Hafsid dynasty
Hafsids[a] | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1229–1574 | |||||||||||||||||
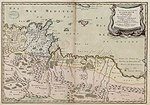
 Realm of the Hafsid dynasty in 1400 (orange) | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Tunis | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Arabic,Berber | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Islam(Sunni,Ibadi),Christianity(Roman Catholic),Judaism | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| Sultan | |||||||||||||||||
• 1229–1249 | Abu Zakariya | ||||||||||||||||
• 1574 | Muhammad VI | ||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||
• Established | 1229 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1535 | |||||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1574 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||
TheHafsids(Arabic:الحفصيونal-Ḥafṣiyūn) were aSunni Muslimdynasty ofBerberdescent[3]who ruledIfriqiya(modern dayTunisia,westernLibya,and easternAlgeria) from 1229 to 1574.
History
[edit]Almohad Ifriqiya
[edit]The Hafsids were ofBerberdescent,[3]although to further legitimize their rule, they claimedArabancestry from the secondRashiduncaliphOmar.[4]The ancestor of the dynasty (from whom their name is derived), wasAbu Hafs Umar ibn Yahya al-Hintati,a Berber from theHintatatribal confederation,[5]which belonged to the greaterMasmudaconfederation in present-day Morocco.[6]He was a member of the Council of Ten, one of the highestAlmohadpolitical bodies, and a close companion ofIbn Tumart,the Almohad movement's founder.[5]
The son of Abu Hafs,Abu Muhammad Abd al-Wahid ibn Abi Hafs,was appointed by the Almohad caliphMuhammad al-Nasiras governor ofIfriqiya(generally present-dayTunisia,easternAlgeria,and westernLibya) where he ruled from 1207 to 1221.[7]He was established inTunis,which the Almohads had chosen as the province's administrative capital.[8]: 133 His appointment came in the wake of the defeat ofYahya Ibn Ghaniya,who had launched aserious attackagainst Almohad authority in the region. Abu Muhammad Abd al-Wahid was ultimately quite effective in keeping order. The caliph had granted him a significant degree of autonomy in governing, partly to help persuade him to accept this difficult position in the first place. This laid the groundwork for a future Hafsid state.[9]: 101, 119
When Abu Muhammad Abd al-Wahid died in 1221, the Almohad chiefs in Ifriqiya initially elected his son, Abu Zayd Abd al-Rahman, as the next governor. However, the Almohad caliph in Marrakesh,Yusuf II al-Mustansir,had not consented to this and was able to overrule this and appoint his own relative to the position.[9]: 119 As Almohad authority weakened over the following years, local opposition to the Almohad governor compelled the Almohad caliphAbdallah al-Adilto appoint another Hafsid family member to the post in 1226. He chose Abu Muhammad Abdallah, a grandson of Abu Hafs. Abu Muhammad Abdallah's brother,Abu Zakariya Yahya,arrived in Tunis before him and began to reestablish order.[9]: 119 Whenal-Ma'mun,the brother of Abdallah al-Adil, rebelled against the latter's authority fromal-Andalus,Abu Zakariya sided with him, whereas Abu Muhammad Abdallah remained loyal to the caliph in Marrakesh. Al-Ma'mun's eventual victory resulted in Abu Zakariya being placed in charge of Ifriqiya in 1228.[9]: 119
Rise to power
[edit]A year later, in 1229, al-Ma'mun officially renouncedAlmohad doctrine.Abu Zakariya used this as a pretext to repudiate his authority and to declare himself independent. By this point, Al-Ma'mun did not have the means to stop him or to reassert control over Ifriqiya.[9]: 119 Initially, Abu Zakariya had his name mentioned in thekhutba(the sermon duringFriday prayer) with the title of amir, but in 1236 or 1237 he began to adopt thecaliphaltitle ofAmir al-Mu'minin,in direct challenge to the Almohad caliph in Marrakesh.[9]: 119
