Himeji Castle
| Himeji Castle Cơ lộ thành | |
|---|---|
| Himeji,Hyōgo, Japan | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 34°50′22″N134°41′38″E/ 34.83944°N 134.69389°E |
| Type | Azuchi-Momoyama castle[1] |
| Height | 46.4 m (152 ft) |
| Site information | |
| Condition | Intact, restoration work for preservation recently completed[2] |
| Site history | |
| Built | |
| Built by |
|
| In use | 1333–1868,[3][6]1945(as military camp) |
| Materials | Wood, stone, plaster, tile[5] |
| Demolished | |
| Garrison information | |
| Garrison | |
| Official name | Himeji-jo |
| Criteria | Cultural: i, iv |
| Reference | 661 |
| Inscription | 1993 (17thSession) |
| Area | 107 ha |
| Buffer zone | 143 ha |
| Himeji Castle | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"Himeji Castle" inkanji | |||||
| Japanese name | |||||
| Kanji | Cơ lộ thành | ||||
| |||||
Himeji Castle(Cơ lộ thành,Himeji-jō)([çimeʑiꜜʑoː]) is a hilltopJapanese castlecomplex situated inHimeji,a city in theHyōgo PrefectureofJapan.The castle is regarded as the finest surviving example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, comprising a network of 83 rooms with advanced defensive systems from thefeudal period.[7]The castle is frequently known asHakuro-jōorShirasagi-jō( "WhiteEgretCastle "or"White HeronCastle ") because of its brilliant white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.[6][8]
As with almost all Japanese castles from theAzuchi-Momoyama periodonward, thetenshu(Thiên thủ,main keep),the most prominent structure, was used as a storehouse in times of peace and as afortified towerin times of war, and thedaimyo(Đại danh,feudal lord)'s government offices and residences were located in a group of single-story buildings near thetenshuand the surroundingyagura(Lỗ,turrets).[9]
Himeji Castle dates to 1333 whenAkamatsu Norimurabuilt a fort on top of Himeyama hill. The fort was dismantled and rebuilt as Himeyama Castle in 1346 and then remodeled into Himeji Castle two centuries later. Himeji Castle was then significantly remodeled in 1581 byToyotomi Hideyoshi,who added a three-story castlekeep.In 1600,Tokugawa Ieyasuawarded the castle toIkeda Terumasafor his help in theBattle of Sekigahara,and Ikeda completely rebuilt the castle from 1601 to 1609, expanding it into a large castle complex.[3]Several buildings were later added to the castle complex byHonda Tadamasafrom 1617 to 1618.[5]For almost 700 years, Himeji Castle has remained intact, even throughout the bombing of Himeji inWorld War II,and natural disasters including the 1995Great Hanshin earthquake.[3][2][10]
Himeji Castle is the largest and most visited castle in Japan, and it was registered in 1993 as one of the firstUNESCOWorld Heritage Sitesin the country.[2]The area within the middlemoatof the castle complex is a designatedSpecial Historic Siteand five structures of the castle are also designatedNational Treasures.[5][11]Along withMatsumoto CastleandKumamoto Castle,Himeji Castle is considered one of Japan's three premier castles.[12]In order to preserve the castle buildings, it underwent restoration work for several years and reopened to the public on March 27, 2015.[13]The works also removed decades of dirt and grime, restoring the formerly grey roof to its original brilliant white color.
History[edit]
Himeji Castle's construction dates to 1333, when a fort was constructed on Himeyama hill byAkamatsu Norimura,the ruler of the ancientHarima Province.[3]In 1346, his son Sadanori demolished this fort and built Himeyama Castle in its place.[3][14]In 1545, the Kuroda clan was stationed here by order of the Kodera clan, and feudal rulerKuroda Shigetakaremodeled the castle into Himeji Castle, completing the work in 1561.[3][15]In 1580,Kuroda Yoshitakapresented the castle toToyotomi Hideyoshi,and in 1581 Hideyoshi significantly remodeled the castle, building a three-storykeepwith an area of about 55 m2(590 sq ft).[5][15]
Following theBattle of Sekigaharain 1600,Tokugawa Ieyasugranted Himeji Castle to his son-in-law,Ikeda Terumasa,as a reward for his help in battle.[3]Ikeda demolished the three-story keep that had been created by Hideyoshi, and completely rebuilt and expanded the castle from 1601 to 1609, adding threemoatsand transforming it into the castle complex that is seen today.[3][5]The expenditure of labor involved in this expansion is believed to have totaled 2.5 millionman-days.[3]Ikeda died in 1613, passing the castle to his son, who also died three years later.[4]In 1617,Honda Tadamasaand his family inherited the castle, and Honda added several buildings to the castle complex, including a special tower for his daughter-in-law,Princess Sen(Ngàn cơ,Senhime)[4]calledkeshō yagura(Dressing Tower).
