Extensor indicis muscle
| Extensor indicis proprius | |
|---|---|
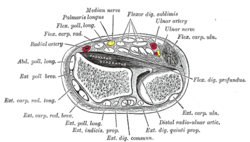 | |
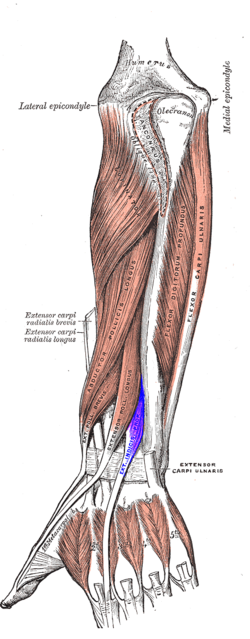 Posterior surface of the left forearm. Deep muscles. Extensor indicis muscle is labeled in purple. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Posterior distal third ofulnaandinterosseous membrane |
| Insertion | Index finger(extensor hood) |
| Artery | Posterior interosseous artery |
| Nerve | Posterior interosseous nerve |
| Actions | Extendsindex finger,wrist |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus extensor indicis |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.052 |
| TA2 | 2515 |
| FMA | 38524 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Inhuman anatomy,theextensor indicis (proprius)is a narrow, elongatedskeletal musclein the deep layer of the dorsalforearm,placed medial to, and parallel with, theextensor pollicis longus.Its tendon goes to theindex finger,which it extends.
Structure
[edit]It arises from the distal third of the dorsal part of thebody of ulnaand from theinterosseous membrane.It runs through the fourth tendon compartment together with theextensor digitorum,from where it projects into the dorsalaponeurosisof the index finger. [1]
Opposite the head of thesecond metacarpalbone, it joins the ulnar side of the tendon of the extensor digitorum which belongs to the index finger.
Like theextensor digiti minimi(i.e. the extensor of the little finger), the tendon of the extensor indicis runs and inserts on the ulnar side of the tendon of the common extensor digitorum.[2]The extensor indicis lacks thejuncturae tendinuminterlinking the tendons of the extensor digitorum on the dorsal side of the hand. [3]
Variation
[edit]The extensor indicis proprius does not show much variation. It exists as a single tendon most of the time.[4]Double tendons of the extensor indicis proprius was also reported.[2][5][6]
It is known that the extensor indicis proprius inserts to the index finger on the ulnar side of the extensor digitorum.[7]However, the insertion on the radial side of the common extensor digitorum infrequently seen, namely theextensor indicis radialis.[2]Split tendons of the muscle inserting on both ulnar and the radial side of the common extensor digitorum was also reported.[2]
Anomalous hand extensors including theextensor medii propriusand theextensor indicis et medii communisare often seen as variations of the extensor indicis[2]due to the shared characteristics and embryonic origin.[8]
Function
[edit]The extensor indicisextendstheindex finger,and by its continued action assists in extending (dorsiflexion) thewristand themidcarpal joints.[1]
Because the index finger and little finger have separate extensors, these fingers can be moved more independently than the other fingers.[3]
Additional images
[edit]-
The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the back of the wrist. (Extensor indicis proprius visible going into second digit.)
-
Bones of left forearm. Posterior aspect.
-
Posterior surface of the forearm. Deep muscles.
-
Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
-
Extensor indicis muscle
-
Extensor indicis muscle
-
Extensor indicis muscle
-
Extensor indicis muscle
-
Extensor indicis muscle
-
Muscles of hand. Posterior view.
-
Muscles of hand. Posterior view.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^abPlatzer 2004,p. 168
- ^abcdeKomiyama, M.; Nwe, T. M.; Toyota, N.; Shimada, Y. (1999)."Variations of the Extensor Indicis Muscle and Tendon"(PDF).Journal of Hand Surgery, British Volume.24(5): 575–578.doi:10.1054/jhsb.1999.0239.PMID10597935.S2CID23240783.Retrieved2015-06-09.
- ^abRoss & Lamperti 2006,p. 300
- ^Dass, Prameela; Prabhu, Latha V.; Pai, Mangala M.; Nayak, Varsha; Kumar, Ganesh; Janardhanan, Jiji P. (Nov–Dec 2011). "A comprehensive study of the extensor tendons to the medial four digits of the hand".Chang Gung Medical Journal.34(6): 612–619.ISSN2309-835X.PMID22196064.
- ^"Double tendon of the Human Extensor Indicis Muscle provides" insight' into individual development -- Kumka 22 (1): 983.2 -- The FASEB Journal ".fasebj.org.Retrieved2015-06-09.
- ^Aziz, M. Ashraf; Dunlap, Samuel Strong (1986-07-01). "The human extensor digitorum profundus muscle with comments on the evolution of the primate hand".Primates.27(3): 293–319.doi:10.1007/BF02382073.ISSN0032-8332.S2CID39525970.
- ^"Anatomy of the human body".archive.org.Retrieved2015-06-09.
- ^Straus, W.I. (1941). "Phylogeny of human forearm extensors".Ann Hum Biol(13): 203–238.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in thepublic domainfrompage 456of the 20th edition ofGray's Anatomy(1918)
This article incorporates text in thepublic domainfrompage 456of the 20th edition ofGray's Anatomy(1918)
- Platzer, Werner (2004).Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System(5th ed.).Thieme.ISBN3-13-533305-1.
- Ross, Lawrence M.; Lamperti, Edward D., eds. (2006).Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System.Thieme.ISBN978-1-58890-419-5.
External links
[edit]- Anatomy photo:09:05-0106at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Extensor Region of Forearm and Dorsum of Hand: Deep Muscles of Extensor Region"
- lesson5musofpostforearmat The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Extensor indicisat theDuke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- Ritter, Merrill A.; Inglis, Allen E. (1969)."The Extensor Indicis Proprius Syndrome"(PDF).J Bone Joint Surg Am.51(8): 1645–1648.doi:10.2106/00004623-196951080-00016.PMID5357184.[permanent dead link]











