Demersal fish


Demersal fish,also known asgroundfish,live and feed on or near the bottom ofseasorlakes(thedemersal zone).[1]They occupy the sea floors and lake beds, which usually consist of mud, sand, gravel or rocks.[1]In coastal waters, they are found on or near thecontinental shelf,and in deep waters, they are found on or near thecontinental slopeor along the continental rise. They are not generally found in the deepest waters, such asabyssaldepths or on theabyssal plain,but they can be found aroundseamountsand islands. The worddemersalcomes from theLatindemergere,which meansto sink.
Demersal fish arebottom feeders.They can be contrasted withpelagic fish,which live and feed away from the bottom in the openwater column. Demersal fish fillets contain littlefish oil(one to four per cent), whereas pelagic fish can contain up to 30 per cent.[not verified in body]
Types
[edit]
Demersal fish can be divided into two main types: strictlybenthicfish which can rest on the sea floor, andbenthopelagicfish which can float in thewater columnjust above the sea floor.
Benthopelagic fish haveneutral buoyancy,so they can float at depth without much effort, while strictly benthic fish are denser, with negative buoyancy so they can lie on the bottom without any effort.[2]Most demersal fish are benthopelagic.[1]
As with other bottom feeders, a mechanism to deal withsubstrateis often necessary. With demersal fish the sand is usually pumped out of the mouth through thegill slit.Most demersal fish exhibit a flat ventral region so as to more easily rest their body on the substrate. The exception may be theflatfish,which are laterally depressed but lie on their sides. Also, many exhibit what is termed an "inferior" mouth, which means that the mouth is pointed downwards; this is beneficial as their food is often below them in the substrate. Those bottom feeders with upward-pointing mouths, such asstargazers,tend to seize swimming prey.
Benthic fish
[edit]Benthic fish are denser than water, so they can rest on the sea floor. They either lie-and-wait asambush predators,at times covering themselves with sand or otherwise camouflaging themselves, or move actively over the bottom in search for food.[3]Benthic fish which can bury themselves includedragonets,flatfishandstingrays.
Flatfishare anorderofray-finnedbenthic fishes which lie flat on the ocean floor. Examples areflounder,sole,turbot,plaice,andhalibut.The adult fish of many species have both eyes on one side of the head. When the fish hatches, one eye is located on each side of its head. But as the fish grows from the larval stage, one eye migrates to the other side of the body as a process ofmetamorphosis.The flatfish then changes its habits, and camouflages itself by lying on the bottom of the ocean floor with both eyes facing upwards.[4]The side to which one eye migrates depends on the species; with some species both eyes are ultimately on the left side, whereas with other species the eyes are on the right.
-
Flounderhave both eyes on one side of their head
-
Some flatfish can camouflage themselves on the ocean floor
-
Bluespotted ribbontail raysmigrate in schools onto shallow sands to feed on mollusks, shrimps, crabs and worms.[5]
-
Thegreat hammerheaddetects the electrical signatures of stingrays buried in the sand and pins them with its "hammer".[6]
Flounder ambush their prey, feeding at soft muddy area of the sea bottom, near bridge piles, docks, artificial and coral reefs. Their diet consists mainly of fish spawn,crustaceans,polychaetesand small fish.
Thegreat hammerheadswings its head in broad angles over the sea floor to pick up the electrical signatures of stingrays buried in the sand. It then uses its "hammer" to pin down the stingray.[7]
-
Pacific hagfishresting on bottom. Hagfish coat themselves and any dead fish they find with noxious slime making them inedible to other species.
