Thuringian Basin
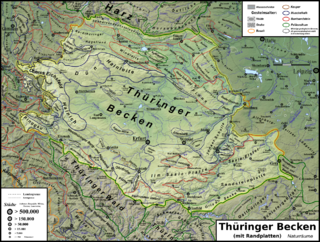
TheThuringian Basin[1][2](German:Thüringer Becken) is adepressionin the central and northwest part ofThuringiain Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is theUnstrut.It stretches about 60 kilometres (37 mi) from north to south and around 120 kilometres (75 mi) from east to west. Its height varies from about 150 to250 m abovesea level (NN).
The Basin is surrounded by a wide outer girdle of limestone (Muschelkalk) ridges (includingHainich,Dün,Hainleite,Hohe Schrecke,Schmücke,Finne), and to the southwest by theThuringian Forestand to the southeast by sharply divided terraces (the Ilm-Saale and Ohrdruf Muschelkalk plateaus, and the Saale-Elster Bunter sandstone plateau). The Thuringian Basin belongs to thetriassicperiod, during which horizontal beds ofBunter sandstone,MuschelkalkandKeuperwere laid down. Below those lie the salt and gypsum layers ofMagnesian Limestone(Zechstein). In theCenozoicera the surrounding ridges were uplifted, whilst the Thuringian Basin sank to form a saucer-shaped depression.
The elevation of the Thuringian Basin descends from the south and west to the east. While some of the marginal ridges have the character of low mountain ranges, there are no really noteworthy uplands within it, apart from the Ettersberg and Fahnerscher Höhe.
The Thuringian Basin is dominated by agriculture. Along with theMagdeburg BördeandLeipzig Bayit is one of the richest arable lands in Germany.[3]It was settled in the 8th and 9th century which makes most of the villages and towns in the basin well over 1000 years old. As a result of the fertile countryside, large cities were established very early on in the Basin and on its perimeter (Erfurtand thefree imperial cityofMühlhausen).
Other towns in the Thuringian Basin are (year of foundation and year of achieving town status in brackets):
- Schlotheim(974/1277)
- Ebeleben(1198/1928)
- Großenehrich
- Greußen/Clingen(?/1353 and 860/1282) to the north,
- Kindelbrück(775/1291)
- Weißensee(?/1265)
- Sömmerda(876/1350)
- Kölleda(786/1392)
- Rastenberg(1294/1412)
- Buttstädt(?/1331)
- Buttelstedt(780/1454)
- Neumark(1179/1326) to the east,
- Gebesee(786/1638)
- Bad Tennstedt(772/1340)
- Bad Langensalza(932/1212) in the centre
- Gotha(775/?) in the south
Large parts of the Basin in the former ThuringianLandgraviatewere held by theHouse of Wettinfrom 1264 and, after the 1485Treaty of Leipzig,formed the Thuringian Circle of theSaxon Electorate.Smaller areas used to belong to the WettinErnestine duchiesand theCounty of Schwarzburg;the city of Erfurt was a possession of theMainz Archbishops.According to the 1815Congress of Vienna,the Albertine and Mainz lands passed to theKingdom of Prussia,while the smaller areas on the northern and southern rim formed theThuringian states.
References[edit]
- ^Elkins, T.H. (1972).Germany(3rd ed.). London: Chatto & Windus, 1972.ASINB0011Z9KJA.
- ^Kohl, Horst; Marcinek, Joachim and Nitz, Bernhard (1986).Geography of the German Democratic Republic,VEB Hermann Haack, Gotha, pp. 32 ff.ISBN978-3-7301-0522-1.
- ^Dickinson, Robert E. (1964).Germany: A regional and economic geography(2nd ed.). London: Methuen.
External links[edit]
