French Polynesia
French Polynesia | |
|---|---|
| Motto: | |
| Anthem:La Marseillaise ( "The Marseillaise" ) | |
| Regional anthem:"Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui" | |
 Location of French Polynesia (circled in red) | |
| Sovereign state | |
| Protectorate proclaimed | 9 September 1842 |
| Territorial status | 27 October 1946 |
| Collectivity status | 28 March 2003 |
| Country status (nominal title) | 27 February 2004 |
| Capital | Papeete 17°34′S149°36′W/ 17.567°S 149.600°W |
| Largest city | Fa'a'ā |
| Official languages | French |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Ethnic groups (1988[1]) | 66.5% unmixedPolynesians 7.1% mixed Polynesians[a] 9.3% Demis[b] 11.9%Europeans[c] 4.7%East Asians[d] |
| Demonym(s) | French Polynesian |
| Government | Devolvedparliamentarydependency |
| Emmanuel Macron | |
| Dominique Sorain | |
| Moetai Brotherson | |
| Legislature | Assembly of French Polynesia |
| French Parliament | |
| 2 senators(of 348) | |
| 3 seats(of 577) | |
| Area | |
• Total | 4,167 km2(1,609 sq mi) |
• Land | 3,521.2[2]km2(1,359.5 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 12 |
| Population | |
• Aug. 2022 census | 278,786[3](175th) |
• Density | 79/km2(204.6/sq mi) (130th) |
| GDP(nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | US$6.01 billion[4] |
• Per capita | US$21,615[4] |
| Currency | CFP franc(₣) (XPF) |
| Time zone | |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Mains electricity |
|
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +689 |
| ISO 3166 code | |
| Internet TLD | .pf |
French Polynesia(/ˌpɒlɪˈniːʒə/POL-in-EE-zhə;French:Polynésie française[pɔlinezifʁɑ̃sɛːz];Tahitian:Pōrīnetia Farāni) is anoverseas collectivityofFranceand its soleoverseas country.It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands andatolls[5]stretching over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in theSouth Pacific Ocean.The total land area of French Polynesia is 3,521 square kilometres (1,359 sq mi),[2]with a population of 278,786 (Aug. 2022 census)[3]of which at least 205,000 live in theSociety Islandsand the remaining population lives in the rest of the archipelago.
French Polynesia is divided into five groups of islands:
- theSociety Islandsarchipelago, comprising theWindward Islandsand theLeeward Islands
- theTuamotu Archipelago
- theGambier Islands
- theMarquesas Islands
- theAustral Islands.
Among its 121 islands and atolls, 75 were inhabited at the 2017 census.[5]Tahiti,which is in the Society Islands group, is the most populous island, being home to nearly 69% of the population of French Polynesia as of 2017[update].Papeete,located on Tahiti, is the capital of French Polynesia. Although not an integral part of its territory,Clipperton Islandwas administered from French Polynesia until 2007.
Hundreds of years after theGreat Polynesian Migration,European explorers began traveling through the region, visiting the islands of French Polynesia on several occasions. Traders and whaling ships also visited. In 1842, the French took over the islands and established a Frenchprotectoratethat they calledÉtablissements français d'Océanie (EFO)(French Establishments/Settlements of Oceania).
In 1946, theEFObecame anoverseas territoryunder the constitution of theFrench Fourth Republic,andPolynesianswere granted the right to vote through citizenship. In 1957, theEFOwere renamed French Polynesia. In 1983 French Polynesia became a member of thePacific Community,a regional development organization. Since 28 March 2003, French Polynesia has been an overseas collectivity of the French Republic under the constitutional revision of article 74, and later gained, with law 2004-192 of 27 February 2004, an administrative autonomy, two symbolic manifestations of which are the title of thePresident of French Polynesiaand its additional designation as anoverseas country.[6]
History[edit]

Anthropologists and historians believe the Great Polynesian Migration commenced around 1500 BC asAustronesian peopleswent on a journey usingcelestial navigationto find islands in the South Pacific Ocean. The first islands of French Polynesia to be settled were the Marquesas Islands in about 200 BC. ThePolynesianslater ventured southwest and discovered the Society Islands around AD 300.[7]
European encounters began in 1521 when Portuguese explorerFerdinand Magellan,sailing at the service of theSpanish Crown,sightedPuka-Pukain theTuāmotu-Gambier Archipelago.In 1606 another Spanish expedition underPedro Fernandes de Queiróssailed through Polynesia sighting an inhabited island on 10 February[8]which they called Sagitaria (or Sagittaria), probably the island ofRekarekato the southeast of Tahiti.[9]In 1722, DutchmanJakob Roggeveenwhile on an expedition sponsored by the Dutch West India Company, charted the location of six islands in the Tuamotu Archipelago and two islands in the Society Islands, one of which wasBora Bora.
British explorerSamuel Wallisbecame the first European navigator to visit Tahiti in 1767. French explorerLouis Antoine de Bougainvillealso visited Tahiti in 1768, while British explorerJames Cookarrived in 1769,[7]andobserved the transit of Venus.He would stop in Tahiti again in 1773 during his second voyage to the Pacific, and once more in 1777 during his third and last voyage before being killed in Hawaii.
In 1772, the SpanishViceroy of PeruDonManuel de Amatordered a number of expeditions to Tahiti under the command ofDomingo de Bonecheawho was the first European to explore all of the main islands beyond Tahiti.[10]A short-lived Spanish settlement was created in 1774,[7]and for a time some maps bore the nameIsla de Amatafter Viceroy Amat.[11]Christian missionsbegan with Spanish priests who stayed in Tahiti for a year. Protestants from theLondon Missionary Societysettled permanently in Polynesia in 1797.

KingPōmare IIof Tahiti was forced to flee toMo'oreain 1803[why?];he and his subjects were converted to Protestantism in 1812. French Catholic missionaries arrived on Tahiti in 1834; their expulsion in 1836 caused France to send a gunboat in 1838. In 1842, Tahiti andTahuatawere declared aFrench protectorate,to allow Catholic missionaries to work undisturbed. The capital ofPapeetēwas founded in 1843. In 1880, France annexed Tahiti, changing the status from that of a protectorate to that of acolony.The island groups were not officially united until the establishment of the French protectorate in 1889.[12]
After France declared a protectorate over Tahiti in 1842 andfought a war with Tahiti (1844–1847),the British and French signed theJarnac Conventionin 1847, declaring that the kingdoms ofRaiatea,HuahineandBora Borawere to remain independent from both powers and that no single chief was to be allowed to reign over the entire archipelago. France eventually broke the agreement, and the islands were annexed and became a colony in 1888 (eight years after the Windward Islands) after many native resistances and conflicts called theLeewards War,lasting until 1897.[13][14]
In the 1880s, France claimed theTuamotu Archipelago,which formerly belonged to thePōmare Dynasty,without formally anne xing it. Having declared a protectorate over Tahuata in 1842, the French regarded the entire Marquesas Islands as French. In 1885, France appointed a governor and established a general council, thus giving it the proper administration for a colony. The islands ofRimataraandRūrutuunsuccessfully lobbied for British protection in 1888, so in 1889 they were annexed by France. Postage stamps were first issued in the colony in 1892. The first official name for the colony wasÉtablissements de l'Océanie(Establishments in Oceania); in 1903 the general council was changed to an advisory council and the colony's name was changed toÉtablissements Français de l'Océanie(French Establishments in Oceania).[15]
In 1940, the administration of French Polynesia recognised theFree French Forcesand many Polynesians served in World War II. Unknown at the time to the French and Polynesians, theKonoeCabinet inImperial Japanon 16 September 1940 included French Polynesia among the many territories which were to becomeJapanese possessions,as part of the "Eastern Pacific Government-General"in thepost-war world.[16]However, in the course of the war in the Pacific the Japanese were not able to launch an actual invasion of the French islands.