In theMeiji Period(1868–1912), manyJapanese castleswere destroyed.[2]Himeji Castle was abandoned in 1871 and some of the castle corridors and gates were destroyed to make room for Japanese armybarracks.[5][15]The entirety of the castle complex was slated to be demolished by government policy, but it was spared by the efforts of Nakamura Shigeto, an army colonel.[5]A stone monument honoring Nakamura was placed in the castle complex within the first gate, the Hishi Gate(Lăng の môn,Hishinomon).[5][16]Although Himeji Castle was spared, Japanese castles had become obsolete and their preservation was costly.[5]

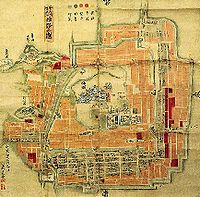
When thehan feudal system was abolishedin 1871, Himeji Castle was put up for auction.[5]The castle was purchased by a Himeji resident for 23Japanese yen(about 200,000 yen orUS$2,258 today).[5]The buyer wanted to demolish the castle complex and develop the land, but the cost of destroying the castle was estimated to be too great, and it was again spared.[5]
Himejiwas heavily bombed in 1945, at the end ofWorld War II,and although most of the surrounding area was burned to the ground, the castle survived intact.[7]Onefirebombwas dropped on the top floor of the castle butfailed to explode.[17]In order to preserve the castle complex, substantial repair work was undertaken starting in 1956, with a labor expenditure of 250,000man-daysand a cost of 550 million yen.[5][15]In January 1995, the city of Himeji was substantially damaged by theGreat Hanshin earthquake,but Himeji Castle again survived virtually undamaged, demonstrating remarkable earthquake resistance.[10]Even the bottle ofsakeplaced on the altar at the top floor of the keep remained in place.[10]

Historical recognition[edit]
Himeji Castle was registered on 11 December 1993 as one of the firstUNESCOWorld Heritage Sitesin Japan.[5][2][7]Five structures of the castle are also designatedNational Treasures:Themain keep(Đại thiên thủ,daitenshu),[18][19]northwest small keep(Càn tiểu thiên thủ,inui kotenshu),[20]west small keep(Tây tiểu thiên thủ,nishi kotenshu),[21]east small keep(Đông tiểu thiên thủ,higashi kotenshu),[22]andI,Ro,Ha,Ni-corridors and kitchen(イ, ロ, ハ, ニ の độ lỗ phụ đài sở 1 đống,i, ro, ha, ni no watariyagura tsuketari daidokoro 1 to).[11][23]The area within the middle moat of the castle complex is a designatedSpecial Historic Site.[5]
Along withMatsumoto CastleandKumamoto Castle,Himeji Castle is considered one of Japan's three premier castles.[12]It is the most visited castle in Japan, receiving over 2,860,000 visitors in 2015.[3][2]Starting in April 2010, Himeji Castle underwent restoration work to preserve the castle buildings, and reopened to the public on March 27, 2015.[13]
Design details[edit]
Himeji Castle is the largestcastle in Japan.[2]It serves as an excellent example of prototypical Japanese castle architecture, containing many of the defensive and architectural features associated with Japanese castles.[7]The curved walls of Himeji Castle are sometimes said to resemble giant fans(Cây quạt,sensu),but the principal materials used in the structures are stone and wood.[5][6]Feudal family crests(Gia văn,kamon)are installed throughout the architecture of the building, signifying the various lords that inhabited the castle throughout its history.[5]
The specific style of the castle is ahirayama( bình thành phố núi flat hilltop). Two castles that were built during the same time and shared many of the architectural features areMatsuyama Castle (Iyo)andTsuyama Castle.


