Fixed-wing aircraft
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(March 2024) |


Afixed-wing aircraftis a heavier-than-airflying machine,such as anairplane,which is capable offlightusingaerodynamic lift.Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct fromrotary-wing aircraft(in which arotormounted on a spinning shaft generates lift), andornithopters(in which the wings oscillate to generate lift). The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites,hang gliders,variable-sweep wingaircraft, and airplanes that usewing morphingare all classified as fixed wing.
Glidingfixed-wing aircraft, including free-flyingglidersand tetheredkites,can use moving air to gain altitude.Poweredfixed-wing aircraft (airplanes) that gain forwardthrustfrom anengineincludepowered paragliders,powered hang glidersandground effect vehicles.Most fixed-wing aircraft are operated by apilot,but some areunmannedand controlled eitherremotelyor autonomously.
History[edit]
Kites[edit]
Kites were used approximately 2,800 years ago in China, where kite building materials were available. Leaf kites may have been flown earlier in what is nowSulawesi,based on their interpretation of cave paintings on nearbyMuna Island.[1]By at least 549 AD paper kites were flying, as recorded that year, a paper kite was used as a message for a rescue mission.[2]Ancient and medieval Chinese sources report kites used for measuring distances, testing the wind, lifting men, signaling, and communication for military operations.[2]

Kite stories were brought to Europe byMarco Polotowards the end of the 13th century, and kites were brought back by sailors from Japan andMalaysiain the 16th and 17th centuries.[3]Although initially regarded as curiosities, by the 18th and 19th centuries kites were used for scientific research.[3]
Gliders and powered devices[edit]
Around400 BC in Greece,Archytaswas reputed to have designed and built the first self-propelled flying device, shaped like a bird and propelled by a jet of what was probably steam, said to have flown some 200 m (660 ft).[4][5]This machine may have been suspended during its flight.[6][7]
One of the earliest attempts withgliderswas by 11th-century monkEilmer of Malmesbury,which failed. A 17th-century account states that 9th-century poetAbbas Ibn Firnasmade a similar attempt, though no earlier sources record this event.[8]

In 1799,Sir George Cayleylaid out the concept of the modern airplane as a fixed-wing machine with systems for lift, propulsion, and control.[9][10]Cayley was building and flying models of fixed-wing aircraft as early as 1803, and built a successful passenger-carryinggliderin 1853.[11]In 1856, FrenchmanJean-Marie Le Brismade the first powered flight, had his glider L'Albatros artificiel towed by a horse along a beach.[12]In 1884, AmericanJohn J. Montgomerymade controlled flights in a glider as a part of a series of gliders he built between 1883 and 1886.[13]Other aviators who made similar flights at that time wereOtto Lilienthal,Percy Pilcher,and protégés ofOctave Chanute.
In the 1890s,Lawrence Hargraveconducted research on wing structures and developed abox kitethat lifted the weight of a man. His designs were widely adopted. He also developed a type of rotary aircraft engine, but did not create a powered fixed-wing aircraft.[14]
Powered flight[edit]
Sir Hiram Maximbuilt a craft that weighed 3.5 tons, with a 110-foot (34-meter) wingspan powered by two 360-horsepower (270-kW) steam engines driving two propellers. In 1894, his machine was tested with overhead rails to prevent it from rising. The test showed that it had enough lift to take off. The craft was uncontrollable, and Maxim abandoned work on it.[15]

TheWright brothers' flights in 1903 with theirFlyer Iare recognized by theFédération Aéronautique Internationale(FAI), the standard setting and record-keeping body foraeronautics,as "the first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight".[16]By 1905, theWright Flyer IIIwas capable of fully controllable, stable flight for substantial periods.

In 1906, Brazilian inventorAlberto Santos Dumontdesigned,built and piloted an aircraftthat set the first world record recognized by theAéro-Club de Franceby flying the14 bis220 metres (720 ft) in less than 22 seconds.[17]The flight was certified by the FAI.[18]
TheBleriot VIIIdesign of 1908 was an early aircraft design that had the modernmonoplanetractor configuration.It had movable tail surfaces controlling both yaw and pitch, a form of roll control supplied either by wing warping or by ailerons and controlled by its pilot with ajoystickand rudder bar. It was an important predecessor of his laterBleriot XIChannel-crossing aircraft of the summer of 1909.[19]