-
The tripodfish (Bathypterois grallator), a species of spiderfish, uses its fin extensions to "stand" on the bottom.[8]
-
Thefringe-lipped flatheadis found in estuaries
Some fishes do not fit into the above classification. For example, the family of nearly blindspiderfishes,common and widely distributed, feed on benthopelagic zooplankton. Yet they are strictly benthic fish, since they stay in contact with the bottom. Their fins have long rays they use to "stand" on the bottom while they face the current and grab zooplankton as it passes by.[9]
The bodies of benthic fish are adapted for ongoing contact with the sea floor. Swimbladders are usually absent or reduced, and the bodies are usually flattened in one way or another.[10]Following Moyle and Cech (2004) they can be divided into five overlapping body shapes:[10]
| Body types of benthic fish | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bottom rovers | Bottom rovers "have a rover-predator-like body, except that the head tends to be flattened, the back humped, and the pectoral fins enlarged.North American catfishwith large mouths at the end of the snout, smallarmoured catfishwith small mouths beneath the snout, andsturgeons,with fleshy protusible lips located well below the snout that are used to suck plant and animal matter off the bottom. "[11] | |
| Bottom clingers |  |
Bottom clingers "are mainly small fish with flattened heads, large pectoral fins, and structures (usually modified pelvic fins) that enable them to adhere to the bottom. Such structures are handy in swift streams, or intertidal areas with strong currents. The simplest arrangement is possessed bysculpins,which use their small, closely spaced pelvic fins, as antiskid devices. However, other families of fishes, such asgobies,andclingfisheshave evolved suction cups. "[11] |
| Bottom hiders |  |
Bottom hiders "are similar in many ways to bottom clingers. but they lack the clinging devices and tend to have more elongate bodies and smaller heads. These forms usually live under rocks or in crevices or lie quietly on the bottom in still waters. Thedartersof North American streams are in the category, as are manyblennies."[11] |
| Flatfish |  |
Flatfish "have the most extreme morphologies of the bottom fish.Floundersare essentially deep-bodied fish which live with one side on the bottom. In these fish, the eye on the downward side migrates during development to the upward side, and the mouth often assumes a peculiar twist to enable bottom feeding. In contrast,skatesandraysare flatteneddorsoventrally,and mostly move about by flapping their extremely largepectoral fins.Not only is the mouth completelyventralon these fish, the main water intakes for respiration (thespiracles) are located on the top of the head. "[11] |
| Rattail-shaped fish | Rattail-shaped fish "have bodies that begin with large pointy-snouted heads and largepectoral finsand end in long pointed rat-like tails. These fish are almost all bottom-dwelling (benthic) inhabitants of the deep sea, but exactly why this peculiar morphology is so popular among them is poorly understood. The fish live by scavenging and preying on benthic invertebrates. Examples are thegrenadiers,viviparous brotulas(pictured), andchimaeras."[11] | |
Benthopelagic fish
[edit]
Benthopelagic fish inhabit the water just above the bottom, feeding onbenthosandzooplankton.[15]Most demersal fish are benthopelagic.[1]
Deep sea benthopelagicteleostsall haveswimbladders.The dominant species,rattailsandcusk eels,have considerable biomass. Other species include deep seacods(morids), deep sea eels,halosaursandnotacanths.[16]
Benthopelagic sharks, like the deep seasqualoid sharks,achieve neutral buoyancy with the use of largeoil-filled livers.[2]Sharks adapt well to fairly high pressures. They can often be found on slopes down to about 2000 metres, scavenging on food falls such asdead whales.However, the energy demands of sharks are high, since they need to swim constantly and maintain a large amount of oil for buoyancy. These energy needs cannot be met in the extremeoligotrophicconditions that occur at great depths.[2]
Shallow water stingrays are benthic, and can lie on the bottom because of their negative buoyancy. Deep sea stingrays are benthopelagic, and like the squaloids have very large livers which give them neutral buoyancy.[2]
Benthopelagic fish can be divided into flabby or robust body types. Flabby benthopelagic fishes are likebathypelagic fishes;they have a reduced body mass, and low metabolic rates, expending minimal energy as they lie and wait toambushprey.[17]An example of a flabby fish is thecusk-eelAcanthonus armatus,[18]a predator with a huge head and a body that is 90 per cent water. This fish has the largest ears (otoliths) and the smallest brain in relation to its body size of all known vertebrates.[19]
Deepwater benthopelagic fish are robust, muscular swimmers that actively cruise the bottom searching for prey. They often live around features, such asseamounts,which have strong currents.[19]Commercial examples are theorange roughyandPatagonian toothfish.
