Hakucho
Appearance
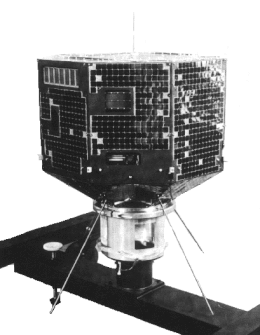 | |
| Mission type | X Ray Celestial Observation |
|---|---|
| Operator | Institute of Space and Astronautical Science(Japan) |
| COSPAR ID | 1979-014A |
| SATCATno. | 11272 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Launch mass | 96.0 kilograms (211.6 lb) |
| Dimensions | ⌀760mm×650mm |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 21 February 1979UTC |
| Rocket | M-3C-Rocket (mission 4) |
| Launch site | Uchinoura Space Center,Kagoshima Prefecture,Japan |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | April 15, 1985 |
Hakucho(also known asCORSA-bbefore launch; CORSA stands forCosmic Radiation Satellite) wasJapan's firstX-ray astronomysatellite,developed by theInstitute of Space and Aeronautical Science(then a division of theUniversity of Tokyo). It was launched from theKagoshima Space Centerby the ISASM-3Crocket on the M-3C-4 mission on February 21, 1979[1]and reentered the atmosphere on April 15, 1985.[2]
Hakucho was a replacement for theCosmic Radiation Satellite(CORSA)satellite which failed to launch due to rocket failure on February 4, 1976.[3]
Highlights[edit]
- Discovery of soft X-ray transient Cen X-4 and Aql X-1
- Discovery of many burst sources
- Long-term monitoring of X-ray pulsar (e.g. Vela X-1)
- Discovery of 2 Hz variability in the Rapid Burster later named Quasi Period Oscillation.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^"Hakucho",JAKA Institute of Space and Astronautical Science
- ^"CelesTrak: Search Satellite Catalog".celestrak.RetrievedNov 28,2020.
- ^"Corsa A, B (Hakucho)".Gunter's Space Page.RetrievedNov 28,2020.
