History of Albania
| History ofAlbania |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
Duringclassical antiquity,Albaniawas home to severalIllyrian tribessuch as theAlbanoi,Ardiaei,Bylliones,Dassaretii,Enchele,Labeatae,Taulantii,Parthini,Penestae,Amantes,and many others, but alsoBrygesandEpirotetribes, as well as severalGreek coloniesestablished on theIllyrian coastin cooperation with the local Illyrians, notablyEpidamnos-DyrrhachiumandApollonia.
The Enchele's polity was the earliest to emerge and centered in Albania. Also the earliest known Illyrian king,Bardylis,emerged in what is now Albania around 400 BC, aiming to make Illyria a regional power interfering withMacedon.He united many southernIllyrian tribesunder his realm and defeated theMacedoniansandMolossiansseveral times, expanding his dominion overUpper MacedoniaandLynkestis.Before theRise of MacedonIllyrians were the dominant power in the region. The kingdom of theTaulantiiunderGlaukias' rule was based in central Albania and dominated southern Illyrian affairs in the late 4th century BC, exerting great influence on theEpirote statethrough the close ties with theMolossiankingPyrrhus.Under the Ardiaei the greatest known Illyrian kingdom emerged in the 3rd century BC encompassing also northern Albania in its core territory. It became a formidable power both on land and sea by assembling a great army and fleet, and directly ruling over a large area made up of different Illyrian tribes and cities that stretched from theNeretva Riverin the north to the borders of Epirus in the south, while its influence extended throughout Epirus and down intoAcarnania.The dominant power of the Illyrian kingdom in the region ceased after the Illyrian defeat in theIllyro-Roman Wars(229–168 BC). The last known "King of the Illyrians" wasGentius,of the Labeatae tribe.
In the early 2nd century BC, the area was annexed byRomeand became part of theRoman provincesofDalmatia,MacedoniaandMoesia Superior.Afterwards, the territory remained under Roman andByzantinecontrol until theSlavic migrationsof the 7th century. It was integrated into theBulgarian Empirein the 9th century.
In theMiddle Ages,thePrincipality of Arbërand a Sicilian union known as themedieval Kingdom of Albaniawere established. Some areas became part of theVenetianand laterSerbian Empire.Between the mid-14th and the late 15th centuries, most of modern-day Albania was dominated byAlbanian principalities,when the Albanian principalities fell to the rapid invasion of theOttoman Empire.Albania remained under Ottoman control as part of the province ofRumeliauntil 1912; with some interruptions during the 18th and 19th century with the establishment of autonomy-minded Albanian lords. The first independent Albanian state was founded by theAlbanian Declaration of Independencefollowing a short occupation by theKingdom of Serbia.The formation of anAlbanian national consciousnessdates to the later 19th century and is part of the larger phenomenon of therise of nationalism under the Ottoman Empire.
A short-lived monarchical state known as thePrincipality of Albania(1914–1925) was succeeded by an even shorter-lived firstAlbanian Republic(1925-1928). Another monarchy, theKingdom of Albania (1928–1939),replaced the republic. The country enduredoccupation by Italyjust prior toWorld War II(1939–1945). After theArmistice of CassibilebetweenItalyand theAllies,Albania wasoccupied by Nazi Germany.Following the collapse of theAxis powers,Albania became aone-partycommunist state,thePeople's Socialist Republic of Albania,which for most of its duration was dominated by dictatorEnver Hoxha(died 1985). Hoxha's political heirRamiz Aliaoversaw the disintegration of the "Hoxhaist"state during the wider collapse of theEastern Blocin the later 1980s.
The communist regime collapsed in 1990, and the former communistParty of Labour of Albaniawas routed in elections in March 1992, amid economic collapse and social unrest. The unstable economic situation led to anAlbanian diaspora,mostly toItaly,Greece,Switzerland,Germanyand North America during the 1990s. The crisis peaked in theAlbanian Turmoil of 1997.An amelioration of the economic and political conditions in the early years of the 21st century enabled Albania to become a full member ofNATOin 2009. The country is applying to join theEuropean Union.
Prehistory[edit]
Mesolithic & Neolithic[edit]

The first traces of human presence in Albania, dating to theMiddle PaleolithicandUpper Paleolithiceras, were found in the village of Xarrë, nearSarandëandDajtinearTirana.[1]The objects found in a cave near Xarrë include flint and jasper objects and fossilized animal bones, while those found at Mount Dajt comprise bone and stone tools similar to those of theAurignacian culture.The Paleolithic finds of Albania show great similarities with objects of the same era found at Crvena Stijena inMontenegroand north-westernGreece.[1]There are severalarchaeological sitesin Albania that carry artifacts dating from theNeolithicera, and they are dated between 6,000 and the end of the EBA. The most important are found inMaliq,Gruemirë,Dushman (Dukagjin),on theErzenriver (close toShijak), nearDurrës,Ziçisht,Nepravishtë,Finiq,andButrint.[2]
Bronze Age[edit]
The next period in the prehistory of Albania coincides with the Indo-Europeanization of the Balkans, which involvedPontic steppe migrationswhich brought the Indo-European languages in the region and the formation of thePaleo-Balkanpeoples as the result of fusion between the Indo-European-speaking population and the Neolithic population. In Albania, consecutive movements from the northern parts of the region which became known asIllyriain the Iron Age had a significant impact in the formation of the new post-Indo-European migration population. The ancestral groups to Iron AgeIllyriansare usually identified in Albania towards the end of the EBA with movements from north of Albania and are linked to the construction oftumuliburial grounds of patrilineally organized clans.[3]Some of the first tumuli date to 26th century BCE. These burial mounds belong to the southern expression of the Adriatic-Ljubljana culture (related toCetina culture) which moved southwards along the Adriatic from the northern Balkans. The same community built similar mounds in Montenegro (Rakića Kuće) and northern Albania (Shtoj).[4]
In the late Bronze Age and earlyIron Agea number of possible population movements occurred in the territories of modern Albania, for example the settlement of theBrygesin areas of southern Albania-northwestern Greece[5]andIllyriantribes into central Albania.[6]The latter derived from early an Indo-European presence in the westernBalkan Peninsula.The movement of the Byrgian tribes can be assumed to coincide with the beginning Iron Age in the Balkans during the early 1st millennium BC.[7]
Antiquity[edit]
Illyrians[edit]

TheIllyrianswere a group of tribes who inhabited the westernBalkansduring theclassical times.The territory the tribes covered came to be known asIllyriatoGreekandRomanauthors, corresponding roughly to the area between theAdriatic Seain the west, theDravariver in the north, theMoravariver in the east and the mouth ofVjosëriver in the south.[8][9]The first account of theIllyrian peoplescomes from the Coastal Passage contained in aperiplus,an ancient Greek text of the middle of the 4th century BC.[10]
Several Illyrian tribes that resided in the region of Albania were theArdiaei,TaulantiiandAlbanoi[11]in central Albania,[12]theParthini,theAbriand theCaviiiin the north, theEncheleiin the east,[13]theByllionesin the south andseveral others.In the westernmost parts of the territory of Albania, along with the Illyrian tribes, lived theBryges,[14]aPhrygianpeople, and in the south[15][16]lived the Greek tribe of theChaonians.[14][17][18]

In the 4th century BC, the Illyrian kingBardylisunited several Illyrian tribes and engaged in conflicts withMacedonto the south-east, but was defeated. Bardyllis was succeeded byGrabos II,[19]then byBardylis II,[20]and then byCleitus the Illyrian,[20]who was defeated byAlexander the Great.
Around 230 BC, the Ardiaei briefly attained military might under the reign of king Agron. Agron extended his rule over other neighbouring tribes as well.[21]He raided parts ofEpirus,Epidamnus,and the islands of Corcyra and Pharos. His state stretched from Narona in Dalmatia south to the river Aoos and Corcyra. During his reign, the Ardiaean Kingdom reached the height of its power. The army and fleet made it a major regional power in the Balkans and the southern Adriatic. The king regained control of the Adriatic with his warships (lembi), a domination once enjoyed by theLiburnians.None of his neighbours were nearly as powerful. Agron divorced his (first) wife.
Agron suddenly died,c. 231 BC,after his triumph over theAetolians.Agron's (second) wife was QueenTeuta,who acted as regent after Agron's death. According toPolybius,she ruled "by women's reasoning".[22]Teuta started to address the neighbouring states malevolently, supporting the piratical raids of her subjects. After capturingDyrrhachiumand Phoenice, Teuta's forces extended their operations further southward into theIonian Sea,defeating the combinedAchaeanand Aetolian fleet in theBattle of Paxosand capturing the island ofCorcyra.[citation needed]Later on, in 229 BC, she clashed with the Romans and initiated theIllyrian Wars.These wars, which were spread out over 60 years, eventually resulted in defeat for the Illyrians by 168 BC and the end of Illyrian independence when KingGentiuswas defeated by a Roman army after heavy clashes with Rome and Roman allied cities such asApolloniaandDyrrhachiumunderAnicius Gallus.[citation needed]After his defeat, the Romans split the region into three administrative divisions,[23]calledmeris.[24]
Greeks and Romans[edit]

Beginning in the 7th century BC, Greek colonies were established on the Illyrian coast. The most important wereApollonia,Aulon (modern-dayVlorë),Epidamnos(modern-dayDurrës), andLissus(modern-dayLezhë). The city ofButhrotum(modern-day Butrint), aUNESCO World Heritage Site,is probably more significant today than it was whenJulius Caesarused it as a provisions depot for his troops during his campaigns in the 1st century BC. At that time, it was considered an unimportant outpost, overshadowed by Apollonia and Epidamnos.[25]

The lands comprising modern-day Albania were incorporated into the Roman Empire as part of the province ofIllyricumabove the riverDrin,and RomanMacedonia(specifically asEpirus Nova) below it. The western part of theVia Egnatiaran inside modern Albania, ending atDyrrachium.Illyricumwas later divided into the provinces ofDalmatiaandPannonia.
TheRoman provinceofIllyricumor[26][27]Illyris RomanaorIllyris BarbaraorIllyria Barbarareplaced most of the region ofIllyria.It stretched from theDrilonRiver in modernAlbaniatoIstria(Croatia) in the west and to theSavaRiver (Bosnia and Herzegovina) in the north.Salona(near modernSplitin Croatia) functioned as its capital. The regions which it included changed through the centuries though a great part of ancientIllyriaremained part ofIllyricum.
South Illyria becameEpirus Nova,part of the Roman province of Macedonia. In 357 AD the region was part of thePraetorian prefecture of Illyricumone of four largepraetorian prefecturesinto which theLate Roman Empirewas divided. By 395 AD dioceses in which the region was divided were theDiocese of Dacia(as Pravealitana), and theDiocese of Macedonia(as Epirus Nova). Most of the region of modern Albania corresponds to theEpirus Nova.
Christianization[edit]

Christianity came toEpirus nova,then part of the Roman province ofMacedonia.[28]Since the 3rd and 4th century AD, Christianity had become the established religion inByzantium,supplanting pagan polytheism and eclipsing for the most part the humanistic world outlook and institutions inherited from the Greek and Roman civilizations. TheDurrës Amphitheatre(Albanian: Amfiteatri i Durrësit)is a historic monument from the time period located in Durrës, Albania, that was used to preach Christianity to civilians during that time.
When theRoman Empirewas divided into eastern and western halves in AD 395, Illyria east of the Drinus River (DrinabetweenBosniaandSerbia), including the lands form Albania, were administered by the Eastern Empire but were ecclesiastically dependent onRome.Though the country was in the fold ofByzantium,Christians in the region remained under the jurisdiction of thePopeuntil 732. In that year the iconoclast Byzantine emperorLeo III,angered by archbishops of the region because they had supported Rome in theIconoclastic Controversy,detached the church of the province from the Roman pope and placed it under thepatriarch of Constantinople.
When theChristian church split in 1054 between Eastern Orthodoxy and Catholicism,the region of southern Albania retained its ties toConstantinople,while the north reverted to the jurisdiction of Rome. This split marked the first significant religious fragmentation of the country. After the formation of the Slav principality of Dioclia (modernMontenegro), the metropolitan see ofBarwas created in 1089, and dioceses in northern Albania (Shkodër,Ulcinj) became its suffragans. Starting in 1019, Albanian dioceses of the Byzantine rite were suffragans of the independentArchdiocese of OhriduntilDyrrachionandNicopolis,were re-established as metropolitan sees. Thereafter, only the dioceses in inner Albania (Elbasan,Krujë) remained attached toOhrid.In the 13th century during theVenetianoccupation, the Latin Archdiocese of Durrës was founded.
Middle Ages[edit]
Early Middle Ages[edit]
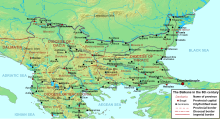