Habitats
[edit]
The edge of thecontinental shelfmarks the boundary where the shelf gives way to, and then gradually drops intoabyssaldepths. This edge marks the boundary between coastal, relatively shallow, benthic habitats, and the deep benthic habitats. Coastal demersal fishes live on the bottom of inshore waters, such as bays and estuaries, and further out, on the floor of thecontinental shelf.Deep water demersal fish live beyond this edge, mostly down thecontinental slopesand along the continental rises which drop to theabyssal plains.This is thecontinental margin,constituting about 28% of the total oceanic area.[20]Other deep sea demersal fish can also be found aroundseamountsand islands.
The termbathydemersal fishis sometimes used instead of "deep water demersal fish".Bathydemersalrefers to demersal fish which live at depths greater than 200 metres.
The termepibenthicis also used to refer to organism that live on top of the ocean floor, as opposed to those that burrow into the seafloor substrate. However the termsmesodemersal,epidemersal,mesobenthicandbathybenthicare not used.
Coastal
[edit]Coastal demersal fish are found on or near the seabed of coastal waters between theshorelineand the edge of thecontinental shelf,where the shelf drops into the deep ocean. Since the continental shelf is generally less than 200 metres deep, this means that coastal waters are generallyepipelagic.The term includes demersalreef fishand demersal fish that inhabitestuaries,inletsandbays.
-
Themangrove jackeatscrustaceans
-
Manypuffer fishspecies crush the shells ofmolluscs
-
Triggerfishuse a jet of water to uncoversand dollarsburied in sand
Youngmangrove jacks,a sought after eating andsport fish,dwell inestuariesaroundmangroveroots, fallen trees, rock walls, and any other snag areas where smaller prey reside for protection. When they mature, they migrate into open waters, sometimes hundreds of kilometres from the coast to spawn.[22][23]

Stargazersare found worldwide in shallow waters. They have eyes on top of their heads and a large upward-facing mouth. They bury themselves in sand, and leap upwards to ambush benthopelagic fish andinvertebratesthat pass overhead. Some species have a worm-shaped lure growing out of the floor of the mouth, which they wiggle to attract prey. Stargazers arevenomousand can deliverelectric shocks.They have been called "the meanest things in creation."[25][26][27]
Other examples of coastal demersal fish arecod,plaice,monkfishandsole.
Deep water
[edit]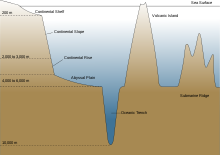
Deep water demersal fish occupy thebenthic regionsbeyond the continental margins.
On thecontinental slope,demersal fishes are common. They are more diverse than coastal demersal fish, since there is more habitat diversity. Further out are theabyssal plains.These flat, featureless regions occupy about 40 per cent of the ocean floor. They are covered withsedimentbut largely devoid of benthic life (benthos). Deep sea benthic fishes are more likely to associate with canyons or rock outcroppings among the plains, where invertebrate communities are established. Undersea mountains (seamounts) can intercept deep sea currents, and cause productive upwellings which support benthic fish. Undersea mountain ranges can separate underwater regions into different ecosystems.[28]
Rattailsandbrotulasare common, and other well-established families areeels,eelpouts,hagfishes,greeneyes,batfishesandlumpfishes.[28]
The bodies of deep water demersal fishes are muscular with well developed organs. In this way they are closer tomesopelagic fishesthanbathypelagic fishes.In other ways, they are more variable.Photophoresare usually absent, eyes andswimbladdersrange from absent to well developed. They vary in size, and larger species, greater than one metre, are not uncommon.

Deep sea demersal fish are usually long and narrow. Many areeelsor shaped like eels. This may be because long bodies have longlateral lines.Lateral lines detect low-frequency sounds, and some demersal fishes have muscles that drum such sounds to attract mates.[29]Smell is also important, as indicated by the rapidity with which demersal fish find traps baited withbait fish.
