Grumman XTSF
| XTSF | |
|---|---|
 Mockup of the XTSF-1's forward fuselage | |
| General information | |
| Type | Torpedo scout |
| Manufacturer | Grumman |
| Primary user | United States Navy |
| Number built | None |
| History | |
| Developed from | Grumman F7F Tigercat |
TheGrumman XTSFwas a proposed twin-enginetorpedo scoutaircraft, designed byGrummanfor theUnited States Navytowards the end ofWorld War II.Based on the design of theGrumman F7F Tigercatfighter, but enlarged and with the addition of a bomb bay, the XTSF was deemed too large for carrier operations, and the project was cancelled before any aircraft were built. Instead, the Navy chose to order the single-engine XTB3F, which became the successfulAF Guardian.[1]
Design and development
[edit]In 1944, it was determined that theGrumman XTB2F,then under development for the Navy, would be too large to practically and safely operate from aircraft carriers.[1]Even the newMidway-classaircraft carriers,known as "battle carriers" (CVB) and the largest aircraft carriers built by any nation to that point, would have difficulty operating the massive aircraft, which was the size of aU.S. Army Air Forcemedium bomber.[2]As a result, in late June 1944, Grumman submitted itsG-66design to theBureau of Aeronautics(BuAer).[2]After a review of the design by BuAer during the following month, a revised design was submitted, and on August 17 the existing contract for the XTB2F was modified to instead order two XTSF-1 aircraft,[2]to be based on Grumman's F7F-2 Tigercat two-seat, twin-engined fighter-bomber, the first prototype intended to be a conversion of a F7F airframe.[3]
A mid-wing, all-metal,cantilevermonoplane with twoPratt & Whitney Double Waspradial engines mounted in streamlinednacellesunder the wing,[4]the XTSF-1 was intended to carry two crew members in tandem seats, and featured an internal bomb bay and anSCR-720radar set, the radar later being replaced in the design by an AN/APS-3 or AN/APS-4set.[2]A second seat was added for the radar operator.[2]
The outer wing of the XTSF was lengthened by 7.8 feet (2.4 m) compared to that of the F7F-2, while the size of thehorizontal stabilizerwas increased by 28 inches (71 cm)).[2]Thevertical stabilizerwas also enlarged, while the aircraft's weight increased by almost two thousand pounds (910 kg) over that of the Tigercat.[2]
The wingsfolded upwardsforstowageaboard aircraft carriers, while the undercarriage andarrestor hookwerehydraulicallyoperated.[4]Gun armament was planned to be four.50caliber(12.7 mm)Browning M2machine guns,[5]or, alternatively, two20 mm Hispanocannon,[2]while abomb baybased on that of theGrumman TBF Avengerwas installed in afuselagestretched by 5.5 inches (14 cm).[2]
Cancellation
[edit]Amockupof the cockpit, center fuselage, and wing center section was built and was inspected by the BuAer in the fall 1944.[6]However, the contract for the prototype XTSF-1s was terminated in January 1945. This was due to a variety of factors, including the Navy's belief that the Grumman engineers and factory were already at capacity producing theF6F Hellcat,the F7F, and theF8F Bearcat,[7]that the XTSF-1 would be too large for practical operations fromescort carriers,[2]and because it was believed the Grumman G-70, to be built as the XTB3F, was a better prospect.[1]In addition, the F7F was proving difficult to certify for operations from aircraft carriers,[8]further prejudicing the Navy against the design.