After the region fell to the Romans in 168 BC it became part ofEpirus novathat was, in turn, part of the Roman province ofMacedonia.When theRoman Empirewas divided into East and West in 395, the territories of modern Albania became part of theByzantine Empire.Beginning in the first decades of Byzantine rule (until 461), the region suffered devastating raids byVisigoths,Huns,andOstrogoths.In the 6th and 7th centuries, theSlavic migrations to Southeastern EuropeforcedAlbaniansandVlachsto pull back into the mountainous regions and adopt nomadic lifestyle, or flee intoByzantine Greece.[29]
In general, the invaders destroyed or weakened Roman andByzantinecultural centres in the lands that would become Albania.[30]
In the late 11th and 12th centuries, the region played a crucial part in theByzantine–Norman wars;Dyrrhachium was the westernmost terminus of theVia Egnatia,the main overland route to Constantinople, and was one of the main targets of the Normans (cf. Battle of Dyrrhachium (1081)). Towards the end of the 12th century, as Byzantine central authority weakened and rebellions and regionalist secessionism became more common, the region ofArbanonbecame an autonomous principality ruled by its own hereditary princes. In 1258, the Sicilians took possession of the island ofCorfuand the Albanian coast, from Dyrrhachium to Valona and Buthrotum and as far inland as Berat. This foothold, reformed in 1272 as the "Kingdom of Albania",was intended by the dynamic Sicilian ruler,Charles of Anjou,to become the launchpad for an overland invasion of the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines, however, managed to recover most of Albania by 1274, leaving only Valona and Dyrrhachium in Charles' hands. Finally, when Charles launched his much-delayed advance, it was stopped at the Siege of Berat in 1280–1281. Albania would remain largely part of the Byzantine empire until theByzantine civil war of 1341–1347when it fell shortly to the hands of the Serbian rulerStephen Dushan.During this time, the territory becameAlbanianmajority as theBlack Deathwiped out much of itsGreek population.[29]
In the mid-9th century, most of eastern Albania became part of theBulgarian Empire.The area, known asKutmichevitsa,became an important Bulgarian cultural center in the 10th century with many thriving towns such asDevol,Glavinitsa (Ballsh) and Belgrad (Berat). When the Byzantines managed to conquer the First Bulgarian Empire the fortresses in eastern Albania were some of the last Bulgarian strongholds to submit to the Byzantines. Later the region was recovered by theSecond Bulgarian Empire.
In theMiddle Ages,the name Arberia began to be increasingly applied to the region now comprising the nation of Albania. The first undisputed mention of Albanians in the historical record is attested in a Byzantine source for the first time in 1079–1080, in a work titledHistoryby Byzantine historianMichael Attaliates,who referred to theAlbanoias having taken part in a revolt againstConstantinoplein 1043 and to theArbanitaias subjects of the duke ofDyrrhachium.A later reference to Albanians from the same Attaliates, regarding the participation of Albanians in a rebellion around 1078, is undisputed.[31]
Principality of Arbër[edit]

In 1190, thePrincipality of Arbër(Arbanon) was founded by archonProgonin the region ofKrujë.Progon was succeeded byGjin Progoniand thenDhimitër Progoni.Arbanon extended over the modern districts ofcentral Albania,with its capital located atKrujë.
The principality of Arbanon was established in 1190 by the nativearchonProgonin the region surroundingKruja,to the east and northeast ofVenetianterritories.[32]Progon was succeeded by his sonsGjinand thenDemetrius(Dhimitër), who managed to retain a considerable degree of autonomy from theByzantine Empire.[33]In 1204, Arbanon attained full, though temporary, political independence, taking advantage of the weakening of Constantinople following itspillageduring theFourth Crusade.[34]However, Arbanon lost its large autonomy ca. 1216, when the ruler ofEpirus,Michael I Komnenos Doukas,started an invasion northward intoAlbaniaandMacedonia,takingKrujaand ending the independence of the principality of Arbanon following the death of Dhimitër.[35]After the death of Demetrius, the last ruler of the Progon family, the same year, Arbanon was successively controlled subsequently by theDespotate of Epirus,theBulgarian Empireand, from 1235, by theEmpire of Nicaea.[36]
During the conflicts betweenMichael II Komnenos Doukasof Epirus and EmperorJohn III Doukas Vatatzes,Golem (ruler of Arbanon at the time) and Theodore Petraliphas, who were initially Michael's allies, defected to John III in 1252.[37]He is last mentioned in the sources among other local leaders, in a meeting with George Akropolites in Durrës in 1256. Arbanon was a beneficiary of the Via Egnatia trade road, which brought wealth and benefits from the more developed Byzantine civilization.[38]
High Middle Ages[edit]

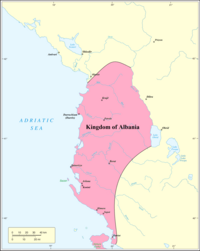
After the fall of thePrincipality of Arberin territories captured by theDespotate of Epirus,theKingdom of Albaniawas established byCharles of Anjou.He took the title of King ofAlbaniain February 1272. The kingdom extended from the region of Durrës (then known as Dyrrhachium) south along the coast to Butrint. After the failure of the Eighth Crusade, Charles of Anjou returned his attention to Albania. He began contacting local Albanian leaders through local catholic clergy. Two local Catholic priests, namely John from Durrës and Nicola from Arbanon, acted as negotiators between Charles of Anjou and the local noblemen. During 1271 they made several trips between Albania and Italy eventually succeeding in their mission.[39]
On 21 February 1272, a delegation of Albanian noblemen and citizens from Durrës made their way to Charles' court. Charles signed a treaty with them and was proclaimed King of Albania "by common consent of the bishops, counts, barons, soldiers and citizens" promising to protect them and to honor the privileges they had from Byzantine Empire.[40]The treaty declared the union between the Kingdom of Albania (Latin:Regnum Albanie) with the Kingdom of Sicily under King Charles of Anjou (Carolus I, dei gratia rex Siciliae et Albaniae).[39]He appointed Gazzo Chinardo as his Vicar-General and hoped to take up his expedition against Constantinople again. Throughout 1272 and 1273 he sent huge provisions to the towns of Durrës and Vlorë. This alarmed the Byzantine Emperor, Michael VIII Palaiologos, who began sending letters to local Albanian nobles, trying to convince them to stop their support for Charles of Anjou and to switch sides. However, the Albanian nobles placed their trust on Charles, who praised them for their loyalty. Throughout its existence the Kingdom saw armed conflict with the Byzantine empire. The kingdom was reduced to a small area in Durrës. Even before the city of Durrës was captured, it was landlocked by Karl Thopia's principality. Declaring himself as Angevin descendant, with the capture ofDurrësin 1368Karl Thopiacreated thePrincedom of Albania.During its existence Catholicism saw rapid spread among the population which affected the society as well as the architecture of the Kingdom. AWestern type of feudalismwas introduced and it replaced the ByzantinePronoia.
Principalities and League of Lezhë[edit]

In 1371, theSerbian Empirewas dissolved and several Albanian principalities were formed including thePrincipality of Kastrioti,Principality of AlbaniaandDespotate of Artaas the major ones. In the late 14th and the early 15th century theOttoman Empireconquered parts of south and central Albania. The Albanians regained control of their territories in 1444 when theLeague of Lezhëwas established, under the rule ofGeorge KastriotiSkanderbeg,the Albanian national hero. The League was a military alliance of feudal lords in Albania forged in Lezhë on 2 March 1444, initiated and organised under Venetian patronage[41]with Skanderbeg as leader of the regional Albanian and Serbian chieftains united against the Ottoman Empire.[42]The main members of the league were the Arianiti, Balšić, Dukagjini, Muzaka, Spani, Thopia and Crnojevići. For 25 years, from 1443 to 1468, Skanderbeg's 10,000-man army marched through Ottoman territory winning against consistently larger and better supplied Ottoman forces.[43]Threatened by Ottoman advances in their homeland, Hungary, and later Naples and Venice – their former enemies – provided the financial backbone and support for Skanderbeg's army.[44]By 1450 it had certainly ceased to function as originally intended, and only the core of the alliance under Skanderbeg and Araniti Comino continued to fight on.[45]After Skanderbeg's death in 1468, the sultan "easily subdued Albania," but Skanderbeg's death did not end the struggle for independence,[46]and fighting continued until the Ottomansiege of Shkodrain 1478–79, a siege ending when the Republic of Venice ceded Shkodra to the Ottomans in the peace treaty of 1479.
Ottoman Era[edit]
Early Ottoman period[edit]
Ottomansupremacy in the westBalkanregion began in 1385 with their success in theBattle of Savra.Following that battle, theOttoman Empirein 1415 established theSanjak of Albania[47]covering the conquered parts of Albania, which included territory stretching from theMat Riverin the north toChameriain the south. In 1419,Gjirokastrabecame the administrative centre of the Sanjak of Albania.[48]
The northern Albanian nobility, although tributary of the Ottoman Empire they still had autonomy to rule over their lands, but the southern part which was put under the direct rule of theOttoman Empire,prompted by the replacement of large parts of the local nobility with Ottoman landowners, centralized governance and the Ottoman taxation system, the population and the nobles, led principally byGjergj Arianiti,revolted against the Ottomans.
During the early phases of the revolt, many land (timar) holders were killed or expelled. As the revolt spread, the nobles, whose holdings had been annexed by the Ottomans, returned to join the revolt and attempted to form alliances with theHoly Roman Empire.While the leaders of the revolt were successful in defeating successive Ottoman campaigns, they failed to capture many of the important towns in theSanjak of Albania.Major combatants included members of theDukagjini,Zenebishi,Thopia,KastriotiandArianitifamilies. In the initial phase, the rebels were successful in capturing some major towns such as Dagnum. Protracted sieges such as that ofGjirokastër,the capital of the Sanjak, gave the Ottoman army time to assemble large forces from other parts of the empire and to subdue the main revolt by the end of 1436. Because the rebel leaders acted autonomously without a central leadership, their lack of coordination of the revolt contributed greatly to their final defeat.[49]Ottoman forces conducted a number of massacres in the aftermath of the revolt.
Ottoman-Albanian Wars[edit]

Many Albanians had been recruited into theJanissarycorps, including the feudal heirGeorge Kastriotiwho was renamedSkanderbeg(Iskandar Bey) by his Turkish officers atEdirne.After the Ottoman defeat in theBattle of Nišat the hands of theHungarians,Skanderbeg deserted in November 1443 and began a rebellion against the Ottoman Empire.[50]