The Himeji Castle complex is located in the centre ofHimeji, Hyōgoon top of a hill called Himeyama, which is 45.6 m (150 ft) above sea level. The castle complex comprises a network of 83 buildings such as storehouses, gates, corridors, and turrets(Lỗ,yagura).[5][16]Of these 83 buildings, 74 are designated as Important Cultural Assets: 11 corridors, 16 turrets, 15 gates, and 32 earthen walls.[10]The highest walls in the castle complex have a height of 26 m (85 ft).[5]Joining the castle complex isKōko-en(Thích cổ viên),aJapanese gardencreated in 1992 to commemorateHimeji city's 100th anniversary.[24]
From east to west, the Himeji Castle complex has a length of 950 to 1,600 m (3,120 to 5,250 ft), and from north to south, it has a length of 900 to 1,700 m (3,000 to 5,600 ft).[5]The castle complex has acircumferenceof 4,200 m (2.6 mi).[5]It covers an area of 233 hectares (2,330,000 m2or 576 acres), making it roughly 50 times as large as theTokyo Domeor 60 times as large asKoshien Stadium.[3][5][7]

Themain keep(Đại thiên thủ,daitenshu)at the center of the complex is 46.4 m (152 ft) high, standing 92 m (302 ft) above sea level. Together with the main keep, three smaller subsidiary keeps(Tiểu thiên thủ,kotenshu)form a cluster of towers.[5]Externally, the keep appears to have five floors, because the second and third floors from the top appear to be a single floor; however, it actually has six floors and a basement.[8]The basement of the main keep has an area of 385 m2(4,140 sq ft), and its interior contains special facilities that are not seen in other keeps, includinglavatories,a drain board, and a kitchen corridor.[5]
The main keep has two pillars, with one standing in the east and one standing in the west.[5]The east pillar, which has a base diameter of 97 cm (38 in), was originally a singlefir tree,but it has since been mostly replaced.[5] [25]The base of the west pillar is 85 by 95 cm (33 by 37 in), and it is made ofJapanese cypress.[5]During theShōwa Restoration(1956–1964) a Japanese cypress tree with a length of 26.4 m (87 ft) was brought down from theKiso Mountainsand replaced the old pillar.[5]The tree was broken in this process, so another tree was brought down fromMount Kasagata,and the two trees were joined on the third floor.[5]
The first floor of the main keep has an area of 554 m2(5,960 sq ft) and is often called the "thousand-mat room" because it has over 330Tatamimats.[5]The walls of the first floor have weapon racks(Võ cụ quải け,bugukake)for holdingmatchlocksand spears, and at one point, the castle contained as many as 280 guns and 90 spears.[5]The second floor has an area of roughly 550 m2(5,900 sq ft).[5]
The third floor has an area of 440 m2(4,700 sq ft) and the fourth floor has an area of 240 m2(2,600 sq ft).[5]Both the third and fourth floors have platforms situated at the north and south windows called "stone-throwing platforms"(Thạch đánh lều,ishiuchidana),where defenders could observe or throw objects at attackers.[5]They also have small enclosed rooms called "warrior hiding places"(Võ giả ẩn し,mushakakushi),where defenders could hide themselves and kill attackers by surprise as they entered the keep.[5]The final floor, the sixth floor, has an area of only 115 m2(1,240 sq ft).[5]The sixth floor windows now have iron bars in place, but in the feudal period the panoramic view from the windows was unobstructed.[5]
Defences[edit]


