Glacis
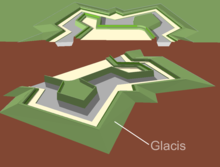
Aglacis(/ˈɡleɪ.sɪs/,French:[ɡlasi]) inmilitary engineeringis an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or inearly modern fortresses.They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis is any slope, natural or artificial, which fulfils the above requirements. The etymology of this French word suggests a slope made dangerous with ice, hence the relationship withglacier.
Aglacis plateis theslopedfront-most section of the hull of atankor otherarmoured fighting vehicle.
Ancient fortifications[edit]

A glacis could also appear in ancient fortresses, such as the one theancient Egyptiansbuilt atSemnainNubia.Here it was used by them to prevent enemysiege enginesfrom weakeningdefensive walls.
Hillforts in Britainstarted to incorporate glacis around 350 BC. Those atMaiden Castle,Dorset were 25 metres (82 ft) high.[1]
Medieval fortifications[edit]

Glacis, also calledtalus,were incorporated into medieval fortifications to strengthen the walls against undermining, to hamperescaladesand so that missiles dropped from the battlements would ricochet off the glacis into attacking forces.[2]
Towards the end of the medieval period some castles were modified to make them defensible against cannons. Glacis consisting of earthen slopes faced with stones were placed in front of the curtain walls and bastions (towers) to absorb the impact of cannon shots or to deflect them. Towers were lowered to the same height as the curtain walls and converted into gun platforms.[3]
Early modern European fortifications[edit]
Early modern European fortresses were so constructed as to keep any potential assailant under the fire of the defenders until the last possible moment. On natural, level ground, troops attacking any high work have a degree of shelter from its fire when close up to it; the glacis consists of a slope with a low grade inclined towards the top of the wall. This gave defenders a direct line of sight into the assaulting force, allowing them to efficiently sweep the field with fire from theparapet.Additionally, but secondarily, the bank of earth would shield the walls from being hit directly by cannon fire.[4][5]
Though defenders on high ground already have a direct line of sight, a glacis allows thefield of fireto be swept more efficiently by minimizing changes to the angle of their guns while firing. Furthermore, the glacis prevents attacking cannon from having a clear shot at the walls of a fortress, as usually these cannot be seen until the glacis is crossed and the ditch, bounded on either side by the smooth, masoned scarp andcounterscarp,is reached.[4]
Armored vehicles[edit]

The termglacis platedescribes the sloped front-most section of the hull of atankor other armored fighting vehicle,[6]often composed of upper and lower halves. In a head-on-head armored engagement, the glacis plate is the largest and most obvious target available to an enemy gunner.
Sloped armourhas two advantages: many projectiles will deflect rather than penetrate; those that attempt to will have to travel on a longer diagonal route through any given thickness of armor than if it were perpendicular to their trajectory.
Anti-tank minesthat employ atilt-rod fuzeare also designed to detonate directly underneath the glacis plate. As a result, it is generally the thickest, most robust armored section of a tank, followed by the turret face andgun mantlet.
Gallery[edit]
-
Iron Age ramparts and ditches inMaiden Castle.
-
Glacis,Mont-LouisFortress,Pyrénées-Orientales,France
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Dyer 1992,p. 19.
- ^Decaëns & Dubois 2010,p. 17.
- ^Stokstad 2005,p. 84.
- ^abJackson 1911.
- ^"The Terminology of a Fortress:Glacis".fortadams.org.RetrievedJune 14,2014.
- ^"Glacis plate".Encarta Online Dictionary. December 14, 2008. Archived fromthe originalon May 24, 2024.
Bibliography[edit]
- Jackson, Louis (1911)..InChisholm, Hugh(ed.).Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 10 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 679–725.
- Decaëns, Joseph; Dubois, Adrien, eds. (2010).Caen Castle: A Ten Centuries Old Fortress(illustrated ed.). Publications du Crahm. p.17.ISBN9782902685752.
- Dyer, James (1992).Hillforts of England and Wales.Shire Series. Vol. 16 (illustrated, revised ed.). Osprey Publishing. p.19.ISBN9780747801801.
- Stokstad, Marilyn (2005).Medieval Castles.Greenwood guides to historic events of the medieval world (illustrated, annotated ed.). Greenwood Publishing Group. p.84.ISBN9780313325250.


