Explorer 60
 Explorer 60 (SAGE) satellite | |
| Names | Explorer 60 AEM-B Applications Explorer Mission-B |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Earth science |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1979-013A |
| SATCATno. | 11270 |
| Mission duration | 1 year (planned) 3 years (achieved) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Explorer LX |
| Spacecraft type | Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment |
| Bus | SAGE |
| Manufacturer | Langley Research Center |
| Launch mass | 148.7 kg (328 lb) |
| Power | Solar panelsandbatteries |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 18 February 1979, 16:18UTC[1] |
| Rocket | Scout D-1(S-202C) |
| Launch site | Wallops,LA-3A |
| Contractor | Vought |
| Entered service | 18 February 1979 |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | 7 January 1982 |
| Decay date | 11 April 1989 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[2] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 547.5 km (340.2 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 660.2 km (410.2 mi) |
| Inclination | 54.90° |
| Period | 96.80 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) | |
Explorer program | |
Explorer 60,also called asSAGE(Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment) and was the second of the Applications Explorer Missions (AEM),AEM-B(Applications Explorer Mission-B), was aNASAscientific satellite launched on 18 February 1979, fromWallops Flight Facility(WFF) by aScout D-1launch vehicle.[3]
Spacecraft[edit]
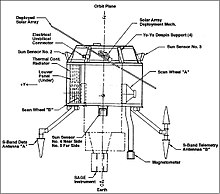
Explorer 60 had a launchmassof 148.7 kg (328 lb). The spacecraft was designed for a 1-year life in orbit. Explorer 60 was a small, versatile, and low-cost spacecraft made of two distinct parts: (1) the SAGE instrument module containing the detectors and the associated hardware, and (2) the base module containing the necessary data handling, power, communications, command, and attitude control subsystem to support the instrument mode.[3]The base module includes the telemetry data system and a communications subsystem that makes use of a conical log spiralS-bandantenna and twoVery high frequency(VHF)antennas.[4]
Mission[edit]
The objective of the SAGE mission was to obtainstratospheric aerosolandozonedata on a global scale for a better understanding of the Earth's environmental quality and radiation budget.[3]
Experiment[edit]
Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE)[edit]
The objectives of theStratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment(SAGE) were to determine the spatial distribution of stratospheric aerosols and ozone on a global scale. Specific objectives were (1) to develop a satellite-based remote-sensing technique for stratospheric aerosols and ozone measurements, (2) to map aerosol and ozone concentrations on a time scale shorter than major stratospheric changes, (3) to locate stratospheric aerosol and ozone sources and sinks, (4) to monitor circulation and transfer phenomena, (5) to observe hemisphere differences, and (6) to investigate the optical properties of aerosols and assess their effects on global climate. The SAGE instrument was aradiometerconsisting of agregorian telescopeand a detector subassembly which measured the attenuation ofsolar radiationat four wavelengths (0.385, 0.45, 0.6, and 1.0micrometre) during solar occultation. As the spacecraft emerged from the Earth's shadow, the sensor scanned theatmosphere of Earthfrom the horizon up, and measured the attenuation of solar radiation by different atmospheric layers. This procedure was repeated during spacecraft sunset. Two vertical scannings were obtained during each orbit, with each scan requiring approximately 1 minute of time to cover the atmosphere above thetroposphere.The instrument had afield of viewof approximately 0.15milliradianwhich resulted in a vertical resolution of about 1 km (0.62 mi). Spatial coverage extended from about 79°N to 79°Slatitudeand thus complemented the coverage (64°N to 80°N and 64°S to 80°S) of the SAM II onNimbus 7.The instrument performed satisfactorily. Because of power problems, the data collection was limited to sunset events after June 1979, and was eventually terminated on 18 November 1981.[5]
Results[edit]
Explorer 60 experienced power problems after 15 May 1979. However, the spacecraft operations continued until 19 November 1981. Explorer 60 detected and tracked also 5volcanic eruption plumesthat penetrated in thestratosphere.It determined the amount of new material for each volcano added to the stratosphere. The signal from the spacecraft was last received on 7 January 1982, when the battery failed.[3]On 11 April 1989, the spacecraft decayed in the atmosphere.[4]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^"Launch Log".Jonathan's Space Report. 21 July 2021.Retrieved22 November2021.
- ^"Trajectory: Explorer 60 (SAGE) 1979-013A".NASA. 28 October 2021.Retrieved22 November2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in thepublic domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in thepublic domain.
- ^abcd"Display: Explorer 60 (SAGE) 1979-013A".NASA. 28 October 2021.Retrieved22 November2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in thepublic domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in thepublic domain.
- ^ab"AEM-2 (Applications Explorer Mission-2)".ESA eoPortal Directory.Retrieved22 November2021.
- ^"Experiment: Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE)".NASA. 28 October 2021.Retrieved22 November2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in thepublic domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in thepublic domain.