After his desertion,Skanderbegre-converted to Christianity and declared war against the Ottoman Empire,[50]which he led from 1443 to 1468. Skanderbeg summoned the Albanian princes to the Venetian-controlled town of Lezhë where they formed the League of Lezhë.[51]Gibbon reports that the "Albanians, a martial race, were unanimous to live and die with their hereditary prince", and that "in the assembly of the states of Epirus, Skanderbeg was elected general of the Turkish war and each of the allies engaged to furnish his respective proportion of men and money".[52]Under a red flag bearing Skanderbeg's heraldic emblem, an Albanian force held off Ottoman campaigns for twenty-five years and overcame a number of the major sieges:Siege of Krujë (1450),Second Siege of Krujë(1466–67),Third Siege of Krujë(1467) against forces led by the Ottoman sultansMurad IIandMehmed II.For 25 years Skanderbeg's army of around 10,000 men marched through Ottoman territory winning against consistently larger and better supplied Ottoman forces.[43]
Throughout his rebellion, Skanderbeg defeated the Ottomans in a number of battles, includingTorvioll,Oranik,Otonetë,Modric,OhridandMokra;with his most brilliant being inAlbulena.However, Skanderbeg did not receive any of the help which had been promised to him by the popes or the Italian states, Venice, Naples and Milan. He died in 1468, leaving no clear successor. After his death the rebellion continued, but without its former success. The loyalties and alliances created and nurtured by Skanderbeg faltered and fell apart and the Ottomans reconquered the territory of Albania, culminating with thesiege of Shkodrain 1479. However, some territories in Northern Albania remained underVenetian control.Shortly after the fall of the castles of northern Albania, many Albanians fled to neighbouring Italy, giving rise to theArbëreshëcommunities still living in that country.
Skanderbeg's long struggle to keep Albania free became highly significant to the Albanian people, as it strengthened their solidarity, made them more conscious of their national identity, and served later as a great source of inspiration in their struggle for national unity, freedom and independence.[53]
Late Ottoman period[edit]
Upon theOttomansreturn in 1479, a large number ofAlbaniansfled to Italy,Egyptand other parts of the Ottoman Empire and Europe and maintained theirArbëreshidentity. Many Albanians won fame and fortune as soldiers, administrators, and merchants in far-flung parts of the Empire. As the centuries passed, however, Ottoman rulers lost the capacity to command the loyalty of localpashas,which threatened stability in the region. TheOttomanrulers of the 19th century struggled to shore up central authority, introducing reforms aimed at harnessing unruly pashas and checking the spread of nationalist ideas.Albaniawould be a part of theOttoman Empireuntil the early 20th century.
The Ottoman period that followed was characterized by a change in the landscape through a gradual modification of the settlements with the introduction ofbazaars,military garrisons and mosques in many Albanian regions. Part of the Albanian population gradually converted to Islam, with many joining theSufiOrder of theBektashi.Converting from Christianity to Islam brought considerable advantages, including access to Ottoman trade networks, bureaucratic positions and the army. As a result, many Albanians came to serve in the eliteJanissaryand the administrativeDevşirmesystem. Among these were important historical figures, includingIljaz Hoxha,Hamza Kastrioti,Koca Davud Pasha,Zağanos Pasha,Köprülü Mehmed Pasha(head of theKöprülü familyofGrand Viziers), theBushatifamily,Sulejman Pasha,Edhem Pasha,Nezim Frakulla,Haxhi Shekreti,Hasan Zyko Kamberi,Ali Pasha of Gucia,Muhammad Aliruler ofEgypt,[54]Ali Pasha of Tepelenarose to become one of the most powerful Muslim Albanian rulers in westernRumelia.His diplomatic and administrative skills, his interest in modernist ideas and concepts, his popular religiousness, his religious neutrality, his win over the bands terrorizing the area, his ferocity and harshness in imposing law and order, and his looting practices towards persons and communities in order to increase his proceeds cause both the admiration and the criticism of his contemporaries. His court was in Ioannina, but the territory he governed incorporated most of Epirus and the western parts of Thessaly and Greek Macedonia in Northern Greece.
Many Albanians gained prominent positions in theOttomangovernment, Albanians highly active during theOttoman eraand leaders such as Ali Pasha of Tepelena might have aidedHusein Gradaščević.The Albanians proved generally faithful to Ottoman rule following the end of the resistance led by Skanderbeg, and accepted Islam more easily than their neighbors.[55]
Semi-independent Albanian Pashaliks[edit]
A period of semi-independence started during the mid 18th century. AsOttomanpower began to decline in the 18th century, the central authority of the empire in Albania gave way to the local authority of autonomy-minded lords. The most successful of those lords were three generations of pashas of theBushati family,who dominated most of northern Albania from 1757 to 1831, andAli Pasha TepelenaofJanina(now Ioánnina, Greece), a brigand-turned-despot who ruled over southern Albania and northern Greece from 1788 to 1822.
Those pashas created separate states within the Ottoman state until they were overthrown by the sultan.[56][57]
Modern[edit]
National Renaissance[edit]
In the 1870s, theSublime Porte's reforms aimed at checking theOttoman Empire's disintegration had failed. The image of the "Turkish yoke" had become fixed in the nationalist mythologies and psyches of the empire's Balkan peoples and their march toward independence quickened. TheAlbanians,because of the higher degree of Islamic influence, their internal social divisions, and the fear that they would lose theirAlbanian-speakingterritories to the emergingSerbia,Montenegro,Bulgaria,andGreece,were the last of the Balkan peoples to desire division from theOttoman Empire.[58]With the rise of the Albanian National Awakening,Albaniansregained a sense of statehood and engaged in military resistance against the Ottoman Empire as well as instigating a massive literary revival. Albanian émigrés in Bulgaria, Egypt, Italy, Romania and the United States supported the writing and distribution of Albanian textbooks and writings.
League of Prizren[edit]

In the second quarter of the 19th century, after the fall of theAlbanian pashaliksand theMassacre of the Albanian Beys,anAlbanian National Awakeningtook place and many revolts against the Ottoman Empire were organized. These revolts included theAlbanian Revolts of 1833–1839,theRevolt of 1843–44,and theRevolt of 1847.A culmination of the Albanian National Awakening was the League of Prizren. The league was formed at a meeting of 47 Ottoman beys inPrizrenon 18 June 1878. An initial position of the league was presented in a document known asKararname.Through this document Albanian leaders emphasized their intention to preserve and maintain the territorial integrity of the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans by supporting theporte,and "to struggle in arms to defend the wholeness of the territories of Albania". In this early period, the League participated in battles against Montenegro and successfully wrestled control over Plav and Gusinje after brutal warfare with Montenegrin troops. In August 1878, theCongress of Berlinordered a commission to determine the border between theOttoman EmpireandMontenegro.Finally, theGreat Powersblockaded Ulcinj by sea and pressured the Ottoman authorities to bring the Albanians under control. Albanian diplomatic and military efforts were successful in wresting control of Epirus, however some lands were still ceded to Greece by 1881.
The League's founding figureAbdyl Frashëriinfluenced the League to demand autonomy and wage open war against the Ottomans. Faced with growing international pressure "to pacify" the refractory Albanians, the sultan dispatched a large army underDervish Turgut Pashato suppress the League of Prizren and deliver Ulcinj to Montenegro. The League of Prizren's leaders and their families were arrested and deported. Frashëri, who originally received a death sentence, was imprisoned until 1885 and exiled until his death seven years later. A similar league was established in 1899 in Peja by former League memberHaxhi Zeka.The league ended its activity in 1900 after an armed conflict with the Ottoman forces. Zeka was assassinated by a Serbian agent Adem Zajmi in 1902.
Independence[edit]

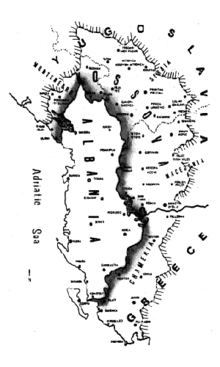
The initial sparks of theFirst Balkan warin 1912 were ignited by theAlbanian uprisingbetween 1908 and 1910, which had the aim of opposing theYoung Turkpolicies of consolidation of theOttoman Empire.[59]Following the eventual weakening of the Ottoman Empire in theBalkans,Serbia,Greece,andBulgariadeclared war, seizing the remaining Ottoman territory inEurope.The territory of Albania was occupied by Serbia in the north and Greece in the south, leaving only a patch of land around the southern coastal city ofVlora.The short-livedAlbanian Control Commission(17 October 1912 to 30 May 1913) was set up by them to rule Albania.[60]
The unsuccessful uprising of1910,1911andthe successful and final Albanian revolt in 1912,as well as the Serbian and Greek occupation and attempts to incorporate the land into their respective countries, led to a proclamation of independence byIsmail KemalinVlorëon 28 November 1912. The same day, Kemal waved the national flag of Albania, from the balcony of theAssembly of Vlorë,in the presence of hundreds ofAlbanians.This flag was sewn afterSkanderbeg's principality flag, which had been used more than 500 years earlier.
Albanian independence was recognized by theConference of Londonon 29 July 1913.[61][62]The Conference of London thendelineated the border between Albania and its neighbors,leaving more than half of ethnic Albanians outside Albania. This population was largely divided between Montenegro and Serbia in the north and east (including what is nowKosovoandNorth Macedonia), and Greece in the south. A substantial number of Albanians thus came under Serbian rule.[63]
At the same time, an uprising in the country's south by local Greeks led to the formation of theAutonomous Republic of Northern Epirusin the southern provinces (1914).[64]The republic proved short-lived as Albania collapsed with the onset ofWorld War I.Greece held the area between 1914 and 1916, and unsuccessfully tried to annex it in March 1916;[64]however in 1917 the Greeks were driven from the area by Italy, which took over most of Albania.[65]TheParis Peace Conference of 1919awarded the area to Greece. However the area definitively reverted to Albanian control in November 1921, following Greece's defeat in theGreco-Turkish War.[66]
Principality of Albania[edit]

In supporting the independence of Albania, the Great Powers were assisted byAubrey Herbert,a BritishMPwho passionately advocated the Albanian cause in London. As a result, Herbert was offered the crown of Albania, but was dissuaded by the British Prime Minister,H. H. Asquith,from accepting. Instead the offer went toWilliam of Wied,a German prince who accepted and became sovereign of the newPrincipality of Albania.[67]
ThePrincipalitywas established on 21 February 1914. The Great Powers selectedPrince William of Wied,a nephew ofQueen Elisabeth of Romaniato become the sovereign of the newly independent Albania. A formal offer was made by 18 Albanian delegates representing the 18 districts of Albania on 21 February 1914, an offer which he accepted. Outside of Albania William was styled prince, but inAlbaniahe was referred to asMbret(King) so as not to seem inferior to theKing of Montenegro.This is the period when Albanian religions gained independence. The ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople recognized theautocephalyof theAlbanian Orthodox Churchafter a meeting of the country's Albanian Orthodox congregations in Berat in August 1922. The most energetic reformers inAlbaniacame from the Orthodox population who wanted to see Albania move quickly away from its Turkish-ruled past, during which Christians made up the underclass. Albania's conservativeSunni Muslimcommunity broke its last ties with Constantinople in 1923, formally declaring that there had been no caliph since Muhammad himself and that MuslimAlbanianspledged primary allegiance to their native country. The Muslims also banned polygamy and allowed women to choose whether or not they wanted to wear a veil. Upon termination of Albania from Turkey in 1912, as in all other fields, the customs administration continued its operation under legislation approved specifically for the procedure. After the new laws were issued for the operation of customs, its duty was 11% of the value of goods imported and 1% on the value of those exported.
The security was to be provided by aGendarmeriecommanded by Dutch officers. William left Albania on 3 September 1914 following a pan-Islamic revolt initiated byEssad Pasha Toptaniand later headed by Haxhi Qamili, the latter the military commander of the "Muslim State of Central Albania" centered inTirana.William never renounced his claim to the throne.[68]
World War I[edit]
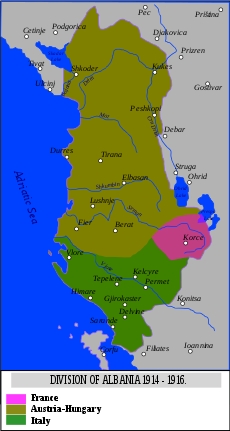
World War Iinterrupted all government activities in Albania, while the country was split in a number of regional governments.[58]Political chaos engulfed Albania after the outbreak of World War I. The Albanian people split along religious and tribal lines after the prince's departure. Muslims demanded a Muslim prince and looked to Turkey as the protector of the privileges they had enjoyed. Other Albanians looked to Italy for support. Still others, including many beys and clan chiefs, recognized no superior authority.[69]
Prince William left Albania on 3 September 1914, as a result of thePeasant Revoltinitiated byEssad Pashaand later taken over byHaxhi Qamili.[70]William subsequently joined the German army and served on the Eastern Front, but never renounced his claim to the throne.[citation needed]
In the country's south, the local Greek population revolted against the incorporation of the area into the new Albanian state and declared theAutonomous Republic of Northern Epirusat 28 February.[71][72]
In late 1914, Greece occupied the Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus, includingKorçëandGjirokastër.Italy occupiedVlorë,and Serbia and Montenegro occupied parts of northern Albania until aCentral Powersoffensive scattered the Serbian army, which was evacuated by the French toThessaloniki.Austro-Hungarianand Bulgarian forces then occupied about two-thirds of the country (Bulgarian occupation of Albania).
Under the secretTreaty of Londonsigned in April 1915,Triple Ententepowers promised Italy that it would gain Vlorë (Valona) and nearby lands and a protectorate over Albania in exchange for entering the war against Austria-Hungary. Serbia and Montenegro were promised much of northern Albania, and Greece was promised much of the country's southern half. The treaty left a tiny Albanian state that would be represented by Italy in its relations with the other major powers.
In September 1918,Ententeforces broke through the Central Powers' lines north of Thessaloniki and within days Austro-Hungarian forces began to withdraw from Albania. On 2 October 1918 the city ofDurrëswas shelled on the orders ofLouis Franchet d'Espèrey,during theBattle of Durazzo:according to d'Espèrey, thePort of Durrës,if not destroyed, would have served the evacuation of the Bulgarian and German armies, involved in World War I.[73]
When the war ended on 11 November 1918, Italy's army had occupied most of Albania; Serbia held much of the country's northern mountains; Greece occupied a sliver of land within Albania's 1913 borders; and French forces occupied Korçë and Shkodër as well as other regions with sizable Albanian populations.
Projects of partition in 1919–1920[edit]