In 1946, Polynesians were granted French citizenship and the islands' status was changed to an overseas territory; the islands' name was changed in 1957 toPolynésie Française(French Polynesia). In 1962, France's earlynuclear testingground inAlgeriawas no longer usable when Algeria became independent and theMoruroa atollin the Tuamotu Archipelago was selected as the new testing site; tests were conducted underground after 1974.[17]In 1977, French Polynesia was granted partial internal autonomy; in 1984, the autonomy was extended. French Polynesia became a full overseas collectivity of France in 2003.[18]
In September 1995, France stirred up widespread protests by resuming nuclear testing atFangataufaatoll after a three-year moratorium. The last test was on 27 January 1996. On 29 January 1996, France announced that it would accede to theComprehensive Test Ban Treaty,and no longer test nuclear weapons.[19]
French Polynesia was relisted in theUnited Nations list of non-self-governing territoriesin 2013, making it eligible for a UN-backed independence referendum. The relisting was made after the indigenous opposition was voiced and supported by the Polynesian Leaders Group, Pacific Conference of Churches, Women's International League for Peace and Freedom, Non-Aligned Movement, World Council of Churches, and Melanesian Spearhead Group.[20]
Governance[edit]
Under the terms of Article 74 of theFrench constitutionand theOrganic Law2014–192 on the statute of autonomy of French Polynesia, politics of French Polynesia takes place in a framework of aparliamentaryrepresentative democraticFrench overseas collectivity, whereby the President of French Polynesia is thehead of government,and of amulti-party system.Executive poweris exercised by the government.Legislative poweris vested in both the government and theAssembly of French Polynesia(the territorial assembly).
Political life in French Polynesia was marked by great instability from the mid-2000s to the mid-2010s. The anti-independence right-wing president of French Polynesia,Gaston Flosse,who had been in power since 1991, had supported the resumption of theFrench nuclear weapons testsin 1995, and had obtained from his longtime friend and political allyJacques Chirac,then president of France, a status of expanded autonomy for French Polynesia in 2004, failed to secure an absolute majority in the2004 French Polynesian legislative election,resulting in deadlock at theAssembly of French Polynesia.Flosse's longtime opponent, the pro-independence leaderOscar Temaru,whose pro-independence coalition had won one less seat than Flosse's party in the Assembly, was nonetheless elected president of French Polynesia by the Assembly in June 2004 thanks to the votes of two non-aligned Assembly members. This resulted in several years of political instability, as neither the pro- nor the anti-independence camps were assured of a majority, depending on the votes of smaller non-aligned parties representing the interests of the distant islands of French Polynesia (as opposed to Tahiti). Temaru was toppled from the presidency of French Polynesia in October 2004, succeeded by Flosse who was toppled in March 2005, succeeded by Temaru again who was toppled in December 2006, succeeded byGaston Tong Sang,a close ally of Flosse.
On 14 September 2007, the pro-independence leaderOscar Temaruwas elected president of French Polynesia for the third time in three years (with 27 of 44 votes cast in the territorial assembly).[21]He replaced former presidentGaston Tong Sang,opposed to independence, who lost ano-confidence votein the Assembly of French Polynesia on 31 August after the longtime former president of French Polynesia,Gaston Flosse,hitherto opposed to independence, sided with his long enemy Oscar Temaru to topple the government of Gaston Tong Sang. Oscar Temaru, however, had no stable majority in the Assembly of French Polynesia, and new territorial elections were held in February 2008 to solve the political crisis.

The party of Gaston Tong Sang won the territorial elections, but that did not solve the political crisis: the two minority parties of Oscar Temaru and Gaston Flosse, who together had one more member in the territorial assembly than the political party of Gaston Tong Sang, allied to prevent Gaston Tong Sang from becoming president of French Polynesia. Gaston Flosse was then elected president of French Polynesia by the territorial assembly on 23 February 2008 with the support of the pro-independence party led by Oscar Temaru, while Oscar Temaru was elected speaker of the territorial assembly with the support of the anti-independence party led by Gaston Flosse. Both formed a coalition cabinet. Many observers doubted that the alliance between the anti-independence Gaston Flosse and the pro-independence Oscar Temaru, designed to prevent Gaston Tong Sang from becoming president of French Polynesia, could last very long.[22]
At theFrench municipal elections held in March 2008,several prominent mayors who were member of the Flosse-Temaru coalition lost their offices in key municipalities of French Polynesia, which was interpreted as a disapproval of the way Gaston Tong Sang, whose party French Polynesian voters had placed first in the territorial elections the month before, had been prevented from becoming president of French Polynesia by the last minute alliance between Flosse and Temaru's parties. Eventually, on 15 April 2008 the government of Gaston Flosse was toppled by aconstructive vote of no confidencein the territorial assembly when two members of the Flosse-Temaru coalition left the coalition and sided with Tong Sang's party. Tong Sang's majority in the territorial assembly was very narrow, and he was toppled in February 2009, succeeded by Temaru (supported again by Flosse).
Oscar Temaru's return to power was brief as he fell out with Gaston Flosse and was toppled in November 2009, succeeded by Gaston Tong Sang. Tong Sang remained in power for a year and a half before being toppled in a vote of no confidence in April 2011, and succeeded by Temaru. Oscar Temaru's fifth stint as president of French Polynesia lasted two years, during which he campaigned for the re-inscription of French Polynesia on theUnited Nations list of non-self-governing territories.Temaru lost the2013 French Polynesian legislative electionby a wide margin, only two weeks before theUnited Nationsre-registered French Polynesia on its list of non-self governing territories. This was interpreted by political analysts as a rejection by French Polynesian voters of Temaru's push for independence as well as the consequence of the socioeconomic crisis affecting French Polynesia after years of political instability and corruption scandals.
Gaston Flosse, whose anti-independence party was the big winner of the 2013 election, succeeded Oscar Temaru as president of French Polynesia in May 2013, but he was removed from office in September 2014 due to a corruption conviction by France's highest court. Flosse was replaced as president of French Polynesia by his second-in-command in the anti-independence camp,Édouard Fritch,who was also Flosse's former son-in-law (divorced from Flosse's daughter). Fritch fell out with Flosse in 2015 as both leaders were vying for control of the anti-independence camp, and Fritch was excluded from Gaston Flosse's party in September 2015, before founding his own anti-independence party,Tapura Huiraatira,in February 2016. His new party managed to keep a majority in the Assembly of French Polynesia, and Fritch remained president of French Polynesia.