World War I[edit]
World War Iserved initiated the use of aircraft as weapons and observation platforms. The earliest known aerial victory with a synchronizedmachine gun-armedfighter aircraftoccurred in 1915, flown by GermanLuftstreitkräfteLieutenantKurt Wintgens.Fighter acesappeared; the greatest (by number of air victories) wasManfred von Richthofen.[citation needed]
Alcock and Browncrossed the Atlantic non-stop for the first time in 1919. The first commercial flights traveled between the United States and Canada in 1919.[citation needed]
Interwar aviation; the "Golden Age"[edit]
The so-called Golden Age of Aviation occurred between the two World Wars, during which updated interpretations of earlier breakthroughs. Innovations includeHugo Junkers' all-metal air framesin 1915leading to multi-engine aircraftof up to 60+ meter wingspansizes by the early 1930s, adoption of the mostly air-cooledradial engineas a practical aircraft power plant alongside V-12 liquid-cooled aviation engines, and longer and longer flights – as witha Vickers Vimy in 1919,followed months later bythe U.S. Navy's NC-4 transatlantic flight;culminating in May 1927 withCharles Lindbergh's solo trans-Atlantic flight in theSpirit of St. Louisspurring ever-longer flight attempts.
World War II[edit]
Airplanes had a presence in the major battles of World War II. They were an essential component of military strategies, such as the GermanBlitzkriegor the American and Japaneseaircraft carriercampaigns of the Pacific.
Military gliderswere developed and used in several campaigns, but were limited by the high casualty rate encountered. TheFocke-Achgelis Fa 330Bachstelze(Wagtail) rotor kite of 1942 was notable for its use by GermanU-boats.
Before and during the war, British and German designers worked onjet engines.The firstjet aircraftto fly, in 1939, was the GermanHeinkel He 178.In 1943, the first operational jet fighter, theMesserschmitt Me 262,went into service with the GermanLuftwaffe.Later in the war the BritishGloster Meteorentered service, but never saw action – top air speeds for that era went as high as 1,130 km/h (700 mph), with the early July 1944 unofficial record flight of the GermanMe 163B V18rocket fighter prototype.[20]
Postwar[edit]
In October 1947, theBell X-1was the first aircraft to exceed the speed of sound, flown byChuck Yeager.[21]
In 1948–49, aircraft transported supplies during theBerlin Blockade.New aircraft types, such as theB-52,were produced during theCold War.
The firstjet airliner,thede Havilland Comet,was introduced in 1952, followed by the SovietTupolev Tu-104in 1956. TheBoeing 707,the first widely successful commercial jet, was in commercial service for more than 50 years, from 1958 to 2010. TheBoeing 747was the world's biggest passenger aircraft from 1970 until it was surpassed by theAirbus A380in 2005. The most successful aircraft is theDouglas DC-3,a medium twin engine passenger aircraft that has been in service since 1936 and is still used forskydivingand other recreational flights. Some of the thousands of versions found other purposes, like theAC-47,aVietnam Warera gunship, which is still used in some militaries.[citation needed]
Types[edit]
This sectionneeds additional citations forverification.(March 2024) |
Airplane/aeroplane[edit]

An airplane (aeroplane or plane) is a powered fixed-wing aircraft propelled bythrustfrom ajet engineorpropeller.Planes come in many sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. Uses include recreation, transportation of goods and people, military, and research.
Seaplane[edit]
A seaplane (hydroplane) is capable oftaking offandlanding(alighting) on water. Seaplanes that can also operate from dry land are a subclass calledamphibian aircraft.[22]Seaplanes and amphibians divide into two categories:float planesandflying boats.
- Afloat planeis similar to a land-based airplane. Thefuselageis not specialized. The wheels are replaced/enveloped byfloats,allowing the craft to make remain afloat for water landings.
- Aflying boatis aseaplanewith a watertighthullfor the lower (ventral) areas of its fuselage. The fuselage lands and then rests directly on the water's surface, held afloat by the hull. It does not need additional floats for buoyancy, although small underwing floats or fuselage-mountedsponsonsmay be used to stabilize it. Large seaplanes are usually flying boats, embodying most classic amphibian aircraft designs.
Powered gliders[edit]
Many forms of glider may include a small power plant. These include:
- Motor glider– a conventionalgliderorsailplanewith an auxiliary power plant that may be used when in flight to increase performance.[23]
- Powered hang glider– ahang gliderwith a power plant added.
- Powered parachute– aparaglidertype of parachute with an integrated air frame, seat, undercarriage and power plant hung beneath.[24]
- Powered paraglideror paramotor – aparagliderwith a power plant suspended behind the pilot.[25]
Ground effect vehicle[edit]
A ground effect vehicle (GEV) flies close to the terrain, making use of theground effect– the interaction between the wings and the surface. Some GEVs are able to fly higher out of ground effect (OGE) when required – these are classed as powered fixed-wing aircraft.[26]
Glider[edit]