Himeji Castle contains advanced defensive systems from thefeudal period.[7]Loopholes(Hiệp gian,sama)in the shape of circles, triangles, squares, and rectangles are located throughout Himeji Castle, intended to allow defenders armed withtanegashimaorarchersto fire on attackers without exposing themselves.[8]Roughly 1,000 loopholes exist in the castle buildings remaining today.[5]Angled chutes called "stone drop windows"(Thạch lạc song,ishi-otoshi-mado)were also set at numerous points in the castle walls, enabling stones or boiling oil to be poured on the heads of attackers passing by underneath, and white plaster was used in the castle's construction for its resistance to fire.[26]
The castle complex included threemoats,one of which—the outer moat—is now buried.[6]Parts of the central moat and all of the inner moats survive.[6]The moats have an average width of 20 m (66 ft), a maximum width of 34.5 m (113 ft), and a depth of about 2.7 m (8.9 ft).[10]The Three Country Moat(Tam quốc quật,sangoku-bori)is a 2,500 m2(27,000 sq ft) pond which exists inside the castle; one of the purposes of this moat was to store water for use in fire prevention.[5]
The castle complex, particularly the Waist Quarter(Eo khúc luân,koshikuruwa),contains numerous warehouses that were used to store rice, salt, and water in case of a siege.[5]A building known as the Salt Turret(Diêm lỗ,shioyagura)[16]was used specifically to store salt, and it is estimated that it contained as many as 3,000 bags of salt when the castle complex was in use.[5]The castle complex also contained 33 wells within the inner moat, 13 of which remain; the deepest of these has a depth of 30 m (98 ft).[5]

One of the castle's most important defensive elements is the confusing maze of paths leading to the castle's keep.[8]The gates,baileys,and outer walls of the complex are organized so as to confuse an approaching force, causing it to travel in a spiral pattern around the complex on its way to the keep.[8]The castle complex originally contained 84 gates, 15 of which were named according to the Japanese syllabaryiroha(I,Ro,Ha,Ni,Ho,He,To,etc.).[5]At present, 21 gates from the castle complex remain intact, 13 of which are named according to the Japanese syllabary.[5]
In many cases, the castle walkways even turn back on themselves, greatly inhibiting navigation.[26]For example, the straight distance from the Hishi Gate(Lăng の môn,hishinomon)[16]to the main keep(Đại thiên thủ,daitenshu)is only 130 m (430 ft), but the path itself is a much longer 325 m (1,066 ft).[5]The passages are also steep and narrow, further inhibiting entry.[5]This system allowed the intruders to be watched and fired upon from the keep during their lengthy approach, but Himeji Castle was never attacked in this manner so the system remains untested.[7][8]However, even today with the route clearly marked, many visitors have trouble navigating the castle complex.
Cultural impact[edit]
Himeji Castle is frequently known asHakuro-jōorShirasagi-jō( "White Egret Castle" or "White HeronCastle ") because of its brilliant white exterior and supposed resemblance to a bird taking flight.[6][8]The castle has been featured extensively in foreign and Japanese films, including the James Bond movie "You Only Live Twice"(1967), andAkira Kurosawa'sKagemusha(1980) andRan(1985).[12]In thetelevision miniseriesShōgun(1980) it served as a stand-in for feudal-eraOsaka Castle.[17]In the video gamesCivilization RevolutionandCivilization V,Himeji Castle is available to build as a world wonder. It is also to be found as a Great Building in Forge of Empires.
In 2023 the LEGO Group launched a model of Himeji Castle as part of its LEGO Architecture Series.
