Grey junglefowl
| Grey junglefowl | |
|---|---|

| |
| Cock inBandipur National Park | |

| |
| Hen inThattekad Bird Sanctuary | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Galliformes |
| Family: | Phasianidae |
| Genus: | Gallus |
| Species: | G. sonneratii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Gallus sonneratii Temminck,1813
| |
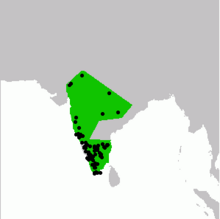
| |
| Actual spot records and presumed distribution | |
Thegray junglefowl(Gallus sonneratii), also known asSonnerat's junglefowl,is one of the wild ancestors of thedomestic chickentogether with thered junglefowland otherjunglefowls.
The species epithet commemorates the French explorerPierre Sonnerat.Local names includeKomriinRajasthan,Geera kurorParda komriinGondi,Jangli MurghiinHindi,Raan kombdiinMarathi,Kattu KozhiinTamilandMalayalam,Kaadu koliinKannadaandTella adavi kodiinTelugu.[3]
Description
[edit]

The male has a black cape with ochre spots and the body plumage on a grey ground colour is finely patterned. The elongated neck feathers are dark and end in a small, hard, yellowish plate; this peculiar structure making them popular for making high-gradeartificial flies.[4]The male has red wattles and combs but not as strongly developed as in thered junglefowl.Legs of males are red and have spurs while the yellow legs of females usually lack spurs.[5][6]The central tail feathers are long and sickle shaped. Males have an eclipse plumage in which they moult their colourful neck feathers in summer during or after the breeding season.[7]
The female is duller and has black and white streaking on the underparts and yellow legs.
Distribution and habitat
[edit]This species isendemictoIndia,and even today it is found mainly in peninsular India and towards the northern boundary. They are found in thickets, on the forest floor and open scrub. The species occurs mainly in theIndian Peninsula,but extends intoGujarat,Madhya Pradeshand southern Rajasthan. Thered junglefowlis found more along the foothills of theHimalayas;a region of overlap occurs in theAravallirange.[5]although the ranges are largely non-overlapping.[8]
Disputed subspecies
[edit]The populations from theregionofMount Abuin Rajasthan named as thesubspecieswangyeliis usually not recognized[9]although it is said that the calls of the cock from this region differs from the call of birds from southern India and the plumage is much paler.[8]
Behaviour
[edit]Their loud calls ofKu-kayak-kyuk-kyuk() are loud and distinctive, and can be heard in the early mornings and at dusk. Unlike the red junglefowl, the male does not flap its wings before uttering the call.[10]They breed from February to May.[5]They lay 4 to 7 eggs which are pale creamy in a scrape. Eggs hatch in about 21 days. Although mostly seen on the ground, grey junglefowl fly into trees to escape predators and to roost. They forage in small mixed or single sex groups. They feed on grains includingbambooseeds, berries, insects andtermites,and are hunted for meat and for the long neck hackle feathers that are sought after for makingfishing lures.
Relationships
[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cladogramshowing the species in the genusGallus.[11][12] |
Gray junglefowl have been bred domestically inEnglandsince 1862[13]and their feathers have been commercially supplied from domestic U.K. stocks forfly tyingsince 1978.[13]A gene from the gray junglefowl is responsible for the yellow pigment in the legs and different body parts of all the domestic chicken breeds.[14]A more recent study revealed multiple gray junglefowl genomic regions introgressed the genome of the domestic chicken, with evidence of some domestic chicken genes also found in the gray junglefowl.[11]
The gray junglefowl will sometimeshybridizein the wild with thered junglefowl.It also hybridizes readily in captivity and sometimes with free-range domestic chickens kept in habitations close to forests. The gray junglefowl and red junglefowl diverged about 2.6 million years ago.[11] The species has been isolated by a variety of mechanisms, including behavioural differences and genic incompatibility, but hybridization is not unknown.[15][16]Some phylogenetic studies of gray junglefowl show that this species is more closely related to theSri Lankan junglefowlGallus lafayetiithan to the red junglefowl,Gallus gallus,[11][17]but another study shows a more ambiguous position due to hybridization.[18]However, the time of divergence between the gray junglefowl andSri Lankan junglefowlaround 1.8 million years ago is more recent than 2.6 million years ago calculated for between the gray junglefowl and red junglefowl.[11]This divergence time supports a sister relationship between gray junglefowl and Sri Lankan junglefowl.[11]