The main diet of deep sea demersal fish isinvertebratesof the deep seabenthosandcarrion.Smell, touch and lateral line sensitivities seem to be the main sensory devices for locating these.[3]
Like coastal demersal fish, deep sea demersal fish can be divided into benthic fish and benthopelagic fish, where the benthic fish are negatively buoyant and benthopelagic fish are neutrally buoyant.[3]
The availability of plankton for food diminishes rapidly with depth. At 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), the biomass of plankton is typically about 1 per cent of that at the surface, and at 5,000 metres (16,000 ft) about 0.01 per cent.[16]Given there is no sunlight, energy enters deep water zones as organic matter. There are three main ways this happens. Firstly, organic matter can move into the zone from the continental landmass, for example, through currents that carry the matter down rivers, then plume along the continental shelf and finally spill down the continental slope. Other matter enters as particulate matter raining down from the overhead water column in the form ofmarine snow,or as sinking overhead plant material such aseelgrass,or as "large particles" such as dead fish and whales sinking to the bottom. A third way energy can arrive is through fish, such as vertically migrating mesopelagic fishes that can enter into the demersal zone as they ascend or descend. The demersal fish and invertebrates consume organic matter that does arrive, break it down and recycle it. A consequence of these energy delivery mechanisms is that the abundance of demersal fish and invertebrates gradually decrease as the distance from continental shorelines increases.[30]
Although deep water demersal fish species are not generally picky about what they eat, there is still some degree of specialisation. For example, different fish have different mouth sizes, which determines the size of the prey they can handle. Some feed mostly on benthopelagic organisms. Others fed mostly onepifauna(invertebrates on top of the seafloor surface, also calledepibenthos), or alternatively oninfauna(invertebrates that burrow into the seafloor substrate). Infauna feeders can have considerable sediment in their stomachs. Scavengers, such assnubnosed eelsandhagfish,also eat infauna as a secondary food source.[31]
Some feed on carrion. Cameras show that when a dead fish is placed on the bottom, vertebrate and invertebrate scavengers appear very quickly. If the fish is large, some scavengers burrow in and eat it from the inside out. Some fish, such asgrenadiers,also appear and start feeding on the scavenging invertebrates andamphipods.Other specialization is based on depth distribution. Some of the more abundant upper continental slope fish species, such ascutthroat eelandlongfinned hake,[33]mainly feed onepipelagic fish.But generally, the most abundant deep water demersal fish species feed on invertebrates.[31][34]
At great depths, food scarcity and extreme pressure limits the ability of fish to survive. The deepest point of the ocean is about 11,000 metres.Bathypelagic fishesare not normally found below 3,000 metres.[35]It may be that extreme pressures interfere with essential enzyme functions.[36]
The deepest-living fish known, the strictly benthicAbyssobrotula galatheae,eel-like and blind, feeds on benthic invertebrates. A living example was trawled from the bottom of thePuerto Rico Trenchin 1970 from a depth of 8,370 metres (27,453 ft).[37][38]
In 2008, a shoal of 17hadal snailfish,a species of deep watersnailfish,was filmed by a UK-Japan team using remote operated landers at depths of 7.7 km (4.8 mi) in theJapan Trenchin the Pacific. The fish were 30 centimetres long (12 in), and were darting about, using vibration sensors on their nose to catch shrimps. The team also reported that the appearance of the fish, unlike that of most deep sea fish, was surprisingly "cute", and that they were surprised by how active the fish were at these depths.[39][40]
Demersal fisheries
[edit]This section needs to beupdated.(November 2017) |
Most demersal fish of commercial or recreational interest are coastal, confined to the upper 200 metres. Commercially important demersalfood fishspecies includeflatfish,such asflounder,sole,turbot,plaice,andhalibut.Also important arecod,hake,redfish,haddock,bass,congers,sharks,raysandchimaeras.[41]
The following table shows the world capture production of some groups of demersal species in tonnes.[42]
| Capture production by groups of species in tonnes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 |  |