A glider is a heavier-than-air craft whose free flight does not require an engine. A sailplane is a fixed-wing glider designed for soaring – gaining height using updrafts of air and to fly for long periods.
Gliders are mainly used for recreation but have found use for purposes such as aerodynamics research, warfare and spacecraft recovery.
Motor glidersare equipped with a limited propulsion system for takeoff, or to extend flight duration.
As is the case with planes, gliders come in diverse forms with varied wings, aerodynamic efficiency, pilot location, and controls.
Large gliders are most commonly born aloft by a tow-plane or by awinch.Military glidershave been used in combat to deliver troops and equipment, while specialized gliders have been used in atmospheric andaerodynamicresearch.Rocket-powered aircraftandspaceplaneshave made unpowered landings similar to a glider.
Gliders and sailplanes that are used for the sport ofglidinghave high aerodynamic efficiency. The highestlift-to-drag ratiois 70:1, though 50:1 is common. After take-off, further altitude can be gained through the skillful exploitation of rising air. Flights of thousands of kilometers at average speeds over 200 km/h have been achieved.
One small-scale example of a glider is thepaper airplane.An ordinary sheet of paper can be folded into an aerodynamic shape fairly easily; its lowmassrelative to its surface area reduces the required lift for flight, allowing it to glide some distance.
Gliders and sailplanes share many design elements and aerodynamic principles with powered aircraft. For example, theHorten H.IVwas a taillessflying wingglider, and thedelta-wingedSpace Shuttle orbiterglided during its descent phase. Many gliders adopt similar control surfaces and instruments as airplanes.
Types[edit]
The main application of modern glider aircraft is sport and recreation.
Sailplane[edit]
Gliders were developed in the 1920s for recreational purposes. As pilots began to understand how to use rising air,sailplanegliders were developed with a highlift-to-drag ratio.These allowed the craft to glide to the next source of "lift",increasing their range. This gave rise to the popular sport ofgliding.
Early gliders were built mainly of wood and metal, later replaced by composite materials incorporating glass, carbon oraramidfibers. To minimizedrag,these types have a streamlinedfuselageand long narrow wings incorporating ahigh aspect ratio.Single-seat and two-seat gliders are available.
Initially, training was done by short "hops" inprimary gliders,which have nocockpitand minimal instruments.[27]Since shortly after World War II, training is done in two-seat dual control gliders, but high-performance two-seaters can make long flights. Originally skids were used for landing, later replaced by wheels, often retractable. Gliders known asmotor glidersare designed for unpowered flight, but can deploypiston,rotary,jetorelectric engines.[28]Gliders are classified by theFAIfor competitions intoglider competition classesmainly on the basis of wingspan and flaps.

A class of ultralight sailplanes, including some known asmicrolift glidersand some known as airchairs, has been defined by the FAI based on weight. They are light enough to be transported easily, and can be flown without licensing in some countries. Ultralight gliders have performance similar tohang gliders,but offer some crash safety as the pilot can strap into an upright seat within a deform-able structure. Landing is usually on one or two wheels which distinguishes these craft from hang gliders. Most are built by individual designers and hobbyists.
Military gliders[edit]

Military gliderswere used during World War II for carrying troops (glider infantry) and heavy equipment to combat zones. The gliders were towed into the air and most of the way to their target by transport planes, e.g.C-47 Dakota,or by one-time bombers that had been relegated to secondary activities, e.g.Short Stirling.The advantage over paratroopers were that heavy equipment could be landed and that troops were quickly assembled rather than dispersed over aparachutedrop zone.The gliders were treated as disposable, constructed from inexpensive materials such as wood, though a few were re-used. By the time of theKorean War,transport aircraft had become larger and more efficient so that even light tanks could be dropped by parachute, obsoleting gliders.
Research gliders[edit]
Even after the development of powered aircraft, gliders continued to be used foraviation research.TheNASA Paresev Rogallo flexible wingwas developed to investigate alternative methods of recovering spacecraft. Although this application was abandoned, publicity inspired hobbyists to adapt the flexible-wingairfoilfor hang gliders.
Initial research into many types of fixed-wing craft, includingflying wingsandlifting bodieswas also carried out using unpowered prototypes.
Hang glider[edit]

