Persian language
| Persian | |
|---|---|
| فارسی(fārsī) | |
 Fārsiwritten inPersian calligraphy(Nastaʿlīq) | |
| Pronunciation | [fɒːɾˈsiː] |
| Native to |
|
| Speakers | L1:72 million (2017–2021)[7] L2:38 million (2021–2022)[7] Total (L1+L2): 130 million[8] |
Early forms | |
Standard forms | |
| Dialects | |
| |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Regulated by |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | fa |
| ISO 639-2 | per(B)fas(T) |
| ISO 639-3 | fas– inclusive codeIndividual codes: pes–Iranian Persianprs–Daritgk–Tajik languageaiq–Aimaq dialectbhh–Bukhori dialecthaz–Hazaragi dialectjpr–Judeo-Persianphv–Pahlavanideh–Dehwarijdt–Judeo-Tatttt–Caucasian Tat |
| Glottolog | fars1254 |
| Linguasphere | 58-AAC (Wider Persian) > 58-AAC-c (Central Persian) |
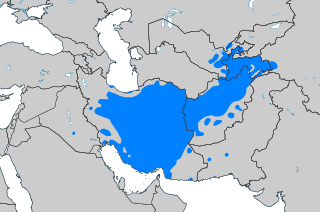 Areas with significant numbers of people whose first language is Persian (including dialects) | |
 Persian linguasphere Legend Official language
More than 1,000,000 speakers
Between 500,000 and 1,000,000 speakers
Between 100,000 and 500,000 speakers
Between 25,000 and 100,000 speakers
Fewer than 25,000 speakers to none | |
Persian(/ˈpɜːrʒən,-ʃən/PUR-zhən, -shən), also known by itsendonymFarsi(فارسی[fɒːɾˈsiː]), is aWestern Iranian languagebelonging to theIranian branchof theIndo-Iranian subdivisionof theIndo-European languages.Persian is apluricentric languagepredominantly spoken and used officially withinIran,Afghanistan,andTajikistanin threemutually intelligiblestandard varieties,respectivelyIranian Persian(officially known asPersian),[11][12][13]Dari Persian(officially known asDarisince 1964),[14]andTajiki Persian(officially known asTajiksince 1999).[15][16]It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population withinUzbekistan,[17][18][19]as well as within other regions with aPersianatehistory in the cultural sphere ofGreater Iran.It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in thePersian Alpha bet,a derivative of theArabic script,and within Tajikistan in theTajik Alpha bet,a derivative of theCyrillic script.
Modern Persian is a continuation ofMiddle Persian,an official language of theSasanian Empire(224–651 CE), itself a continuation ofOld Persian,which was used in theAchaemenid Empire(550–330 BCE).[20][21]It originated in the region ofPars(Persia) in southwestern Iran.[22]Its grammar is similar to that of many European languages.[23]
Throughout history, Persian was considered prestigious by various empires centered inWest Asia,Central Asia,andSouth Asia.[24]Old Persian is attested inOld Persian cuneiformon inscriptions from between the 6th and 4th century BC. Middle Persian is attested inAramaic-derived scripts (PahlaviandManichaean) oninscriptionsand inZoroastrianandManichaeanscriptures from between the third to the tenth centuries (seeMiddle Persian literature). New Persian literature was first recorded in the ninth century, after theMuslim conquest of Persia,since then adopting the Perso-Arabic script.[25]
Persian was the first language to break through the monopoly ofArabicon writing in theMuslim world,withPersian poetrybecoming a tradition in many eastern courts.[24]It was used officially as a language of bureaucracy even by non-native speakers, such as theOttomansinAnatolia,[26]theMughalsin South Asia, and thePashtunsin Afghanistan. It influenced languages spoken in neighboring regions and beyond, including other Iranian languages, theTurkic,Armenian,Georgian,andIndo-Aryan languages.It also exerted some influence on Arabic,[27]while borrowing a lot of vocabulary from it in the Middle Ages.[20][23][28][29][30][31]
Some of the world's most famous pieces of literature from the Middle Ages, such as theShahnamehbyFerdowsi,the works ofRumi,theRubáiyát of Omar Khayyám,thePanj GanjofNizami Ganjavi,The Divānof Hafez,The Conference of the BirdsbyAttar of Nishapur,and the miscellanea ofGulistanandBustanbySaadi Shirazi,are written in Persian.[32]Some of the prominent modern Persian poets wereNima Yooshij,Ahmad Shamlou,Simin Behbahani,Sohrab Sepehri,Rahi Mo'ayyeri,Mehdi Akhavan-Sales,andForugh Farrokhzad.
There are approximately 130 million Persian speakers worldwide, includingPersians,Lurs,Tajiks,Hazaras,Iranian Azeris,Iranian Kurds,Balochs,Tats,Afghan Pashtuns,andAimaqs.The termPersophonemight also be used to refer to a speaker of Persian.[33][34]
Classification
Persian is a member of theWestern Iranian groupof theIranian languages,which make up a branch of theIndo-European languagesin theirIndo-Iranian subdivision.The Western Iranian languages themselves are divided into two subgroups: Southwestern Iranian languages, of which Persian is the most widely spoken, and Northwestern Iranian languages, of whichKurdishandBalochiare the most widely spoken.[35]
Name
The termPersianis an English derivation ofLatinPersiānus,the adjectival form ofPersia,itself deriving fromGreekPersís(Περσίς),[36]a Hellenized form ofOld PersianPārsa(𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿),[37]which means "Persia"(a region in southwestern Iran, corresponding to modern-dayFars). According to theOxford English Dictionary,the termPersianas a language name is first attested in English in the mid-16th century.[38]
Farsi,which is the Persian word for the Persian language, has also been used widely in English in recent decades, more often to refer to Iran's standard Persian. However, the namePersianis still more widely used. TheAcademy of Persian Language and Literaturehas maintained that theendonymFarsiis to be avoided in foreign languages, and thatPersianis the appropriate designation of the language in English, as it has the longer tradition in western languages and better expresses the role of the language as a mark of cultural and national continuity.[39]Iranian historian and linguistEhsan Yarshater,founder of theEncyclopædia IranicaandColumbia University's Center for Iranian Studies, mentions the same concern in an academic journal onIranology,rejecting the use ofFarsiin foreign languages.[40]
Etymologically, the Persian termFarsiderives from its earlier formPārsi(PārsikinMiddle Persian), which in turn comes from the same root as the English termPersian.[41]In the same process, the Middle Persian toponymPārs( "Persia" ) evolved into the modern name Fars.[42]The phonemic shift from/p/to/f/is due to theinfluence of Arabicin the Middle Ages, and is because of the lack of the phoneme/p/in Standard Arabic.[43][44][45][46]
Standard varieties' names
The standard Persian of Iran has been called, apart fromPersianandFarsi,by names such asIranian PersianandWestern Persian,exclusively.[47][48]Officially, the official language of Iran is designated simply asPersian(فارسی,fārsi).[9]
The standard Persian of Afghanistan has been officially namedDari(دری,dari) since 1958.[14]Also referred to asAfghan Persianin English, it is one of Afghanistan's two official languages, together withPashto.The termDari,meaning "of the court", originally referred to the variety of Persian used in the court of the Sasanian Empire in capitalCtesiphon,which was spread to the northeast of the empire and gradually replaced the former Iranian dialects ofParthia(Parthian).[49][50]
Tajik Persian (форси́и тоҷикӣ́,forsi-i tojikī), the standard Persian of Tajikistan, has been officially designated asTajik(тоҷикӣ,tojikī) since the time of theSoviet Union.[16]It is the name given to the varieties of Persian spoken in Central Asia in general.[51]
ISO codes
The international language-encoding standardISO 639-1uses the codefafor the Persian language, as its coding system is mostly based on the native-language designations. The more detailed standardISO 639-3uses the codefasfor the dialects spoken across Iran and Afghanistan.[52]This consists of the individual languages Dari (prs) and Iranian Persian (pes). It usestgkfor Tajik, separately.[53]
History
In general, the Iranian languages are known from three periods: namely Old, Middle, and New (Modern). These correspond to three historical eras ofIranian history;Old era being sometime around theAchaemenid Empire(i.e., 400–300 BC), Middle era being the next period most officially around theSasanian Empire,and New era being the period afterward down to present day.[54]
According to available documents, the Persian language is "the only Iranian language"[20]for which close philological relationships between all of its three stages are established and so that Old, Middle, and New Persian represent[20][55]one and the same language of Persian; that is, New Persian is a direct descendant of Middle and Old Persian.[55]Gernot Windfuhr considers new Persian as an evolution of the Old Persian language and the Middle Persian language[56]but also states that none of the known Middle Persian dialects is the direct predecessor of Modern Persian.[57][58]Ludwig Paul states: "The language of the Shahnameh should be seen as one instance of continuous historical development from Middle to New Persian."[59]
The known history of the Persian language can be divided into the following three distinct periods:
Old Persian

As awritten language,Old Persian is attested in royalAchaemenidinscriptions. The oldest known text written in Old Persian is from theBehistun Inscription,dating to the time of KingDarius I(reigned 522–486 BC).[60][citation not found]Examples of Old Persian have been found in what is nowIran,Romania (Gherla),[61][62][63]Armenia,Bahrain,Iraq,Turkey, andEgypt.[64][65]Old Persian is one of the earliest attested Indo-European languages.[66]
According to certain historical assumptions about the early history and origin of ancient Persians inSouthwestern Iran(where Achaemenids hailed from), Old Persian was originally spoken by a tribe calledParsuwash,who arrived in the Iranian Plateau early in the 1st millennium BCE and finally migrated down into the area of present-day Fārs province. Their language, Old Persian, became the official language of the Achaemenid kings.[66]Assyrian records, which in fact appear to provide the earliest evidence for ancient Iranian (Persian and Median) presence on the Iranian Plateau, give a good chronology but only an approximate geographical indication of what seem to be ancient Persians. In these records of the 9th century BCE,Parsuwash(along withMatai,presumably Medians) are first mentioned in the area ofLake Urmiain the records ofShalmaneser III.[67]The exact identity of the Parsuwash is not known for certain, but from a linguistic viewpoint the word matches Old Persianpārsaitself coming directly from the older word*pārćwa.[67]Also, as Old Persian contains many words from another extinct Iranian language,Median,according toP. O. Skjærvøit is probable that Old Persian had already been spoken before the formation of theAchaemenid Empireand was spoken during most of the first half of the first millennium BCE.[66]Xenophon,a Greek general serving in some of the Persian expeditions, describes many aspects of Armenian village life and hospitality in around 401 BCE, which is when Old Persian was still spoken and extensively used. He relates that theArmenian peoplespoke alanguagethat to his ear sounded like the language of the Persians.[68]
Related to Old Persian, but from a different branch of the Iranian language family, wasAvestan,the language of theZoroastrianliturgical texts.