Albanian soldiers during theVlora war,1920.
AfterWorld War I,Albania was still under the occupation of Serbian and Italian forces. It was a rebellion of the respective populations of Northern and Southern Albania that pushed back the Serbs and Italians behind the recognized borders of Albania.
Albania's political confusion continued in the wake ofWorld War I.The country lacked a single recognized government, and Albanians feared, with justification, thatItaly,Yugoslavia,andGreecewould succeed in extinguishing Albania's independence and carve up the country. Italian forces controlled Albanian political activity in the areas they occupied. TheSerbs,who largely dictated Yugoslavia's foreign policy after World War I, strove to take over northern Albania, and the Greeks sought to control southern Albania.
A delegation sent by a postwarAlbanian National Assemblythat met atDurrësin December 1918 defended Albanian interests at theParis Peace Conference,but the conference denied Albania official representation. The National Assembly, anxious to keep Albania intact, expressed willingness to accept Italian protection and even an Italian prince as a ruler so long as it would mean Albania did not lose territory.Serbiantroops conducted actions in Albanian-populated border areas, while Albanian guerrillas operated in bothSerbiaandMontenegro.
In January 1920, at theParis Peace Conference,negotiators from France, Britain, andGreeceagreed to allow Albania to fall under Yugoslav, Italian, and Greek spheres of influence as a diplomatic expedient aimed at finding a compromising solution to the territorial conflicts between Italy and Yugoslavia.
Members of a secondAlbanian National Assembly held at Lushnjëin January 1920 rejected the partition plan and warned that Albanians would take up arms to defend their country's independence and territorial integrity.[74]The Lushnjë National Assembly appointed a four-man regency to rule the country. Abicameral parliamentwas also created, in which an elected lower chamber, theChamber of Deputies(with one deputy for every 12,000 people in Albania and one for the Albanian community in the United States), appointed members of its own ranks to an upper chamber, the Senate. In February 1920, the government moved toTirana,which became Albania's capital.
One month later, in March 1920, U.S. PresidentWoodrow Wilsonintervened to block the Paris agreement. The United States underscored its support for Albania's independence by recognizing an official Albanian representative to Washington, and in December theLeague of Nationsrecognized Albania's sovereignty by admitting it as a full member. The country's borders, however, remained unsettled following theVlora Warin which all territory (exceptSasenoisland) under Italian control in Albania was relinquished to the Albanian state.
Albania achieved a degree of statehood after the First World War, in part because of the diplomatic intercession of the United States government. The country suffered from a debilitating lack of economic and social development, however, and its first years of independence were fraught with political instability. Unable to survive a predatory environment without a foreign protector, Albania became the object of tensions betweenItalyand theKingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes,which both sought to dominate the country.[75]
Zogu Government[edit]
Interwar Albanian governments appeared and disappeared in rapid succession. Between July and December 1921 alone, the premiership changed hands five times. The Popular Party's head,Xhafer Ypi,formed a government in December 1921 withFan S. Nolias foreign minister andAhmed Bey Zoguas internal affairs minister, but Noli resigned soon after Zogu resorted to repression in an attempt to disarm the lowland Albanians despite the fact that bearing arms was a traditional custom.
When the government's enemies attacked Tirana in early 1922, Zogu stayed in the capital and, with the support of the British ambassador, repulsed the assault. He took over the premiership later in the year and turned his back on the Popular Party by announcing his engagement to the daughter ofShefqet Verlaci,the Progressive Party leader.
Zogu's protégés organized themselves into the Government Party. Noli and other Western-oriented leaders formed the Opposition Party of Democrats, which attracted all of Zogu's many personal enemies, ideological opponents, and people left unrewarded by hispolitical machine.Ideologically, the Democrats included a broad sweep of people who advocated everything from conservative Islam to Noli's dreams of rapid modernization.
Opposition to Zogu was formidable.Orthodoxpeasants in Albania's southern lowlands loathed him because he supported Muslim landowners' efforts to block land reform;Shkodër's citizens felt shortchanged because their city did not become Albania's capital, while nationalists were dissatisfied because Zogu's government did not press Albania's claims toKosovoor speak more energetically for the rights of ethnic Albanian minorities in the Balkans.
Despite that, Zogu's party won the elections for a National Assembly in early 1924. He soon stepped aside, however, handing over the premiership toVerlaciin the wake of a financial scandal and an assassination attempt by a young radical which left him wounded. The opposition withdrew from the assembly after the leader of a nationalist youth organization,Avni Rustemi,was murdered in the street outside the parliament building.[76][77]
June Revolution[edit]



Noli's supporters blamed theRustemimurder on Zogu's Mati clansmen, who continued to practice blood vengeance. After the walkout, discontent mounted, and in June 1924 a peasant-backed insurgency had won control of Tirana. Because few people were willing to risk their lives in its defense, the government's fall was remarkably simple and entailed practically little violence. According to US estimates, 20 people were killed and 35 were injured in the northern theatre, while 6 people were killed and 15 were injured in the southern theater. In fact, only Zogu and his meagre group put up any resistance at all. However, fundamental concerns remained unanswered, and Noli's power grab was unstable to say the least.[78]A far more unified group than Noli's was required to execute a new order; it also required crucial political and financial backing from overseas, as well as talented lawmakers prepared to make the necessary sacrifices and concessions. Noli formed his own administration, a small cabinet, on 16 June 1924, with representatives from all factions involved in the June rebellion, including the army, beys, liberals, progressives, and the Shkodra lobby.The Kosovo Committeewas not a part of the government. The government cabinet consisted of:
- Fan Noli– Prime Minister
- Sulejman Delvina- Minister of Foreign Affairs
- Luigj Gurakuqi– Minister of Finance
- Stavro Vinjau– Minister of Education
- Kasëm Qafëzezi– Minister of War
- Rexhep Shala– Minister of Interior
- Qazim Koculi– Minister of Agriculture
- Xhemal Bushati– Minister without portfolio
Fan Noli, an idealist, rejected demands for new elections on the grounds that Albania needed a "paternal" government. On 19 June, Noli's coalition administration proposed a twenty-point reform program that, if completed, would have resulted in a country-wide revolution. Jacques calls the program "too radical," Austin calls it "a really ambitious program,....had it been implemented, it would have led to a revolutionary change of country," and Fischer writes, "Every Western Democrat would be proud of Noli's program, but the Prime Minister lacked two crucial elements, without which no one could carry out such a long series of radical reforms: financial support and support from the governmental cabinet."[79]
Noli went on to say that once normalcy was restored, a national election would be held with secret and direct voting to decide the people's support. Noli planned to rule by decree for ten to twelve months, believing that the country's past elections did not reflect the desires of the Albanian people. Noli subsequently stated that his party "had the majority when we put the agrarian reforms on our programme. When it came to putting them in place, we were in the minority." The takeover of wealthy owners' property, particularly in central Albania, would be the principal source of additional land for the peasants. Each farmer was to receive 4–6 hectares of land for a household of up to 10 individuals. Families with more than 10 members would receive eight hectares of land.
Scaling back the bureaucracy, strengthening local government, assisting peasants, throwing Albania open to foreign investment, and improving the country's bleak transportation, public health, and education facilities filled out the Noli government's overly ambitious agenda. Noli encountered resistance to his program from people who had helped him oust Zogu, and he never attracted the foreign aid necessary to carry out his reform plans. Noli criticized the League of Nations for failing to settle the threat facing Albania on its land borders.
Under Fan Noli, the government set up a special tribunal that passed death sentences, in absentia, on Zogu, Verlaci, and others and confiscated their property.
In Yugoslavia Zogu recruited a mercenary army, andBelgradefurnished the Albanian leader with weapons, about 1,000 Yugoslav army regulars, andRussian White Emigresto mount an invasion that the Serbs hoped would bring them disputed areas along the border. After Noli decided to establish diplomatic relations with theSoviet Union,a bitter enemy of the Serbian ruling family, Belgrade began making wild allegations that Albania was about to embrace Bolshevism.
On 13 December 1924, Zogu's Yugoslav-backed army crossed into Albanian territory. By Christmas Eve, Zogu had reclaimed the capital, and Noli and his government had fled to Italy. The Noli government lasted just 6 months and a week.
First Republic[edit]

After defeatingFan Noli's government,Ahmet Zogurecalled theparliament,in order to find a solution for the uncrowned principality ofAlbania.The parliament quickly adopted a new constitution, proclaimed the first republic, and grantedZogudictatorial powers that allowed him to appoint and dismiss ministers, veto legislation, and name all major administrative personnel and a third of the Senate. The Constitution provided for aparliamentary republicwith a powerful president serving as head of state and government.
On 31 January, Zogu was elected president for a seven-year term. Opposition parties and civil liberties disappeared; opponents of the regime were murdered; and the press suffered strict censorship. Zogu ruled Albania using four military governors responsible to him alone. He appointed clan chieftains as reserve army officers who were kept on call to protect the regime against domestic or foreign threats.
Zogu, however, quickly turned his back onBelgradeand looked instead toBenito Mussolini's Italy for patronage.[75]Under Zogu, Albania joined the Italian coalition against Yugoslavia ofKingdom of Italy,Hungary, andBulgariain 1924–1927. After the United Kingdom's and France's political intervention in 1927 with theKingdom of Yugoslavia,the alliance crumbled.
Zogu maintained good relations withBenito Mussolini's fascist regime in Italy and supported Italy's foreign policy. He would be the first and only Albanian to hold the title of president until 1991.
Kingdom of Albania[edit]
In 1928,Zogu Isecured theParliament's consent to its own dissolution. Afterwards,Albaniawas declared amonarchywithZogu Ifirst as thePrime Minister,then as thePresidentand at last as the King of Albania.[75]International recognition arrived forthwith. The new formed constitution abolished theAlbanian Senateand created aunicameralparliament,but King Zog retained the dictatorial powers he had enjoyed as president. Zogu I remained a conservative, but initiated reforms. For example, in an attempt at social modernisation the custom of adding one's region to one's name was dropped. He also made donations of land to international organisations for the building of schools and hospitals.[80]
Soon after his incoronation, Zog broke off his engagement toShefqet Verlaci's daughter, and Verlaci withdrew his support for the king and began plotting against him. Zog had accumulated a great number of enemies over the years, and the Albanian tradition of blood vengeance required them to try to kill him. Zog surrounded himself with guards and rarely appeared in public.[81]The king's loyalists disarmed all of Albania's tribes except for his own Mati tribesmen and their allies, the Dibra.[82]Nevertheless, on a visit toViennain 1931, Zog and his bodyguards fought a gun battle with would-be assassinsAziz ÇamiandNdok Gjeloshion the Opera House steps.[63]
Zog remained sensitive to steadily mounting disillusion withItaly's domination of Albania. TheAlbanian army,though always less than 15,000-strong, sapped the country's funds, and the Italians' monopoly on training the armed forces rankled public opinion. As a counterweight, Zog kept British officers in theGendarmeriedespite strong Italian pressure to remove them. In 1931, Zog openly stood up to the Italians, refusing to renew the 1926 First Treaty ofTirana.
Financial crisis[edit]
In 1932 and 1933, Albania could not make the interest payments on its loans from the Society for the Economic Development of Albania. In response, Rome turned up the pressure, demanding thatTirananame Italians to direct the Gendarmerie; join Italy in a customs union; grant Italy control of the country's sugar, telegraph, and electrical monopolies; teach theItalian languagein all Albanian schools; and admit Italian colonists. Zog refused. Instead, he ordered the national budget slashed by 30 percent, dismissed the Italian military advisers, and nationalized Italian-run Roman Catholic schools in the northern part of the country. In 1934, Albania had signed trade agreements with Yugoslavia and Greece, and Mussolini had suspended all payments to Tirana. An Italian attempt to intimidate the Albanians by sending a fleet of warships to Albania failed because the Albanians only allowed the forces to land unarmed. Mussolini then attempted to buy off the Albanians. In 1935 he presented the Albanian government 3 million gold francs as a gift.[83]
Zog's success in defeating two local rebellions convinced Mussolini that the Italians had to reach a new agreement with the Albanian king. A government of young men led byMehdi Frasheri,an enlightenedBektashiadministrator, won a commitment from Italy to fulfill financial promises that Mussolini had made to Albania and to grant new loans for harbor improvements at Durrës and other projects that kept the Albanian government afloat. Soon Italians began taking positions in Albania's civil service, and Italian settlers were allowed into the country. Mussolini's forces overthrew King Zog whenItaly invaded Albaniain 1939.[75]
World War II[edit]
Starting in 1928, but especially during theGreat Depression,the government ofKing Zog,which brought law and order to the country, began to increase the Italian influence more and more. Despite some significant resistance, especially atDurrës,Italy invaded Albania on 7 April 1939 and took control of the country, with the Italian Fascist dictatorBenito Mussoliniproclaiming Italy's figurehead KingVictor Emmanuel III of Italyas King of Albania. The nation thus became one of the first to be occupied by theAxis PowersinWorld War II.[84]
AsHitlerbegan his aggression against other European countries, Mussolini decided to occupy Albania as a means of competing with Hitler's territorial gains. Mussolini and the Italian Fascists saw Albania as a historical part of theRoman Empire,and the occupation was intended to fulfill Mussolini's dream of creating anItalian Empire.During the Italian occupation, Albania's population was subject to a policy of forcedItalianizationby the kingdom's Italian governors, in which the use of the Albanian language was discouraged in schools while the Italian language was promoted. At the same time, the colonization of Albania by Italians was encouraged.
Mussolini, in October 1940, used his Albanian base to launch an attack on Greece, which led to the defeat of the Italian forces and the Greek occupation of Southern Albania in what was seen by the Greeks as the liberation ofNorthern Epirus.While preparing for theInvasion of Russia,Hitler decided to attack Greece in December 1940 to prevent a British attack on his southern flank.[85]
Italian penetration[edit]
The Italian invasion of Albania in April 1939 was the conclusion of centuries of Italian interest in the country and twenty years of direct, if unsuccessful, economic and political participation in Albania, primarily under Benito Mussolini. The Straits of Otranto, which cross the Adriatic Sea and connect Albania and southern Italy by forty miles, have always operated as a bridge rather than a barrier, offering escape, cultural exchange, and an easy invasion path. BeforeWorld War IItaly andAustria-Hungaryhad been instrumental in the creation of an independent Albanian state. At the outbreak of war, Italy had seized the chance to occupy the southern half of Albania, to avoid it being captured by the Austro-Hungarians. That success did not last long, as post-war domestic problems, Albanian resistance, and pressure from United States PresidentWoodrow Wilson,forced Italy to pull out in 1920.[86]
When Mussolini took power in Italy he turned with renewed interest to Albania. Italy began penetration of Albania's economy in 1925, when Albania agreed to allow it to exploit its mineral resources.[87]That was followed by the First Treaty of Tirana in 1926 and the Second Treaty of Tirana in 1927, whereby Italy and Albania entered into a defensive alliance.[87]The Albanian government and economy were subsidised by Italian loans, the Albanian army was trained by Italian military instructors, and Italian colonial settlement was encouraged. Despite strong Italian influence, Zog refused to completely give in to Italian pressure.[88]In 1931 he openly stood up to the Italians, refusing to renew the 1926 Treaty of Tirana. After Albania signed trade agreements withYugoslaviaandGreecein 1934, Mussolini made a failed attempt to intimidate the Albanians by sending a fleet of warships to Albania.[89]
AsNazi Germanyannexed Austriaandmoved againstCzechoslovakia,Italy saw itself becoming a second-rate member of the Axis.[90]The imminent birth of an Albanian royal child meanwhile threatened to give Zog a lasting dynasty. After Hitler invaded Czechoslovakia (15 March 1939) without notifying Mussolini in advance, the Italian dictator decided to proceed with his own annexation of Albania. Italy's KingVictor Emmanuel IIIcriticized the plan to take Albania as an unnecessary risk. Rome, however, delivered Tirana an ultimatum on 25 March 1939, demanding that it accede to Italy's occupation of Albania. Zog refused to accept money in exchange for countenancing a full Italian takeover and colonization of Albania.
Italian invasion[edit]
On 7 April Mussolini's troops invaded Albania. The operation was led by GeneralAlfredo Guzzoni.The invasion force was divided into three groups, which were to land successively. The most important was the first group, which was divided in four columns, each assigned to a landing area at a harbor and an inland target on which to advance. Despite some stubborn resistance by some patriots, especially atDurrës,the Italians made short work of the Albanians.[90]Durrës was captured on 7 April, Tirana the following day, Shkodër and Gjirokastër on 9 April, and almost the entire country by 10 April.
Unwilling to become an Italian puppet, King Zog, his wife, QueenGeraldine Apponyi,and their infant sonLekafled to Greece and eventually to London. On 12 April, the Albanian parliament voted to depose Zog and unite the nation with Italy "in personal union" by offering the Albanian crown to Victor Emmanuel III.[91]
The parliament elected Albania's largest landowner,Shefqet Bej Verlaci,as Prime Minister. Verlaci additionally served as head of state for five days until Victor Emmanuel III formally accepted the Albanian crown in a ceremony at theQuirinalepalace in Rome. Victor Emmanuel III appointedFrancesco Jacomoni di San Savino,a former ambassador to Albania, to represent him in Albania as "Lieutenant-General of the King" (effectively aviceroy).
Albania under Italy[edit]