Ahang glideris aglider aircraftin which the pilot is suspended in a harness suspended from theair frame,and exercises control by shifting body weight in opposition to a control frame. Hang gliders are typically made of analuminum alloyorcomposite-framed fabric wing. Pilots cansoarfor hours, gain thousands of meters of altitude inthermalupdrafts, perform aerobatics, and glide cross-country for hundreds of kilometers.
Paraglider[edit]
Aparaglideris a lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched glider with no rigid body.[29]The pilot is suspended in aharnessbelow a hollow fabric wing whose shape is formed by its suspension lines. Air entering vents in the front of the wing and the aerodynamic forces of the air flowing over the outside power the craft. Paragliding is most often a recreational activity.
Unmanned gliders[edit]
Apaper planeis a toy aircraft (usually a glider) made out of paper or paperboard.
Model glider aircraftare models of aircraft using lightweight materials such aspolystyreneandbalsa wood.Designs range from simple glider aircraft to accuratescale models,some of which can be very large.
Glide bombsare bombs with aerodynamic surfaces to allow a gliding flight path rather than a ballistic one. This enables stand-off aircraft to attack a target from a distance.
Kite[edit]

A kite is a tethered aircraft held aloft by wind that blows over its wing(s).[30]High pressure below the wing deflects the airflow downwards. This deflection generates horizontaldragin the direction of the wind. The resultant force vector from the lift and drag force components is opposed by the tension of thetether.
Kites are mostly flown for recreational purposes, but have many other uses. Early pioneers such as theWright BrothersandJ.W. Dunnesometimes flew an aircraft as a kite in order to confirm its flight characteristics, before adding an engine and flight controls.
Applications[edit]

Military[edit]
Kites have been used for signaling, for delivery ofmunitions,and forobservation,by lifting an observer above the field of battle, and by usingkite aerial photography.
Science and meteorology[edit]
Kites have been used for scientific purposes, such asBenjamin Franklin's famous experiment proving thatlightningiselectricity.Kites were the precursors to the traditionalaircraft,and were instrumental in the development of early flying craft.Alexander Graham Bellexperimented with largeman-lifting kites,as did theWright brothersandLawrence Hargrave.Kites had a historical role in lifting scientific instruments to measure atmospheric conditions forweather forecasting.
Radio aerials and light beacons[edit]
Kites can be used to carry radio antennas. This method was used for the reception station of the first transatlantic transmission byMarconi.Captive balloonsmay be more convenient for such experiments, because kite-carried antennas require strong wind, which may be not always available with heavy equipment and a ground conductor.
Kites can be used to carry light sources such as light sticks or battery-powered lights.
Kite traction[edit]

Kites can be used to pull people and vehicles downwind. Efficientfoil-type kitessuch aspower kitescan also be used to sail upwind under the same principles as used by other sailing craft, provided that lateral forces on the ground or in the water are redirected as with the keels, center boards, wheels and ice blades of traditional sailing craft. In the last two decades,kite sailingsports have become popular, such askite buggying,kite landboarding,kite boatingand kite surfing.Snow kitingis also popular.
Kite sailing opens several possibilities not available in traditional sailing:
- Wind speeds are greater at higher altitudes
- Kites may be maneuvered dynamically, which dramatically increases the available force
- Mechanical structures are not needed to withstand bending forces; vehicles/hulls can be light or eliminated.
Power generation[edit]
Research and development projects investigate kites for harnessing high altitude wind currents for electricity generation.[31]
Cultural uses[edit]
Kite festivals are a popular form of entertainment throughout the world. They include local events, traditional festivals and major international festivals.
Designs[edit]


- Bermuda kite
- Bowed kite,e.g.Rokkaku
- Cellular orbox kite
- Chapi-chapi
- Delta kite
- Foil,parafoilorbow kite
- Malay kitesee alsowau bulan
- Tetrahedral kite
Types[edit]
- Expanded polystyrene kite
- Fighter kite
- Indoor kite
- Inflatable single-line kite
- Kytoon
- Man-lifting kite
- Rogallo parawing kite
- Stunt (sport) kite
- Water kite
Characteristics[edit]

Air frame[edit]
The structural element of a fixed-wing aircraft is the air frame. It varies according to the aircraft's type, purpose, and technology. Early airframes were made of wood with fabric wing surfaces, When engines became available for powered flight, their mounts were made of metal. As speeds increased metal became more common until by the end of World War II, all-metal (and glass) aircraft were common. In modern times,composite materialsbecame more common.
Typical structural elements include:
- One or more mostly horizontal wings, often with anairfoilcross-section. The wing deflects air downward as the aircraft moves forward, generatinglifting forceto support it in flight. The wing also provides lateral stability to stop the aircraft level in steady flight. Other roles are to hold the fuel and mount the engines.