Middle Persian

The complexgrammatical conjugationanddeclensionof Old Persian yielded to the structure of Middle Persian in which the dual number disappeared, leaving only singular and plural, as did gender. Middle Persian developed theezāfeconstruction, expressed throughī(moderne/ye), to indicate some of the relations between words that have been lost with the simplification of the earlier grammatical system.
Although the "middle period" of the Iranian languages formally begins with the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, the transition from Old to Middle Persian had probably already begun before the 4th century BC. However, Middle Persian is not actually attested until 600 years later when it appears in the Sassanid era (224–651 AD) inscriptions, so any form of the language before this date cannot be described with any degree of certainty. Moreover, as a literary language, Middle Persian is not attested until much later, in the 6th or 7th century. From the 8th century onward, Middle Persian gradually began yielding to New Persian, with the middle-period form only continuing in the texts ofZoroastrianism.
Middle Persian is considered to be a later form of the same dialect as Old Persian.[69]Thenative nameof Middle Persian wasParsigorParsik,after the name of the ethnic group of the southwest, that is, "ofPars",Old PersianParsa,New PersianFars.This is the origin of the nameFarsias it is today used to signify New Persian. Following the collapse of the Sassanid state,Parsikcame to be applied exclusively to (either Middle or New) Persian that was written in theArabic script.From about the 9th century onward, as Middle Persian was on the threshold of becoming New Persian, the older form of the language came to be erroneously calledPahlavi,which was actually but one of thewriting systemsused to render both Middle Persian as well as various other Middle Iranian languages. That writing system had previously been adopted by the Sassanids (who were Persians, i.e. from the southwest) from the preceding Arsacids (who were Parthians, i.e. from the northeast). WhileIbn al-Muqaffa'(eighth century) still distinguished betweenPahlavi(i.e. Parthian) andPersian(in Arabic text: al-Farisiyah) (i.e. Middle Persian), this distinction is not evident in Arab commentaries written after that date.
New Persian

"New Persian" (also referred to as Modern Persian) is conventionally divided into three stages:
- Early New Persian (8th/9th centuries)
- Classical Persian (10th–18th centuries)
- Contemporary Persian (19th century to present)
Early New Persian remains largely intelligible to speakers of Contemporary Persian, as the morphology and, to a lesser extent, the lexicon of the language have remained relatively stable.[70]
Early New Persian
New Persian texts written in theArabic scriptfirst appear in the 9th-century.[71]The language is a direct descendant of Middle Persian, the official, religious, and literary language of the Sasanian Empire (224–651).[72]However, it is not descended from the literary form of Middle Persian (known aspārsīk,commonly called Pahlavi), which was spoken by the people ofFarsand used inZoroastrianreligious writings. Instead, it is descended from the dialect spoken by the court of the Sasanian capitalCtesiphonand the northeastern Iranian region ofKhorasan,known as Dari.[71][73]The region, which comprised the present territories of northwestern Afghanistan as well as parts of Central Asia, played a leading role in the rise of New Persian. Khorasan, which was the homeland of the Parthians, was Persianized under the Sasanians. Dari Persian thus supplantedParthian language,which by the end of the Sasanian era had fallen out of use.[71]New Persian has incorporated many foreign words, including fromeasternnorthern and northern Iranian languages such asSogdianand especially Parthian.[74]
The transition to New Persian was already complete by the era of the three princely dynasties of Iranian origin, theTahirid dynasty(820–872),Saffarid dynasty(860–903), andSamanid Empire(874–999).[75]Abbas ofMervis mentioned as being the earliest minstrel to chant verse in the New Persian tongue and after him the poems ofHanzala Badghisiwere among the most famous between the Persian-speakers of the time.[76]
The first poems of the Persian language, a language historically called Dari, emerged in present-day Afghanistan.[77]The first significant Persian poet wasRudaki.He flourished in the 10th century, when the Samanids were at the height of their power. His reputation as a court poet and as an accomplished musician and singer has survived, although little of his poetry has been preserved. Among his lost works are versified fables collected in theKalila wa Dimna.[24]
The language spread geographically from the 11th century on and was the medium through which, among others, Central Asian Turks became familiar with Islam and urban culture. New Persian was widely used as a trans-regionallingua franca,a task aided due to its relatively simple morphology, and this situation persisted until at least the 19th century.[78]In the late Middle Ages, new Islamic literary languages were created on the Persian model:Ottoman Turkish,Chagatai Turkic,Dobhashi Bengali,and Urdu, which are regarded as "structural daughter languages" of Persian.[78]
Classical Persian

"Classical Persian" loosely refers to the standardized language ofmedieval Persiaused inliteratureandpoetry. This is the language of the 10th to 12th centuries, which continued to be used as literary language andlingua francaunder the "Persianized"Turko-Mongol dynasties during the 12th to 15th centuries, and under restored Persian rule during the 16th to 19th centuries.[79]
Persian during this time served as lingua franca ofGreater Persiaand of much of theIndian subcontinent. It was also the official and cultural language of many Islamic dynasties, including the Samanids,Buyids,Tahirids,Ziyarids,theMughal Empire,Timurids,Ghaznavids,Karakhanids,Seljuqs,Khwarazmians,theSultanate of Rum,Turkmen beyliks of Anatolia,Delhi Sultanate,theShirvanshahs,Safavids,Afsharids,Zands,Qajars,Khanate of Bukhara,Khanate of Kokand,Emirate of Bukhara,Khanate of Khiva,Ottomans,and also many Mughal successors such as theNizam of Hyderabad. Persian was the only non-European language known and used byMarco Poloat the Court ofKublai Khanand in his journeys through China.[80][81]
Use in Asia Minor

A branch of the Seljuks, theSultanate of Rum,took Persian language, art, and letters to Anatolia.[82]They adopted the Persian language as theofficial languageof the empire.[83]TheOttomans,who can roughly be seen as their eventual successors, inherited this tradition. Persian was the official court language of the empire, and for some time, the official language of the empire.[84]The educated and noble class of the Ottoman Empire all spoke Persian, such as SultanSelim I,despite being Safavid Iran's archrival and a staunch opposer ofShia Islam.[85]It was a major literary language in the empire.[86]Some of the noted earlier Persian works during the Ottoman rule areIdris Bidlisi'sHasht Bihisht,which began in 1502 and covered the reign of the first eight Ottoman rulers, and theSalim-Namah,a glorification of Selim I.[85]After a period of several centuries,Ottoman Turkish(which was highly Persianised itself) had developed toward a fully accepted language of literature, and which was even able to lexically satisfy the demands of a scientific presentation.[87]However, the number of Persian and Arabic loanwords contained in those works increased at times up to 88%.[87]In the Ottoman Empire, Persian was used at the royal court, for diplomacy, poetry, historiographical works, literary works, and was taught in state schools, and was also offered as an elective course or recommended for study in somemadrasas.[88]
Use in the Balkans
Persian learning was also widespread in the Ottoman-heldBalkans(Rumelia), with a range of cities being famed for their long-standing traditions in the study of Persian and its classics, amongst them Saraybosna (modernSarajevo,Bosnia and Herzegovina),Mostar(also in Bosnia and Herzegovina), and Vardar Yenicesi (or Yenice-i Vardar, nowGiannitsa,in the northern part of Greece).[89]
Vardar Yenicesi differed from other localities in the Balkans insofar as that it was a town where Persian was also widely spoken.[90]However, the Persian of Vardar Yenicesi and throughout the rest of the Ottoman-held Balkans was different from formal Persian both in accent and vocabulary.[90]The difference was apparent to such a degree that the Ottomans referred to it as "Rumelian Persian" (Rumili Farsisi).[90]As learned people such as students, scholars and literati often frequented Vardar Yenicesi, it soon became the site of a flourishingPersianatelinguistic and literary culture.[90]The 16th-century OttomanAşık Çelebi(died 1572), who hailed fromPrizrenin modern-dayKosovo,was galvanized by the abundant Persian-speaking and Persian-writing communities of Vardar Yenicesi, and he referred to the city as a "hotbed of Persian".[90]
Many Ottoman Persianists who established a career in the Ottoman capital of Constantinople (modern-dayIstanbul) pursued early Persian training in Saraybosna, amongst themAhmed Sudi.[91]
Use in Indian subcontinent


The Persian language influenced the formation of many modern languages in West Asia, Europe,Central Asia,andSouth Asia.Following the Turko-PersianGhaznavidconquest ofSouth Asia,Persian was firstly introduced in the region by Turkic Central Asians.[92]The basis in general for the introduction of Persian language into the subcontinent was set, from its earliest days, by various Persianized Central Asian Turkic and Afghan dynasties.[82]For five centuries prior to theBritish colonization,Persian was widely used as a second language in theIndian subcontinent.It took prominence as the language of culture and education in several Muslim courts on the subcontinent and became the sole "official language" under theMughal emperors.
TheBengal Sultanatewitnessed an influx of Persian scholars, lawyers, teachers, and clerics. Thousands of Persian books and manuscripts were published in Bengal. The period of the reign of SultanGhiyathuddin Azam Shahis described as the "golden age of Persian literature in Bengal". Its stature was illustrated by the Sultan's own correspondence and collaboration with the Persian poetHafez;a poem which can be found in theDivan of Hafeztoday.[93]ABengalidialect emerged among the commonBengali Muslimfolk, based on a Persian model and known asDobhashi;meaningmixed language.Dobhashi Bengali was patronised and given official status under theSultans of Bengal,and was a popular literary form used by Bengalis during the pre-colonial period, irrespective of their religion.[94]
Following the defeat of theHindu Shahidynasty, classical Persian was established as a courtly language in the region during the late 10th century underGhaznavidrule over the northwestern frontier of thesubcontinent.[95]Employed byPunjabisin literature, Persian achieved prominence in the region during the following centuries.[95]Persian continued to act as a courtly language for various empires inPunjabthrough the early 19th century serving finally as the official state language of theSikh Empire,precedingBritish conquestand the decline of Persian in South Asia.[96][97][98]
Beginning in 1843, though, English andHindustanigradually replaced Persian in importance on the subcontinent.[99]Evidence of Persian's historical influence there can be seen in the extent of its influence on certain languages of the Indian subcontinent. Words borrowed from Persian are still quite commonly used in certain Indo-Aryan languages, especiallyHindi-Urdu(also historically known asHindustani),Punjabi,Kashmiri,andSindhi.[100]There is also a small population of ZoroastrianIranisin India, who migrated in the 19th century to escape religious execution inQajar Iranand speak a Dari dialect.