| Cods,hakes,haddocks | 9,431,141 | 8,695,910 | 9,304,922 | 8,474,044 | 9,385,328 | 9,398,780 | 8,964,873 | |
| Flounders,halibuts,soles | 956,926 | 1,009,253 | 948,427 | 915,177 | 917,326 | 862,162 | 900,012 | |
| Other demersal fishes | 2,955,849 | 3,033,384 | 3,008,283 | 3,062,222 | 3,059,707 | 3,163,050 | 2,986,081 | |
Black sea bassinhabit US coasts fromMaineto NEFloridaand the easternGulf of Mexico,and are most abundant off the waters ofNew York.They are found in inshore waters (bays and sounds) and offshore in waters up to a depth of 130 m (425'). They spend most of their time close to the sea floor and are often congregated around bottom formations such as rocks,man-made reefs,wrecks, jetties, piers, andbridge pilings.Black sea bass are sought after recreational and commercial fish, and have beenoverfished.[43]
-
American plaiceare usually found between 90 and 250 metres (but have been found at 3000 m). They feed on small fishes and invertebrates.[44]
-
Atlantic codare usually found between 150 and 200 metres, they are omnivorous and feed on invertebrates and fish, including young cod.[45]
-
Grouperare ambush predators with a powerful sucking system that sucks their prey in from a distance
Grouperare often found around reefs. They have stout bodies and large mouths. They are not built for long-distance or fast swimming. They can be quite large, and lengths over a meter and weights up to 100 kg are not uncommon. They swallow prey rather than biting pieces off it. They do not have many teeth on the edges of their jaws, but they have heavy crushing tooth plates inside thepharynx.They lie in wait, rather than chasing in open water. They are found in areas of hard or consolidated substrate, and use structural features such as ledges, rocks, and coral reefs (as well asartificial reefslike wrecks and sunken barges) as their habitat. Their mouth andgillsform a powerful sucking system that sucks their prey in from a distance. They also use their mouth to dig into sand to form their shelters under big rocks, jetting it out through their gills. Their gill muscles are so powerful that it is nearly impossible to pull them out of their cave if they feel attacked and extend those muscles to lock themselves in. There is some research indicating that roving coral groupers (Plectropomus pessuliferus) sometimes cooperate withgiant moraysin hunting.[46]
-
ThePatagonian toothfishis a robust benthopelagic fish
-
Theorange roughyis also a robust benthopelagic fish
-
Theblue grenadier(hoki), a deep water demersal fish, is subjected to a largesustainable fishingindustry in New Zealand.[47]
Deepwater benthopelagic fish are robust, muscular swimmers that actively cruise the bottom searching for prey. They often live around features, such asseamounts,which have strong currents.[19]Commercial examples are theorange roughyandPatagonian toothfish.Because these fish were once abundant, and because their robust bodies are good to eat, these fish have been commercially harvested.[48][49]
Conservation status
[edit]| This article is part of a series on |
| Commercial fish |
|---|
| Large pelagic |
| Forage |
| Demersal |
| Mixed |
Major demersal fishery species in theNorth Seasuch ascod,plaice,monkfishandsole,are listed by theICESas "outside safe biological limits."
The by-catch problem
A major problem in conservation of demersal fish populations is that of by-catch, whereby fish are caught by accident when targeting other species. The European Commission has written that “A key issue is that many of the most important demersal stocks (i.e. those that live on or near the bottom of the sea) are caught in mixed fisheries. In practice, this means that each time a vessel retrieves its fishing gear, its catch will consist of a mix of different species.”[50]This has led to a situation whereby, even when the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea recommends a Total Allowable Catch of zero for a given demersal species in order to allow replenishment of population, the European Council nonetheless sets the Total Allowable Catch far above zero so long as the catch is by-catch, in order not to prevent trawlers fishing for other species.[51]This means that those threatened species do not get the chance to replenish even when not directly targeted by trawlers.
- The Common Sole,Solea solea,is sufficiently broadly distributed that it is not considered a threatened species; however,overfishingin Europe has produced severely diminished populations, with declining catches in many regions. For example, the westernEnglish ChannelandIrish Seasole fisheries face potential collapse according to data in the UKBiodiversity Action Plan.