- Afuselage,typically a long, thin body, usually with tapered or rounded ends to make its shapeaerodynamicallyslippery. The fuselage joins the other parts of the air frame and contains the payload, and flight systems.
- Avertical stabilizeror fin is a rigid surface mounted at the rear of the plane and typically protruding above it. The fin stabilizes the plane'syaw(turn left or right) and mounts therudderwhich controls its rotation along that axis.
- Ahorizontal stabilizer,usually mounted at the tail near the vertical stabilizer. The horizontal stabilizer is used to stabilize the plane'spitch(tilt up or down) and mounts theelevatorsthat provide pitch control.
- Landing gear,a set of wheels, skids, or floats that support the plane while it is not in flight. On seaplanes, the bottom of the fuselage or floats (pontoons) support it while on the water. On some planes, the landing gear retracts during the flight to reduce drag.
Wings[edit]
The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are static planes extending to either side of the aircraft. When the aircraft travels forwards, air flows over the wings that are shaped to create lift.
Structure[edit]
Kites and some lightweight gliders and airplanes have flexible wing surfaces that are stretched across a frame and made rigid by the lift forces exerted by the airflow over them. Larger aircraft have rigid wing surfaces.
Whether flexible or rigid, most wings have a strong frame to give them shape and to transfer lift from the wing surface to the rest of the aircraft. The main structural elements are one or more spars running from root to tip, and ribs running from the leading (front) to the trailing (rear) edge.
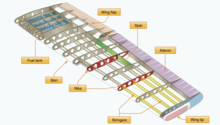
Early airplane engines had little power and light weight was critical. Also, early airfoil sections were thin, and could not support a strong frame. Until the 1930s, most wings were so fragile that external bracing struts and wires were added. As engine power increased, wings could be made heavy and strong enough that bracing was unnecessary. Such an unbraced wing is called acantileverwing.
Configuration[edit]

The number and shape of wings vary widely. Some designs blend the wing with the fuselage, while left and right wings separated by the fuselage are more common.
Occasionally more wings have been used, such as the three-wingedtriplanefrom World War I. Four-wingedquadruplanesand othermultiplanedesigns have had little success.
Most planes aremonoplanes,with one or two parallel wings.Biplanesandtriplanesstack one wing above the other.Tandem wingsplace one wing behind the other, possibly joined at the tips. When the available engine power increased during the 1920s and 1930s and bracing was no longer needed, the unbraced or cantilever monoplane became the most common form.
Theplanformis the shape when seen from above/below. To be aerodynamically efficient, wings are straight with a long span, but a short chord (highaspect ratio). To be structurally efficient, and hence lightweight, wingspan must be as small as possible, but offer enough area to provide lift.
To travel attransonicspeeds, variable geometry wings change orientation, angling backward to reduce drag from supersonic shock waves. Thevariable-sweep wingtransforms between an efficient straight configuration fortakeoff and landing,to a low-drag swept configuration for high-speed flight. Other forms of variable planform have been flown, but none have gone beyond the research stage. Theswept wingis a straight wing swept backward or forwards.

Thedelta wingis a triangular shape that serves various purposes. As a flexibleRogallo wing,it allows a stable shape under aerodynamic forces, and is often used for kites and other ultralight craft. It is supersonic capable, combining high strength with low drag.
Wings are typically hollow, also serving as fuel tanks. They are equipped withflaps,which allow the wing to increase/decrease drag/lift, for take-off and landing, and acting in opposition, to change direction.
Fuselage[edit]
The fuselage is typically long and thin, usually with tapered or rounded ends to make its shapeaerodynamicallysmooth. Most fixed-wing aircraft have a single fuselage. Others may have multiple fuselages, or the fuselage may be fitted with booms on either side of the tail to allow the extreme rear of the fuselage to be utilized.
The fuselage typically carries theflight crew,passengers, cargo, and sometimes fuel and engine(s).Gliderstypically omit fuel andengines, although some variations such asmotor glidersandrocket glidershave them for temporary or optional use.
Pilots of manned commercial fixed-wing aircraft control them from inside acockpitwithin the fuselage, typically located at the front/top, equipped with controls, windows, and instruments, separated from passengers by a secure door. In small aircraft, the passengers typically sit behind the pilot(s) in the cabin, Occasionally, a passenger may sit beside or in front of the pilot. Largerpassenger aircrafthave a separate passenger cabin or occasionally cabins that are physically separated from the cockpit.
Aircraft often have two or more pilots, with one in overall command (the "pilot" ) and one or more "co-pilots". On larger aircraft anavigatoris typically also seated in the cockpit as well. Some military or specialized aircraft may have other flight crew members in the cockpit as well.
Wings vs. bodies[edit]
Flying wing[edit]