Lore and legend[edit]

Himeji Castle is associated with a number of local legends.[5]The well-knownkaidan(or Japaneseghost story) ofBanchō Sarayashiki(Phiên đinh mãnh phòng đắp,"The Dish Mansion at Banchō")is set in Edo (Tokyo), but a variant calledBanshū Sarayashiki(Bá châu mãnh phòng đắp,"The Dish mansion inHarima Province")is set in Himeji Castle. There is a disputed claim that the castle is thebona fidelocation of the entire legend, and the alleged Okiku's Well remains in the castle to this day.[4]According to the legend, Okiku was falsely accused of losing dishes that were valuable family treasures, and then killed and thrown into the well.[5]Her ghost remained to haunt the well at night, counting dishes in a despondent tone.[5]
Himeji Castle is said to be inhabited by theyōkaiOsakabehime,who lives in the castle tower and avoids humans, whom she hates.[27]In some legends she takes the form of an old woman (or woman in her 30s) in ceremonial, twelve-layered kimono.[28]She can read human minds and control lesser animal-like yōkai,kenzokushin.[28]
The legend of the "Old Widow's Stone"(Mỗ が thạch,Ubagaishi)is another folklore story associated with the castle.[5]According to the legend,Toyotomi Hideyoshiran out of stones when building the original three-story keep, and an old woman heard about his trouble.[5]She gave him her hand millstone even though she needed it for her trade.[5]It was said that people who heard the story were inspired and also offered stones to Hideyoshi, speeding up the construction of the castle.[5]To this day, the supposed stone can be seen covered with a wire net in the middle of one of the stone walls in the castle complex.[5]
A folklore story is also associated with Sakurai Genbei, who wasIkeda Terumasa's master carpenter in the construction of the keep.[5]According to the legend, Sakurai was dissatisfied with his construction, feeling that the keep leaned a little to the southeast.[5]Eventually, he became distraught and climbed to the top of the keep, where he jumped to his death with a chisel in his mouth.[5]
Visitor statistics[edit]
- On 14 April 2009, the total number of visits since the Showa-era restoration surpassed 40 million.[29]
- 1964 – 1,738,000 (Showa-era restoration work completed)
- 1989 – 1,197,000
- 1990 – 811,000
- 1991 – 871,000
- 1992 – 885,000
- 1993 – 1,019,000
- 1994 – 983,000
- 1995 – 695,000
- 1996 – 861,000
- 1997 – 716,000
- 1998 – 792,000
- 1999 – 713,000
- 2000 – 662,000
- 2001 – 708,000
- 2002 – 729,000
- 2003 – 814,000
- 2004 – 771,000
- 2005 – 778,000
- 2006 – 899,000
- 2007 – 1,023,000
- 2008 – 1,195,000
- 2009 – 1,561,000
- 2010 – 458,000 (restoration work started)
- 2011 – 611,000
- 2012 – 711,000
- 2013 – 881,000[30]
- 2014 – 919,000[30]
- 2015 – 2,860,000 (restoration work completed in March)[31]
Additional information[edit]

National treasures and sister castles[edit]
Other national treasures (castles) besides Himeji Castle include Matsumoto Castle, Inuyama Castle, Matsue Castle, and Hikone Castle. The sister castles of Himeji Castle areChâteau de Chantillyin France andConwy Castlein Wales.[32]Castles that were of the samehirayamahilltop styles areMatsuyama Castle (Iyo)built in 1603 andTsuyama Castle.
Gallery[edit]
Panoramic overview

Views from afar
-
The castle's keeps and city as seen fromEngyō-ji
-
The castle complex as seen from the west
-
Keeps and bridge as seen from the entrance
-
A view of keeps and the lush castle grounds below
-
Keeps as seen from the grounds below
Views from below
-
One of the steep, narrow walkways controlling access to the castle
-
One of the steep castle walls
-
Himeji castle as seen from the princess's quarters
-
The keep as seen from within the inner circle(Bổn hoàn,honmaru)
-
Curved gables(Ngàn điểu phá phong,chidori hafu)
-
Detail of keep
-
Various external views with tourists, 2019
-
Himeji Castle view from below in May 2017
Views at night
Views from above
-
Castle walls and rooftops
-
East tower and corridors
-
The castle rooftops and surrounding city
-
Part of the intricate castle complex
-
A mythical tiger-headed fish calledshachi(鯱). This motif was used atop the castle towers as a talisman for fire prevention.[8]
Views from the interior
-
A stone drop window(Thạch lạc song,ishi-otoshi-mado)
-
An interior room withtatamimats
-
A hallway
-
Castle windows
-
Hallway with displays
-
A hallway
-
Weapon racks
Views with cherry blossoms
-
Taken at Three Country Moats
-
Sakura at Himeji Castle
-
Taken at Himeji City Zoo
-
Taken from the south
Views of the restoration
-
Temporary cover and gantry
-
Temporary cover
-
Different stages of applying plaster to the roof tiles. The plaster protects the roof from water ingress and stops the tiles from being dislodged by typhoon winds.