Contemporary Persian
Qajar dynasty

In the 19th century, under theQajar dynasty,the dialect that is spoken inTehranrose to prominence. There was still substantial Arabic vocabulary, but many of these words have been integrated into Persian phonology and grammar. In addition, under the Qajar rule, numerousRussian,French,and English terms entered the Persian language, especially vocabulary related to technology.
The first official attentions to the necessity of protecting the Persian language against foreign words, and to the standardization ofPersian orthography,were under the reign ofNaser ed Din Shahof theQajar dynastyin 1871.[citation needed]After Naser ed Din Shah,Mozaffar ed Din Shahordered the establishment of the first Persian association in 1903.[39]This association officially declared that it used Persian andArabicas acceptable sources for coining words. The ultimate goal was to prevent books from being printed with wrong use of words. According to the executive guarantee of this association, the government was responsible for wrongfully printed books. Words coined by this association, such asrāh-āhan(راهآهن) for "railway", were printed inSoltani Newspaper;but the association was eventually closed due to inattention.[citation needed]
A scientific association was founded in 1911, resulting in a dictionary calledWords of Scientific Association(لغت انجمن علمی), which was completed in the future and renamedKatouzian Dictionary(فرهنگ کاتوزیان).[101]
Pahlavi dynasty
The first academy for the Persian language was founded on 20 May 1935, under the nameAcademy of Iran.It was established by the initiative ofReza Shah Pahlavi,and mainly byHekmat e ShiraziandMohammad Ali Foroughi,all prominent names in the nationalist movement of the time. The academy was a key institution in the struggle to re-build Iran as a nation-state after the collapse of the Qajar dynasty. During the 1930s and 1940s, the academy led massive campaigns to replace the manyArabic,Russian,French,andGreekloanwords whose widespread use in Persian during the centuries preceding the foundation of the Pahlavi dynasty had created a literary language considerably different from the spoken Persian of the time. This became the basis of what is now known as "Contemporary Standard Persian".
Varieties
There are three standard varieties of modern Persian:
- Iranian Persian(Persian,Western Persian,orFarsi) is spoken inIran,and by minorities inIraqand thePersian Gulfstates.
- Eastern Persian(Dari Persian,Afghan Persian,orDari) is spoken inAfghanistan.
- Tajiki(Tajik Persian) is spoken inTajikistanandUzbekistan.It is written in theCyrillic script.
All these three varieties are based on the classic Persian literature and its literary tradition. There are also several local dialects from Iran, Afghanistan and Tajikistan which slightly differ from the standard Persian. TheHazaragi dialect(in Central Afghanistan and Pakistan),Herati(in Western Afghanistan), Darwazi (in Afghanistan and Tajikistan),Basseri(in Southern Iran), and theTehrani accent(in Iran, the basis of standard Iranian Persian) are examples of these dialects. Persian-speaking peoples of Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan can understand one another with a relatively high degree ofmutual intelligibility.[102]Nevertheless, theEncyclopædia Iranicanotes that the Iranian, Afghan, and Tajiki varieties comprise distinct branches of the Persian language, and within each branch a wide variety of local dialects exist.[103]
The following are some languages closely related to Persian, or in some cases are considered dialects:
- Luri(orLori), spoken mainly in the southwestern Iranian provinces ofLorestan,Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad,Chaharmahal and Bakhtiarisome western parts ofFars Province,and some parts ofKhuzestan Province.
- Achomi(orLari), spoken mainly in southern Iranian provinces ofFarsandHormozgan.
- Tat,spoken in parts of Azerbaijan, Russia, and Transcaucasia. It is classified as a variety of Persian.[104][105][106][107][108](This dialect is not to be confused with theTati languageof northwestern Iran, which is a member of a different branch of the Iranian languages.)
- Judeo-Tat.Part of the Tat-Persian continuum, spoken in Azerbaijan, Russia, as well as by immigrant communities in Israel and New York.
More distantly related branches of theIranian language familyinclude Kurdish andBalochi.
TheGlottologdatabase proposes the following phylogenetic classification:
- Farsic–Caucasian Tat
- Caucasian Tat
- Judeo-Tat
- Muslim Tat(including Armeno-Tat)
- Farsic
- Eastern Farsic
- Judeo-Persian
- Western Farsi
- Caucasian Tat
Phonology
Iranian Persian and Tajik have six vowels; Dari has 8. Iranian Persian has twenty-three consonants, but both Dari and Tajiki have twenty-four consonants. (due to the phonemic merger of /q/ and /ɣ/ in Iranian Persian).[109]
Vowels
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Historically, Persian distinguished length. Early New Persian had a series of five long vowels (/iː/,/uː/,/ɑː/,/oː/,and/eː/) along with three short vowels/æ/,/i/,and/u/.At some point prior to the 16th century in the general area now modern Iran,/eː/and/iː/merged into/iː/,and/oː/and/uː/merged into/uː/.Thus, older contrasts such asشیرshēr"lion" vs.شیرshīr"milk", andزودzūd"quick" vsزورzōr"strength" were lost. However, there are exceptions to this rule, and in some words,ēandōare merged into the diphthongs[eɪ]and[oʊ](which are descendants of the diphthongs[æɪ]and[æʊ]in Early New Persian), instead of merging into/iː/and/uː/.Examples of the exception can be found in words such asروشن[roʊʃæn](bright). Numerous other instances exist.
However, in Dari, the archaic distinction of/eː/and/iː/(respectively known asیای مجهولYā-ye majhūlandیای معروفYā-ye ma'rūf) is still preserved as well as the distinction of/oː/and/uː/(known asواو مجهولWāw-e majhūlandواو معروفWāw-e ma'rūf). On the other hand, in standard Tajik, the length distinction has disappeared, and/iː/merged with/i/and/uː/with/u/.[110]Therefore, contemporary Afghan Dari dialects are the closest to the vowel inventory of Early New Persian.
According to most studies on the subject (e.g.Samareh 1977[citation not found],Pisowicz 1985[citation not found],Najafi 2001)[citation not found],the three vowels traditionally considered long (/i/,/u/,/ɒ/) are currently distinguished from their short counterparts (/e/,/o/,/æ/) by position of articulation rather than by length. However, there are studies (e.g.Hayes 1979[citation not found],Windfuhr 1979) that consider vowel length to be the active feature of the system, with/ɒ/,/i/,and/u/phonologically long or bimoraic and/æ/,/e/,and/o/phonologically short or monomoraic.
There are also some studies that consider quality and quantity to be both active in the Iranian system (such as Toosarvandani 2004). That offers a synthetic analysis including both quality and quantity, which often suggests that Modern Persian vowels are in a transition state between the quantitative system of Classical Persian and a hypothetical future Iranian language, which will eliminate all traces of quantity and retain quality as the only active feature.
The length distinction is still strictly observed by careful reciters of classic-style poetry for all varieties (including Tajik).
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Post-alv./ Palatal |
Velar | Uvular | Glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ||||
| Stop | pb | td | t͡ʃd͡ʒ | kɡ | (q) | ʔ |
| Fricative | fv | sz | ʃʒ | xɣ | h | |
| Tap | ɾ | |||||
| Approximant | l | j |
Notes:
- inIranian Persian/ɣ/and/q/have merged into [ɣ~ɢ], as a voiced velar fricative[ɣ]when positionedintervocalicallyand unstressed, and as a voiced uvular stop[ɢ]otherwise.[111][112][113]
• /n/ turns to /ŋ/ in words that ن comes before گ ک
Grammar
Morphology
Suffixes predominate Persianmorphology,though there are a small number of prefixes.[114]Verbs can express tense andaspect,and they agree with the subject in person and number.[115]There is nogrammatical genderin modern Persian, and pronouns are not marked fornatural gender.In other words, in Persian, pronouns are gender-neutral. When referring to a masculine or a feminine subject, the same pronounاوis used (pronounced "ou", ū).[116]
Syntax
Persian adheres mainly to Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) word order. However, case endings (e.g. for subject, object, etc.) expressed via suffixes may allow users to vary word order. Verbs agree with the subject in person and number. Normal declarative sentences are structured as(S) (PP) (O) V:sentences have optionalsubjects,prepositional phrases,andobjectsfollowed by a compulsoryverb.If the object is specific, the object is followed by the wordrāand precedes prepositional phrases:(S) (O +rā) (PP) V.[115]
Vocabulary
Native word formation
Persian makes extensive use of word building and combining affixes, stems, nouns, and adjectives. Persian frequently uses derivationalagglutinationtoform new wordsfrom nouns, adjectives, and verbal stems. New words are extensively formed bycompounding– two existing words combining into a new one.
Influences
While having a lesser influence fromArabic[29]and other languages ofMesopotamiaand its core vocabulary being ofMiddle Persianorigin,[23]New Persian contains a considerable number of Arabic lexical items,[20][28][30]which were Persianized[31]and often took a different meaning and usage than theArabicoriginal. Persian loanwords of Arabic origin especially includeIslamicterms. The Arabic vocabulary in other Iranian, Turkic, and Indic languages is generally understood to have been copied from New Persian, not from Arabic itself.[117]
John R. Perry,in his article "Lexical Areas and Semantic Fields of Arabic", estimates that about 20 percent of everyday vocabulary in current Persian, and around 25 percent of the vocabulary of classical and modern Persian literature, are of Arabic origin. The text frequency of these loan words is generally lower and varies by style and topic area. It may approach 25 percent of a text in literature.[118]According to another source, about 40% of everyday Persian literary vocabulary is of Arabic origin.[119]Among the Arabic loan words, relatively few (14 percent) are from the semantic domain of material culture, while a larger number are from domains of intellectual and spiritual life.[120]Most of the Arabic words used in Persian are either synonyms of native terms or could be glossed in Persian.[120]
The inclusion ofMongolicandTurkicelements in the Persian language should also be mentioned,[121]not only because of the political role a succession of Turkic dynasties played in Iranian history, but also because of the immense prestige Persian language and literature enjoyed in the wider (non-Arab) Islamic world, which was often ruled by sultans and emirs with a Turkic background. The Turkish and Mongolian vocabulary in Persian is minor in comparison to that of Arabic and these words were mainly confined to military, pastoral terms and political sector (titles, administration, etc.).[122]New military and political titles were coined based partially on Middle Persian (e.g.ارتشartešfor "army", instead of the Uzbekقؤشینqoʻshin;سرلشکرsarlaškar;دریابانdaryābān;etc.) in the 20th century. Persian has likewise influenced the vocabularies of other languages, especially otherIndo-European languagessuch asArmenian,[123]Urdu, Bengali, and Hindi; the latter three through conquests of Persianized Central Asian Turkic and Afghan invaders;[124]Turkic languagessuch asOttoman Turkish,Chagatai,Tatar,Turkish,[125]Turkmen,Azeri,[126]Uzbek,andKarachay-Balkar;[127]Caucasian languagessuch asGeorgian,[128]and, to a lesser extent,AvarandLezgin;[129]Afro-Asiatic languages likeAssyrian(List of loanwords in Assyrian Neo-Aramaic) andArabic,particularlyBahrani Arabic;[27][130]and evenDravidian languagesindirectly especiallyMalayalam,Tamil,Telugu,andBrahui;as well asAustronesian languagessuch asIndonesianandMalaysianMalay.Persian has also had a significant lexical influence, via Turkish, onAlbanianandSerbo-Croatian,particularly as spoken inBosnia and Herzegovina.