A flying wing is atailless aircraftthat has no distinctfuselage,housing the crew, payload, and equipment inside.[32]: 224
The flying wing configuration was studied extensively in the 1930s and 1940s, notably byJack NorthropandCheston L. Eshelmanin the United States, andAlexander Lippischand theHorten brothersin Germany. After the war, numerous experimental designs were based on the flying wing concept. General interest continued into the 1950s, but designs did not offer a great advantage in range and presented technical problems. The flying wing is most practical for designs in the slow-to-medium speed range, and drew continual interest as a tacticalairlifterdesign.
Interest in flying wings reemerged in the 1980s due to their potentially lowradar cross-sections.Stealth technologyrelies on shapes that reflect radar waves only in certain directions, thus making it harder to detect. This approach eventually led to the NorthropB-2 Spiritstealthbomber (pictured). The flying wing's aerodynamics are not the primary concern. Computer-controlledfly-by-wiresystems compensated for many of the aerodynamic drawbacks, enabling an efficient and stable long-range aircraft.
Blended wing body[edit]
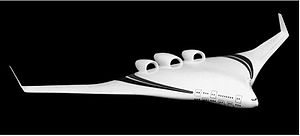
Blended wing body aircraft have a flattened airfoil-shaped body, which produces most of the lift to keep itself aloft, and distinct and separate wing structures, though the wings are blended with the body.
Blended wing bodied aircraft incorporate design features from both fuselage and flying wing designs. The purported advantages of the blended wing body approach are efficient, high-lift wings and a wide,airfoil-shaped body. This enables the entire craft to contribute toliftgeneration with potentially increased fuel economy.
Lifting body[edit]

A lifting body is a configuration in which the body produceslift.In contrast to aflying wing,which is a wing with minimal or no conventionalfuselage,a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage with little or no conventional wing. Whereas a flying wing seeks to maximize cruise efficiency atsubsonicspeeds by eliminating non-lifting surfaces, lifting bodies generally minimize the drag and structure of a wing for subsonic,supersonic,andhypersonicflight, or,spacecraftre-entry.All of these flight regimes pose challenges for flight stability.
Lifting bodies were a major area of research in the 1960s and 1970s as a means to build small and lightweight manned spacecraft. The US built lifting body rocket planes to test the concept, as well as several rocket-launched re-entry vehicles. Interest waned as theUS Air Forcelost interest in the manned mission, and major development ended during theSpace Shuttle design processwhen it became clear that highly shaped fuselages made it difficult to fit fuel tanks.
Empennage and foreplane[edit]
The classic airfoil section wing is unstable in flight. Flexible-wing planes often rely on an anchor line or the weight of a pilot hanging beneath to maintain the correct attitude. Some free-flying types use an adapted airfoil that is stable, or other mechanisms including electronic artificial stability.
In order to achieve trim, stability, and control, most fixed-wing types have anempennagecomprising a fin and rudder that act horizontally, and a tailplane and elevator that act vertically. This is so common that it is known as the conventional layout. Sometimes two or more fins are spaced out along the tailplane.

Some types have a horizontal "canard"foreplane ahead of the main wing, instead of behind it.[32]: 86 [33][34]This foreplane may contribute to the trim, stability or control of the aircraft, or to several of these.
Aircraft controls[edit]
Kite control[edit]
Kites are controlled by one or more tethers.
Free-flying aircraft controls[edit]
Gliders and airplanes have sophisticated control systems, especially if they are piloted.

The controls allow the pilot to direct the aircraft in the air and on the ground. Typically these are:
- Theyokeorjoystickcontrols rotation of the plane about the pitch and roll axes. Ayokeresembles a steering wheel. The pilot can pitch the plane down by pushing on the yoke or joystick, and pitch the plane up by pulling on it. Rolling the plane is accomplished by turning the yoke in the direction of the desired roll, or by tilting the joystick in that direction.
- Rudderpedals control rotation of the plane about the yaw axis. Two pedals pivot so that when one is pressed forward the other moves backward, and vice versa. The pilot presses on the right rudder pedal to make the plane yaw to the right, and pushes on the left pedal to make it yaw to the left. The rudder is used mainly to balance the plane in turns, or to compensate for winds or other effects that push the plane about the yaw axis.
- On powered types, an engine stop control ( "fuel cutoff", for example) and, usually, aThrottleorthrust leverand other controls, such as a fuel-mixture control (to compensate for air density changes with altitude change).
Other common controls include:
- Flaplevers, which are used to control the deflection position of flaps on the wings.
- Spoilerlevers, which are used to control the position of spoilers on the wings, and to arm their automatic deployment in planes designed to deploy them upon landing. The spoilers reduce lift for landing.
- Trimcontrols, which usually take the form of knobs or wheels and are used to adjust pitch, roll, or yaw trim. These are often connected to small airfoils on the trailing edge of the control surfaces and are called "trim tabs". Trim is used to reduce the amount of pressure on the control forces needed to maintain a steady course.
- On wheeled types,brakesare used to slow and stop the plane on the ground, and sometimes for turns on the ground.
A craft may have two pilot seats with dual controls, allowing two to take turns.
The control system may allow full or partial automation, such as anautopilot,a wing leveler, or aflight management system.Anunmanned aircrafthas no pilot and is controlled remotely or via gyroscopes, computers/sensors or other forms of autonomous control.
Cockpit instrumentation[edit]
On manned fixed-wing aircraft, instruments provide information to the pilots, includingflight,engines,navigation,communications,and other aircraft systems that may be installed.