-
Roof structure underneath the tiles
-
View of the keep roof nearing completion, taken from the public view gallery
Views of pictures
-
A fish
See also[edit]
- Kōko-en,garden joining the castle complex
- Tsuyama CastleandMatsuyama Castle (Iyo),also built in thehirayama( bình thành phố núi flat hilltop castle) style
- List of National Treasures of Japan (castles)
- List of reportedly haunted locations
- List of Special Places of Scenic Beauty, Special Historic Sites and Special Natural Monuments
- List of World Heritage Sites in Japan
References[edit]
- ^"Himeji Castle and its surroundings".Sansen-ya.RetrievedJuly 6,2010.
- ^abcdefg"Himeji Castle starts its renovation in April".Official Tourism Guide for Japan Travel. Archived fromthe originalon March 24, 2011.RetrievedJuly 1,2010.
- ^abcdefghijklmnopqr"A hilltop white heron 400 years old".The Daily Yomiuri.RetrievedJuly 5,2010.
- ^abcdeJacqueline A., Ball (2005).Himeji Castle: Japan's Samurai Past.New York: Bearport Publishing. p. 32.ISBN1-59716-001-6.
- ^abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzaaabacadaeafagahaiajakalamanaoapaqarasatauavawaxayazbabbbcbdbebfbgbhbibjbkblbm"National Treasure Himeji Castle Guide book"(PDF).Himeji Rojyo Lions Club. 2000. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on July 10, 2011.RetrievedJuly 10,2010.
- ^abcdefBornoff, Nicholas (2000).The National Geographic Traveler: Japan.Washington: National Geographic Society. pp. 256–257.ISBN0-7894-5545-5.
- ^abcdefg"Himeji-jo".UNESCOWorld Heritage Centre.RetrievedJuly 4,2010.
- ^abcdefghEyewitness Travel Guides: Japan.New York: Dorling Kindersley Publishing. 2000. pp. 200–203.ISBN0-7894-5545-5.
- ^Thiên thủ các は vật trí だった? 「 Nhật Bản の thành 」 の giáo dưỡng 10 tuyển(in Japanese).Toyo Keizai.June 23, 2016. Archived fromthe originalon July 30, 2019.RetrievedApril 7,2024.
- ^abcde"Himeji Castle".Japan Atlas.RetrievedJuly 5,2010.
- ^abQuốc bảo một lãm(in Japanese).Himeji city.Archived fromthe originalon September 27, 2010.RetrievedJuly 5,2010.
- ^abc"The Three Famous Castles of Japan".Kobayashi Travel Service. Archived fromthe originalon March 22, 2010.RetrievedJuly 4,2010.
- ^ab"Cơ lộ thị | nay chu の cơ lộ thành ( 27 năm 2 nguyệt 9 ngày hiện tại )".Archived fromthe originalon February 15, 2015.RetrievedJanuary 28,2015.
- ^Hinago, Motoo (1986).Japanese Castles.Kodansha International Ltd. and Shibundo. pp. 121–125.ISBN0-87011-766-1.
- ^abcdO'Grady, Daniel."Japanese Castle Explorer – Himeji Castle".Japanese Castle Explorer.RetrievedJuly 11,2010.
- ^abcd"Thế giới di sản cơ lộ thành thành の lặc しみ phương".RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^abLowe, Sam (May 11, 2010)."Restoring a Japanese Treasure".Best Western's Travel Blog. Archived fromthe originalon May 24, 2010.RetrievedJuly 11,2010.
- ^"Cơ lộ thành đại thiên thủ".Archived fromthe originalon June 24, 2016.RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^"National Treasure, World Heritage, Himeji Castle".RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^"Cơ lộ thành càn tiểu thiên thủ".RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^"Cơ lộ thành tây tiểu thiên thủ".Archived fromthe originalon June 24, 2016.RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^"Cơ lộ thành đông tiểu thiên thủ".Archived fromthe originalon June 24, 2016.RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^"Cơ lộ thành イ・ロ・ハ・ニ の độ lỗ phụ đài sở 1 đống".Archived fromthe originalon May 8, 2016.RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^"Kokoen Garden, Traditional Japanese Garden in Himeji City".EOK.RetrievedJuly 4,2010.