Use of occasional foreign synonyms instead of Persian words can be a common practice in everyday communications as an alternative expression. In some instances in addition to the Persian vocabulary, the equivalent synonyms from multiple foreign languages can be used. For example, in Iranian colloquial Persian (not in Afghanistan or Tajikistan), the phrase "thank you" may be expressed using the French wordمرسیmerci(stressed, however, on the first syllable), the hybrid Persian-Arabic phraseمتشکّرَمmotešakkeram(متشکّرmotešakkerbeing "thankful" in Arabic, commonly pronouncedmoččakkerin Persian, and the verbـَمammeaning "I am" in Persian), or by the pure Persian phraseسپاسگزارمsepās-gozāram.
Orthography



The vast majority of modern Iranian Persian and Dari text is written with theArabic script.Tajiki, which is considered by some linguists to be a Persian dialect influenced byRussianand theTurkic languagesofCentral Asia,[110][132]is written with theCyrillic scriptinTajikistan(seeTajik Alpha bet). There also exist severalromanization systems for Persian.
Persian Alpha bet
Modern Iranian Persian and Afghan Persian are written using thePersian Alpha betwhich is a modified variant of theArabic Alpha bet,which uses different pronunciation and additional letters not found in Arabic language. After theArab conquest of Persia,it took approximately 200 years before Persians adopted the Arabic script in place of the older Alpha bet. Previously, two different scripts were used,Pahlavi,used for Middle Persian, and theAvestan Alpha bet(in Persian, Dīndapirak, or Din Dabire—literally: religion script), used for religious purposes, primarily for theAvestanbut sometimes for Middle Persian.
In the modern Persian script,historically short vowelsare usually not written, only the historically long ones are represented in the text, so words distinguished from each other only by short vowels are ambiguous in writing: Iranian Persiankerm"worm",karam"generosity",kerem"cream", andkrom"chrome" are all spelledkrm(کرم) in Persian. The reader must determine the word from context. The Arabic system of vocalization marks known asharakatis also used in Persian, although some of the symbols have different pronunciations. For example, aḍammahis pronounced[ʊ~u],while in Iranian Persian it is pronounced[o].This system is not used in mainstream Persian literature; it is primarily used for teaching and in some (but not all) dictionaries.


There are several letters generally only used in Arabic loanwords. These letters are pronounced the same as similar Persian letters. For example, there are four functionally identical letters for/z/(ز ذ ض ظ), three letters for/s/(س ص ث), two letters for/t/(ط ت), two letters for/h/(ح ه). On the other hand, there are four letters that do not exist in Arabicپ چ ژ گ.
Additions
ThePersian Alpha betadds four letters to the Arabic Alpha bet:
| Sound | Isolated form | Final form | Medial form | Initial form | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /p/ | پ | ـپ | ـپـ | پـ | pe |
| /tʃ/ | چ | ـچ | ـچـ | چـ | če (che) |
| /ʒ/ | ژ | ـژ | ـژ | ژ | že (zhe or jhe) |
| /ɡ/ | گ | ـگ | ـگـ | گـ | ge (gāf) |
Historically, there was also a special letter for the sound/β/.This letter is no longer used, as the/β/-sound changed to/b/,e.g. archaicزڤان/zaβaːn/>زبان/zæbɒn/'language'[133]
| Sound | Isolated form | Final form | Medial form | Initial form | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /β/ | ڤ | ـڤ | ـڤـ | ڤـ | βe |
Variations
The Persian Alpha bet also modifies some letters of the Arabic Alpha bet. For example,alef with hamza below(إ) changes toalef(ا); words using varioushamzasget spelled with yet another kind of hamza (so thatمسؤولbecomesمسئول) even though the latter has been accepted in Arabic since the 1980s; andteh marbuta(ة) changes toheh(ه) orteh(ت).
The letters different in shape are:
| Arabic style letter | Persian style letter | Name |
|---|---|---|
| ك | ک | ke(kāf) |
| ي | ی | ye |
However,یin shape and form is the traditional Arabic style that continues in the Nile Valley, namely,Egypt,Sudan,andSouth Sudan.
Latin Alpha bet
TheInternational Organization for Standardizationhas published a standard for simplifiedtransliterationof Persian into Latin, ISO 233-3, titled "Information and documentation – Transliteration of Arabic characters into Latin characters – Part 3: Persian language – Simplified transliteration"[134]but the transliteration scheme is not in widespread use.
Another Latin Alpha bet, based on theNew Turkic Alphabet,was used inTajikistanin the 1920s and 1930s. The Alpha bet was phased out in favor ofCyrillicin the late 1930s.[110]
Fingilishis Persian usingISO basic Latin Alpha bet.It is most commonly used inchat,emails,andSMSapplications. The orthography is not standardized, and varies among writers and even media (for example, typing 'aa' for the[ɒ]phoneme is easier on computer keyboards than on cellphone keyboards, resulting in smaller usage of the combination on cellphones).
Tajik Alpha bet
The Cyrillic script was introduced for writing theTajik languageunder theTajik Soviet Socialist Republicin the late 1930s, replacing theLatin Alpha betthat had been used since theOctober Revolutionand the Persian script that had been used earlier. After 1939, materials published in Persian in the Persian script were banned in the country.[110][135]

Examples
The following text is from Article 1 of theUniversal Declaration of Human Rights.
| Iranian Persian (Nastaʿlīq) | همهی افراد بشر آزاد به دنیا میآیند و حیثیت و حقوقشان با هم برابر است، همه اندیشه و وجدان دارند و باید در برابر یکدیگر با روح برادری رفتار کنند. |
|---|---|
| Iranian Persian (Naskh) | همهی افراد بشر آزاد به دنیا میآیند و حیثیت و حقوقشان با هم برابر است، همه اندیشه و وجدان دارند و باید در برابر یکدیگر با روح برادری رفتار کنند. |
| Iranian Persian transliteration |
Hame-ye afrād-e bashar āzād be donyā mi āyand o heysiyat o hoquq-e shān bā ham barābar ast, hame andishe o vejdān dārand o bāyad dar barābare yekdigar bā ruh-e barādari raftār konand. |
| Iranian PersianIPA | [hæmejeæfrɒdebæʃærɒzɒdbedonjɒmiɒjændohejsijætohoɢuɢeʃɒnbɒhæmbærɒbæræsthæmeʃɒnændiʃeovedʒdɒndɒrændobɒjæddærbærɒbærejekdiɡærbɒruhebærɒdæriræftɒrkonænd] |
| Tajiki | Ҳамаи афроди башар озод ба дунё меоянд ва ҳайсияту ҳуқуқашон бо ҳам баробар аст, ҳамаашон андешаву виҷдон доранд ва бояд дар баробари якдигар бо рӯҳи бародарӣ рафтор кунанд. |
| Tajiki transliteration |
Hamai afrodi bashar ozod ba dunjo meoyand va haysiyatu huquqashon bo ham barobar ast, hamaashon andeshavu vijdon dorand va boyad dar barobari yakdigar bo rūhi barodarī raftor kunand. |
| English translation | All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act toward one another in a spirit of brotherhood. |
See also
- Iranian Persian,Western Persian
- List of countries and territories where Persian is an official language
- List of English words of Persian origin
- List of French loanwords in Persian
- Middle Persian
- Parthian language
- Persian Braille
- Persian metres
- Persian name
- Romanization of Persian
- List of link languages
- Dialect continuum
- Geolinguistics
- Language geography
Notes
Citations
- ^abcSamadi, Habibeh; Nick Perkins (2012). Martin Ball; David Crystal; Paul Fletcher (eds.).Assessing Grammar: The Languages of Lars.Multilingual Matters. p. 169.ISBN978-1-84769-637-3.
- ^Foltz, Richard (1996). "The Tajiks of Uzbekistan".Central Asian Survey.15(2): 213–216.doi:10.1080/02634939608400946.ISSN0263-4937.
- ^"IRAQ".Encyclopædia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2014.Retrieved7 November2014.
- ^Akiner, Shirin (1986).Islamic Peoples of the Soviet Union.London: Routledge. p. 362.ISBN0-7103-0188-X.
- ^abWindfuhr, Gernot:The Iranian Languages,Routledge 2009, p. 417–418.
- ^"Kuwaiti Persian".UNESCO.
- ^abPersianatEthnologue(27th ed., 2024)

Iranian PersianatEthnologue(27th ed., 2024)
DariatEthnologue(27th ed., 2024)
Tajik languageatEthnologue(27th ed., 2024)
Aimaq dialectatEthnologue(27th ed., 2024)
Bukhori dialectatEthnologue(27th ed., 2024)
(Additional references under 'Language codes' in the information box) - ^abcdWindfuhr, Gernot:The Iranian Languages,Routledge 2009, p. 418.
- ^abConstitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran:Chapter II, Article 15: "The official language and script of Iran, thelingua francaof its people, is Persian. Official documents, correspondence, and texts, as well as text-books, must be in this language and script. However, the use of regional and tribal languages in the press and mass media, as well as for teaching of their literature in schools, is allowed in addition to Persian. "
- ^Constitution of the Republic of Dagestan:Chapter I, Article 11: "The state languages of the Republic of Dagestan are Russian and the languages of the peoples of Dagestan."
- ^"Persian, Iranian".Ethnologue.Archivedfrom the original on 5 January 2022.Retrieved25 February2021.
- ^"639 Identifier Documentation: fas".Sil.org.Archivedfrom the original on 16 February 2022.Retrieved25 February2021.
- ^"The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran".Islamic Parliament of Iran.Archived fromthe originalon 27 October 2016.Retrieved18 January2022.
- ^abOlesen, Asta (1995).Islam and Politics in Afghanistan.Vol. 3. Psychology Press. p. 205.