Political stability has returned in French Polynesia since the split of the anti-independence camp in 2015–2016. Tapura Huiraatira won 70% of the seats in the Assembly of French Polynesia at the2018 French Polynesian legislative election,defeating both Oscar Temaru's pro-independence party and Gaston Flosse's anti-independence party, and Édouard Fritch was re-elected president of French Polynesia by the Assembly in May 2018. By 2022, Édouard Fritch was the longest-serving president of French Polynesia since Gaston Flosse in the 1990s and early 2000s.
Administration[edit]

Between 1946 and 2003, French Polynesia had the status of an overseas territory (territoire d'outre-mer,orTOM). In 2003, it became an overseas collectivity (collectivité d'outre-mer,or COM). Its statutory law of 27 February 2004 gives it the particular designation ofoverseas country inside the Republic(pays d'outre-mer au sein de la République,or POM), but without legal modification of its status.[23]
Relations with mainland France[edit]

Despite a local assembly and government, French Polynesia is not in afree associationwith France, like theCook IslandswithNew Zealand.As a French overseas collectivity, the local government has no competence in justice, university education, security and defense. Services in these areas are directly provided and administered by the Government of France, including theNational Gendarmerie(which also polices rural and border areas in metropolitan France), andFrench military forces.The collectivity government retains control over primary and secondary education, health, town planning, and the environment.[24]The highest representative of the State in the territory is theHigh Commissioner of the Republic in French Polynesia(French:Haut commissaire de la République en Polynésie française).
French Polynesia also sends threedeputiesto theFrench National Assemblyin three constituencies,the 1strepresenting Papeete and its north-eastern suburbs, plus thecommune(municipality) ofMo'orea-Mai'ao,theTuāmotu-Gambieradministrative division, and the Marquesas Islands administrative division,the 2ndrepresenting much of Tahiti outside Papeete and the Austral Islands administrative subdivision, andthe 3rdrepresenting theLeeward Islandsadministrative subdivisionand the south-western suburbs of Papeete. French Polynesia also sends two senators to theFrench Senate.
Defence[edit]
The defence of the collectivity is the responsibility of theFrench Armed Forces.Some 900 military personnel are deployed in the territory – incorporating the Pacific-Polynesian Marine Infantry Regiment (RIMaP-P)[25][26]– along with modest air transport and surveillance assets.[27]The latter include threeFalcon 200 Gardian maritime surveillance aircraftfromFrench Naval Aviation,which are to be replaced by the more modernFalcon 2000 Albatrosstarting in 2025.[28][29]The former is composed of twoCN-235tactical transport aircraft drawn from the Air Force's ET 82 "Maine" transport squadron.[26]
Three principalFrench Navyvessels are based in the territory, including: the surveillance frigatePrairial,the patrol and support shipBougainvilleand the coast guard vesselArago.As of 2021, two smaller port and coastal tugs (RPCs),MaroaandManini,were also operational in the territory.[30][31]Flottille 35F of French naval aviation deploys a detachment of threeAS 365N Dauphinhelicopters in Tahiti.[32]The helicopters carry out a variety of roles in the territory or may be embarked onPrairialas required.[33]In 2024Aragois to be replaced byTeriieroo to Teriierooiterai,a vessel of the newFélix Ébouéclassof patrol vessels. The French Navy will further reinforce its offshore patrol capabilities in the region by deploying a second vessel of the class (Philip Bernardino) to Tahiti by 2025.[34][35]
TheNational Gendarmeriedeploys some 500 active personnel and civilians, plus around 150 reservists, in French Polynesia.[36]The patrol boatJasminof theMaritime Gendarmerieis also based in the territory and is to be replaced by a new PCG-NG patrol boat in about 2025–2026.[37][38]
Geography[edit]
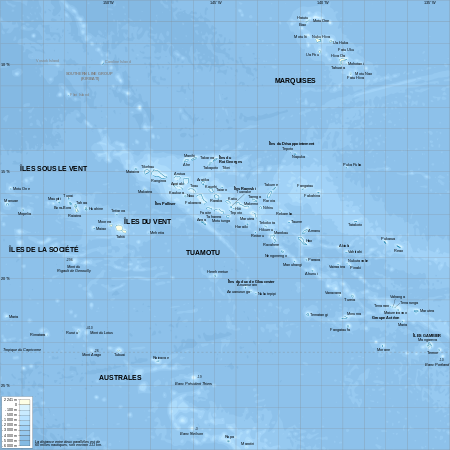

The islands of French Polynesia make up a total land area of 3,521 square kilometres (1,359 sq mi),[2]scattered over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) of ocean. There are 121 islands in French Polynesia and many more islets ormotusaroundatolls.[5]The highest point isMount Orohenaon Tahiti.
It is made up of five archipelagos. The largest and most populated island is Tahiti, in the Society Islands. The archipelagos are:
| Name | Land area (km2)[2] | Population 2022 Census |
Density (per km2) 2022 |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marquesas Islands | 1,049.3 | 9,478 | 9 | 12 high islands; administratively making the Marquesas Islands subdivision |
| Society Islands | 1,597.6 | 245,987 | 154 | administratively subdivided into the Windward Islands subdivision (4 high islands and 1 atoll) and the Leeward Islands subdivision (5 high islands and 4 atolls) |
| Tuamotu Archipelago | 698.7 | 15,159 | 22 | 80 atolls, grouping over 3,100 islands or islets; administratively part of the Tuamotu-Gambier subdivision |
| Gambier Islands | 27.8[39][40] | 1,570 | 56 | 6 high islands and 1 atoll; administratively part of the Tuamotu-Gambier subdivision |
| Austral Islands | 147.8 | 6,592 | 45 | 5 high islands and 1 atoll; administratively part of the Austral Islands subdivision |
| TOTAL | 3,521.2 | 278,786 | 79 | 121 high islands and atolls (75 inhabited at the 2017 census; 46 uninhabited)[5] |
Aside from Tahiti, some other important atolls, islands, and island groups in French Polynesia are:Ahē,Bora Bora,Hiva 'Oa,Huahine,Mai'ao,Maupiti,Meheti'a,Mo'orea,Nuku Hiva,Raiatea,Taha'a,Tetiaroa,Tupua'iandTūpai.
French Polynesia is home to four terrestrial ecoregions:Marquesas tropical moist forests,Society Islands tropical moist forests,Tuamotu tropical moist forests,andTubuai tropical moist forests.[41]
Administrative divisions[edit]

French Polynesia is divided in five administrative subdivisions (subdivisions administratives):
- Marquesas Islands(French:les îles Marquisesor officiallyla subdivision administrative des îles Marquises)
- Leeward Islands(French:les îles Sous-le-Ventor officiallyla subdivision administrative des îles Sous-le-Vent) (the twosubdivisions administrativesWindward Islands and Leeward Islands are part of the Society Islands)
- Windward Islands(French:les îles du Ventor officiallyla subdivision administrative des îles du Vent) (the twosubdivisions administrativesWindward Islands and Leeward Islands are part of the Society Islands)
- Tuāmotu-Gambier(French:les Îles Tuamotu-Gambieror officiallyla subdivision administrative des îles Tuamotu-Gambier) (the Tuamotus and the Gambier Islands)
- Austral Islands(French:les îles Australesor officiallyla subdivision administrative des îles Australes) (including theBass Islands)
The five administrative subdivisions are not local councils; they are solelydeconcentratedsubdivisions of the French central State. At the head of each administrative subdivision is anadministrateur d'État( "State administrator" ), generally simply known asadministrateur,also sometimes calledchef de la subdivision administrative( "head of the administrative subdivision" ). Theadministrateuris a civil servant under the authority of the High Commissioner of the French Republic in French Polynesia inPapeete.