- ^Cơ lộ thị sử đệ thập tứ quyển đừng biên cơ lộ thành.Himeji City: City of Himeji. 2001. p. 494.
- ^abTurnbull, Stephen (2003).Japanese Castles 1540–1640.Oxford: Osprey Publishing. p. 64.ISBN978-1-84176-429-0.
- ^Ishikawa, Ichirō; thạch xuyên một lang (1989).Edo bungaku zokushin jiten(Shohan ed.). Tōkyō: Tōkyōdō Shuppan. p. 63.ISBN4-490-10255-0.OCLC22591554.
- ^abMeyer, Mathew."Osakabe hime".Yokai.Archivedfrom the original on February 2, 2021.RetrievedFebruary 12,2021.
- ^Cơ lộ thành, vào bàn giả 4000 vạn người đột phá chiêu cùng の đại tu lý から45 năm でArchivedJuly 12, 2014, at theWayback Machine( cộng đồng thông tín 2009 năm 4 nguyệt 14 ngày )
- ^ab"Bình thành 26 niên độ cơ lộ thị nhập 込 khách số, quan quang hướng đi ・イベントアンケート điều tra báo cáo thư P3"(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on June 16, 2016.RetrievedMay 18,2016.
- ^Yoshiko Yukinaga."“Cơ lộ thành tới tràng giả, Nhật Bản một に. Qua đi nhiều nhất 286 vạn người” ".Mainichi Shinbun.RetrievedMay 13,2016.
- ^"Cơ lộ thị | tỷ muội đô thị ( hải ngoại ・ quốc nội ) / tỷ muội thành".city.himeji.lg.jp/(in Japanese).RetrievedNovember 14,2021.
- Further reading
- Benesch, Oleg. "Castles and the Militarisation of Urban Society in Imperial Japan,"Transactions of the Royal Historical Society,Vol. 28 (Dec. 2018), pp. 107-134.
- Benesch, Oleg and Ran Zwigenberg (2019).Japan's Castles: Citadels of Modernity in War and Peace.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 375.ISBN9781108481946.
- De Lange, William (2021).An Encyclopedia of Japanese Castles.Groningen: Toyo Press. pp. 600 pages.ISBN978-9492722300.
- Mitchelhill, Jennifer (2013).Castles of the Samurai:Power & Beauty.USA: Kodansha.ISBN978-1-56836-512-1.
- Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974).Castles in Japan.Tokyo: Charles E. Tuttle Co. pp.123–125.ISBN0-8048-1102-4.
- Motoo, Hinago (1986).Japanese Castles.Tokyo: Kodansha.ISBN0-87011-766-1.
External links[edit]
- Official website
- Asian Historical Architecture – Himeji Castle
- Japanese Castle Explorer – Himeji Castle
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre – Himeji Castle
- Japan Atlas: Himeji Castle
- Video
- The White Fortress: Himeji-jo(UNESCOvideo on YouTube)
- Himeji Castle timelapseonYouTube
- Discover the Himeji Castle in Japan
- Virtual tour of Himeji Castle examining its modern history on the Japan's Modern Castles YouTube channel
- 1581 establishments in Japan
- Buildings and structures completed in 1346
- Buildings and structures completed in 1581
- Buildings and structures completed in 1609
- Castles in Hyōgo Prefecture
- Buildings and structures in Himeji
- Tourist attractions in Himeji
- Honda clan
- Houses completed in 1618
- Ikeda clan
- Important Cultural Properties of Hyōgo Prefecture
- Kuroda clan
- Maebashi-Matsudaira clan
- National Treasures of Japan
- Okudaira-Matsudaira clan
- Reportedly haunted locations in Japan
- Sakai clan
- Sakakibara clan
- Special Historic Sites
- Toyotomi clan
- World Heritage Sites in Japan

























![A mythical tiger-headed fish called shachi (鯱). This motif was used atop the castle towers as a talisman for fire prevention.[8]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/88/Himeji_Castle_No09_125.jpg/120px-Himeji_Castle_No09_125.jpg)




