There began a general promotion of the Pashto language at the expense of Farsi – previously dominant in the educational and administrative system (...) — and the term 'Dari' for the Afghan version of Farsi came into common use, being officially adopted in 1958.
- ^Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" inMedia Insight Central Asia #27,August 2002.
- ^abBaker, Mona (2001).Routledge Encyclopedia of Translation Studies.Psychology Press. p. 518.ISBN978-0-415-25517-2.Archivedfrom the original on 2 October 2022.Retrieved20 June2015.
All this affected translation activities in Persian, seriously undermining the international character of the language. The problem was compounded in modern times by several factors, among them the realignment of Central Asian Persian, renamed Tajiki by the Soviet Union, with Uzbek and Russian languages, as well as the emergence of a language reform movement in Iran which paid no attention to the consequences of its pronouncements and actions for the language as a whole.
- ^Foltz, Richard (1996). "The Tajiks of Uzbekistan".Central Asian Survey.15(2): 213–216.doi:10.1080/02634939608400946.ISSN0263-4937.
- ^Jonson, Lena (2006).Tajikistan in the new Central Asia.p. 108.
- ^Cordell, Karl (1998).Ethnicity and Democratisation in the New Europe.Routledge. p. 201.ISBN0415173124.
Consequently the number of citizens who regard themselves as Tajiks is difficult to determine. Tajiks within and outside of the republic, Samarkand State University (SamGU) academics and international commentators suggest that there may be between six and seven million Tajiks in Uzbekistan, constituting 30 per cent of the republic's twenty-two million population, rather than the official figure of 4.7 per cent (Foltz 1996:213; Carlisle 1995:88).
- ^abcdeLazard 1975:"The language known as New Persian, which usually is called at this period (early Islamic times) by the name of Dari or Farsi-Dari, can be classified linguistically as a continuation of Middle Persian, the official religious and literary language of Sassanian Iran, itself a continuation of Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenids. Unlike the other languages and dialects, ancient and modern, of the Iranian group such as Avestan, Parthian, Soghdian, Kurdish, Balochi, Pashto, etc., Old Persian, Middle Persian, and New Persian represent one and the same language at three states of its history. It had its origin in Fars (the true Persian country from the historical point of view) and is differentiated by dialectical features, still easily recognizable from the dialect prevailing in north-western and eastern Iran."
- ^Ammon, Ulrich; Dittmar, Norbert; Mattheier, Klaus J.; Trudgill, Peter (2006).Sociolinguistics: An International Handbook of the Science of Language and Society.Vol. 3 (2nd ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 1912.
The Pahlavi language (also known as Middle Persian) was the official language of Iran during the Sassanid dynasty (from 3rd to 7th century A. D.). Pahlavi is the direct continuation of old Persian, and was used as the written official language of the country. However, after the Moslem conquest and the collapse of the Sassanids, Arabic became the dominant language of the country and Pahlavi lost its importance, and was gradually replaced by Dari, a variety of Middle Persian, with considerable loan elements from Arabic and Parthian (Moshref 2001).
- ^Skjærvø, Prods Oktor (2006)."Iran, vi. Iranian languages and scripts".Encyclopædia Iranica.Vol. XIII. pp. 344–377.Archivedfrom the original on 23 April 2020.Retrieved10 July2019.
(...) Persian, the language originally spoken in the province of Fārs, which is descended from Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenid empire (6th–4th centuries B.C.E.), and Middle Persian, the language of the Sasanian empire (3rd–7th centuries C.E.).
- ^abcDavis, Richard (2006). "Persian". In Meri, Josef W.; Bacharach, Jere L. (eds.).Medieval Islamic Civilization.Taylor & Francis. pp. 602–603.
Similarly, the core vocabulary of Persian continued to be derived from Pahlavi, but Arabic lexical items predominated for more abstract or abstruse subjects and often replaced their Persian equivalents in polite discourse. (...) The grammar of New Persian is similar to that of many contemporary European languages.
- ^abcde Bruijn, J.T.P. (14 December 2015)."Persian literature".Encyclopædia Britannica.Archivedfrom the original on 10 June 2019.Retrieved10 July2019.
- ^Skjærvø, Prods Oktor."Iran vi. Iranian languages and scripts (2) Documentation".Encyclopædia Iranica.Vol. XIII. pp. 348–366.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2016.Retrieved30 December2012.
- ^Egger, Vernon O. (16 September 2016).A History of the Muslim World since 1260: The Making of a Global Community.Routledge.ISBN9781315511078.Archivedfrom the original on 2 October 2022.Retrieved12 June2020.
- ^abHoles, Clive (2001).Dialect, Culture, and Society in Eastern Arabia: Glossary.BRILL. p. XXX.ISBN90-04-10763-0.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2016.Retrieved4 September2013.
- ^abLazard, Gilbert (1971). "Pahlavi, Pârsi, dari: Les langues d'Iran d'apès Ibn al-Muqaffa". In Frye, R.N. (ed.).Iran and Islam. In Memory of the late Vladimir Minorsky.Edinburgh University Press.
- ^abNamazi, Nushin (24 November 2008)."Persian Loan Words in Arabic".Archived fromthe originalon 20 May 2011.Retrieved1 June2009.
- ^abClasse, Olive (2000).Encyclopedia of literary translation into English.Taylor & Francis. p. 1057.ISBN1-884964-36-2.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved28 September2020.
Since the Arab conquest of the country in 7th century AD, many loan words have entered the language (which from this time has been written with a slightly modified version of the Arabic script) and the literature has been heavily influenced by the conventions of Arabic literature.
- ^abLambton, Ann K. S. (1953).Persian grammar.Cambridge University Press.
The Arabic words incorporated into the Persian language have become Persianized.
- ^Vafa, A; Abedinifard, M; Azadibougar, O (2021).Persian Literature as World Literature.US: Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 2–14.ISBN978-1-501-35420-5.
- ^Perry 2005,p. 284.
- ^Green, Nile (2012).Making Space: Sufis and Settlers in Early Modern India.Oxford University Press. pp. 12–13.ISBN9780199088751.Archivedfrom the original on 13 February 2020.Retrieved10 July2019.
- ^Windfuhr, Gernot (1987). Comrie, Berard (ed.).The World's Major Languages.Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp.523–546.ISBN978-0-19-506511-4.
- ^Περσίς.Liddell, Henry George;Scott, Robert;A Greek–English Lexiconat thePerseus Project.
- ^Harper, Douglas."Persia".Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^Oxford English Dictionaryonline,s.v. "Persian", draft revision June 2007.
- ^abJazayeri, M. A. (15 December 1999)."Farhangestān".Encyclopædia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 25 April 2017.Retrieved3 October2014.
- ^"Zaban-i Nozohur".Iran-Shenasi: A Journal of Iranian Studies.IV(I): 27–30. 1992.
- ^Spooner, Brian; Hanaway, William L. (2012).Literacy in the Persianate World: Writing and the Social Order.University of Pennsylvania Press. pp. 6, 81.ISBN978-1934536568.Archivedfrom the original on 13 February 2020.Retrieved22 July2019.
- ^Spooner, Brian (2012)."Dari, Farsi, and Tojiki".In Schiffman, Harold (ed.).Language Policy and Language Conflict in Afghanistan and Its Neighbors: The Changing Politics of Language Choice.Leiden: Brill. p. 94.ISBN978-9004201453.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved30 October2015.
- ^Campbell, George L.; King, Gareth, eds. (2013)."Persian".Compendium of the World's Languages(3rd ed.). Routledge. p. 1339.ISBN9781136258466.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved30 October2015.
- ^Perry, John R. "Persian morphology." Morphologies of Asia and Africa 2 (2007): 975–1019.
- ^Seraji, Mojgan, Beáta Megyesi, and Joakim Nivre. "A basic language resource kit for Persian." Eight International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2012), 23–25 May 2012, Istanbul, Turkey. European Language Resources Association, 2012.
- ^Sahranavard, Neda, and Jerry Won Lee. "The Persianization of English in multilingual Tehran." World Englishes (2020).
- ^Richardson, Charles Francis (1892).The International Cyclopedia: A Compendium of Human Knowledge.Dodd, Mead. p. 541.
- ^Strazny, Philipp (2013).Encyclopedia of Linguistics.Routledge. p. 324.ISBN978-1-135-45522-4.
- ^Lazard, Gilbert (17 November 2011)."Darī".Encyclopædia Iranica.Vol. VII. pp. 34–35.Archivedfrom the original on 24 November 2020.Retrieved22 July2019.
It is derived from the word fordar(court, lit., "gate" ).Darīwas thus the language of the court and of the capital, Ctesiphon. On the other hand, it is equally clear from this passage thatdarīwas also in use in the eastern part of the empire, in Khorasan, where it is known that in the course of the Sasanian period Persian gradually supplanted Parthian and where no dialect that was not Persian survived. The passage thus suggests thatdarīwas actually a form of Persian, the common language of Persia. (...) Both were calledpārsī(Persian), but it is very likely that the language of the north, that is, the Persian used on former Parthian territory and also in the Sasanian capital, was distinguished from its congener by a new name,darī([language] of the court).
- ^Paul, Ludwig (19 November 2013)."Persian Language: i: Early New Persian".Encyclopædia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 17 March 2019.Retrieved18 March2019.
Northeast.Khorasan, the homeland of the Parthians (calledabaršahr"the upper lands" in MP), had been partly Persianized already in late Sasanian times. Following Ebn al-Moqaffaʿ, the variant of Persian spoken there was calledDarīand was based upon the one used in the Sasanian capital Seleucia-Ctesiphon (Ar.al-Madāʾen). (...) Under the specific historical conditions that have been sketched above, the Dari (Middle) Persian of the 7th century was developed, within two centuries, to the Dari (New) Persian that is attested in the earliest specimens of NP poetry in the late 9th century.
- ^Perry, John (20 July 2009)."Tajik ii. Tajik Persian".Encyclopædia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 1 February 2020.Retrieved22 July2019.
- ^"639 Identifier Documentation: fas".Sil.org.Archivedfrom the original on 16 February 2022.Retrieved5 March2021.
- ^"639 Identifier Documentation: tgk".Sil.org.Archivedfrom the original on 2 March 2021.Retrieved5 March2021.
- ^Skjærvø 2006vi(2). Documentation.