While Victor Emmanuel ruled as king,Shefqet Bej Verlaciserved as the Prime Minister. Shefqet Verlaci controlled the day-to-day activities of the new Italian protectorate. On 3 December 1941, Shefqet Bej Verlaci was replaced as Prime Minister and Head of State byMustafa Merlika Kruja.[92]
From the start, Albanian foreign affairs, customs, as well as natural resources came under direct control of Italy. The puppetAlbanian Fascist Partybecame the ruling party of the country and theFascistsallowedItalian citizensto settle in Albania and to own land so that they could gradually transform it into Italian soil.
In October 1940, during theGreco-Italian War,Albania served as a staging-area for Italian dictatorBenito Mussolini's unsuccessful invasion ofGreece.Mussolini planned to invade Greece and other countries likeYugoslaviain the area to give Italy territorial control of most of theMediterranean Seacoastline, as part of the Fascists objective of creating the objective ofMare Nostrum( "Our Sea" ) in which Italy would dominate the Mediterranean.
But, soon after the Italian invasion, the Greeks counter-attacked and a sizeable portion of Albania was in Greek hands (including the cities ofGjirokastërandKorçë). In April 1941, after Greece capitulated to the German forces, the Greek territorial gains in southern Albania returned to Italian command. Under Italian command came also large areas of Greece after the successful Germaninvasion of Greece.
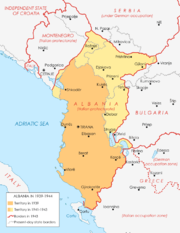
After the fall of Yugoslavia and Greece in April 1941, the Italian Fascists added to the territory of the Kingdom of Albania most of the Albanian-inhabited areas that had been previously given to theKingdom of Yugoslavia.The Albanian fascists claimed in May 1941 that nearly all the Albanian populated territories were united to Albania (see map). Even areas of northern Greece (Chameria) were administered by Albanians.[93]But this was even a consequence of borders that Italy and Germany agreed on when dividing their spheres of influence. Some small portions of territories with Albanian majority remained outside the new borders and contact between the two parts was practically impossible: the Albanian population under the Bulgarian rule was heavily oppressed.
Albania under Germany[edit]

After the surrender of the Italian Army in September 1943, Albania wasoccupied by the Germans.
With the collapse of the Mussolini government in line with the Allied invasion of Italy, Germany occupied Albania in September 1943, dropping paratroopers intoTiranabefore the Albanian guerrillas could take the capital. TheGerman Armysoon drove the guerrillas into the hills and to the south. The Nazi German government subsequently announced it would recognize the independence of a neutral Albania and set about organizing a new government, police and armed forces.
The Germans did not exert heavy-handed control over Albania's administration. Rather, they sought to gain popular support by backing causes popular with Albanians, especially the annexation of Kosovo. ManyBalli Kombëtarunits cooperated with the Germans against the communists and several Balli Kombëtar leaders held positions in the German-sponsored regime. Albanian collaborators, especially theSkanderbeg SS Division,also expelled and killedSerbsliving in Kosovo. In December 1943, a third resistance organization, an anticommunist, anti-German royalist group known asLegaliteti,took shape in Albania's northern mountains. Led byAbaz Kupi,it largely consisted of Geg guerrillas, supplied mainly with weapons from the allies, who withdrew their support for the NLM after the communists renounced Albania's claims on Kosovo. The capital Tirana was liberated by the partisans on 17 November 1944 after a 20-day battle. The communist partizans entirely liberated Albania from German occupation on 29 November 1944, pursuing the German army untilVišegrad,Bosnia(thenYugoslavia) in collaboration with the Yugoslav communist forces.
The Albanian partisans also liberated Kosovo, part of Montenegro, and southern Bosnia and Herzegovina. By November 1944, they had thrown out the Germans, being withYugoslaviathe only European nations to do so without any assistance from the allies.Enver Hoxhabecame the leader of the country by virtue of his position as Secretary General of theAlbanian Communist Party. After having taken over power of the country, the Albanian communists launched a tremendous terror campaign, shooting intellectuals and arresting thousands of innocent people. Some died due to suffering torture.[94]
Albania was one of the only European country occupied by theAxis powersthat ended World War II with a larger Jewish population than before the war.[95][96][97][98]Some 1,200 Jewish residents and refugees from otherBalkancountries were hidden by Albanian families during World War II, according to official records.[99]
Albanian resistance in World War II[edit]
The National Liberation War of the Albanian people started with the Italian invasion in Albania on 7 April 1939 and ended on 28 November 1944. During the antifascist national liberation war, the Albanian people fought against Italy and Germany, which occupied the country. In the 1939–1941 period, the antifascist resistance was led by the National Front nationalist groups and later by the Communist Party.
Communist resistance[edit]

In October 1941, the small Albanian communist groups established inTiranaanAlbanian Communist Partyof 130 members under the leadership of Hoxha and an eleven-man Central Committee. The Albanian communists supported theMolotov–Ribbentrop Pact,and did not participate in the antifascist struggle until Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. The party at first had little mass appeal, and even its youth organization netted recruits. In mid-1942, however, party leaders increased their popularity by calling the young peoples to fight for the liberation of their country, that was occupied byFascist Italy.
This propaganda increased the number of new recruits by many young peoples eager for freedom. In September 1942, the party organized a popular front organization, theNational Liberation Movement(NLM), from a number of resistance groups, including several that were strongly anticommunist. During the war, the NLM's communist-dominated partisans, in the form of theNational Liberation Army,did not heed warnings from the Italian occupiers that there would be reprisals for guerrilla attacks. Partisan leaders, on the contrary, counted on using the lust for revenge such reprisals would elicit to win recruits.
The communists turned the so-called war of liberation into a civil war, especially after the discovery of the Dalmazzo-Kelcyra protocol, signed by theBalli Kombëtar. With the intention of organizing a partisan resistance, they called a general conference in Pezë on 16 September 1942 where theAlbanian National Liberation Frontwas set up. The Front included nationalist groups, but it was dominated by communist partisans.
In December 1942, more Albanian nationalist groups were organized. Albanians fought against the Italians while, duringNazi Germanoccupation, Balli Kombëtar allied itself with the Germans and clashed with Albanian communists, which continued their fight against Germans and Balli Kombëtar at the same time.
Nationalist resistance[edit]
A nationalist resistance to the Italian occupiers emerged in November 1942.Ali KëlcyraandMidhat Frashëriformed the Western-orientedBalli Kombëtar(National Front).[100]Balli Kombëtar was a movement that recruited supporters from both the large landowners and peasantry. It opposed King Zog's return and called for the creation of a republic and the introduction of some economic and social reforms. The Balli Kombëtar's leaders acted conservatively, however, fearing that the occupiers would carry out reprisals against them or confiscate the landowners' estates.
Communist revolution in Albania (1944)[edit]

The communist partisans regrouped and gained control of southern Albania in January 1944. In May they called a congress of members of theNational Liberation Front(NLF), as the movement was by then called, atPërmet,which chose an Anti-Fascist Council of National Liberation to act as Albania's administration and legislature. Hoxha became the chairman of the council's executive committee and the National Liberation Army's supreme commander.
The communist partisans defeated the last Balli Kombëtar forces in southern Albania by mid-summer 1944 and encountered only scattered resistance from the Balli Kombëtar and Legality when they entered central and northern Albania by the end of July. The British military mission urged the remnants of the nationalists not to oppose the communists' advance, and the Allies evacuated Kupi to Italy. Before the end of November, the main German troops had withdrawn from Tirana, and the communists took control of the capital by fighting what was left of the German army. A provisional government the communists had formed atBeratin October administered Albania with Enver Hoxha as prime minister.
Consequences of the war[edit]
The NLF's strong links with Yugoslavia's communists, who also enjoyed British military and diplomatic support, guaranteed thatBelgradewould play a key role in Albania's postwar order. The Allies never recognized an Albanian government in exile or King Zog, nor did they ever raise the question of Albania or its borders at any of the major wartime conferences.
No reliable statistics on Albania's wartime losses exist, but the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration reported about 30,000 Albanian war dead, 200 destroyed villages, 18,000 destroyed houses, and about 100,000 people left homeless. Albanian official statistics claim somewhat higher losses. Furthermore, thousands ofChams(Tsams, Albanians living in Northern Greece) were driven out of Greece with the justification that they had collaborated with the Nazis.
Second Republic[edit]
Communism[edit]