Four administrative subdivisions (Marquesas Islands, Leeward Islands, Tuamotu-Gambier, and Austral Islands) each also form a deconcentrated subdivision of the government of French Polynesia. These are calledcirconscriptions( "districts" ). The head of acirconscriptionis thetavana hau,known asadministrateur territorialin French ( "territorial administrator" ), but theTahitiantitletavana hauis most often used. Thetavana hauis the direct representative of thepresident of French Polynesia's governmentwho appoints him or her. The Windward Islands, due to their proximity to Papeete, do not form a deconcentrated subdivision of the government of French Polynesia.
The 5 administrative subdivisions are themselves divided in 48communes.Like all other communes in the French Republic, these are municipalities in which local residents with either a French or anotherEUcitizenship elect a municipal council and a mayor in charge of managing local affairs within the commune. Municipal elections occur every six years on the same date as in the rest of the French Republic (the last municipal electionstook place in 2020).
| Commune | Island | Population (2022) |
|---|---|---|
| Faaa | Tahiti | 29,826 |
| Punaauia | Tahiti | 28,781 |
| Papeete | Tahiti | 26,654 |
30 communes are further subdivided in 98associated communeswhich have each a delegate mayor and a registry office. These 30 communes were subdivided in associated communes either because they have a large land territory (particularly in the larger islands such asTahitiorNuku Hiva) or because they are made up ofatollsdistant from each other (particularly in the Tuamotu archipelago), which led to the creation of associated communes for each inhabited atoll.
17 communes (out of French Polynesia's 48 communes) have banded together in three separatecommunities of communes.These indirectly electedintercommunal councilsare still relatively new in French Polynesia, and unlike inmetropolitan Franceand itsoverseas regionsit is not mandatory for the communes in French Polynesia to join an intercommunal council. The three intercommunal councils in existence as of 2022, all formed on a voluntary basis, were:
- community of communes of the Marquesas Islands (in French:communauté de communes des îles Marquises,or CODIM), formed in 2010 by all the communes in the administrative subdivision of the Marquesas Islands
- community of communes Hava'i (in French:communauté de communes Hava'i,or CCH), formed in 2012 by all the communes in the administrative subdivision of the Leeward Islands, with the exception ofBora-Borawhich preferred to remain separate for financial reasons
- community of communes Terehēamanu (in French:communauté de communes Terehēamanu), formed in 2021 by 5exurbanand rural communes on the eastern side of the island ofTahiti:Hitiaa O Te Ra,Taiarapu-Est,Taiarapu-Ouest,Teva I Uta,andPapara.
These communities of communes, as elsewhere in the French Republic, are not full-fledgedterritorial collectivities,but only federations of communes. From a legal standpoint, the only territorial collectivities in French Polynesia are the overseas collectivity of French Polynesia and the 48 communes.
Demographics[edit]

Total population was 278,786 according to the August 18, 2022 census,[3]68.7% of whom lived on the island ofTahitialone. The urban area of Papeete, the capital city, has 136,771 inhabitants (2017 census).[42]
At the 2017 census, 89.0% of people living in French Polynesia had been born there (up from 87.3% in 2007); 8.1% had been born inMetropolitan France(down from 9.3% in 2007); 1.2% were born elsewhere inoverseas France(down from 1.4% in 2007); and 1.7% were from foreign countries (down from 2.0% in 2007).[43]The population of natives of Metropolitan France living in French Polynesia has declined in relative terms since the 1980s, but in absolute terms their population peaked at the 2007 census, when 24,265 lived in French Polynesia (not counting their children born there).[44]With the local economic crisis, their population declined to 22,278 at the 2012 census,[44]and 22,387 at the 2017 census.[43]
| Census | Born in French Polynesia |
Born in Metropolitan France |
Born in Overseas France |
Born in foreign countries with French citizenship at birth¹ |
Immigrants² | |
| 2017 | 89.0% | 8.1% | 1.2% | 0.9% | 0.8% | |
| 2012 | 88.7% | 8.3% | 1.3% | 0.9% | 0.8% | |
| 2007 | 87.3% | 9.3% | 1.4% | 1.1% | 0.9% | |
| 2002 | 87.2% | 9.5% | 1.4% | 1.2% | 0.8% | |
| 1996 | 86.9% | 9.3% | 1.5% | 1.3% | 0.9% | |
| 1988 | 86.7% | 9.2% | 1.5% | 1.5% | 1.0% | |
| 1983 | 86.1% | 10.1% | 1.0% | 1.5% | 1.3% | |
| ¹Persons born abroad of French parents, such asPieds-Noirsand children of Frenchexpatriates. ²An immigrant is by French definition a person born in a foreign country and who didn't have French citizenship at birth. Note that an immigrant may have acquired French citizenship since moving to France, but is still listed as an immigrant in French statistics. On the other hand, persons born in France with foreign citizenship (the children of immigrants) are not listed as immigrants. | ||||||
| Source: ISPF,[44][43] | ||||||
At the 1988 census, the last census which asked questions regarding ethnicity, 66.5% of people were ethnically unmixedPolynesians,7.1% were ethnically Polynesians with light European or East Asian mi xing, 11.9% wereEuropeans(mostlyFrench), 9.3% were people of mixed European and Polynesian descent, the so-called Demis (literally meaning "Half" ), and 4.7% wereEast Asians(mainlyChinese).[1]
Chinese, Demis, and the white populace are essentially concentrated on the island of Tahiti, particularly in the urban area of Papeete, where their share of the population is thus much greater than in French Polynesia overall.[1]Despite a long history of ethnic mi xing, ethnic tensions have been growing in recent years, with politicians using axenophobicdiscourse and fanning the flame of nationalism.[45][46]
Historical population[edit]
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official figures from past censuses.[3][47][48][49][50] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Culture[edit]
Languages[edit]
All the indigenous languages of French Polynesia arePolynesian.French Polynesia has been linguistically diverse since ancient times, with each community having its own local speech variety. These dialects can be grouped into seven languages on the basis ofmutual intelligibility:Tahitian,Tuamotuan,Rapa,Austral,North Marquesan,South Marquesan,andMangarevan.Some of these, especially Tuamotuan, are reallydialect continuaformed by a patchwork of different dialects. The distinction between languages and dialects is notoriously difficult to establish, and so some authors may view two varieties as dialects of the same language, while others may view them as distinct languages. In this way, North and South Marquesan are often grouped together as a single Marquesan language, and Rapa is often viewed as part of Austral subfamily. At the same time, Ra'ivavae is often viewed as distinct from them.[51]
Frenchis the sole official language of French Polynesia.[52]Anorganic lawof 12 April 1996 states that "French is the official language, Tahitian and other Polynesian languages can be used." At the 2017 census, among the population whose age was 15 and older, 73.9% of people reported that the language they spoke the most at home was French (up from 68.6% at the 2007 census), 20.2% reported that the language they spoke the most at home wasTahitian(down from 24.3% at the 2007 census), 2.6% reportedMarquesanand 0.2% the relatedMangareva language(same percentages for both at the 2007 census), 1.2% reported any of theAustral languages(down from 1.3% at the 2007 census), 1.0% reportedTuamotuan(down from 1.5% at the 2007 census), 0.6% reported aChinese dialect(41% of which wasHakka) (down from 1.0% at the 2007 census), and 0.4% another language (more than half of which wasEnglish) (down from 0.5% at the 2007 census).[53]