Abu Zakariya annexedConstantine(Qusantina) andBéjaïa(Bijaya) in 1230.[7]In 1234, he chased Yahya Ibn Ghaniya out of the countryside south of Constantine in 1234, ending this lingering threat.[7]In 1235 he capturedAlgiersand then established his authority as far as theChelif Riverto the west.[7]In the following years he subdued various rural tribes, such as theHawwara,but allowed some of the Banu Tujin tribes in the central Maghreb to govern themselves as small vassal states that secured his eastern borders.[7]He welcomed many refugees and immigrants from al-Andalus who were fleeing the advance of theReconquista.He appointed some of them to important political positions and recruited Andalusi military regiments as a way of counteracting the power and influence of traditional Almohad elites.[10]
For a time, theNasridruler ofGranadain al-Andalus,Ibn al-Ahmar,briefly acknowledged Abu Zakariya's suzerainty in an attempt to enlist his help against Christian forces. Ultimately, Hafsid intervention on theIberian Peninsulawas limited to sending a fleet to MuslimValencia's aid in 1238.[9]: 119–120 Abu Zakariya showed more interest in trying to recreate some of the former authority of the Almohads over the Maghreb and he made attempts to extend his control further west. In 1242, he capturedTlemcenfrom theZayyanids,but the Zayyanid leaderYaghmurasanevaded him. The two leaders eventually came to an agreement, with Yaghmurasan continuing to rule in Tlemcen but agreeing to formally recognize Abu Zakariya's authority.[9]: 120 That same year,SijilmasaandCeuta(Sabta) also recognized his authority,[9]: 120 though these would later fall under Marinid control.[9]: 107, 136 This policy of western expansion ended with Abu Zakariya's death (1249).[9]: 120
Consolidation and division
[edit]
His successor,Muhammad I al-Mustansir(r. 1249–1277), focused on consolidating the Hafsid state in Ifriqiya. The state benefited from expanding trade with both Europe and theSudanregion (south of the Sahara).[9]: 120–121 In the western Maghreb (present-day Morocco), the Marinids, who had not yet fully established their rule in the region, formally recognized his authority in 1258.[9]: 120 With thefall of Baghdad,the home of theAbbasid caliphs,that same year, the Hafsids were briefly seen as the most important rulers of the Muslim world. TheSharif of Mecca,Abu Numayy,temporarily recognized him as caliph in 1259.[9]: 120 [11]: 97
It was during his reign that the failedEighth Crusadetook place, led byLouis IX of France.After landing atCarthage,Louis died of dysentery in the middle of his army decimated by disease in 1270.
After al-Mustansir's death in 1277, the Hafsids were riven by internal conflict, aggravated by interference fromAragon.[9]: 123 This resulted in a split in the dynasty: one branch ruled from Tunis in the east andanother branchruled fromBéjaïa (Bijaya)andConstantine (Qusantina)in the west. This division continued to characterize Hafsid politics for much of its history, with the balance of power sometimes shifting from one side to another and with intermittent successes at unifying both branches under one rule.[10]After the initial split, the first successful reunification took place underAbu Yahya Abu Bakr II(r. 1318–1346), the ruler of the western branch who managed to take control of Tunis.[10]
Marinid invasions and internal crisis