- ^abcf.Skjærvø 2006vi(2). Documentation. Excerpt 1: "Only the official languages Old, Middle, and New Persian represent three stages of one and the same language, whereas close genetic relationships are difficult to establish between other Middle and Modern Iranian languages. Modern Yaḡnōbi belongs to the same dialect group as Sogdian, but is not a direct descendant; Bactrian may be closely related to modern Yidḡa and Munji (Munjāni); and Wakhi (Wāḵi) belongs with Khotanese.Excerpt 2:New Persian, the descendant of Middle Persian and official language of Iranian states for centuries. "
- ^Comrie, Bernard (2003).The Major Languages of South Asia, the Middle East and Africa.Routledge.ISBN978-1-134-93257-3.,p. 82. "The evolution of Persian as the culturally dominant language of major parts of the Near East, from Anatolia and Iran, to Central Asia, to northwest India until recent centuries, began with the political domination of these areas by dynasties originating in southwestern province of Iran, Pars, later Arabicised to Fars: first the Achaemenids (599–331 BC) whose official language was Old Persian; then the Sassanids (c. AD 225–651) whose official language was Middle Persian. Hence, the entire country used to be called Perse by the ancient Greeks, a practice continued to this day. The more general designation 'Iran(-shahr)" derives from Old Iranian aryanam (Khshathra)' (the realm) of Aryans'. The dominance of these two dynasties resulted in Old and Middle-Persian colonies throughout the empire, most importantly for the course of the development of Persian, in the north-east i.e., what is now Khorasan, northern Afghanistan, and Central Asia, as documented by the Middle Persian texts of the Manichean found in the oasis city of Turfan in Chinese Turkistan (Sinkiang). This led to certain degree of regionalisation ".
- ^Comrie, Bernard (1990)The major languages of South Asia, the Middle East and Africa,Taylor & Francis, p. 82
- ^Barbara M. Horvath, Paul Vaughan,Community languages,1991, p. 276
- ^L. Paul (2005), "The Language of the Shahnameh in historical and dialectical perspective", p. 150: "The language of the Shahnameh should be seen as one instance of continuous historical development from Middle to New Persian.",inWeber, Dieter; MacKenzie, D. N. (2005).Languages of Iran: Past and Present: Iranian Studies in Memoriam David Neil MacKenzie.Otto Harrassowitz Verlag.ISBN978-3-447-05299-3.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2016.Retrieved20 June2015.
- ^Schmitt 2008,pp. 80–1.
- ^Kuhrt 2013,p. 197.
- ^Frye 1984,p. 103.
- ^Schmitt 2000,p. 53.
- ^"Roland G. Kent, Old Persian, 1953".Archivedfrom the original on 19 July 2017.Retrieved5 September2015.
- ^Kent, R. G.: "Old Persian: Grammar Texts Lexicon", page 6. American Oriental Society, 1950.
- ^abcSkjærvø 2006,vi(2). Documentation. Old Persian.
- ^abSkjærvø 2006,vi(1). Earliest Evidence
- ^Xenophon.Anabasis.pp. IV.v.2–9.
- ^Nicholas Sims-Williams, "The Iranian Languages", in Steever, Sanford (ed.) (1993),The Indo-European Languages,p. 129.
- ^Jeremias, Eva M. (2004). "Iran, iii. (f). New Persian".Encyclopaedia of Islam.Vol. 12 (New Edition, Supplement ed.). p. 432.ISBN90-04-13974-5.
- ^abcPaul 2000.
- ^Lazard 1975,p. 596.
- ^Perry 2011.
- ^Lazard 1975,p. 597.
- ^Jackson, A. V. Williams. 1920. Early Persian poetry, from the beginnings down to the time of Firdausi. New York: The Macmillan Company. pp.17–19. (inPublic Domain)
- ^Jackson, A. V. Williams.pp.17–19.
- ^Adamec, Ludwig W. (2011).Historical Dictionary of Afghanistan(4th Revised ed.). Scarecrow. p. 105.ISBN978-0-8108-7815-0.
- ^abJohanson, Lars, and Christiane Bulut. 2006.Turkic-Iranian contact areas: historical and linguistic aspectsArchived2 October 2011 at theWayback Machine.Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- ^ according toiranchamberArchived29 June 2018 at theWayback Machine"the language (ninth to thirteenth centuries), preserved in the literature of the Empire, is known as Classical Persian, due to the eminence and distinction of poets such as Roudaki, Ferdowsi, and Khayyam. During this period, Persian was adopted as the lingua franca of the eastern Islamic nations. Extensive contact with Arabic led to a large influx of Arab vocabulary. In fact, a writer of Classical Persian had at one's disposal the entire Arabic lexicon and could use Arab terms freely either for literary effect or to display erudition. Classical Persian remained essentially unchanged until the nineteenth century, when the dialect of Teheran rose in prominence, having been chosen as the capital of Persia by the Qajar Dynasty in 1787. This Modern Persian dialect became the basis of what is now called Contemporary Standard Persian. Although it still contains a large number of Arab terms, most borrowings have been nativized, with a much lower percentage of Arabic words in colloquial forms of the language."
- ^Yazıcı, Tahsin (2010)."Persian authors of Asia Minor part 1".Encyclopaedia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2020.Retrieved6 July2021.
Persian language and culture were actually so popular and dominant in this period that in the late 14th century, Moḥammad (Meḥmed) Bey, the founder and the governing head of the Qaramanids, published an official edict to end this supremacy, saying that: "The Turkish language should be spoken in courts, palaces, and at official institutions from now on!"
- ^John Andrew Boyle,Some thoughts on the sources for the Il-Khanid period of Persian history,inIran:Journal of the British Institute of Persian Studies, British Institute of Persian Studies, vol. 12 (1974), p. 175.
- ^abde Laet, Sigfried J. (1994).History of Humanity: From the seventh to the sixteenth century.UNESCO.ISBN978-92-3-102813-7.Archivedfrom the original on 27 July 2020.Retrieved18 April2016.,p 734
- ^Ágoston, Gábor; Masters, Bruce Alan (2010).Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire.Infobase Publishing. p. 322.ISBN978-1-4381-1025-7.Archivedfrom the original on 1 August 2020.Retrieved18 April2016.
- ^Wastl-Walter, Doris (2011).The Ashgate Research Companion to Border Studies.Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 409.ISBN978-0-7546-7406-1.Archivedfrom the original on 1 August 2020.Retrieved21 October2019.
- ^abSpuler 2003,p. 68.
- ^Lewis, Franklin D. (2014).Rumi – Past and Present, East and West: The Life, Teachings, and Poetry of Jalâl al-Din Rumi.Oneworld Publications. p. 340.ISBN978-1-78074-737-8.Archivedfrom the original on 26 February 2020.Retrieved21 October2019.
- ^abSpuler 2003,p. 69.
- ^
- Chapter "Imperial Ambitions, Mystical Aspirations: Persian Learning in the Ottoman World" by Inan, Murat Umut. In Green, Nile (ed.), 2019, The Persianate World: The Frontiers of a Eurasian Lingua Franca. University of California Press. pp. 88–89. "As the Ottoman Turks learned Persian, the language and the culture it carried seeped not only into their court and imperial institutions but also into their vernacular language and culture. The appropriation of Persian, both as a second language and as a language to be steeped together with Turkish, was encouraged notably by the sultans, the ruling class, and leading members of the mystical communities."
- Chapter "Ottoman Historical Writing" by Tezcan, Baki. In Rabasa, José (ed.), 2012, The Oxford History of Historical Writing: Volume 3: 1400-1800 The Oxford History of Historical Writing: Volume 3: 1400-1800. Oxford University Press. pp. 192–211. "Persian served as a 'minority' prestige language of culture at the largely Turcophone Ottoman court."
- Learning to Read in the Late Ottoman Empire and the Early Turkish Republic,B. Fortna, page 50; "Although in the late Ottoman period Persian was taught in the state schools...."
- Persian Historiography and Geography,Bertold Spuler, page 68, "On the whole, the circumstance in Turkey took a similar course: in Anatolia, the Persian language had played a significant role as the carrier of civilization.[..]..where it was at time, to some extent, the language of diplomacy...However Persian maintained its position also during the early Ottoman period in the composition of histories and even Sultan Salim I, a bitter enemy of Iran and the Shi'ites, wrote poetry in Persian. Besides some poetical adaptations, the most important historiographical works are: Idris Bidlisi's flowery "Hasht Bihist", or Seven Paradises, begun in 1502 by the request of Sultan Bayazid II and covering the first eight Ottoman rulers.."
- Picturing History at the Ottoman Court,Emine Fetvacı, page 31, "Persian literature, and belles-lettres in particular, were part of the curriculum: a Persian dictionary, a manual on prose composition; and Sa'dis "Gulistan", one of the classics of Persian poetry, were borrowed. All these title would be appropriate in the religious and cultural education of the newly converted young men.
- Persian Historiography: History of Persian Literature A, Volume 10,edited by Ehsan Yarshater, Charles Melville, page 437; "...Persian held a privileged place in Ottoman letters. Persian historical literature was first patronized during the reign of Mehmed II and continued unabated until the end of the 16th century.
- ChapterImperial Ambitions, Mystical Aspirations: Persian learning in the Ottoman World,Murat Umut Inan, page 92 (note 27), edited byNile Green,(title:The Persianate World The Frontiers of a Eurasian Lingua Franca); "Though Persian, unlike Arabic, was not included in the typical curriculum of an Ottoman madrasa, the language was offered as an elective course or recommended for study in some madrasas. For those Ottoman madrasa curricula featuring Persian, see Cevat İzgi, Osmanlı Medreselerinde İlim, 2 vols. (Istanbul: İz, 1997),1: 167–69."
- ^Inan, Murat Umut (2019). "Imperial Ambitions, Mystical Aspirations: Persian learning in the Ottoman World". InGreen, Nile(ed.).The Persianate World The Frontiers of a Eurasian Lingua Franca.University of California Press. pp. 85–86.
- ^abcdeInan, Murat Umut (2019). "Imperial Ambitions, Mystical Aspirations: Persian learning in the Ottoman World". InGreen, Nile(ed.).The Persianate World The Frontiers of a Eurasian Lingua Franca.University of California Press. p. 86.
- ^Inan, Murat Umut (2019). "Imperial Ambitions, Mystical Aspirations: Persian learning in the Ottoman World". InGreen, Nile(ed.).The Persianate World The Frontiers of a Eurasian Lingua Franca.University of California Press. p. 85.
- ^Bennett, Clinton; Ramsey, Charles M. (2012).South Asian Sufis: Devotion, Deviation, and Destiny.A&C Black. p. 18.ISBN978-1-4411-5127-8.Archivedfrom the original on 11 February 2020.Retrieved21 October2019.