At the same census, 95.2% of people whose age was 15 or older reported that they could speak, read and write French (up from 94.7% at the 2007 census), whereas only 1.3% reported that they had no knowledge of French (down from 2.0% at the 2007 census).[53]86.5% of people whose age was 15 or older reported that they had some form of knowledge of at least one Polynesian language (up from 86.4% at the 2007 census but down from 87.8% at the 2012 census), whereas 13.5% reported that they had no knowledge of any of the Polynesian languages (down from 13.6% at the 2007 census but up from 12.2% at the 2012 census).[53]
Music[edit]
French Polynesia appeared in theworld musicscene in 1992, recorded by French musicologistPascal Nabet-Meyerwith the release ofThe Tahitian Choir's recordings of unaccompanied vocal Christian music calledhimene tārava.[54]This form of singing is common in French Polynesia and the Cook Islands, and is notable for a unique drop in pitch at the end of the phrases, a characteristic formed by several different voices, accompanied by a steady grunting of staccato,nonlexicalsyllables.[55]
Dance[edit]
Tahitian dance as a movement art evolved alongside Tahitian oral transmission of cultural knowledge.[56]In fact, dance movement or gesture has significance, that supported the transmission of cultural knowledge.[57]Dance styles include'Aparimaand'upa'upa.
However, after theLondon Missionary Societybrought their religion to the islands, they pressured KingPōmare II(whom they had converted from traditional beliefs to theirReformed tradition) to introduce a new legal code.[58]This code, now known as the Pōmare Code, came into effect in 1819[59]and banned numerous traditional practices including dancing, chants, floral costumes, tattooing and more.[60]
Religion[edit]

Christianityis the main religion of the islands. A majority of 54% belongs to variousProtestantchurches, especially theMaohi Protestant Church,which is the largest and accounts for more than 50% of the population.[61]It traces its origins toPōmare II,the king of Tahiti, who converted from traditional beliefs to theReformed traditionbrought to the islands by theLondon Missionary Society.
Catholicsconstitute a large minority of 38.3%[62]of the population (2019)[62]which has its ownecclesiastical province,comprising the MetropolitanArchdiocese of Papeeteand its onlysuffragan,theDiocese of Taiohae.[63]The number and proportion of Catholics has increased significantly since 1950, when they represented 21.6% of the total population.[62]
Data from 1991 revealed that Catholics were in the majority in theTuamotu Islands,[64]Gambier Islands[64]and theMarquesas Islands,[64]while Protestants formed the majority in theAustral Islands[64]and several of theSociety Islandssuch as Tahiti.[64]This diversity is due to the fact that Protestant missionaries (fromEnglandand theUnited States) first came to one group of islands, and after French colonisation theCatholic Churchspread to several more scattered islands, but also to the main island of Tahiti.[64]
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saintshad 28,147 members as of 2018[update].[65]Community of Christ,another denomination within theLatter-Day Sainttradition, claimed 9,256 total French Polynesian members as of 2018[66]including Mareva Arnaud Tchong who serves in the church's governingCouncil of Twelve Apostles.There were about 3,000Jehovah's Witnessesin Tahiti as of 2014[update],[67]and an estimated 500 Muslims in French Polynesia.[68]
Cuisine[edit]
Due to the island location and the fact that the French Polynesia produce a significant array of fruits and vegetables, natural local produce, especially coconut, features in many of the dishes of the islands as does fresh seafood. foods likeFaraoa 'ipo,Poisson cruandRēti'a.
Sports[edit]

Football[edit]
Thesportoffootballin the island ofTahitiis run by theFédération Tahitienne de Football.
Va'a[edit]
The Polynesian traditional sportva'ais practiced in all the islands.[69]French Polynesia hosts theHawaiki nui va'aan international race between Tahiti, Huahine and Bora Bora.
Surfing[edit]
French Polynesia is famous for itsreef breakwaves.Teahupo'ois probably the most renowned, regularly ranked in the best waves of the world.[70]This site hosts the annualBillabong Pro Tahitisurf competition, the 7th stop of theWorld Championship Tour,[71]and is scheduled to host the surfing events of the2024 Summer Olympics.[72]
Kitesurfing[edit]
There are many spots to practice kitesurfing in French Polynesia, with Tahiti, Moorea, Bora-Bora, Maupiti and Raivavae being among the most iconic.[73]

Diving[edit]
French Polynesia is internationally known for diving. Each archipelago offers opportunities for divers.RangiroaandFakaravain theTuamotuislands are the most famous spots in the area.[74]
Rugby[edit]
Rugby is also popular in French Polynesia, specifically Rugby union.[75]
Television[edit]
Television channels with local programming includePolynésie la 1ère(established in 1965) andTahiti Nui Television(established in 2000). Channels from metropolitan France are also available.
Economy and infrastructure[edit]

The legal tender of French Polynesia is theCFP francwhich has a fixed exchange rate with theeuro.The nominalgross domestic product(or GDP) of French Polynesia in 2019 was 6.01 billionU.S. dollarsat market exchange rates, the seventh-largest economy in Oceania afterAustralia,New Zealand,Hawaii,Papua New Guinea,New Caledonia,andGuam.[4]The GDP per capita was US$21,615 in 2019 (at market exchange rates, not atPPP), lower than in Hawaii, Australia, New Zealand, Guam, and New Caledonia, but higher than in all other independent insular states and dependent territories ofOceania.[4]
French Polynesia was severely affected by theGlobal Financial Crisis of 2008and subsequentGreat Recession,and experienced as a result 4 years ofrecessionfrom 2009 to 2012. French Polynesia renewed with economic growth in 2013, and experienced strong economic growth in the 2nd half of the 2010s, with an averagereal GDPgrowth rate of +2.8% per year from 2016 to 2019, before being affected by theCOVID-19 pandemicin 2020, which has led to another recession.[76]
French Polynesia has a moderately developed economy, which is dependent on imported goods, tourism, and the financial assistance of mainland France. Tourist facilities are well developed and are available on the major islands. Main agricultural productions arecoconuts(copra), vegetables and fruits. French Polynesia exportsnonijuice, a high qualityvanilla,and the famousblack Tahitian pearlswhich accounted for 55% of exports (in value) in 2008.[77]
French Polynesia's seafloor contains rich deposits ofnickel,cobalt,manganese,andcopperthat are not exploited.[78]
In 2008, French Polynesia's imports amounted to 2.2 billion U.S. dollars and exports amounted to 0.2 billion U.S. dollars.[77]
Transportation[edit]
There are 53 airports in French Polynesia; 46 are paved.[18]Fa'a'ā International Airportis the only international airport in French Polynesia. Each island has its own airport that serves flights to other islands.Air Tahitiis the main airline that flies around the islands.