An endogenous retroviral DNA sequence, of the EAV-HP group noted in domestic chickens is also found in the genome of this species pointing to the early integration of the virus DNA into the genome ofGallus.[19]
References
[edit]- ^BirdLife International (2016)."Gallus sonneratii".IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.2016:e.T22679203A92807338.doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22679203A92807338.en.Retrieved12 November2021.
- ^"Appendices | CITES".cites.org.Retrieved2022-01-14.
- ^Anonymous (1998)."Vernacular Names of the Birds of the Indian Subcontinent"(PDF).Buceros.3(1): 53–109. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2010-04-01.
- ^"Identification Notes"(PDF).US Fish and Wildlife. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2006-09-25.Retrieved2006-10-31.
- ^abcRasmussen PC; JC Anderton (2005).Birds of South Asia: The Ripley Guide. Volume 2.Smithsonian Institution and Lynx Edicions. p. 132.
- ^"Occurrence of spurs in the female junglefowl (Gallus sonnerati) ".J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc.52(2–3): 603–604. 1954.
- ^Morejohn, G. V. (1968). "Study of the plumage of the four species of the genusGallus".The Condor.70(1): 56–65.doi:10.2307/1366508.JSTOR1366508.
- ^abAli, S.; Ripley, S. D.Handbook of the birds of India and Pakistan.Vol. 2 (2nd ed.).Oxford University Press.pp. 106–109.
- ^Storer, R. W. (1988).Type Specimens of Birds in the Collections of the University of Michigan Museum of Zoology(PDF).University of Michigan, Miscellaneous publications No. 174.
- ^Finn, Frank (1911).The game birds of India and Asia.Thacker, Spink and Co., Calcutta. pp. 21–23.
- ^abcdefLawal, R.A.; et al. (2020)."The wild species genome ancestry of domestic chickens".BMC Biology.18(13): 13.doi:10.1186/s12915-020-0738-1.PMC7014787.PMID32050971.
- ^Tiley, G.P.; Pandey, A.; Kimball, R.T.; Braun, E.L.; Burleigh, J.G. (2020)."Whole genome phylogeny ofGallus:introgression and data‑type effects ".Avian Research.11(7).doi:10.1186/s40657-020-00194-w.
- ^abBransford Game Fisheries."Jungle Cock".Bransford Game Fisheries.Fisherman's feathers.Retrieved28 September2013.
- ^"Darwin Was Wrong About Wild Origin Of The Chicken, New Research Shows".sciencedaily.
- ^Eriksson J, Larson G, Gunnarsson U, Bed'hom B, Tixier-Boichard M, et al. (2008). Georges M (ed.)."Identification of theYellow SkinGene Reveals a Hybrid Origin of the Domestic Chicken ".PLOS Genetics.4(2): e1000010.doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000010.PMC2265484.PMID18454198.
- ^Morejohn, G. Victor (1968). "Breakdown of Isolation Mechanisms in Two Species of Captive Junglefowl (Gallus gallusandGallus sonneratii) ".Evolution.22(3): 576–582.doi:10.2307/2406881.JSTOR2406881.PMID28564768.
- ^Fumihito, Akishinonomiya; Tetsuo Miyake; Masaru Takada; Ryosuke Shingut; Toshinori Endo; Takashi Gojobori; Norio Kondo & Susumu Ohno (1996)."Monophyletic origin and unique dispersal patterns of domestic fowls"(PDF).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.93(13): 6792–6795.Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.6792F.doi:10.1073/pnas.93.13.6792.PMC39106.PMID8692897.
- ^Nishibori, M.; Shimogiri, T.; Hayashi, T.; Yasue, H. (2005). "Molecular evidence for hybridization of species in the genusGallusexcept forGallus varius".Animal Genetics.36(5): 367–375.doi:10.1111/j.1365-2052.2005.01318.x.PMID16167978.
- ^Sacci, MA; K Howes; K Venugopal (2001)."Intact EAV-HP Endogenous Retrovirus in Sonnerat's Jungle Fowl".Journal of Virology.75(4): 2029–2032.doi:10.1128/JVI.75.4.2029-2032.2001.PMC115153.PMID11160706.
Other sources
[edit]- Tehsin, Raza H (1988) Inducing sleep in birds. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 85(2):435-436.
- Chitampalli, MB (1977) Occurrence of Grey Junglefowl and Red Junglefowl together. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 74(3):527.
- Abdulali, Humayun (1957) The Grey Junglefowl in Salsette. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 54(4):946.
- Tehsin, Raza; Tehsin, Fatema (1990) Jungle CatFelis chausand Grey JunglefowlGallus sonneratii.J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 87(1):144.
- Morris, RC (1927) A jungle fowl problem. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 32(2):374.
- Sethna, KR (1969)."Grey Junglefowl in South India".Newsletter for Birdwatchers.9(11): 10.
- Ali, S (1968) The case of the Indian Grey Junglefowl.Newsletter for Birdwatchers.8(5):5-6.
- Subramanian, C; Kambarajan, P; Sathyanarayana, MC (2001) Roosting tree preference by Grey Junglefowl, (Gallus sonneratti) at Theni Forest Division, Western Ghats, Tamil Nadu, south India. Mor 4(February), 9:11.
- Zacharias, VJ (1993) Grey Jungle Fowl in Kerala. WPA-India News 1(1):9-10.