- ^Abu Musa Mohammad Arif Billah (2012)."Persian".InIslam, Sirajul;Miah, Sajahan;Khanam, Mahfuza;Ahmed, Sabbir (eds.).Banglapedia: the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh(Online ed.). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Banglapedia Trust,Asiatic Society of Bangladesh.ISBN984-32-0576-6.OCLC52727562.OL30677644M.Retrieved27 August2024.
- ^Sarah Anjum Bari (12 April 2019)."A Tale of Two Languages: How the Persian language seeped into Bengali".The Daily Star (Bangladesh).Archivedfrom the original on 21 June 2020.Retrieved2 March2020.
- ^abMir, F. (2010).The Social Space of Language: Vernacular Culture in British Colonial Punjab.University of California Press. p. 35.ISBN9780520262690.Archivedfrom the original on 9 February 2018.Retrieved13 January2017.
- ^Chisholm, Hugh,ed. (1911)..Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 22 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 892.
- ^Grewal, J. S. (1990).The Sikhs of the Punjab, Chapter 6: The Sikh empire (1799–1849).The New Cambridge History of India. Cambridge University Press. p. 112.ISBN0-521-63764-3.Archivedfrom the original on 4 May 2019.Retrieved29 July2020.
The continuance of Persian as the language of administration.
- ^Fenech, Louis E. (2013).The Sikh Zafar-namah of Guru Gobind Singh: A Discursive Blade in the Heart of the Mughal Empire.Oxford University Press (USA). p. 239.ISBN978-0199931453.Archivedfrom the original on 1 August 2020.Retrieved29 July2020.
We see such acquaintance clearly within the Sikh court of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, for example, the principal language of which was Persian.
- ^Clawson, Patrick (2004).Eternal Iran.Palgrave Macmillan. p. 6.ISBN1-4039-6276-6.
- ^Menon, A.S.; Kusuman, K.K. (1990).A Panorama of Indian Culture: Professor A. Sreedhara Menon Felicitation Volume.Mittal Publications. p. 87.ISBN9788170992141.Archivedfrom the original on 9 February 2018.Retrieved13 January2017.
- ^نگار داوری اردکانی (1389).برنامهریزی زبان فارسی.روایت فتح. p. 33.ISBN978-600-6128-05-4.
- ^Beeman, William."Persian, Dari and Tajik"(PDF).Brown University.Archived(PDF)from the original on 25 October 2012.Retrieved30 March2013.
- ^Aliev, Bahriddin; Okawa, Aya (2010)."TAJIK iii. COLLOQUIAL TAJIKI IN COMPARISON WITH PERSIAN OF IRAN".Encyclopaedia Iranica.Archivedfrom the original on 25 February 2021.Retrieved27 February2021.
- ^Windfuhr 1979,p. 4: "Tat-Persian spoken in the East Caucasus"
- ^V. Minorsky, "Tat" in M. Th. Houtsma et al., eds., The Encyclopædia of Islam: A Dictionary of the Geography, Ethnography and Biography of the Muhammadan Peoples, 4 vols. and Suppl., Leiden: Late E.J. Brill and London: Luzac, 1913–38.
- ^V. Minorsky, "Tat" in M. Th. Houtsma et al., eds., The Encyclopædia of Islam: A Dictionary of the Geography, Ethnography and Biography of the Muhammadan Peoples, 4 vols. and Suppl., Leiden: Late E.J. Brill and London: Luzac, 1913–38. Excerpt: "Like most Persian dialects, Tati is not very regular in its characteristic features"
- ^C Kerslake, Journal of Islamic Studies (2010) 21 (1): 147–151. excerpt: "It is a comparison of the verbal systems of three varieties of Persian—standard Persian, Tat, and Tajik—in terms of the 'innovations' that the latter two have developed for expressing finer differentiations of tense, aspect, and modality..."[1]Archived17 September 2013 at theWayback Machine
- ^Bor gian, Habib (2006). "Tabari Language Materials from Il'ya Berezin's Recherches sur les dialectes persans".Iran & the Caucasus.10(2): 243–258.doi:10.1163/157338406780346005.
It embraces Gilani, Talysh, Tabari, Kurdish, Gabri, and the Tati Persian of the Caucasus, all but the last belonging to the north-western group of Iranian language.
- ^Miller, Corey (January 2012)."Vowel system of Contemporary Iranian Persian".Variation in Persian Vowel Systems.Retrieved7 May2022– via ResearchGate.
- ^abcdPerry 2005.
- ^International Phonetic Association (1999).Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A guide to the use of the International Phonetic Alphabet.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 124–125.ISBN978-0-521-63751-0.
- ^Jahani, Carina (2005)."The Glottal Plosive: A Phoneme in Spoken Modern Persian or Not?".In Éva Ágnes Csató; Bo Isaksson; Carina Jahani (eds.).Linguistic Convergence and Areal Diffusion: Case studies from Iranian, Semitic and Turkic.London: RoutledgeCurzon. pp. 79–96.ISBN0-415-30804-6.
- ^Thackston, W. M. (1 May 1993)."The Phonology of Persian".An Introduction to Persian(3rd Rev ed.). Ibex Publishers. p. xvii.ISBN0-936347-29-5.
- ^Megerdoomian, Karine (2000)."Persian computational morphology: A unification-based approach"(PDF).Memoranda in Computer and Cognitive Science: MCCS-00-320.p. 1. Archived from the original on 2 September 2013.Retrieved9 May2007.
{{cite conference}}:CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^abMahootian, Shahrzad (1997).Persian.London: Routledge.ISBN0-415-02311-4.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved18 November2020.
- ^Yousef, Saeed; Torabi, Hayedeh (2013).Basic Persian: A Grammar and Workbook.New York: Routledge. p. 37.ISBN9781136283888.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved18 November2020.
- ^John R. Perry, "Lexical Areas and Semantic Fields of Arabic" in Éva Ágnes Csató, Eva Agnes Csato, Bo Isaksson, Carina Jahani,Linguistic convergence and areal diffusion: case studies from Iranian, Semitic and Turkic,Routledge, 2005. pg 97: "It is generally understood that the bulk of the Arabic vocabulary in the central, contiguous Iranian, Turkic, and Indic languages was originally borrowed into literary Persian between the ninth and thirteenth centuries"
- ^John R. Perry, "Lexical Areas and Semantic Fields of Arabic" in Éva Ágnes Csató, Eva Agnes Csato, Bo Isaksson, Carina Jahani,Linguistic convergence and areal diffusion: case studies from Iranian, Semitic and Turkic,Routledge, 2005. p.97
- ^Owens, Jonathan (2013).The Oxford Handbook of Arabic Linguistics.OUP USA. p. 352.ISBN978-0-19-976413-6.
- ^abPerry 2005,p. 99.
- ^e.g. The role of Azeri–Turkish in Iranian Persian, on which see John Perry, "The Historical Role of Turkish in Relation to Persian of Iran",Iran & the Caucasus,Vol. 5 (2001), pp. 193–200.
- ^Xavier Planhol, "Land of Iran",Encyclopedia Iranica."The Turks, on the other hand, posed a formidable threat: their penetration into Iranian lands was considerable, to such an extent that vast regions adapted their language. This process was all the more remarkable since, in spite of their almost uninterrupted political domination for nearly 1,500 years, the cultural influence of these rough nomads on Iran's refined civilization remained extremely tenuous. This is demonstrated by the mediocre linguistic contribution, for which exhaustive statistical studies have been made (Doerfer). The number of Turkish or Mongol words that entered Persian, though not negligible, remained limited to 2,135, i.e., 3 percent of the vocabulary at the most. These new words are confined on the one hand to the military and political sector (titles, administration, etc.) and, on the other hand, to technical pastoral terms. The contrast with Arab influence is striking. While cultural pressure of the Arabs on Iran had been intense, they in no way infringed upon the entire Iranian territory, whereas with the Turks, whose contributions to Iranian civilization were modest, vast regions of Iranian lands were assimilated, notwithstanding the fact that resistance by the latter was ultimately victorious. Several reasons may be offered."
- ^"ARMENIA AND IRAN iv. Iranian influences in Armenian Language".Archivedfrom the original on 17 November 2017.Retrieved2 January2015.
- ^Bennett, Clinton; Ramsey, Charles M. (March 2012).South Asian Sufis: Devotion, Deviation, and Destiny.A&C Black.ISBN9781441151278.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved23 April2015.
- ^Andreas Tietze, Persian loanwords in Anatolian Turkish, Oriens, 20 (1967) pp- 125–168.Archived11 September 2007 at theWayback Machine(accessed August 2016)
- ^L. Johanson, "Azerbaijan: Iranian Elements in Azeri Turkish" inEncyclopedia IranicaIranica
- ^George L. Campbell; Gareth King (2013).Compendium of the World Languages.Routledge.ISBN978-1-136-25846-6.Archivedfrom the original on 27 September 2015.Retrieved23 May2014.
- ^"Georgia v. Linguistic Contacts With Iranian Languages".Archivedfrom the original on 18 March 2021.Retrieved2 January2015.
- ^"DAGESTAN".Archivedfrom the original on 29 April 2011.Retrieved2 January2014.
- ^Pasad."Bashgah.net".Bashgah.net. Archived fromthe originalon 23 July 2011.Retrieved13 July2010.
- ^Smith 1989.
- ^Lazard, Gilbert (1956). "Charactères distinctifs de la langue Tadjik".Bulletin de la Société Linguistique de Paris.52:117–186.
- ^"PERSIAN LANGUAGE i. Early New Persian".Iranica Online.Archivedfrom the original on 17 March 2019.Retrieved18 March2019.
- ^"ISO 233-3:1999".International Organization for Standardization. 14 May 2010.Archivedfrom the original on 6 June 2011.Retrieved13 July2010.
- ^"Smallwars.quantico.usmc.mil".Archived fromthe originalon 22 January 2010.Retrieved13 December2012.
Works cited
- Frye, Richard Nelson (1984).Handbuch der Altertumswissenschaft: Alter Orient-Griechische Geschichte-Römische Geschichte. Band III,7: The History of Ancient Iran.C.H. Beck.ISBN978-3-406-09397-5.
- Kuhrt, A. (2013).The Persian Empire: A Corpus of Sources from the Achaemenid Period.Routledge.ISBN978-1-136-01694-3.
- Lazard, G. (1975). "The Rise of the New Persian Language". InFrye, Richard N.(ed.).The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs.Cambridge:Cambridge University Press.pp. 595–633.ISBN0-521-20093-8.
- Paul, Ludwig (2000)."Persian Language i. Early New Persian".Encyclopædia Iranica, online edition.New York.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Perry, John R. (2005).A Tajik Persian Reference Grammar: Handbook of Oriental Studies.Vol. 2. Boston: Brill.ISBN90-04-14323-8.