Communication[edit]
In 2017, Alcatel Submarine Networks, a unit ofNokia,launched a project to connect many of the islands in French Polynesia with underwater fiber optic cable. The project, called NATITUA, is intended to improve French Polynesian broadband connectivity by linking Tahiti to 10 islands in the Tuamotu and Marquesas archipelagos.[79]In August 2018, a celebration was held to commemorate the arrival of a submarine cable fromPapeeteto the atoll of Hao, extending the network by about 1000 kilometres.[80]
Notable people[edit]

- Taïna Barioz(born 1988),World Championskier representing France.
- Billy Besson,Olympic sailor representing France
- Michel Bourez(born 1985), professional surfer.
- Cheyenne Brando(1970–1995), model, daughter ofMarlon BrandoandTarita Teriipaia.
- Jacques Brel(1929–1978), Belgian musician who lived in French Polynesia near the end of his life.
- Jean Gabilou(born 1944), singer, represented France in the1981 Eurovision Song Contest.
- Chantal Galenon(born 1956), politician and women's rights activist.
- Paul Gauguin(1848–1903), Frenchpost-impressionistpainter who spent the last years of his life in French Polynesia.
- Conrad Hall(1926–2003), American cinematographer.
- Vaitiare Hirson-Asars(born 1964), actress.
- Ella Koon(born 1979), singer, actress and model.
- Karina Lombard(born 1969), French-American model and actress.
- Pouvāna'a 'Ō'opa(1895–1977), politician and Tahitian nationalist.
- Fabrice Santoro(born 1972), professional tennis player.
- Tarita Teriipaia(born 1941), actress, third wife of Marlon Brando.
- Marama Vahirua(born 1980), footballer, cousin of Pascal Vahirua.
- Pascal Vahirua(born 1966), French former international footballer.
- Célestine Hitiura Vaite(born 1966), writer.
See also[edit]
- Outline of French Polynesia
- Index of French Polynesia-related articles
- List of colonial and departmental heads of French Polynesia
- French colonial empire
- List of French possessions and colonies
- Lists of islands
Notes[edit]
References[edit]
- ^abcMost recent ethnic census, in 1988."Frontières ethniques et redéfinition du cadre politique à Tahiti"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 26 March 2009.Retrieved31 May2011.
- ^abcd"R1- Population sans doubles comptes, des subdivisions, communes et communes associées de Polynésie française, de 1971 à 1996".Institut Statistique de Polynésie Française (ISPF). Archived fromthe originalon 31 March 2022.Retrieved4 March2022.
- ^abcd"Recensement de la population 2022 - La population légale en Polynésie française au 18 août 2022"(PDF).ISPF.Archived(PDF)from the original on 25 November 2022.Retrieved12 December2022.
- ^abcd"Les grands indicateurs des comptes économiques".Institut de la statistique de la Polynésie française (ISPF). Archived fromthe originalon 14 May 2021.Retrieved3 March2022.
- ^abcd"French Polynesia at a glance 2020"(PDF).Institut de la statistique de la polynésie française (ISPF). p. 91. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 29 December 2021.Retrieved4 March2022.
- ^"Les statuts de la Nouvelle-Calédonie et de la Polynésie".Archived fromthe originalon 8 May 2020.Retrieved17 December2015.
- ^abcGanse, Alexander."History of Polynesia, before 1797".Archived fromthe originalon 30 December 2007.Retrieved20 October2007.
- ^James Burney (1803)A Chronological History of the Voyages or Discoveries in the South Sea or Pacific Ocean,Vol. 5, London, p. 222
- ^Geo. Collingridge (1903)."Who Discovered Tahiti?".Journal of the Polynesian Society.12(3): 184–186.Archivedfrom the original on 28 December 2016.Retrieved18 February2017.
- ^Kirk, Robert K. (8 November 2012).Paradise Past: The Transformation of the South Pacific, 1520–1920.McFarland.ISBN9780786492985.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2023.Retrieved5 May2013.
- ^Manso Porto, Carmen (1997).Cartografía histórica de América: catálogo de manuscritos(in Spanish). Madrid: Real Academia de la Historia. p. 10.ISBN9788489512023.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2023.Retrieved27 November2016.
- ^Ganse, Alexander."History of French Polynesia, 1797 to 1889".Archived fromthe originalon 30 December 2007.Retrieved20 October2007.
- ^Robert D. Craig (2002).Historical Dictionary of Polynesia.Vol. 39 (2 ed.). Scarecrow Press. p. 107.ISBN0-8108-4237-8.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2023.Retrieved2 November2017.
- ^Matt K. Matsuda (2005). "Society Islands: Tahitian Archives".Empire of Love: Histories of France and the Pacific.Oxford University Press. pp. 91–112.ISBN0-19-516294-3.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2023.Retrieved2 November2017.
- ^Ganse, Alexander."History of French Polynesia, 1889 to 1918".Archived fromthe originalon 30 December 2007.Retrieved20 October2007.
- ^The Japanese claim to the French Pacific islands, along with many other vast territories, appears in 16 September 1940 "Sphere of survival for the Establishment of a New Order in Greater East Asia by Imperial Japan", published in 1955 by Japan's Foreign Ministry as part of the two-volume "Chronology and major documents of Diplomacy of Japan 1840–1945" – here quoted from "Interview with Tetsuzo Fuwa: Japan's War: History of Expansionism", Japan Press Service, July 2007
- ^Ganse, Alexander."History of Polynesia, 1939 to 1977".Archived fromthe originalon 30 December 2007.Retrieved20 October2007.
- ^abFrench PolynesiaArchived15 April 2021 at theWayback Machine.The World Factbook.Central Intelligence Agency.. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- ^Whitney, Craig R (30 January 1996)."France Ending Nuclear Tests That Caused Broad Protests".The New York Times.Archivedfrom the original on 1 January 2008.Retrieved20 October2007.
- ^Reeves, Rachel; Hunt, Luke (10 October 2012)."French Polynesia Battles for Independence".The Diplomat.Archivedfrom the original on 28 June 2017.Retrieved30 June2017.
- ^"BBC NEWS, French Polynesia gets new leader".BBC News.14 September 2007.Archivedfrom the original on 30 July 2022.Retrieved31 May2011.
- ^"Polynésie: Gaston Flosse présente un gouvernement d'union"[Polynesia: Gaston Flosse announces a unity government].RFO(in French). 29 February 2008. Archived fromthe originalon 4 March 2008.Retrieved23 March2008.