[edit]Abu Yahya Abu Bakr's rule remained unstable and he resorted to making alliances with the Zayyanids and Marinids to the west.[10]His agreement with the Marinid ruler,Abu al-Hasan(r. 1331–1348), included a marriage to his sister, who subsequently died during afailed Marinid expedition in Spain,followed by another marriage to his daughter.[9]: 110 When Abu Yahya Abu Bakr died in 1346, his intended heir, Abu'l Abbas, was killed in Tunis by his brother, Umar, who seized power. Abu'l Abbas's chamberlain, Abu Muhammad Abdallah ibn Tafrajin, sent a letter to Abu al-Hasan urging him to intervene and invade Ifriqiya. Abu al-Hasan, having alreadyconquered Tlemcenin 1337, seized the opportunity to further expand. He conquered Tunis in 1347 and the Hafsid governors in the region accepted his authority.[9]: 110
The invasion, however, disturbed the balance of power in favour of the Bedouin Arab tribes, whom the Marinids were unable to sway.[9]: 111, 128 Ibn Tafrajin, who had hoped to be placed in power by the Marinids, fled to Egypt. The situation in Ifriqiya devolved into further disorder and internal rivalries, and Abu al-Hasan was forced to return west in 1349, partly to deal with acoup d'étatby his son,Abu Inan.Ibn Tafrajin returned to Ifriqiya and, with Bedouin support, installed another young son of Abu Yahya Abu Bakr, Abu Ishaq, as ruler.[9]: 111, 128 Abu Inan, having successfully taken the throne from his father, invaded Ifriqiya again and captured Tunis in August 1357, but he was soon forced by his own troops to abandon the region. He returned west, retaining control only of Constantine and the cities of the central Maghreb for a time.[9]: 111
During the mid-14th century, plague epidemics brought to Ifriqiya from Sicily caused a considerable fall in population, further weakening the Hafsid realm. To stop raids from southern tribes during plague epidemics, the Hafsids turned to theBanu Hilalto protect their rural population.[12]: 37
Apogee
[edit]
After the Marinid threat ended, attempts to reunify the Hafsids failed untilAbu al-Abbas Ahmad II(r. 1370–1394), the emir of Béjaïa and Constantine, conquered Tunis in 1370.[10]A capable ruler and military leader, he reestablished Hafsid authority on stronger terms, centralizing power to a greater extent than ever before. Meanwhile, the Zayyanids and Marinids were occupied by internal matters.[10]
Abu Faris Abd al-Aziz II's reign (r. 1394–1434) was considered the apogee of Hafsid power and prosperity by contemporary writers. He further consolidated his dynasty's power in Ifriqiya and extended his influence over the Zayyanids and Marinids (and theWattasidswho succeeded the latter).[10]
The beginning of his reign was not easy since the cities of the south revolted against him. However, the new sultan quickly regained control: he reoccupiedTozeur(1404),Gafsa(1401), andBiskra(1402), subdued tribal power in the regions of Constantine and Béjaïa (1397–1402), and appointed governors of these regions to be elected officers.[clarification needed]He also intervened against his western and eastern neighbors. He annexedTripoli(1401) andAlgiers(1410–1411).[14]In 1424, hedefeatedthe Zayyanid sultan, Abu Malik Abd al-Wahid, and placed another Zayyanid, Abu Abdallah Muhammad IV, on the throne of Tlemcen as his vassal.[15][16]In 1428, the latter became embroiled in another war with Abu Malik Abd al-Wahid – who had now won his own support from the Hafsids – and was eventually replaced by yet another Zayyanid relative with Abu Faris Abd al-Aziz's help in 1431.[16]Around the same time (probably in 1426), Abu Faris Abd al-Aziz also helped to installAbd al-Haqq IIon the Marinid throne in Fez – under the regency ofAbu Zakariya Yahya al-Wattasi– and thus obtained from him a recognition of Hafsid suzerainty.[17]