A collection of communists moved quickly after theSecond World Warto subdue all potential political enemies in Albania, break the country's landowners and minuscule middle class, and isolate Albania from western powers in order to establish thePeople's Republic of Albania.In 1945, the communists had liquidated, discredited, or driven into exile most of the country's interwar elite. The Internal Affairs Minister,Koçi Xoxe,a pro-Yugoslav erstwhile tinsmith, presided over the trial and the execution of thousands of opposition politicians, clan chiefs, and members of former Albanian governments who were condemned as "war criminals."
Thousands of their family members were imprisoned for years in work camps and jails and later exiled for decades to miserable state farms built on reclaimed marshlands. The communists' consolidation of control also produced a shift in political power inAlbaniafrom the northernGhegsto the southernTosks.Most communist leaders were middle-class Tosks,VlachsandOrthodox,and the party drew most of its recruits fromTosk-inhabited areas, while theGhegs,with their centuries-old tradition of opposing authority, distrusted the new Albanian rulers and their alienMarxistdoctrines.
In December 1945, Albanians elected a newPeople's Assembly,but only candidates from theDemocratic Front(previously the National Liberation Movement then the National Liberation Front) appeared on the electoral lists, and the communists used propaganda and terror tactics to gag the opposition. Official ballot tallies showed that 92% of the electorate voted and that 93% of the voters chose the Democratic Front ticket. The assembly convened in January 1946, annulled the monarchy, and transformed Albania into a "people's republic."
The new leaders inherited an Albania plagued by many evils: widespread poverty, overwhelming illiteracy,gjakmarrje( "blood feuds" ), epidemics of disease and blatant subjugation of women. In an attempt to eradicate these ills, the Communists have devised a programme of radical modernization. The first important measure was a rapid and uncompromisingagrarian reform,which dismantled the large estates and distributed the plots to the peasants. This reform destroyed the powerful bey class. The government has also decided tonationalizeindustry, banks and all commercial and foreign properties. Shortly after the agrarian reform, the Albanian government began tocollectiviseagriculture, a process that will continue until 1967. In rural areas, the communist regime suppressed the centuries-oldblood feudandpatriarchalstructure of the family and clans, thus destroying the semi-feudalBajraktarsclass. The traditional role of women, confinement to the home and farm, changed dramatically when they achieved legal equality with men and became active participants in all areas of society.[101]

Enver HoxhaandMehmet Shehuemerged as communist leaders in Albania, and are recognized by most western nations. They began to concentrate primarily on securing and maintaining their power base by killing all their political adversaries, and secondarily on preserving Albania's independence and reshaping the country according to the precepts ofStalinismso they could remain in power and develop the nation's economy. A total of 43,000 people have been imprisoned or executed in forty-five years by the Stalinist regime.[102][103][104][105]According to the Albanian Association of Former Political Prisoners, 6,000 people were executed by the Stalinist regime from 1945 to 1991.[106]Albania became an ally of theSoviet Union,but this came to an end after 1956 over the advent ofde-Stalinization,causing theSoviet-Albanian split.A strong political alliance with China followed, leading to several billion dollars in aid, which was curtailed after 1974, causing theSino-Albanian split.China cut off aid in 1978 when Albania attacked itspoliciesafter the death of Chinese leaderMao Zedong.Large-scale purges of officials occurred during the 1970s.
During the period of socialist construction of Albania, the country saw rapid economic growth. For the first time, Albania was beginning to produce the major part of its own commodities domestically, which in some areas were able to compete in foreign markets. During the period of 1960 to 1970, the average annual rate of increase of Albania's national income was 29 percent higher than the world average and 56 percent higher than the European average. Also during this period, because of the monopolised socialist economy, Albania was the only country in the world that imposed no imposts or taxes on its people whatsoever.[107]
Enver Hoxha,who ruled Albania for four decades, died on 11 April 1985. Soon after Hoxha's death, voices for change emerged in the Albanian society and the government began to seek closer ties with the West in order to improve economic conditions. Eventually the new regime ofRamiz Aliaintroduced some liberalisation, and granting the freedom to travel abroad in 1990. The new government made efforts to improve ties with the outside world. The elections of March 1991 kept the former Communists in power, but a general strike and urban opposition led to the formation of a coalition cabinet that included non-Communists.[108]
In 1967, the authorities conducted a violent campaign to extinguish religious practice in Albania, claiming that religion had divided the Albanian nation and kept it mired in backwardness.[109][self-published source?]Student agitators combed the countryside, forcing Albanians to quit practicing their faith. Despite complaints, even by APL members, all churches, mosques, monasteries, and other religious institutions had been closed or converted into warehouses, gymnasiums, and workshops by year's end. A special decree abrogated the charters by which the country's main religious communities had operated.
Albania and Yugoslavia[edit]

Until Yugoslavia's expulsion from theCominformin 1948, Albania acted like a Yugoslav satellite and thePresident of Yugoslavia,Josip Broz Titoaimed to use his choke hold on the Albanian party to incorporate the entire country into Yugoslavia.[110]AfterGermany's withdrawal fromKosovoin late 1944, Yugoslavia's communist partisans took possession of the province and committed retaliatory massacres againstAlbanians.Before thesecond World War,theCommunist Party of Yugoslaviahad supported transferring Kosovo to Albania, but Yugoslavia's postwar communist regime insisted on preserving the country's prewar borders.
In repudiating the 1943Mukaj agreementunder pressure from the Yugoslavs, Albania's communists had consented to restore Kosovo to Yugoslavia after the war. In January 1945, the two governments signed a treaty reincorporating Kosovo into Yugoslavia as an autonomous province. Shortly thereafter, Yugoslavia became the first country to recognize Albania's provisional government.
Relations between Albania and Yugoslavia declined, however, when the Albanians began complaining that the Yugoslavs were paying too little for Albanian raw materials and exploiting Albania through the joint stock companies. In addition, the Albanians sought investment funds to develop light industries and an oil refinery, while the Yugoslavs wanted the Albanians to concentrate on agriculture and raw-material extraction. The head of Albania's Economic Planning Commission and one of Hoxha's allies,Nako Spiru,became the leading critic of Yugoslavia's efforts to exert economic control over Albania. Tito distrusted Hoxha and the other intellectuals in the Albanian party and, through Xoxe and his loyalists, attempted to unseat them.
In 1947, Yugoslavia's leaders engineered an all-out offensive against anti-Yugoslav Albanian communists, including Hoxha and Spiru. In May, Tirana announced the arrest, trial, and conviction of ninePeople's Assemblymembers, all known for opposing Yugoslavia, on charges of antistate activities. A month later, the Communist Party of Yugoslavia's Central Committee accused Hoxha of following "independent" policies and turning the Albanian people against Yugoslavia.
Albania and the Soviet Union[edit]

Albania became dependent on Soviet aid and know-how after the break withYugoslaviain 1948. In February 1949, Albania gained membership in thecommunist bloc's organizationfor coordinating economic planning, theCouncil for Mutual Economic Assistance.Tirana soon entered into trade agreements withPoland,Czechoslovakia,Hungary,Romania,and theSoviet Union.Soviet and central European technical advisers took up residence in Albania, and the Soviet Union also sent Albania military advisers and built a submarine installation onSazan Island.
After theSoviet-Yugoslav split,Albania andBulgariawere the only countries the Soviet Union could use to funnel war material to the communists fighting inGreece.What little strategic value Albania offered the Soviet Union, however, gradually shrank as nuclear arms technology developed.
Anxious to pay homage toStalin,Albania's rulers implemented new elements of the Stalinist economic system. In 1949, Albania adopted the basic elements of the Soviet fiscal system, under which state enterprises paid direct contributions to the treasury from their profits and kept only a share authorized for self-financed investments and other purposes. In 1951, the Albanian government launched its first five-year plan, which emphasized exploiting the country's oil, chromite, copper, nickel, asphalt, and coal resources; expanding electricity production and the power grid; increasing agricultural output; and improving transportation. The government began a program of rapid industrialization after the APL's Second Party Congress and a campaign of forced collectivization of farmland in 1955. At the time, private farms still produced about 87% of Albania's agricultural output, but by 1960 the same percentage came from collective or state farms.
Stalin died in March 1953, and apparently fearing that the Soviet ruler's demise might encourage rivals within the Albanian party's ranks, neither Hoxha nor Shehu risked traveling toMoscowto attend his funeral. The Soviet Union's subsequent movement toward rapprochement with the hated Yugoslavs rankled the two Albanian leaders. Tirana soon came under pressure from Moscow to copy, at least formally, the new Soviet model for acollective leadership.In July 1953, Hoxha handed over the foreign affairs and defense portfolios to loyal followers, but he kept both the top party post and the premiership until 1954, when Shehu became Albania's prime minister. The Soviet Union, responding with an effort to raise the Albanian leaders' morale, elevated diplomatic relations between the two countries to the ambassadorial level.
Despite some initial expressions of enthusiasm, Hoxha and Shehu mistrustedNikita Khrushchev's programs of "peaceful coexistence" and "different roads to socialism" because they appeared to pose the threat that Yugoslavia might again try to take control of Albania. Hoxha and Shehu were also alarmed at the prospect that Moscow might prefer less dogmatic rulers in Albania. Tirana and Belgrade renewed diplomatic relations in December 1953, but Hoxha refused Khrushchev's repeated appeals to rehabilitate posthumously the pro-Yugoslav Xoxe as a gesture to Tito. The Albanian duo instead tightened their grip on their country's domestic life and let the propaganda war with the Yugoslavs grind on.
Albania and China[edit]
ThePeople's Republic of Albaniaplayed a role in theSino-Soviet splitfar outweighing either its size or its importance in thecommunist world.In 1958, the nation stood with thePeople's Republic of China[111]in opposingMoscowon issues ofpeaceful coexistence,de-Stalinization,andYugoslavia'sseparate road to socialismthroughdecentralizationof economic life. TheSoviet Union,central European countries, and China, all offered Albania large amounts of aid. Soviet leaders also promised to build a largePalace of CultureinTiranaas a symbol of the Soviet people's "love and friendship" for the Albanian people.
Despite these gestures, Tirana was dissatisfied with Moscow's economic policy toward Albania. Hoxha and Shehu apparently decided in May or June 1960 that Albania was assured of Chinese support, and they openly sided with the People's Republic of China when sharp polemics erupted between the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union.Ramiz Alia,at the time a candidate-member of the Politburo and Hoxha's adviser on ideological questions, played a prominent role in the rhetoric.
Hoxha and Shehu continued their harangue against the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia at the APL's Fourth Party Congress in February 1961. During the congress, the Albanian government announced the broad outlines of the country's Third Five-Year Plan from 1961 to 65, which allocated 54% of all investment to industry, thereby rejecting Khrushchev's wish to make Albania primarily an agricultural producer. Moscow responded by canceling aid programs and lines of credit for Albania, but the Chinese again came to the rescue.
TheAlbanian-Chinese relationshad stagnated by 1970, and when the Asian giant began to reemerge from isolation in the early 1970s,Mao Zedongand the other communist Chinese leaders reassessed their commitment to tiny Albania, starting theSino-Albanian split.In response, Tirana began broadening its contacts with the outside world. Albania opened trade negotiations withFrance,Italy,and the recently independent Asian and African states, and in 1971 it normalized relations withYugoslaviaandGreece.Albania's leaders abhorred the People's Republic of China's contacts with theUnited Statesin the early 1970s, and its press and radio ignored PresidentRichard Nixon'strip to Beijingin 1972.
Third Republic[edit]
As Hoxha's health declined, thefirst secretaryof thePeople's Socialist Republicbegan planning for an orderly succession.[112]In 1976, the People's Parliament adopted its second communistConstitutionof thepost-war era.[113]The constitution guaranteed the people of Albania thefreedom of speech,press, organization, association, and parliament but subordinated these rights to the individual's duties to society as a whole.[citation needed]The constitution enshrined in law the idea ofautarkyand prohibited the government from seeking financial aid or credits or from forming joint companies with partners fromcapitalistorcommunistcountries perceived to be "revisionist".[citation needed]The constitution's preamble also boasted that the foundations of religious belief in Albania had been abolished.[114]
In 1980, Hoxha turned toRamiz Aliato succeed him as Albania's communist patriarch, overlooking his long-standing comrade-in-arms,[citation needed]Mehmet Shehu.[citation needed]Hoxha first tried to convince Shehu to step aside voluntarily, but when this move failed, Hoxha arranged for all the members of thePolitburoto rebuke him for allowing his son to become engaged to the daughter of a former bourgeois family.[citation needed]Hoxha purged the members of Shehu's family and his supporters within the police and military.[citation needed]In November 1982, Hoxha announced that Shehu had been a foreign spy working simultaneously for the United States, British, Soviet, and Yugoslav intelligence agencies in planning the assassination of Hoxha himself.[citation needed]"He was buried like a dog", the dictator wrote in the Albanian edition of his book, 'The Titoites'.[citation needed]Hoxha went into semi-retirement in early 1983,[citation needed]and Alia assumed responsibility for Albania's administration.[citation needed]Alia traveled extensively around Albania, standing in for Hoxha at major events and delivering addresses laying down new policies and intoning litanies to the enfeebled president.[citation needed]Alia succeeded to the presidency and became legal secretary of the APL two days later. In due course, he became a dominant figure in the Albanian media, and his slogans appeared painted in crimson letters on signboards across the country.[citation needed]
Fourth Republic[edit]
Transition[edit]