- ^Angelo, Tony; Moyrand, A (2010). "Administrative Regimes of French Overseas Territories: New Caledonia and French Polynesia". In Angelo, Tony; Sage, Yves-Louis (eds.).Governance and Selfreliance in Pacific Island Societies: Comparative Studies (Gouvernance et autonomie dans les sociétés du Pacifique Sud: Etudes comparés)(PDF).Revue Juridique Polynesienne. p. 202.Archived(PDF)from the original on 24 January 2022.Retrieved24 January2021.
- ^Rachel Reeves; Luke Hunt; The Diplomat."French Polynesia Battles for Independence".The Diplomat.Archivedfrom the original on 1 January 2016.Retrieved17 December2015.
- ^"FAPF – Bilan de la mission PACIFIC AITO du patrouilleur Arago".Ministère des Armées.28 February 2023.Archivedfrom the original on 28 February 2023.Retrieved28 February2023.
- ^ab"Forces armées de Polynésie française"[Armed Forces of French Polynesia] (in French). Ministère des Armées.Archivedfrom the original on 14 November 2022.Retrieved8 December2022.
- ^"French Military Presence in the Indo-Pacific".United States Naval Institute News.Archivedfrom the original on 24 July 2022.Retrieved28 November2021.
- ^"French Navy to receive new eyes in the sky from Dassault".AeroTime.19 November 2020.Archivedfrom the original on 13 November 2022.Retrieved13 November2022.
- ^Groizeleau, Vincent (17 October 2022)."Un nouvel hélicoptère pour la frégate de surveillance Prairial en Polynésie"[A new helicopter for the surveillance frigate Prairial in Polynesia].Mer et Marine(in French).Archivedfrom the original on 18 October 2022.Retrieved8 December2022.
- ^Groizeleau, Vincent (16 July 2021)."La Marine nationale n'a plus aucun bâtiment disponible en Nouvelle-Calédonie".Mer et Marine(in French).Archivedfrom the original on 5 March 2023.Retrieved5 March2023.
- ^"Marine Nationale Dossier d'Information, pp. 19 and 23"(PDF).Cols Bleus(in French). January 2023.Archived(PDF)from the original on 4 March 2023.Retrieved4 March2023.
- ^"Marine Nationale Dossier d'Information, p. 23"(PDF).Cols Bleus(in French). January 2023.Archived(PDF)from the original on 4 March 2023.Retrieved4 March2023.
- ^Donald, David (7 May 2020)."French Navy Revamps Its Helicopter Fleet".AIN Online.Archivedfrom the original on 14 November 2022.Retrieved8 December2022.
- ^Groizeleau, Vincent (12 September 2022)."Socarenam met à l'eau le second des nouveaux patrouilleurs d'outre-mer"[Socarenam launches the second of the new overseas patrol boats].Mer et Marine(in French).Archivedfrom the original on 12 September 2022.Retrieved16 September2022.
- ^"Le Commandement de la Gendarmerie pour la Polynésie Française"[The Gendarmerie Command for French Polynesia] (in French). Haut-Commissariat de la République en Polynésie Française. 9 October 2022.Archivedfrom the original on 7 November 2022.Retrieved8 December2022.
- ^"Le Jasmin sera remplacé en 2024".Direction Polynésienne des Affaires Maritimes(in French). 12 June 2019.Archivedfrom the original on 4 March 2023.Retrieved4 March2023.
- ^"Le premier des six nouveaux patrouilleurs côtiers de la Gendarmerie maritime officiellement commandé".Archivedfrom the original on 5 March 2023.Retrieved5 March2023.
- ^"Gambier – Guide Floristique"(PDF)(in French). Government of French Polynesia, Directorate of the Environment.Archived(PDF)from the original on 21 January 2022.Retrieved4 March2022.
- ^"Annexe 3: Indicateurs par île et classement par archipel pour la PF"(PDF)(in French). Centre d'Etudes du Tourisme en Océanie-Pacifique (CETOP). p. 91.Archived(PDF)from the original on 7 April 2022.Retrieved4 March2022.
- ^Dinerstein, Eric; Olson, David; Joshi, Anup; Vynne, Carly; Burgess, Neil D.; Wikramanayake, Eric; Hahn, Nathan; Palminteri, Suzanne; Hedao, Prashant; Noss, Reed; Hansen, Matt; Locke, Harvey; Ellis, Erle C; Jones, Benjamin; Barber, Charles Victor; Hayes, Randy; Kormos, Cyril; Martin, Vance; Crist, Eileen; Sechrest, Wes; Price, Lori; Baillie, Jonathan E. M.; Weeden, Don; Suckling, Kierán; Davis, Crystal; Sizer, Nigel; Moore, Rebecca; Thau, David; Birch, Tanya; Potapov, Peter; Turubanova, Svetlana; Tyukavina, Alexandra; de Souza, Nadia; Pintea, Lilian; Brito, José C.; Llewellyn, Othman A.; Miller, Anthony G.; Patzelt, Annette; Ghazanfar, Shahina A.; Timberlake, Jonathan; Klöser, Heinz; Shennan-Farpón, Yara; Kindt, Roeland; Lillesø, Jens-Peter Barnekow; van Breugel, Paulo; Graudal, Lars; Voge, Maianna; Al-Shammari, Khalaf F.; Saleem, Muhammad (2017)."An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm".BioScience.67(6): 534–545.doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014.ISSN0006-3568.PMC5451287.PMID28608869.
- ^"Bilan démographique 2020".Institut de la statistique de la Polynésie française (ISPF). Archived fromthe originalon 4 March 2022.Retrieved4 March2022.
- ^abcInstitut Statistique de Polynésie Française (ISPF)."Recensement 2017 – Données détaillées – Migrations"(in French). Archived fromthe originalon 7 April 2019.Retrieved7 April2019.
- ^abc"Recensements de la population – Evolution des caractéristiques socio-démographiques".ISPF. Archived fromthe originalon 24 June 2015.Retrieved18 February2018.
- ^"Logiques" autonomiste "et" indépendantiste "en Polynésie française".Conflits.org. Archived fromthe originalon 24 January 2009.Retrieved31 May2011.
- ^"Temaru-Flosse: le rebond du nationalisme tahitien".Rue89. 19 January 2011.Archivedfrom the original on 24 May 2011.Retrieved31 May2011.
- ^"La population légale au 17 août 2017: 275 918 habitants".ISPF. Archived fromthe originalon 9 February 2018.Retrieved16 February2018.
- ^"Population des communes de Polynésie française au RP 2007".INSEE.Archivedfrom the original on 19 September 2018.Retrieved13 October2013.
- ^"Population statistique des communes et communes associées aux recensements de 1971 à 2002".ISPF. Archived fromthe originalon 18 December 2012.Retrieved13 October2013.
- ^"Censuses from 1907 to 1962 in Population, 1972, #4–5, pp. 705–706, published by INED".Archived fromthe originalon 29 June 2012.
- ^Charpentier & François 2015,pp. 73–76.
- ^Le tahitien reste interdit à l'assemblée de Polynésie,RFO, 6 October 2010
- ^abcInstitut Statistique de Polynésie Française (ISPF)."Recensement 2017 – Données détaillées Langues".Archived fromthe originalon 7 April 2019.Retrieved7 April2019.