In 1429, the Hafsidsattacked the island of Maltaand took 3000 slaves, although they did not conquer the island.[18]Kaid Ridavanwas the military leader during the attack.[19]The profits were used for a great building programme and to support art and culture. However, piracy also provoked retaliation from the Christians, which several times launched attacks and crusades against Hafsid coastal cities such as theBarbary crusade(1390), theBona crusade(1399) and the capture ofDjerbain 1423.[citation needed]
Abu Faris Abd al-Aziz II died in 1434 during another expedition against Tlemcen.[10]His successor,Abu 'Amr 'Uthman,had the longest reign of any Hafsid (r. 1435–1488). He largely continued the strong rule of his predecessors but he had to contend with greater challenges, including internal politics, restive Bedouin tribes in the south, and the Wattasids in the west.[10]
Uthman conqueredTripolitaniain 1458 and appointed a governor inOuarglain 1463.[20]He led two expeditions to Tlemcen in 1462 and 1466 and made the Zayyanids his vassals, while the Wattasid state in Morocco also formally accepted his authority. The entire Maghreb was thus briefly under Hafsid suzerainty.[21][9]: 132
Fall
[edit]In the 16th century the Hafsids became increasingly caught up in the power struggle between Spain and theOttoman Empire-supportedCorsairs.The Ottomansconquered Tunisin 1534 and held it for one year, driving out the Hafsid rulerMoulay Hassan.A year later the King of Spain and Holy Roman EmperorCharles Vseized Tunis,drove the Ottomans out and restoredMuley Hassan as a Habsburg tributary.[22]Due to the Ottoman threat, the Hafsids were vassals of Spain after 1535. The Ottomans again conquered Tunis in 1569 and held it for four years.Don Juan of Austriarecaptured it in 1573. The Ottomans reconquered Tunis in 1574, andMuhammad VI,the last Caliph of the Hafsids, was brought toConstantinopleand was subsequently executed due to his collaboration with Spain and the desire of the Ottoman Sultan to take the title ofCaliphas he now controlled Mecca and Medina.[citation needed]
Economy
[edit]The Hafsids, with their location in Ifriqiya, was rich in agriculture and trade. Instead of placing the capital at inland cities such asKairouan,Tunis was chosen as the capital due to its position on the coast as a port linking the Western and Eastern Mediterranean. Christian merchants from Europe were given their own enclaves in various cities on the Mediterranean coast, promoting trans-Mediterranean trade. Under the Hafsids, commerce and diplomatic relations with Christian Europe grew significantly,[23]howeverpiracyagainst Christian shipping grew as well, particularly during the rule ofAbd al-Aziz II(1394–1434). By the mid-14th century, the population of Tunis had grown to 100,000. The Hafsids also had a large stake in trans-Saharan trade through the caravan routes from Tunis toTimbuktuand fromTripolito sub-Saharan Africa.[12]: 34–36
Culture
[edit]Intellectual activity
[edit]The Hafsids were effective patrons of culture and education.[10]They were the first to introducemadrasasto the Maghreb.[24]: 209 [10]Arabic literacy and religious education thus increased, with Kairouan, Tunis and Bijaya hosting famous university-mosques. Kairouan continued to serve as a center of theMalikischool of religious doctrine.[12]: 37 As the political center of the country shifted to Tunis, theGreat Mosque of al-Zaytuna,the city's main mosque, became the country's leading center of learning.[25]Of great impact on culture were immigrants from al-Andalus, whom Abu Zakariya encouraged to come to his realm in the 13th century. Among the most important figures was the famous historian and intellectual,Ibn Khaldun.[10]
Architecture
[edit]