- Perry, John R. (2011)."Persian".In Edzard, Lutz; de Jong, Rudolf (eds.).Encyclopedia of Arabic Language and Linguistics.Brill Online.
- Schmitt, Rüdiger (2000).The Old Persian Inscriptions of Naqsh-i Rustam and Persepolis.Corpus Inscriptionum Iranicarum by School of Oriental and African Studies.ISBN978-0-7286-0314-1.
- Skjærvø, Prods Oktor (2006). "Iran, vi. Iranian languages and scripts".Encyclopaedia Iranica.Vol. XIII.
- Spuler, Bertold (2003).Persian Historiography and Geography: Bertold Spuler on Major Works Produced in Iran, the Caucasus, Central Asia, India, and Early Ottoman Turkey.Pustaka Nasional Pte Ltd.ISBN978-9971774882.
- Windfuhr, Gernot (1979).Persian Grammar: history and state of its study.Walter de Gruyter.
General references
- Bosworth, C. E. & Crowe, Yolande (1995)."Sāmānids".InBosworth, C. E.;van Donzel, E.;Heinrichs, W. P.&Lecomte, G.(eds.).The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition.Volume VIII:Ned–Sam.Leiden: E. J. Brill.ISBN978-90-04-09834-3.
- Bosworth, C. E. (1998)."Esmāʿīl, b. Aḥmad b. Asad Sāmānī, Abū Ebrāhīm".InYarshater, Ehsan(ed.).Encyclopædia Iranica, Volume VIII/6: Eršād al-zerāʿa–Eʿteżād-al-Salṭana.London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 636–637.ISBN978-1-56859-055-4.
- Crone, Patricia (2012).The Nativist Prophets of Early Islamic Iran: Rural Revolt and Local Zoroastrianism.Cambridge University Press.ISBN978-1107642386.
- de Blois, Francois (2004).Persian Literature - A Bio-Bibliographical Survey: Poetry of the Pre-Mongol Period (Volume V).Routledge.ISBN978-0947593476.
- de Bruijn, J.T.P. (1978)."Iran, vii.—Literature".Invan Donzel, E.;Lewis, B.;Pellat, Ch.&Bosworth, C. E.(eds.).The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition.Volume IV:Iran–Kha.Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 52–75.OCLC758278456.
- Frye, R. N. (2004)."Iran v. Peoples of Iran (1) A General Survey".InYarshater, Ehsan(ed.).Encyclopædia Iranica, Volume XIII/3: Iran II. Iranian history–Iran V. Peoples of Iran.London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 321–326.ISBN978-0-933273-89-4.
- Jeremiás, Éva (2011)."Iran".In Edzard, Lutz; de Jong, Rudolf (eds.).Encyclopedia of Arabic Language and Linguistics.Brill Online.
- Lazard, G. (1994)."Darī".InYarshater, Ehsan(ed.).Encyclopædia Iranica, Volume VII/1: Dārā(b)–Dastūr al-Afāżel.London and New York: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 34–35.ISBN978-1-56859-019-6.
- Litvinsky, B. A., ed. (1996).History of Civilizations of Central Asia: The crossroads of civilizations, A.D. 250 to 750.UNESCO.ISBN9789231032110.
- Rypka, Jan(1968).History of Iranian Literature.Springer Netherlands.ISBN978-9401034814.
Further reading
- Asatrian, Garnik (2010).Etymological Dictionary of Persian.Leiden Indo-European Etymological Dictionary Series, 12.Brill Academic Publishers.ISBN978-90-04-18341-4.Archived fromthe originalon 27 December 2010.Retrieved23 May2010.
- Bleeck, Arthur Henry (1857).A concise grammar of the Persian language(Oxford University ed.).Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Dahlén, Ashk (April 2014) [1st edition October 2010].Modern persisk grammatik(2nd ed.). Ferdosi International Publication.ISBN9789197988674.Archived fromthe originalon 11 October 2017.Retrieved18 February2011.
- Delshad, Farshid (September 2007).Anthologia Persica.Logos Verlag.ISBN978-3-8325-1620-8.
- Doctor, Sorabshaw Byramji (1880).The student's Persian and English dictionary, pronouncing, etymological, & explanatory.Irish Presbyterian Mission Press. p. 558.Archivedfrom the original on 23 July 2016.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Doctor, Sorabshaw Byramji; Saʻdī (1880).Second book of Persian, to which are added the Pandnámah of Shaikh Saádi and the Gulistán, chapter 1, together with vocabulary and short notes(2 ed.). Irish Presbyterian Mission Press. p. 120.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Doctor, Sorabshaw Byramji (1879).The Persian primer, being an elementary treatise on grammar, with exercises.Irish Presbyterian Mission Press. p. 94.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Doctor, Sorabshaw Byramji (1875).A new grammar of the Persian tongue for the use of schools and colleges.Irish Presbyterian Mission Press. p.84.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Forbes, Duncan (1844).A grammar of the Persian language: To which is added, a selection of easy extracts for reading, together with a copious vocabulary(2nd ed.). Printed for the author, sold by Allen & co. p. 114 & 158.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Forbes, Duncan (1869).A grammar of the Persian language: to which is added, a selection of easy extracts for reading, together with a vocabulary, and translations(4th ed.). Wm. H. Allen & Co. p. 238.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Forbes, Duncan (1876).A grammar of the Persian language: to which is added, a selection of easy extracts for reading, together with a vocabulary, and translations.W.H. Allen. p. 238.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Ibrâhîm, Muḥammad (1841).A grammar of the Persian language.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Jones, Sir William(1783).A grammar of the Persian language(3 ed.).Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Jones, Sir William (1797).A grammar of the Persian language(4 ed.).Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Jones, Sir William (1801).A grammar of the Persian language(5 ed.). Murray and Highley, J. Sewell. p. 194.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Jones, Sir William (1823). Samuel Lee (ed.).A grammar of the Persian language(8 ed.). Printed by W. Nicol, for Parbury, Allen, and co. p. 230.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Jones, Sir William (1828). Samuel Lee (ed.).A grammar of the Persian language(9 ed.). Printed by W. Nicol, for Parbury, Allen, and Co. p.283.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Lazard, Gilbert (January 2006).Grammaire du persan contemporain.Institut Français de Recherche en Iran.ISBN978-2909961378.Archived fromthe originalon 3 May 2012.Retrieved18 February2011.
- Lumsden, Matthew (1810).A grammar of the Persian language; comprising a portion of the elements of Arabic inflexion [etc.].Vol. 2. Calcutta: T. Watley.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Mace, John (18 October 2002).Persian Grammar: For Reference and Revision(illustrated ed.). RoutledgeCurzon.ISBN0-7007-1695-5.
- Moises, Edward (1792).The Persian interpreter: in three parts: A grammar of the Persian language. Persian extracts, in prose and verse. A vocabulary: Persian and English.Printed by L. Hodgson. p. 143.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Palmer, Edward Henry(1883). Guy Le Strange (ed.).A concise dictionary, English-Persian: together with a simplified grammar of the Persian language.London: Trübner & Co. p.42.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Platts, John Thompson (1894).A grammar of the Persian language...Vol. Part I.—Accidence. London & Edinburgh: Williams and Norgate.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Ranking, George Speirs Alexander (1907).A primer of Persian: containing selections for reading and composition with the elements of syntax.The Clarendon Press. p.72.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Richardson, John (1810). Sir Charles Wilkins; David Hopkins (eds.).A vocabulary, Persian, Arabic, and English: abridged from the quarto edition of Richardson's dictionary.Printed for F. and C. Rivingson. p.643.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Rosen, Friedrich; Nāṣir al-Dīn Shāh (Shah of Iran) (1898).Modern Persian colloquial grammar: containing a short grammar, dialogues and extracts from Nasir-Eddin shah's diaries, tales, etc., and a vocabulary.Luzac & C.̊. p. 400.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Schmitt, Rüdiger (1989).Compendium linguarum Iranicarum.L. Reichert.ISBN3-88226-413-6.
- Sen, Ramdhun (1841). Madhub Chunder Sen (ed.).A dictionary in Persian and English, with pronunciation (ed. by M.C. Sen)(2 ed.).Archivedfrom the original on 3 April 2013.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Sen, Ramdhun (1829).A dictionary in Persian and English.Printed for the author at the Baptist Mission Press. p. 226.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Sen, Ramdhun (1833).A dictionary in English and Persian.Printed at the Baptist Mission Press. p. 276.Archivedfrom the original on 3 December 2020.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Sen, Ramdhun (1833).A dictionary in English and Persian.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2021.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Thackston, W. M. (1 May 1993).An Introduction to Persian(3rd Rev ed.). Ibex Publishers.ISBN0-936347-29-5.
- Tucker, William Thornhill (1801).A pocket dictionary of English and Persian.Archivedfrom the original on 3 April 2013.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Tucker, William Thornhill (1850).A pocket dictionary of English and Persian.J. Madden. p. 145.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Tucker, William Thornhill (1850).A pocket dictionary of English and Persian.J. Madden. p. 145.Retrieved6 July2011.
- Windfuhr, Gernot L. (15 January 2009). "Persian". In Bernard Comrie (ed.).The World's Major Languages(2nd ed.). Routledge.ISBN978-0-415-35339-7.
- Wollaston, (Sir) Arthur Naylor (1882).An English-Persian dictionary.W. H. Allen.Retrieved6 July2011.
External links
- Academy of Persian Language and Literature official website(in Persian)(archived 30 August 2009)
- Assembly for the Expansion of the Persian Language official website(in Persian)
- Persian language Resources(in Persian)(archived 9 December 2012)
- Persian Language Resources,parstimes
- Persian language tutorial books for beginners
- Haim, Soleiman.New Persian–English dictionary.Teheran: Librairie-imprimerie Beroukhim, 1934–1936. uchicago.edu
- Steingass, Francis Joseph.A Comprehensive Persian–English dictionary.London: Routledge & K. Paul, 1892. uchicago.edu
- UCLA Language Materials Project:Persian,ucla.edu (archived 20 July 2006)
- How Persian Alphabet Transits into Graffiti,Persian Graffiti
- Basic Persian language course (book + audio files)– USA Foreign Service Institute (FSI)
- Persian language
- Culture of Iran
- Languages attested from the 6th century BC
- Languages of Afghanistan
- Languages of Azerbaijan
- Languages of Bahrain
- Languages of Iran
- Languages of Iraq
- Languages of Kuwait
- Languages of Russia
- Languages of Tajikistan
- Languages of the Caucasus
- Languages of Uzbekistan
- Southwestern Iranian languages
- Stress-timed languages
- Subject–object–verb languages