- Sole, along with the other major bottom-feeding fish in the North Sea such as cod, monkfish, and plaice, is listed by theICESas "outside safe biological limits." Moreover, they are growing less quickly now and are rarely older than six years, although they can reach forty. World stocks of large predatory fish and large ground fish such as sole and flounder were estimated in 2003 to be only about 10% of pre-industrial levels.[52][53][54]According to theWorld Wildlife Fundin 2006, "of the nine sole stocks, seven are overfished with the status of the remaining two unknown." Data is insufficient to assess the remaining stocks; however, landings for all stocks are at or near historical lows. "[55]
- World stocks of large predatory fish and large ground fish such as sole and flounder were estimated in 2003 to be only about 10% of pre-industrial levels, largely due to overfishing. Most overfishing is due to the extensive activities of the fishing industry.[56][57][58][59]Current research indicate that the flounder population could be as low as 15 million due to heavy overfishing and industrial pollution along the Gulf of Mexico surrounding the coast of Texas.
- Seafood Watchhave placed on their list of seafood thatsustainability-minded consumers should avoid the following demersal fish:sturgeon(imported wild),Chilean seabass,cod (Atlantic, imported Pacific),flounder(Atlantic),halibut(Atlantic), sole (Atlantic),grouper,monkfish,orange roughy,demersalshark,red snapperandtilapia(Asia farmed).[60]
See also
[edit]- Benthic zone– Ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water
- Benthos– Community of organisms that live in the benthic zone
- Bottom feeder– Aquatic animal that feeds on the bottom of a body of water
- Bottom trawling– Fishing method for fishing trawlers
- Deep sea– Lowest layer in the ocean
- Deep sea fish– Fauna found in deep-sea areas
- Pelagic fish– Fish in the pelagic zone of ocean waters
- Whitefish– Several species of demersal fish with fins
Notes
[edit]- ^abcdWalrond CCarl. "Coastal fish - Fish of the open sea floor"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009
- ^abcdBone 2008, p. 42.
- ^abcMoyle and Cech, 2004, p. 588
- ^Fairchild, E.A. and Howell, W.H, E. A.; Howell, W. H. (2004)."Factors affecting the post-release survival of cultured juvenile Pseudopleuronectes americanus"(PDF).Journal of Fish Biology.65(Supplementary A): 69–87.CiteSeerX10.1.1.532.3120.doi:10.1111/j.0022-1112.2004.00529.x.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 18 August 2007.
{{cite journal}}:CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)July 17, 2004. Accessed 2009-06-08. - ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Taeniura lymma"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^"Sandy Plains: Great Hammerhead Shark".elasmo-research.org.Retrieved19 January2022.
- ^Hammerschlag, Rick.Sandy Plains: Great Hammerhead Shark.ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research.Retrieved: 6 June 2022.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Bathypterois grallator"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Sulak KJ ()"The systematics and biology ofBathypterois (Pisces, Chlorophthalmidae)with a revised classification of benthic myctophiform fishes "Ichthyological Research,32(4)443-446.
- ^abMoyle and Cech, 2004, p. 13
- ^abcdeMoyle and Cech, 2004, p. 14
- ^Compagno, Leonard J.V. (1984).Sharks of the World: An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Shark Species Known to Date.Rome:Food and Agriculture Organization.ISBN978-92-5-101384-7.
- ^Martin, R.A.Procellariidae and Pseudotriakidae: Finback & False Catsharks.ReefQuest Centre for Shark Research.Retrieved on February 14, 2009.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Pseudotriakis microdon"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Mauchline J and Gordon JDM (1986) "Foraging strategies of deep-sea fish" ]Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.27:227-238.Download
- ^abBone 2008, p. 43.
- ^Koslow JA (1996)"Energetic and life-history patterns of deep-sea benthic, benthopelagic and seamount-associated fish"Journal of Fish Biology,49(sA) 54-74.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Acanthonus armatus"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^abcFine ML, Horn MH and Cox B (1987)"Acanthonus armatus,a Deep-Sea Teleost Fish with a Minute Brain and Large Ears "Proceedings of the Royal Society B,230(1259)257-265.