The Hafsids were significant builders, particularly under the reigns of successful leaders like Abu Zakariya (r. 1229–1249) andAbu Faris(r. 1394–1434), though not many of their monuments have survived intact to the present-day.[24]: 208 While Kairouan remained an important religious center, Tunis was the capital and progressively replaced it as the main city of the region and the main center of architectural patronage. Unlike the architecture further west,Hafsid architecturewas built primarily in stone (rather thanbrickormudbrick) and appears to have featured much less decoration.[24]: 208 In reviewing the history ofarchitecture in the western Islamic world,scholarJonathan Bloomremarks that Hafsid architecture seems to have "largely charted a course independent of the developments elsewhere in the Maghrib."[24]: 213
TheKasbah Mosqueof Tunis was one of the first works of this period, built by Abu Zakariya (the first independent Hafsid ruler) at the beginning of his reign. Its floor plan had noticeable differences from previous Almohad-period mosques but the minaret, completed in 1233, bears very strong resemblance to the minaret of the earlier AlmohadKasbah Mosque in Marrakesh.[24]Other foundations from the Hafsid period in Tunis include theHaliq Mosque(13th century) and theal-Hawa Mosque(1375). TheBardo Palace(today a national museum) was also begun by the Hafsids in the 15th century,[26]and is mentioned in historical records for the first time during the reign of Abu Faris.[24]: 208 The Hafsids also made significant renovations to the much older Great Mosque of Kairouan – renovating its ceiling, reinforcing its walls, and building or rebuilding two of its entrance gates in 1293 – as well as to the Great Mosque of al-Zaytuna in Tunis.[24]: 209
The Hafsids also introduced the first madrasas to the region, beginning with theMadrasa al-Shamma῾iyyabuilt in Tunis in 1238[27][24]: 209 (or in 1249 according to some sources[28]: 296 [29]). This was followed by many others (almost all of them in Tunis) such as the Madrasa al-Hawa founded in the 1250s, the Madrasa al-Ma'ridiya (1282), and theMadrasa al-Unqiya(1341).[24]Many of these early madrasas, however, have been poorly preserved or have been considerably modified in the centuries since their foundation.[24][30]The Madrasa al-Muntasiriya, completed in 1437, is among the best preserved madrasas of the Hafsid period.[24]: 211
Flags
[edit]- Flags of Hafsids on portolans and from other sources
-
Early red flag with white or yellow crescent of the 14th century, reported by Marino Sanudo (ca. 1321), Angelino Dulcerta (1339) and the Catalan Atlas (1385)[2]
-
Yellow with white crescent, the reconstructed flag of the 15th century[1]
-
White with blue crescent according to Jacobo Russo, 1550 (last period of the kingdom)[2]
Hafsid rulers
[edit]| History ofTunisia |
|---|
 |
|
|
| History ofAlgeria |
|---|
 |
| History ofLibya | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. n. | Name | Birth date | Death date | Reign | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| – | Abu Muhammad Abd al-Wahid ibn Abi Hafs | unknown | 1222 | 1207–1222 | Not yet a sultan, just a local minor leader. |
| – | Abu Muhammad Abd Allah ibn Abd al-Wahid | unknown | 1229 | 1222–1229 | Not yet a sultan, just a local minor leader. |
| 1st | Abu Zakariya Yahya | 1203 | 5 October 1249 | 1229–1249 | |
| 2nd | Muhammad I al-Mustansir | 1228 | 1277 | 1249–1277 | |
| 3rd | Yahya II al-Wathiq | unknown | 1279 | 1277–1279 | |
| 4th | Ibrahim I | unknown | 1283 | 1279–1283 | |
| 5th | Abd al-Aziz I | unknown | 1283 | 1283 | |
| 6th | Ibn Abi Umara | unknown | 1284 | 1283–1284 | |
| 7th | Abu Hafs Umar bin Yahya | unknown | 1295 | 1284–1295 | |
| 8th | Abu Asida Muhammad II | 1279 | September 1309 | 1295–1309 | |
| 9th | Abu Yahya Abu Bakr ash-Shahid | unknown | September 1309 | 1309 | |