In 1985,Ramiz Aliabecame thefirstPresident of Albania.Alia tried to follow inEnver Hoxha's footsteps, but the changes had already started and thecollapse of communismthroughoutEuropeled to widespread changes within the society of Albania.Mikhail Gorbachevhad appeared in theSoviet Unionwith new rules and policies (glasnostandperestroika). However, Alia took similar steps, signing theHelsinki Agreementand allowingpluralismunder pressure from students and workers.[115]Afterwards, the firstmulti-party electionstook place since the communists assumed power in Albania. TheSocialist Partyled by Ramiz Alia won the1991 elections.[115]Nevertheless, it was clear that the change would not be stopped. Pursuant to a 29 April 1991 interimbasic law,Albaniansratified aconstitutionon 28 November 1998, establishing ademocratic systemof government based upon therule of lawand guaranteeing the protection offundamental human rights.[116]
Furthermore, the Communists retained support and governmental control in the first round of elections under the interim law, but fell two months later during a general strike. A committee of "national salvation" took over but also collapsed in half a year. On 22 March 1992, the Communists were trumped by theDemocratic Partyafter winning the1992 parliamentary elections.[117]The transition from thesocialist stateto aparliamentary systemhad many challenges. The Democratic Party had to implement the reforms it had promised, but they were either too slow or did not solve the problems, so the people were disappointed when their hopes for fast prosperity went unfulfilled.[citation needed]
Democratization[edit]

TheDemocratic Partytook control after winning the secondmulti-party elections,deposing theCommunist Party.Afterwards,Sali Berishabecame thesecondPresident.In 1995, Albania became the 35th member of theCouncil of Europeand requested membership inNorth Atlantic Treaty Organization(NATO).[118][self-published source?]The people of Albania have continued toemigrateto westernEuropean countries,[why?]especially toGreeceandItalybut also to theUnited States.[citation needed]Deliberate programmes of economic and democratic reforms were put in place, but Albanian inexperience with capitalism led to the proliferation ofpyramid schemes,[when?]which were not banned due to the corruption of the government.Anarchyin late 1996 to early 1997 alarmed the world and prompted international mediation.[citation needed]
In the early spring 1997,Italyled a multinational military and humanitarian intervention (Operation Alba),[119]authorized by theUnited Nations Security Council,to help stabilize the country.[120]The government of Berisha collapsed in 1997 in the wake of the additional collapse ofpyramid schemesand widespread corruption, which caused anarchy and rebellion throughout the country. The government attempted to suppress the rebellion by military force but the attempt failed, due to long-term corrosion of theMilitary of Albaniadue to political and social factors. Few months later, after the1997 parliamentary electionstheDemocratic Partywas defeated by theSocialist Party,winning just 25 seats out of a total of 156.Sali Berisharesigned and the Socialists electedRexhep MeidaniasPresident.Including to that, the leader of the SocialistsFatos Nanowas elected asPrime Minister,a post which he held until October 1998, when he resigned as a result of the tense situation created in the country after the assassination ofAzem Hajdari,a prominent leader of theDemocratic Party.Due to that,Pandeli Majkowas then elected Prime Minister until November 1999, when he was replaced byIlir Meta.TheParliamentadopted the currentConstitutionon 29 November 1998. Albania approved its constitution through a popular referendum which was held in November 1998, but which was boycotted by the opposition. The general local elections of October 2000 marked the loss of control of theDemocratsover the local governments and a victory for theSocialists.
In 2001, Albania made strides toward democratic reform and therule of law,serious deficiencies in the electoral code remain to be addressed, as demonstrated in theelections.[citation needed]International observers judged the elections to be acceptable, but theUnion for Victory Coalition,the second-largest vote recipient, disputed the results and boycotted parliament until 31 January 2002. In June 2005, the democratic coalition formed a government with theSali Berisha.His return to power in the elections of 3 July 2005 ended eight years of Socialist Party rule. AfterAlfred Moisiu,in 2006Bamir Topiwas electedPresident of Albaniauntil 2010. Despite thepolitical situation,theeconomy of Albaniagrew at anestimated5% in 2007. TheAlbanian lekhas strengthened from 143 lekë to the US dollar in 2000 to 92 lekë in 2007.
Present[edit]