Top row (left to right): airspeed indicator, attitude indicator, altimeter.
Bottom row (left to right): turn coordinator, heading indicator, vertical speed indicator.
The six basic instruments, sometimes referred to as the six pack, are:[35]
- Theairspeed indicator(ASI) shows the speed at which the plane is moving through the air.
- Theattitude indicator(AI), sometimes called the artificial horizon, indicates the exact orientation of the aircraft about itspitch and roll axes.
- Thealtimeterindicates the altitude or height of the planeabove mean sea level(AMSL).
- Thevertical speed indicator(VSI), or variometer, shows the rate at which the plane isclimbingordescending.
- Theheading indicator(HI), sometimes called the directional gyro (DG), shows themagnetic compass orientationof the fuselage. Thedirectionis affected by wind conditions andmagnetic declination.
- Theturn coordinator(TC), or turn and bank indicator, helps the pilot to control the plane in a coordinatedattitudewhile turning.
Other cockpit instruments include:
- Atwo-way radio,to enable communications with other planes and withair traffic control.
- Ahorizontal situation indicator(HSI) indicates the position and movement of the plane as seen from above with respect to the ground, including course/heading and other information.
- Instruments showing the status of the plane's engines (operating speed,thrust,temperature,and other variables).
- Combined display systems such asprimary flight displaysornavigation aids.
- Information displays such as onboardweather radardisplays.
- Aradio direction finder(RDF), to indicate the direction to one or more radio beacons, which can be used to determine the plane's position.
- Asatellite navigation(satnav) system, to provide an accurate position.
Some or all of these instruments may appear on a computer display and be operated with touches, ala a phone.
See also[edit]
- Aircraft flight mechanics
- Airliner
- Aviation
- Aviation and the environment
- Aviation history
- Fuel efficiency
- List of altitude records reached by different aircraft types
- Maneuvering speed
- Rotorcraft
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- In 1903, when the Wright brothers used the word, "aeroplane" (aBritish Englishterm that can also meanairplaneinAmerican English) meant wing, not the whole aircraft. See text of their patent.Patent 821,393– Wright brothers' patent for "Flying Machine"
Citations[edit]
- ^"Drachen Foundation Journal Fall 2002, page 18. Two lines of evidence: analysis of leaf kiting and some cave drawings"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 23 July 2011.Retrieved2 February2012.
- ^abNeedham, Volume 4, Part 1, 127.
- ^abAnon."Kite History: A Simple History of Kiting".G-Kites.Archivedfrom the original on 29 May 2010.Retrieved20 June2010.
- ^Aulus Gellius,"Attic Nights", Book X, 12.9 atLacusCurtius
- ^Archytas of Tarentum, Technology Museum of Thessaloniki, Macedonia, Greece.Tmth.edu.gr.Archived26 December 2008 at theWayback Machine
- ^Modern rocketry[dead link].Pressconnects.
- ^Automata historyArchived15 February 2015 at theWayback Machine.Automata.co.uk.
- ^White, Lynn. "Eilmer of Malmesbury, an Eleventh Century Aviator: A Case Study of Technological Innovation, Its Context and Tradition."Technology and Culture,Volume 2, Issue 2, 1961, pp. 97–111 (97–99 resp. 100–101).
- ^"Aviation History".Archivedfrom the original on 13 April 2009.Retrieved26 July2009.
In 1799 he set forth for the first time in history the concept of the modern aeroplane. Cayley had identified the drag vector (parallel to the flow) and the lift vector (perpendicular to the flow).
- ^"Sir George Cayley (British Inventor and Scientist)".Britannica.Archivedfrom the original on 11 March 2009.Retrieved26 July2009.
English pioneer of aerial navigation and aeronautical engineering and designer of the first successful glider to carry a human being aloft. Cayley established the modern configuration of an aeroplane as a fixed-wing flying machine with separate systems for lift, propulsion, and control as early as 1799.
- ^"Cayley, Sir George: Encyclopædia Britannica 2007."Archived11 March 2009 at theWayback MachineEncyclopædia Britannica Online,25 August 2007.