| 10th | Abu-l-Baqa Khalid An-Nasr | unknown | 1311 | 1309–1311 | |
| 11th | Abd al-Wahid Zakariya ibn al-Lihyani | 1253 | 1326 | 1311–1317 | |
| 12th | Abu Darba Muhammad Al-Mustansir | unknown | 1323 | 1317–1318 | |
| 13th | Abu Yahya Abu Bakr II | unknown | 19 October 1346 | 1318–1346 | |
| 14th | Abu-l Abbas Ahmad | unknown | 1346 | 1346 | |
| 15th | Abu Hafs Umar II | unknown | 1347 | 1346–1347 | |
| 16th | Abu al-Abbas Ahmad al-Fadl al-Mutawakkil | unknown | 1350 | 1347–1350 | |
| 17th | Abu Ishaq Ibrahim II | October or November 1336 | 19 February 1369 | 1350–1369 | |
| 18th | Abu-l-Baqa Khalid II | unknown | November 1370 | 1369–1370 | |
| 19th | Ahmad II | 1329 | 3 June 1394 | 1370–1394 | |
| 20th | Abd al-Aziz II | 1361 | July 1434 | 1394–1434 | |
| 21st | Abu Abd-Allah Muhammad al-Muntasir | unknown | 16 September 1435 | 1434–1435 | |
| 22nd | Abu 'Amr 'Uthman | February 1419 | September 1488 | 1435–1488 | |
| 23rd | Abu Zakariya Yahya II | unknown | 1489 | 1488–1489 | |
| 24th | Abd al-Mu'min | unknown | 1490 | 1489–1490 | |
| 25th | Yahya Zakariya | unknown | 1494 | 1490–1494 | |
| 26th | Abu Abdallah Muhammad IV al-Mutawakkil | unknown | 1526 | 1494–1526 | |
| 27th | Muhammad V( “Moulay Hasan” ) | unknown | 1543 | 1526–1543 | |
| 28th | Ahmad III | c. 1500 | August 1575 | 1543–1569 | |
| Ottoman conquest (1569–1573) | |||||
| 29th | Muhammad VI | unknown | 1594 | 1573–1574 | |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^The state was known by several names, including the Hafsid Kingdom (المملكة الحفصية), Hafsid State (الدولة الحفصية), Hafsid Sultanate (السلطنة الحفصية), and Sultanate of Tunis (سلطنة تونس.
- ^ab"الحفصيون/بنو حفص في تونس، بجاية وقسنطينة".hukam.net(in Arabic).
- ^abc"TunisiaArms".hubert-herald.nl.
- ^abC. Magbaily Fyle,Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa,(University Press of America, 1999), 84.
- ^Fromherz, Allen James (2016).Near West: Medieval North Africa, Latin Europe and the Mediterranean in the Second Axial Age.Edinburgh University Press.ISBN978-1-4744-1007-6.
- ^abFromherz, Allen J. (2009). "Abū Ḥafṣ ʿUmar al-Hintātī". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.).Encyclopaedia of Islam, Three.Brill.ISBN9789004161658.
- ^Deverdun, G. (1986) [1971]."Hintāta".InLewis, B.;Ménage, V. L.;Pellat, C.;Schacht, J.(eds.).Encyclopaedia of Islam.Vol. III (2nd ed.). Leiden, Netherlands:E. J. Brill.ISBN9004081186.
- ^abcdeIdris, H. R. (1986) [1971]."Ḥafṣids".InLewis, B.;Ménage, V. L.;Pellat, C.;Schacht, J.(eds.).Encyclopaedia of Islam.Vol. III (2nd ed.). Leiden, Netherlands:E. J. Brill.p. 66.ISBN9004081186.
- ^Abadi, Jacob (2013).Tunisia Since the Arab Conquest: The Saga of a Westernized Muslim State.Apollo Books.ISBN978-0-86372-435-0.
- ^abcdefghijklmnopqrstuAbun-Nasr, Jamil (1987).A history of the Maghrib in the Islamic period.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.ISBN0521337674.
- ^abcdefghijklRouighi, Ramzi (2020). "Ḥafṣids". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.).Encyclopaedia of Islam, Three.Brill.ISBN9789004161658.
- ^Naylor, Phillip (2015).North Africa, Revised Edition: A History from Antiquity to the Present.University of Texas Press.ISBN978-0-292-76192-6.
- ^abcRoland Anthony Oliver; Roland Oliver; Anthony Atmore (2001).Medieval Africa, 1250–1800.Cambridge University Press.ISBN978-0-521-79372-8.
- ^"Papier pourpre et encre d'argent".BnF Essentiels(in French).Retrieved2023-11-27.
- ^نوري, عبد المجيد (March 2017)."العملة وتأثيراتها السياسية في تاريخ الغرب الإسلامي من مطلع القرن الخامس إلى أواخر القرن السابع الهجري 407 هـ - 674 هـ /1017 - 1275 م".Historical Kan Periodical(in Arabic).10(35): 172–175.doi:10.12816/0041490.ISSN2090-0449.