Some sources erroneously state that the XTSF-1 became the XTB2F,[9]however this is not the case.[2]The XTSF-1 was the only aircraft ever designated by the U.S. Navy in the 'TS for Torpedo Scout' category,[6]the designation being superseded and incorporated, along with 'BT for Bomber-Torpedo', 'SB for Scout-Bomber', and 'TB for Torpedo-Bomber', into the new 'A for Attack' series.[10]
Specifications (XTSF-1)
[edit]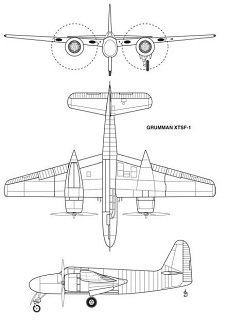
Data from[5]
General characteristics
- Crew:2 (Pilot and radar operator)
- Length:46 ft 4 in (14.12 m)
- Wingspan:59 ft 4 in (18.08 m) (folded span 32 feet (9.8 m))
- Height:16 ft (4.9 m)
- Wing area:500 sq ft (46 m2)
- Airfoil:NACA 23015-23012
- Empty weight:17,288 lb (7,842 kg)
- Gross weight:26,171 lb (11,871 kg)
- Fuel capacity:400 US gallons (1,500 L; 330 imp gal)
- Powerplant:2 ×Pratt & Whitney R-2800-22W Double Waspradial engines,2,400 hp (1,800 kW) each
- Propellers:4-bladed Aeroproducts H-20-156, 13 ft 2 in (4.01 m) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed:414 mph (666 km/h, 360 kn) at 18,600 feet (5,700 m)
- Stall speed:84 mph (135 km/h, 73 kn)
- Range:975 mi (1,569 km, 847 nmi) internal fuel at 172 miles per hour (277 km/h)
- Combat range:395 mi (636 km, 343 nmi) radius with two 150 US gallons (570 L; 120 imp gal) drop tanks
- Service ceiling:36,500 ft (11,100 m)
- Rate of climb:3,920 ft/min (19.9 m/s)
- Wing loading:47.9 lb/sq ft (234 kg/m2)
- Power/mass:6.5lb/bhp
Armament
- Guns:4.50-calibremachine guns
- Hardpoints:Two, 1,000 pounds (450 kg) capacity each
- Bombs:Internal bomb bay, capacity oneMark 13 torpedo,one 2,000 pounds (910 kg) bomb ornaval mine,or up to 4,000 pounds (1,800 kg) smaller bombs, or up to 1,300 pounds (590 kg)depth charges.
See also
[edit]Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^abcGoebel 2009
- ^abcdefghijkNorton 2008, p. 120
- ^American Aviation Historical SocietyJournal,v.14-15,p. 269.
- ^abAngelucci 1987, p. 238.
- ^abJohnson 2008, p. 427
- ^Norton 2008, p. 121
- ^Meyer 2002, p. 55
- ^Lawson and Tillman 2001, p. 87
- ^"U.S. Systems of Aircraft Designation",driko.org.Accessed May 8, 2010.
Bibliography
[edit]- Angellucci, Enzo (1987).The American Fighter from 1917 to the Present.New York: Orion.ISBN0-517-56588-9.
- Goebel, Greg (2009)."The Grumman AF Guardian".vectorsite.net.Retrieved2010-05-06.
- Johnson, E.R. (2008).American Attack Aircraft Since 1926.Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Company.ISBN9780786434640.
- Lawson, Robert; Barrett Tillman (2001).U. S. Navy Dive and Torpedo Bombers of World War II.St. Paul, MN: MBI Publishing.ISBN0-7603-0959-0.
- Meyer, Corwin H.(August 2002). "F7F Tigercat: The Untold Story".Flight Journal.Ridgefield, CT: AirAge Publications.
- Norton, Bill (2008).U.S. Experimental & Prototype Aircraft Projects: Fighters 1939-1945.North Branch, MN: Specialty Press.ISBN978-1-58007-109-3.
- U.S. Navy (August 1, 1944)."XTSF-1 Airplane Characteristics and Performance"(PDF).alternatewars.Retrieved2011-01-08.
External links
[edit]- U.S. Navy (July 1944)."Aircraft Description Card for XTSF-1"(PDF).alternatewars.Retrieved2011-01-08.
- "Grumman Designs and Proposals",The Grumman Pages.
- TS - Torpedo Scout Aircraft,U.S. Military Aircraft and Weapon Designations