- ^P. J. Cook, Chris Carleton (2000) "Continental Shelf Limits: The Scientific and Legal Interface",ISBN0-19-511782-4
- ^Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2009)."Batrachoididae"inFishBase.September 2009 version.
- ^Russell, D.J., et al., "Biology, Management and Genetic Stock Structure of Mangrove Jack (Lutjanus argentimaculatus) in Australia," The State of Queensland, Department of Primary Industries and the Fisheries Research Development Corporation, FRDC Project Number 1999/122, 2003.
- ^"FAO Fisheries & Aquaculture - Aquatic species".fao.org.Archived fromthe originalon 8 May 2005.Retrieved1 September2009.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Uranoscopus sulphureus"inFishBase.September 2009 version.
- ^Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2009)."Uranoscopidae"inFishBase.September 2009 version.
- ^pixelkatt (25 March 2007)."Southern Stargazer in Utila, Honduras".Archivedfrom the original on 21 December 2021 – via YouTube.
- ^Grady, DeniseVenom Runs Thick in Fish Families, Researchers LearnThe New York Times22 August 2006.
- ^abMoyle and Cech, 2004, p. 587
- ^Haedrich RL (1996)"Deep-water fishes: evolution and adaptation in the earth's largest living spaces"Journal of Fish Biology49(sA):40-53.
- ^Moyle and Cech, 2004, p. 594
- ^abSedberry GR and Musick JA (1978)"Feeding strategies of some demersal fishes of the continental slope and rise off the mid-Atlantic coast of the USA"Marine Biology,44:357-375.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Urophycis tenuis"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Phycis chesteri"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Moyle and Cech, 2004, p. 595
- ^Nielsen, J.G. (1977). "The deepest living fishAbyssobrotula galatheae:a new genus and species of oviparous ophidioids (Pisces, Brotulidae) ".Galathea Report.14:41–48.
- ^Ryan P"Deep-sea creatures: The bathypelagic zone"Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand.Updated 21 September 2007.
- ^Nielsen JG (1977) "The deepest living fish Abyssobrotula galatheae: a new genus and species of oviparous ophidioids (Pisces, Brotulidae)".Galathea Report,14:41–48.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Abyssobrotula galatheae"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^'Deepest ever' living fish filmedBBC News,7 October 2008.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Pseudoliparis amblystomopsis"inFishBase.March 2009 version.
- ^Grainger RJK and Garcia SM (1996)"Chronicles of Marine Fishery Landings (1950-1994): Trend Analysis and Fisheries Potential"FAO:Fisheries technical paper 359.Rome.ISBN92-5-103899-6.
- ^FAO(2006)Yearbooks of Fishery Statistics Summary Tables[permanent dead link]
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Centropristis striata"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Hippoglossoides platessoides"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Gadus morhua"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Bshary, Redouan; Hohner, Andrea; Ait-el-Djoudi, Karim; Fricke, Hans (2006)."Interspecific Communicative and Coordinated Hunting between Groupers and Giant Moray Eels in the Red Sea".PLOS Biology.4(12): e431.doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040431.PMC1750927.PMID17147471.
- ^"New Zealand hoki - MSC Fisheries".msc.org.Archived fromthe originalon 6 August 2009.Retrieved31 August2009.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Hoplostethus atlanticus"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.) (2009)."Dissostichus eleginoides"inFishBase.August 2009 version.
- ^Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL establishing a multiannual plan for fish stocks in the Western Waters and adjacent waters, and for fisheries exploiting those stocks, amending Regulation (EU) 2016/1139 establishing a multiannual plan for the Baltic Sea, and repealing Regulations (EC) No 811/2004, (EC) No 2166/2005, (EC) No 388/2006, (EC) 509/2007 and (EC) 1300/2008.(Explanatory Memorandum)
- ^Judgment of the Court (Fifth Chamber) of 11 January 2024. Friends of the Irish Environment CLG v Minister for Agriculture Food and the Marine and Others. Case C-330/22.