- ^Gibbs-Smith, Charles Harvard (2003).Aviation: an historical survey from its origins to the end of the Second World War.London: Science Museum.ISBN1-900747-52-9.OCLC52566384.
- ^Harwood, Craig; Fogel, Gary (2012).Quest for Flight: John J. Montgomery and the Dawn of Aviation in the West.Norman, Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press.ISBN978-0806142647.
- ^Inglis, Amirah."Hargrave, Lawrence (1850–1915)".Australian Dictionary of Biography.Vol. 9.Melbourne University Press.Archived fromthe originalon 29 December 2014.Retrieved28 December2014.
- ^Beril, Becker (1967).Dreams and Realities of the Conquest of the Skies.New York: Atheneum. pp. 124–125
- ^FAI News: 100 Years Ago, the Dream of Icarus Became RealityArchived13 January 2011 at theWayback Machineposted 17 December 2003. (The 1903 flights are not listed in the official FAI flight records, however, because the organization and its predecessors did not yet exist.) Retrieved 5 January 2007.
- ^Jones, Ernest."Santos Dumont in France 1906–1916: The Very Earliest Early Birds."Archived16 March 2016 at theWayback Machineearlyaviators,25 December 2006. Retrieved 17 August 2009.
- ^Les vols du 14bis relatés au fil des éditions du journal l'illustration de 1906.The wording is: "cette prouesse est le premier vol au monde homologué par l'Aéro-Club de France et la toute jeune Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI)." (This achievement is the first flight in the world to be recognized by the France Air Club and by the new International Aeronautical Federation (FAI).)
- ^Crouch, Tom (1982).Bleriot XI, The Story of a Classic Aircraft.Smithsonian Institution Press.pp. 21 and 22.ISBN0-87474-345-1.
- ^de Bie, Rob."Me 163B Komet – Me 163 Production – Me 163B: Werknummern list."Archived22 October 2015 at theWayback Machinerobdebie.home.Retrieved: 28 July 2013.
- ^NASA Armstrong Fact Sheet: First Generation X-1Archived13 July 2015 at theWayback Machine,28 February 2014
- ^de Saint-Exupery, A. (1940). "Wind, Sand and Stars" p33, Harcourt, Brace & World, Inc.
- ^"3. Gliding, chapter 1: General Rules and Definitions".FAI Sporting Code.Archived fromthe originalon 7 October 2007.Retrieved21 March2024.
- ^Code of Federal Regulations (U.S.)."14 CFR 1.1 - General definitions".ecfr.gov.
- ^Goin, Jeff (2006). Dennis Pagen (ed.).The Powered Paragliding Bible.Airhead Creations. p. 253.ISBN0-9770966-0-2.
- ^Michael Halloran and Sean O'Meara,Wing in Ground Effect Craft Review,DSTO, Australia"Archived copy"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 22 May 2013.Retrieved24 August2012.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link),p51. Notes an agreement between ICAO and IMO that WIGs come under the jurisdiction of the International Maritime Organisation although there an exception for craft with a sustained use out of ground effect (OGE) to be considered as aircraft. - ^Schweizer, Paul A:Wings Like Eagles, The Story of Soaring in the United States,pages 14–22. Smithsonian Institution Press, 1988.ISBN0-87474-828-3
- ^"Definition of gliders used for sporting purposes in FAI Sporting Code".Archived fromthe originalon 3 September 2009.
- ^Whittall, Noel (2002).Paragliding: The Complete Guide.Airlife Pub.ISBN1-84037-016-5.
- ^"Beginner's Guide to Aeronautics"Archived25 March 2015 at theWayback Machine,NASA(11 July 2008).
- ^Joseph Faust."Kite Energy Systems".Energykitesystems.net. Archived fromthe originalon 24 August 2012.Retrieved3 October2012.
- ^abCrane, Dale:Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition.Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997.ISBN1-56027-287-2
- ^Aviation Publishers Co. Limited,From the Ground Up,page 10 (27th revised edition)ISBN0-9690054-9-0
- ^Federal Aviation Administration(August 2008)."Title 14: Aeronautics and Space – PART 1—DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS".Archived fromthe originalon 20 December 2013.Retrieved5 August2008.
- ^"Six Pack – The Primary Flight Instruments".LearnToFly.ca. 13 March 2010.Archivedfrom the original on 19 March 2011.Retrieved31 January2011.
Bibliography[edit]
- Blatner, David.The Flying Book: Everything You've Ever Wondered About Flying on Airplanes.ISBN0-8027-7691-4