- ^نوري, عبد المجيد (March 2017)."العملة وتأثيراتها السياسية في تاريخ الغرب الإسلامي من مطلع القرن الخامس إلى أواخر القرن السابع الهجري 407 هـ - 674 هـ / 1017 - 1275 م".Historical Kan Periodical(in Arabic).10(35): 172–175.doi:10.12816/0041490.ISSN2090-0449.
- ^abGarrot, Henri (1910).Histoire générale de l'Algérie(in French). Alger, Impr. P. Crescenzo. pp. 287–288.
- ^Cour, Auguste (1920).La dynastie marocaine des Beni Wattas (1420-1554).Recueil des notices et mémoires de la Société archéologique de la province de Constantine (in French). Imprimerie D. Braham. p. 50.
- ^Castillo, Dennis Angelo (2006).The Maltese Cross: A Strategic History of Malta.Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 36–37.ISBN0313323291.
- ^Cauchi, Fr Mark (12 September 2004)."575th anniversary of the 1429 Siege of Malta".Times of Malta.Retrieved4 August2022.
- ^Braunschvig 1940, p. 260
- ^Julien, Charles André (1970).History of North Africa: Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, from the Arab Conquest to 1830.Routledge & K. Paul.ISBN978-0-7100-6614-5.
- ^Roger Crowley, Empires of the Sea, faber and faber 2008 p. 61
- ^Berry, LaVerle."Hafsids".Libya: A Country Study.Library of Congress.Retrieved5 March2011.
- ^abcdefghijkBloom, Jonathan M. (2020).Architecture of the Islamic West: North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula, 700–1800.Yale University Press.ISBN9780300218701.
- ^Chater, Khalifa (2002). "Zaytūna". In Bearman, P.; Bianquis, Th.; Bosworth, C.E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W.P. (eds.).Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition.Vol. XI. Brill. pp. 488–490.ISBN9789004161214.
- ^M. Bloom, Jonathan; S. Blair, Sheila, eds. (2009). "Tunis".The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture.Oxford University Press.ISBN9780195309911.
- ^Binous, Jamila; Baklouti, Naceur; Ben Tanfous, Aziza; Bouteraa, Kadri; Rammah, Mourad; Zouari, Ali (2002).Ifriqiya: Thirteen Centuries of Art and Architecture in Tunisia(2nd ed.). Museum With No Frontiers, MWNF.ISBN9783902782199.
- ^Marçais, Georges (1954).L'architecture musulmane d'Occident.Paris: Arts et métiers graphiques.
- ^M. Bloom, Jonathan; S. Blair, Sheila, eds. (2009). "Hafsid".The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture.Oxford University Press.ISBN9780195309911.
- ^Bloom, Jonathan M.; Blair, Sheila S., eds. (2009). "Madrasa".The Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art and Architecture.Oxford University Press.


![Early red flag with white or yellow crescent of the 14th century, reported by Marino Sanudo (ca. 1321), Angelino Dulcerta (1339) and the Catalan Atlas (1385)[2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d1/Flag_of_Tunis_during_14th_century.svg/120px-Flag_of_Tunis_during_14th_century.svg.png)
![Yellow with white crescent, the reconstructed flag of the 15th century[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9d/Flag_of_Hafsid_Dynasty_%281229_-_1574%29.svg/120px-Flag_of_Hafsid_Dynasty_%281229_-_1574%29.svg.png)
![White with blue crescent according to Jacobo Russo, 1550 (last period of the kingdom)[2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/02/Flag_of_Hafsid_Tunisia_%281550%29.svg/120px-Flag_of_Hafsid_Tunisia_%281550%29.svg.png)
![The flag of the city of tunis in 14th century. White with black crescent [1][2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/74/Tunis_flag_%2814th_century%29.gif/120px-Tunis_flag_%2814th_century%29.gif)