- ^Clover, Charles. 2004.The End of the Line: How overfishing is changing the world and what we eat.Ebury Press, London.ISBN0-09-189780-7
- ^Myers, Ransom A. and Worm, Boris. "Rapid worldwide depletion of predatory fish communities."Nature423,280-283 (15 May 2003).
- ^Dalton, Rex. 2006. "Save the big fish: Targeting of larger fish makes populations prone to collapse." Published online[1]
- ^"Sustainable seafood: Consumer guides".panda.org.
- ^Clover, Charles. 2004.The End of the Line: How overfishing is changing the world and what we eat.Ebury Press, London. ISBN
- ^Myers, Ransom A. and Worm, Boris. "Rapid worldwide depletion of predatory fish communities."Nature423,280–283 (15 May 2003).
- ^Dalton, Rex (2006)."Save the big fish: Targeting of larger fish makes populations prone to collapse".BioEd Online.Archived fromthe originalon 27 March 2017.Retrieved26 March2017.
- ^Hsieh, Chih-hao; Reiss, Christian S.; Hunter, John R.; Beddington, John R.; May, Robert M.; Sugihara, George (2006). "Fishing elevates variability in the abundance of exploited species".Nature.443(7113): 859–62.Bibcode:2006Natur.443..859H.doi:10.1038/nature05232.PMID17051218.S2CID4398663.
- ^"Monterey Bay Aquarium: Seafood Watch Program - All Seafood List".Monterey Bay Aquarium. Archived fromthe originalon 6 July 2010.Retrieved17 April2008.
References
[edit]- Bone Q and Moore RH (2008)Biology of FishesTaylor & Francis Group.ISBN978-0-415-37562-7
- Merrett NR and Haedrich RL (1997)Deep-sea demersal fish and fisheriesChapman and Hall.ISBN978-0-412-39410-2.
- Moyle, PB and Cech, JJ (2004)Fishes, An Introduction to Ichthyology.5th Ed, Benjamin Cummings.ISBN978-0-13-100847-2
- Demersal fisheriesArchived7 July 2006 at theWayback MachineFishery Research Services. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- Deep water demersal fisheriesArchived7 October 2009 at theWayback MachineJoint Nature Conservation Committee.Retrieved 22 July 2009.



![Bluespotted ribbontail rays migrate in schools onto shallow sands to feed on mollusks, shrimps, crabs and worms.[5]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/39/Taeniura_lymma_2.jpg/253px-Taeniura_lymma_2.jpg)
![The great hammerhead detects the electrical signatures of stingrays buried in the sand and pins them with its "hammer".[6]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/27/Sphyrna_mokarran_head.jpg/248px-Sphyrna_mokarran_head.jpg)

![The tripodfish (Bathypterois grallator), a species of spiderfish, uses its fin extensions to "stand" on the bottom.[8]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/Bathypterois_grallator.jpg/388px-Bathypterois_grallator.jpg)






![The venomous toadfish, a benthic ambush predator, blends into sandy or muddy bottoms.[21]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e1/Opsanus_beta_1.jpg/256px-Opsanus_beta_1.jpg)


![White hake[32]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/24/Urophycis_tenuis.jpg/381px-Urophycis_tenuis.jpg)
![American plaice are usually found between 90 and 250 metres (but have been found at 3000 m). They feed on small fishes and invertebrates.[44]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/70/Hippoglossoides_platessoides.jpg/315px-Hippoglossoides_platessoides.jpg)
![Atlantic cod are usually found between 150 and 200 metres, they are omnivorous and feed on invertebrates and fish, including young cod.[45]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a3/Atlantic_cod.jpg/389px-Atlantic_cod.jpg)




![The blue grenadier (hoki), a deep water demersal fish, is subjected to a large sustainable fishing industry in New Zealand.[47]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bb/Macruronus_novaezelandiae.jpg/436px-Macruronus_novaezelandiae.jpg)





