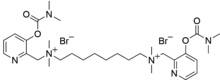
N1,N8-Bis({3-[(dimethylcarbamoyl)oxy]pyridin-2-yl}methyl)-N1,N1,N8,N8-tetramethyloctane-1,8-bis(aminium) dibromide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H50N6Br2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 718.7 g/mol |
| Appearance | white, odorless crystalline solid. |
| Density | 1.33 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 190–191 °C |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohols, acetic acid and chloroform |
| Vapor pressure | negligible |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal doseor concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50(median dose)
|
6.3 µg/kg for mice and 2.6 µg/kg for rabbits via IV |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in theirstandard state(at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
EA-3990is a deadlycarbamatenerve agent.It is lethal because itinhibitsacetylcholinesterase.[1]Inhibition causes an overly high accumulation ofacetylcholinebetween thenerveandmuscle cells.This paralyzes the muscles by preventing their relaxation. The paralyzed muscles include the muscles used for breathing.[2]
Patent assigned toUS armyfor EA-3990 among other similar nerve agents was filed in December 7, 1967.[3]
Lethality
[edit]EA-3990 lethality in humans is unknown but estimates have been made.
Carbamates like EA-3990 are well absorbed by the lungs, gastrointestinal tracts, and the skin.Signsandsymptomsfrom exposure to such carbamates are similar to other nerve agents. In general their penetration through theblood-brain barrieris difficult due toquaternary nitrogensin thesemolecules.[4]Despite this, EA-3990 is claimed to be about three times more toxic thanVX(another nerve agent).[1]For VX, themedian lethal dose(LD50) for 70 kg men via exposure to the skin is estimated to be 10 mg, and thelethal concentration time(LCt50), measuring theconcentrationof the vapor per length of time exposed, is estimated to be 30–50 mg·min/m3.[5]These values for EA-3990 can be estimated to be 3.3 mg and 10–16.7 mg·min/m3bydivision.
IntravenousLD50for EA-3990 is 0.0063 mg/kg for mice and 0.0026 mg/kg for rabbits.[3]
Properties
[edit]EA-3990'sCASis 110913-95-6,mass718.7 g/mol,[1]melting point 190–191 °C,[3]density1.33 g/cm3,vapor pressureis negligible, and it is soluble in alcohols,acetic acidandchloroform.It is a white, odorless crystalline solid. EA-3990 evaporates slowly in to the air; thus it can be classified as being extremely persistent in the environment if any possible effects of external factors like sun light and water (air humidity) upon it are neglected. Varioussaltsother thanbromidehave been reported.[1]
Synthesis
[edit]Two methods have been described for synthesizing EA-3990 along with similar nerve agents.
The 2-dimethylaminomethyl-3-dimethylcarbamoxypyridine precursor is prepared via aMannich reactionusing 3-pyridol (CAS 109-00-2),dimethylamineandformaldehyde.The resulting 2-((Dimethylamino)methyl)pyridin-3-ol (CAS 2168-13-0) is thencarbamoylatedwithdimethylcarbamoyl chloride.Other secondaryaminescan be used, such as those containingmethyl,ethyl,propyl,isopropyl,butylandbenzylgroups.[6]
In the first method 2molesof 2-dimethylaminomethyl-3-dimethylcarbamoxypyridine and app. 1 molα,ω-dihaloalkane(e.g.1,8-dibromooctanein this case) inacetonitrileis heated on asteam bathfor 6 hours. It is then allowed to stand overnight at room temperature. The crystalline product is collected by filtration.[3][6]
In the second method 2 mol and 1 mol of the previous reagents used in the first method are added together, but also a catalytic amount ofsodium iodidein acetonitrile is added to the solution, which is then allowed to stand for 6 days. Crystalline material is usually formed during this period and it is then collected by filtration.[3]
In both methods, after filtration, the crystalline product istrituratedwithacetone.If no solid separates,ethyl acetateis added toprecipitatethe crude product. The product is then dissolved in hotethanoland treated with decolorizingcharcoal.Ethyl acetate is added to the filtered solution to precipitate the crystalline product. E-3990 is then collected and dried.Yieldis 63%.[3][6]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^abcdHank ED (2008).Handbook of chemical and biological warfare agents(2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 113.ISBN9780849314346.OCLC82473582.
- ^Colović MB, Krstić DZ, Lazarević-Pašti TD, Bondžić AM, Vasić VM (May 2013)."Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: pharmacology and toxicology".Current Neuropharmacology.11(3): 315–35.doi:10.2174/1570159X11311030006.PMC3648782.PMID24179466.
- ^abcdefUS patent 04512246,Harold Z. Sommer, Havre De Grace, John Krenzer, Oak Park, Omer O. Owens, Jacob I. Miller, "Chemical agents", issued 1987-06-30, assigned to US Secretary of Army
- ^Gupta RC (2015)."Carbamates".Handbook of toxicology of chemical warfare agents(2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Academic Press. pp. 338–339.ISBN9780128004944.OCLC433545336.
- ^FAS Staff (2013)."Types of Chemical Weapons: Nerve Agents [Table. Toxicological Data]".Washington, DC: Federation of American Scientists [FAS].Archivedfrom the original on November 26, 2016.RetrievedMarch 20,2018.
- ^abcUS patent 4677204A,Harold Z. Sommer, Havre de Grace, Omer O. Owens, "Chemical agents", issued 1987-06-30, assigned to US Secretary of Army