- ^Hayward, Philip (2006).Bounty Chords: Music, Dance and Cultural Heritage on Norfolk and Pitcairn Islands.Bloomington: Indiana University Press. pp. 24–35.ISBN9780861966783.
- ^McLean, Mervyn (1999).Weavers of Song: Polynesian Music and Dance.Auckland University Press. pp. 403–435.ISBN9781869402129.
- ^"Tahitian Dance".
- ^"Traditional Tahitian dances – cultural survivors".
- ^Gunson, N. (1969). Pomare II of Tahiti and Polynesian imperialism. The Journal of Pacific History, 4(1), 65-82
- ^Gille, Bernard.Wistoire des institutions de l'Océanie française: Polynésie, Nouvelle-Calédonie, Wallis et Futuna, L'Harmattan.pp. 403–435.ISBN978-2-296-09234-1.
- ^"Let's celebrate 140 years of Heiva!".
- ^"126th Maohi Protestant Church Synod to last one week".Tahitipresse.26 July 2010. Archived fromthe originalon 29 July 2010.Retrieved31 December2011.
- ^abc"Papeete (Archdiocese) [Catholic-Hierarchy]".catholic-hierarchy.org.Archivedfrom the original on 15 August 2021.Retrieved15 August2021.
- ^"Catholic Church in Territory of French Polynesia".GCatholic.Archivedfrom the original on 10 December 2019.Retrieved1 April2017.
- ^abcdefSaura, Bruno (1991)."The Tahitian Churches and the Problem of the French Presence in 1991".The Journal of Pacific History.26(2): 347–357.doi:10.1080/00223349108572673.ISSN0022-3344.JSTOR25169083.Archivedfrom the original on 15 August 2021.Retrieved15 August2021.
- ^LDS Newsroom Statistical InformationArchived12 July 2019 at theWayback Machine.Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- ^Saturday/Sunday Bulletin World Conference 2019. Community of Christ. 2019. pp. 15–16.
- ^2015 Yearbook of Jehovah's Witnesses.Watch Tower Society. p. 186.
- ^"State of the World's Minorities and Indigenous Peoples 2014 – Case study: Tahiti: Islamophobia in French Polynesia".Archivedfrom the original on 9 January 2017.Retrieved31 May2020.
- ^""Va'a" – the Polynesian Canoe ".Tahiti Nui Travel.Archivedfrom the original on 28 September 2022.Retrieved24 January2022.
- ^Jade Bremner (July 2013)."World's 50 best surf spots - CNN".CNN.Archivedfrom the original on 16 August 2014.Retrieved3 June2016.
- ^"2019 Tahiti Pro Teahupo'o".World Surf League.28 August 2019.Archivedfrom the original on 31 July 2020.Retrieved20 April2020.
- ^"Tahiti approved by IOC as surfing venue for Paris 2024 Olympic Games".Inside the Games.3 March 2020.Archivedfrom the original on 24 October 2020.Retrieved23 February2021.
- ^GR3G."General Info - WWW.TaHiTi-KiTeSuRF.COM".tahiti-kitesurf.Archived fromthe originalon 7 August 2016.Retrieved3 June2016.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^"Top 100 Destination: Diving in French Polynesia".Scuba Diving.Archivedfrom the original on 2 April 2016.Retrieved3 June2016.
- ^"French Polynesian Rugby – Rugby is a hit in Tahiti!".Where to play rugby. 25 February 2020.Archivedfrom the original on 11 August 2022.Retrieved25 June2022.
- ^"Comptes économiques – Données essentielles".Institut de la statistique de la Polynésie française (ISPF).Archivedfrom the original on 3 March 2022.Retrieved3 March2022.
- ^abInstitut d'émission d'Outre-Mer(IEOM)."La Polynésie française en 2008"(PDF)(in French).Archived(PDF)from the original on 17 August 2022.Retrieved14 September2009.
- ^Manheim, F. T. (1986)."Marine Cobalt Resources".Science.232(4750): 600–608.Bibcode:1986Sci...232..600M.doi:10.1126/science.232.4750.600.ISSN0036-8075.PMID17781410.S2CID21146020.Archivedfrom the original on 1 April 2021.Retrieved1 July2019.
- ^"NATITUA submarine cable system to bridge French Polynesian digital divide".lightwaveonline.25 July 2017.Archivedfrom the original on 24 October 2018.Retrieved23 October2018.
- ^"Submarine cable extended to French Polynesia's Hao".Radio New Zealand.7 August 2018.Archivedfrom the original on 24 October 2018.Retrieved23 October2018.
Bibliography[edit]
- Aldrich, Robert(1990).The French Presence in the South Pacific, 1842–1940.Sydney.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Aldrich, Robert(1993).France and the South Pacific since 1940.Sydney.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Charpentier, Jean-Michel;François, Alexandre(2015).Atlas Linguistique de Polynésie Française — Linguistic Atlas of French Polynesia(in French and English). Mouton de Gruyter & Université de la Polynésie Française.ISBN978-3-11-026035-9.
- Danielsson, Bengt(1965).Work and Life on Raroia: An Acculturation Study from the Tuamotu Group, French Oceania.London: G. Allen & Unwin.
- Danielsson, Bengt; Marie-Thérèse Danielsson (1986).Poisoned Reign: French Nuclear Colonialism in the Pacific.New York:Penguin Books.ISBN0-14-008130-5.
- Hough, Richard(1995).Captain James Cook.W W Norton.ISBN0-393-03680-4.
- Pollock, Nancy J.;Ron Crocombe,eds. (1988).French Polynesia: A Book of Selected Readings.Suva, Fiji: Institute of Pacific Studies of the University of the South Pacific.ISBN982-02-0032-6.
- James Rogers and Luis Simón.The Status and Location of the Military Installations of the Member States of the European Union and Their Potential Role for the European Security and Defence Policy (ESDP).Brussels: European Parliament, 2009. 25 pp.
- Jean-Marc Régnault,Le pouvoir confisqué en Polynésie française. L'affrontement Temaru-Flosse.Les Indes savantes, 2005.
- Thompson, Virginia; Richard Adloff (1971).The French Pacific Islands: French Polynesia and New Caledonia.Berkeley: University of California Press.
External links[edit]
- Government
- High Commission of the Republic in French Polynesia
- Presidency of French Polynesia
- Assembly of French Polynesia
- Legal publication service in French Polynesia
- Administrative Subdivisions of French Polynesia
- General information
- (in French)Encyclopédie collaborative du patrimoine culturel et naturel polynésien
- French Polynesia.The World Factbook.Central Intelligence Agency.
- French PolynesiaatUCB Libraries GovPubs
- French PolynesiaatCurlie
 Wikimedia Atlas of French Polynesia
Wikimedia Atlas of French Polynesia
- Travel
- French Polynesia
- 1842 establishments in Oceania
- 1842 establishments in the French colonial empire
- European colonisation in Oceania
- French-speaking countries and territories
- Geography of Polynesia
- Island countries
- Overseas collectivities of France
- Small Island Developing States
- States and territories established in 1842