On 23 June 2013, the seventhparliamentary electionstook place, won byEdi Ramaof theSocialist Party.During his tenure as33rdPrime Minister,Albania has implemented numerous reforms focused on themodernizingtheeconomyand democratizing ofstate institutionslike thejudiciaryandlaw enforcement.Additionally, unemployment has been steadily reduced to the 4th lowestunemployment ratein theBalkans.[121]
After thecollapse of the Eastern Bloc,Albania started to develop closer ties with Western Europe. At the2008 Bucharest summit,theNorth Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)invited Albania to join the alliance. In April 2014 Albania became a full member of theNATO.Albania was among the first southeastern European countries to join the Partnership for peace programme. Albaniaappliedto join theEuropean Union,becoming an official candidate for accession to theEuropean Unionin June 2014.
In 2017, the eighthparliamentary electionstook place, simultaneously with thepresidential elections.[122][123]The presidential elections were held on 19, 20, 27 and 28 April 2017. In the fourth round, the incumbentChairmanand then-Prime Minister,Ilir Metawas elected as the eighthPresident of Albaniawith 87 votes.[124]However, the result of the parliamentary elections held on 25 June 2017 was a victory for theSocialist Partyled byEdi Rama,that received 48.33% of the votes of the elections, ahead of 5 other candidates.Lulzim Basha,theDemocratic Partycandidate and runner-up in the election, received only 28.81% of the votes.[125]
In April 2021 parliamentaryelection,ruling Socialist Party, led by Prime Minister Edi Rama, secured its third consecutive victory, winning nearly half of votes and enough seats in parliament to govern alone.[126]In February 2022, Albania's Constitutional Court overturned parliament's impeachment of PresidentIlir Meta,opponent of the ruling Socialist Party.[127]In June 2022, Albanian parliament electedBajram Begaj,the candidate of the ruling Socialist Party (PS), as the new President of Albania.[128]On 24 July 2022, Bajram Begaj was sworn in as Albania's ninth president.[129]On 19 July 2022, Albania started the negotiations with the European Union.[130]Also in 6 December, in Tirana was held the EU-Western Balkans Summit. It was the first EU Summit hold in Tirana.[131]
See also[edit]
- Albanians
- Albanian nationalism
- Politics of Albania
- Timeline of Albanian history
- Epitaph of Gllavenica
- Gjergj Arianiti
- Greater Albania
- Illyrians
References[edit]
- ^abThe Prehistory of the Balkans; and the Middle East and the Aegean world, tenth to eighth centuries B.C.Archived26 December 2022 at theWayback MachineJohn Boardman p.189–90
- ^S. Adhami (1958).Monumente të kultures ne Shqiperi.Mihal Duri. p. 15.
- ^Kyle, Schepartz & Larsen 2016,p. 1068.
- ^Govedarica 2016,pp. 22–25.
- ^Hammond, N.G.L. (1997)."Ancient Epirus: Prehistory and Protohistory".Epirus, 4000 Years of Greek History and Civilization.p. 38: Ekdotike Athenon: 34–45.ISBN978-960-213-371-2.
{{cite journal}}:CS1 maint: location (link) - ^Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière Hammond.Studies: Further studies on various topicsArchived12 May 2016 at theWayback Machine.A.M. Hakkert, 1993, p. 231: "The leading dans of both groups buried their dead under a circular tumulus of soil in the second millennium BC The main reservoir of the Greek speakers was central Albania and Epirus, and it was from there that the founders of Mycenaean civilization came to Mycenae, c. 1600 BC, and buried their nobles in Grave Circle B. Further waves of immigrants passing through and from Epirus people the Greek peninsula and islands the last wave, called Dorians, settling from 1100 onwards. The lands they left in central Albania were occupied during the so-called Dark Age (U10-800BC) by Illyrians, whose main habitat was in the area now called Bosnia,"
- ^The later (The Peoples of Europe) by John Wilkes,ISBN0-631-19807-5,1996, page 39: "... the other hand, the beginnings of the Iron Age around 1000 BC is held to coincide with the formation of several different peoples in Albania and other countries...."
- ^The Illyrians (The Peoples of Europe) by John Wilkes, 1996,ISBN978-0-631-19807-9,page 92, "Appian's description of the Illyrian territories records a southern boundary with Chaonia and Thesprotia, where ancient Epirus began south of river Aoous (Vjose)"also mapArchived26 December 2022 at theWayback Machine
- ^Cambridge University Press.The Cambridge ancient historyArchived26 December 2022 at theWayback Machine.2000.ISBN0-521-23447-6,page 261, "...down to the mouth of Aous"
- ^The Illyrians (The Peoples of Europe) by John Wilkes, 1996, page 94
- ^(Ptolemy. Geogr. Ill 12,20)
- ^Appian,The Foreign Wars, III, 1.2
- ^Wilkes, J. J. The Illyrians, 1992,ISBN0-631-19807-5,Page 96, "... 25 Enchelei
- ^abThe Illyrians (The Peoples of Europe) by John Wilkes,1996,ISBN9780631198079,page 111.
- ^Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière Hammond, Guy Thompson Griffith.A History of Macedonia: Historical geography and prehistory.Clarendon Press, 1972, p. 92.
- ^Lewis, D. M.; Boardman, John (1994).The Cambridge ancient history: The fourth century B.C.Cambridge University Press. p. 423.ISBN978-0-521-23348-4.Retrieved26 October2010.
- ^Boardman, John; Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1982), The Cambridge Ancient History: The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Six Centuries B.C, Cambridge, p. 261
- ^Wilkes, John J. (1995), The Illyrians, Oxford: Blackwell Publishing,ISBN0-631-19807-5,p. 92
- ^Harding, p. 93. Grabos became the most powerful Illyrian king after the death of Bardylis in 358.
- ^ab"The Journal of Hellenic Studies by Society for the Promotion of Hellenic Studies", 1973, p. 79. Cleitus was evidently the son of Bardylis II the grandson of the very old Bardylis who had fallen in battle against Phillip II in 385 BC.
- ^Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1 January 1993).Studies concerning Epirus and Macedonia before Alexander.Hakkert.ISBN9789025610500.
- ^Eckstein, Arthur M. (1 February 1995).Moral Vision in the Histories of Polybius.University of California Press.ISBN978-0-520-91469-8.
- ^Berranger, Danièle (1 January 2007).Épire, Illyrie, Macédoine: mélanges offerts au professeur Pierre Cabanes(in French). Presses Univ Blaise Pascal. p. 127.ISBN9782845163515.
- ^Berranger, Danièle (1 January 2007).Épire, Illyrie, Macédoine: mélanges offerts au professeur Pierre Cabanes(in French). Presses Univ Blaise Pascal. p. 137.ISBN9782845163515.
- ^An Inventory of Archaic andClassicalPoleis by Mogens Herman,ISBN0-19-814099-1,2004, page 343, "Bouthroton (Bouthrotios)"
- ^Ludwig Schaaff,Enzyklopädie der klassischen Altertumskunde,2002,ISBN0-543-80046-6,page 17
- ^An ancient geography, classical and sacred. By S. Augustus Mitchell. by Michigan Historical Reprint Series, 2005,ISBN1-4255-3778-2,page 215
- ^Paul: His Story by Jerome Murphy-O'Connor, page 247
- ^abKocsis, Károly (2001)."Az albán kérdés etnikai és politikai földrajzi háttere"[The ethnic and geographic background of the Albanian question](PDF).Földrajzi Értesítő(in Hungarian).Budapest:164.eISSN2064-5139.ISSN0015-5403.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 27 September 2022.Retrieved27 September2022.
- ^Zickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R., eds. (1994)."The Barbarian Invasions and the Middle Ages".Albania: A Country Study.U.S. Library of Congress.
- ^Madgearu, Alexandru (2008). Gordon, Martin (ed.).The Wars of the Balkan Peninsula: Their Medieval Origins(illustrated ed.). Scarecrow Press. p. 25.ISBN978-0-8108-5846-6.
It was supposed that those Albanoi from 1042 were Normans from Sicily, called by an archaic name (the Albanoi were an independent tribe from Southern Italy). The following instance is indisputable. It comes from the same Attaliates, who wrote that the Albanians (Arbanitai) were involved in the 1078 rebellion of...
- ^Elsie 2010,pp. iv, xxviii.
- ^Ducellier 1999,p. 780: "As for Albania, its separate identity was real enough, even though it had not truly broken with Constantinople; all the same, the rulers of Arbanon around ἄρχον, Progon and his sons Dhimitër and Gjin, based at Kruja, retained a considerable degree of autonomy, even though Progon bore no title grander than ἄρχων (archon); and the title of πανὑπερσεβαστός (panhypersebastos), borne by Dhimitër at the start of the thirteenth century, can only be seen as a sign of his dependence on the Byzantines."
- ^Elsie 2010,p. xxviii.
- ^Varzos 1984,pp. 555–556.
- ^Fine 1994,p. 68.
- ^Angelidi, Christine (2016).ΕΥΨΥΧΙΑ. Mélanges offerts à Hélène Ahrweiler(in French). Publications de la Sorbonne.ISBN978-2-85944-830-1.
- ^Ellis & Klusáková 2007,p. 134.
- ^abPrifti, Skënder (2002).Historia e popullit shqiptar në katër vëllime (in Albanian).Albania. p. 207.ISBN978-99927-1-622-9.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^Nicol, Donald M. (1 January 1984).The Despotate of Epiros 1267–1479: A Contribution to the History of Greece in the Middle Ages.Cambridge University Press.ISBN9780521261906.
- ^The Encyclopaedia of Islam.1974.
- ^Barbinger, Franz (1978).Mehmed the Conqueror and His Time.Princeton University Press.ISBN0691010781.
- ^abHousley, Norman (1992).The later Crusades, 1274–1580: from Lyons to Alcazar.Oxford University Press. p. 90.ISBN978-0-19-822136-4.
- ^Fine, John V. A.; Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994).The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest.University of Michigan Press.ISBN978-0-472-08260-5.
- ^"Oliver Jens Schmitt: Scanderbeg: an Uprising and its Leader".Archived fromthe originalon 13 March 2016.
- ^Lane-Poole, Stanley (1888).The Story of Turkey.
- ^Zhelyazkova, Antonina (2000)."Albanian Identities"(PDF).Sofia: International Centre for Minority Studies and Intercultural Relations (IMIR).Retrieved18 March2011.
The territories of Central and Southern Albania, stretching between the Mat River to the north and Çameria [modern Tsameria, Greece] to the south, were included in a single sancak known from the records and historical works as Arvanid
- ^Riza, Emin (1992)."Ethnographic and open-air museums"(PDF).UNESCO, Paris.Retrieved18 March2011.
- ^Anamali, Skënder; Prifti, Kristaq; RSH), Instituti i Historisë (Akademia e Shkencave e (1 January 2002).Historia e popullit shqiptar(in Albanian). Botimet Toena. p. 338.ISBN9789992716229.
- ^ab"Library of Congress Country Study of Albania".Lcweb2.loc.gov. 27 July 2010.Retrieved27 August2010.
- ^Gjergj Kastrioti Skënderbeu: jeta dhe vepra (1405–1468)(in Albanian). Botimet Toena. 1 January 2002.ISBN9789992716274.
- ^The Analytical Review, Or History of Literature, Domestic and Foreign, on an Enlarged Plan.1 January 1788.
- ^"Albania | History, Geography, Customs, & Traditions".29 May 2023.
- ^Research Institute for European and American Studies.The Balkan Muslim PresenceArchived21 July 2011 at theWayback Machine
- ^A. Madrugearu, M. Gordon. The wars of the Balkan Peninsula: their medieval origin. Scarecrow Press, 2008. p. 27.[1]
- ^"Albania – Medieval culture".
- ^Gegaj, Athanas; Young, Antonia; Krasniqi, Rexhep; Hodgson, John; Young, Nigel; Bland, William B. (1997).Albania.Clio Press.ISBN9781851092604.
- ^abZickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R., eds. (1994)."National Awakening and the Birth of Albania".Albania: A Country Study.US Library of Congress.
- ^Glenny, Misha.The Balkans (Nationalism, War and the Great Powers, 1804–1999)
- ^Stahn, Carsten (2008).The Law and Practice of International Territorial Administration.doi:10.1017/CBO9780511585937.ISBN978-0-521-87800-5.
- ^"History of Albania".Lonely Planet. Archived fromthe originalon 12 July 2012.Retrieved5 January2012.
- ^Elsie, Robert."1913 The Conference of London".Archived fromthe originalon 17 July 2011.Retrieved5 January2012.
- ^abMiranda Vickers (1999).The Albanians: A Modern History.I.B.Tauris. p. 66.ISBN978-1-86064-541-9.Retrieved10 May2012.
- ^abKonidaris, Gerasimos (2005). Schwandner-Sievers, Stephanie (ed.).The new Albanian migrations.Sussex Academic Publishing. p. 65.ISBN978-1-903900-78-9.
- ^Tucker, Spencer; Roberts, Priscilla Mary (2005).World War I: encyclopedia.ABC-CLIO. p. 77.ISBN978-1-85109-420-2.Retrieved26 January2011.
- ^Miller, William (1966).The Ottoman Empire and Its Successors, 1801–1927.Routledge. pp. 543–544.ISBN978-0-7146-1974-3.
- ^Young, Antonia; Hodgson, John; Young, Nigel (1997).Albania.Clio Press.ISBN1-85109-260-9.
- ^Scheer, Tamara."Wied, Wilhelm, Prinz zu".1914–1918 Online.International Encyclopedia of the First World War.Retrieved25 June2021.
- ^Dušan Fundić, "The Albanian Question in Serbian-Italian Relations 1914–1918." onSerbia and Italy in the Great War(2019)onlineArchived29 July 2021 at theWayback Machine.
- ^Jelavich, Barbara (1999) [1983],History of the Balkans: Twentieth century,vol. 2, Cambridge, UK: The Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, p. 103,ISBN0-521-27459-1,retrieved25 January2011,
Soon the government was faced with major peasant revolt
- ^George B. Leon.Greece and the First World War: from neutrality to intervention, 1917–1918.East European Monographs, 1990.ISBN978-0-88033-181-4,p. 323.
- ^David Turnock.The economy of East Central Europe 1815–1989: stages of transformation in a peripheral region..Routledge, 2006ISBN978-0-415-18053-5,p. 424
- ^Kabashi, Gezim (24 December 2012)."Fotot e Rralla – Bombardimi i Durresit me 2 Tetor 1918"[Rare Photos – Bombing of Durrës on 2 October 1918].Gazeta e Durresit.Archived fromthe originalon 24 October 2014.
- ^Pearson, Owen (2004).Albania in the Twentieth Century, A History: Volume 1: Albania and King Zog.New York: I.B. Tauris. p. 138.
- ^abcdZickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R., eds. (1994)."Interwar Albania, 1918–41".Albania: A Country Study.
- ^Zickel, Raymond E.; Iwaskiw, Walter R.; Keefe, Eugene K. (1994).Albania: a country study.Area handbook series.US Library of Congress.pp. 27–29.ISBN9780844407920.LCCN93042885.
- ^"Albania - Government and Politics".countrystudies.us.Retrieved21 January2024.
- ^Austin, Robert C. (2012).Founding a Balkan State: Albania's Experiment with Democracy, 1920–1925.ROBERT C. AUSTIN. p. 262.ISBN978-1-4426-9973-1.JSTOR10.3138/j.ctt2tv0q6.
- ^""FAN S. NOLI NË 130 – VJETORIN E LINDJES" 1882–2012 KONFERENCA SHKENCORE NDËRKOMBËTARE "(PDF).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 6 July 2022.Retrieved31 May2022.
- ^"Albania: Zog, Not Scanderbeg".Time.17 June 1929. Archived fromthe originalon 8 August 2009.
- ^Paul Lendvai (1969).Eagles in cobwebs: nationalism and communism in the Balkans.Doubleday. p. 181.ISBN9780356030104.Retrieved10 May2012.
- ^Owen Pearson (2004).Albania And King Zog: Independence, Republic And Monarchy 1908–1939.I.B.Tauris. p. 304.ISBN978-1-84511-013-0.Retrieved10 May2012.
He forbade the carrying of arms by civilians, enforcing this prohibition among the tribesmen by ordering all tribes to be disarmed except his own, the Moslem Mati, their allies, the Diber, and the catholic Mirdite
- ^Giovanni Villari, "A Failed Experiment: The Exportation of Fascism to Albania."Modern Italy12.2 (2007): 157–171online[dead link].
- ^Glenny, Misha(2012).The Balkans: Nationalism, War, and the Great Powers, 1804–2012.House of Anansi. p. 418.ISBN9781101610992.
- ^Creveld, Martin van (July–October 1972). "In the Shadow of Barbarossa: Germany and Albania, January–March 1941".Journal of Contemporary History.7(3/4): 22–230.JSTOR259913.
- ^"Albania: A Country Study: Albania's Reemergence after World War I, Library of Congress".Archivedfrom the original on 7 August 2011.Retrieved25 January2011.
- ^abZickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R., eds. (1994)."Italian Penetration".Albania: A Country Study.Library of Congress.
- ^Fischer, B. J:Albania at War, 1939–1945,page 7. Hurst, 1999
- ^Zickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R., eds. (1994)."Zog's Kingdom".Albania: A Country Study.Library of Congress.
- ^abZickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R., eds. (1994)."Italian Occupation".Albania: A Country Study.Library of Congress.
- ^Fischer, B. J:Albania at War, 1939–1945,page 36. Hurst, 1999
- ^Owen Pearson (2006).Albania in the Twentieth Century, A History: Volume II: Albania in Occupation and War, 1939–45.London: I. B. Tauris. p. 167.ISBN1-84511-104-4.
- ^"History of Albania | My Albania! The Official website of Albanian! Open source travel guide".myalbania.eu.Archived fromthe originalon 30 January 2019.Retrieved29 January2019.
- ^"Albania's broken men fear prison horrors will be forgotten".Associated Press News.19 June 2016.
- ^Sarner.Rescue in Albania: One Hundred Percent of Jews in Albania Rescued from the Holocaust,1997.
- ^"Muslim Family Who Hid 26 Jews in Albania from the Nazis Honored by ADL"Anti-Defamation LeagueArchived5 January 2009 at theWayback Machine
- ^Escape Through the Balkans: the Autobiography of Irene Grunbaum (University of Nebraska Press, 1996)
- ^"Shoah Research Center – Albania"(PDF).Retrieved27 August2010.
- ^"Israeli Historians Study How Albanian Jews Escaped Holocaust".Fox News Channel. 20 May 2008.
- ^Robert Elsie (30 March 2010).Historical Dictionary of Albania.Scarecrow Press. p. 30.ISBN978-0-8108-6188-6.Retrieved10 May2012.
- ^"Albania - The Stalinist state | Britannica".britannica.29 May 2023.
- ^"Albania's broken men fear prison horrors will be forgotten".Associated Press News.19 June 2016.
- ^15 February 1994 Washington Times
- ^"WHPSI": The World Handbook of Political and Social Indicators by Charles Lewis Taylor
- ^8 July 1997 NY Times
- ^Mejdini, Fatjona Mejdini, Fatjona (14 October 2015)."Albania To Open Communists' Secret Files".Balkan Insight.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^Pano, Aristotel."Panorama of the Economic-Social Development of Socialist Albania".Albania Today.Retrieved11 April2012.
- ^"Albania."World Almanac & Book of Facts,2008, pp467–545, (AN 28820955)
- ^Popovski, Ivan (10 May 2017).A Short History of South East Europe.Lulu Press, Inc.ISBN978-1-365-95394-1.[permanent dead link][self-published source]
- ^Schwartz, Harry (23 August 1949)."ALBANIA SAYS TITO TRIED ANNEXATION".The New York Times.p. 8.Retrieved29 August2022.
- ^Albania: From Anarchy to a Balkan IdentityISBN1-85065-279-1,by Miranda Vickers & James Pettifer, 1999, page 210, "with the split in the world communist movement it moved into a close relationship with China"
- ^Karen Dawisha; Bruce Parrott (13 June 1997).Politics, Power, and the Struggle for Democracy in South-East Europe.Cambridge University Press. pp. 295–.ISBN978-0-521-59733-3.Retrieved10 May2012.
- ^"THE CONSTITUTION OF THE PEOPLE'S SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF ALBANIA".bjoerna.dk.
Approved by the People's Assembly on 28 December 1976
- ^"THE CONSTITUTION OF THE PEOPLE'S SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF ALBANIA".bjoerna.dk.
The foundations of religious obscurantism were smashed. The moral figure of the working man, his consciousness, and world outlook, are moulded on the basis of the proletarian ideology, which has become the dominant ideology.
- ^ab"Election Watch".Journal of Democracy.2(3). Johns Hopkins University Press: 115–117. Summer 1991.doi:10.1353/jod.1991.0035.Archived fromthe originalon 25 April 2006.
- ^"Albania 1998 (rev. 2012) Constitution - Constitute".constituteproject.org.Retrieved28 June2024.
- ^"Election Watch".Journal of Democracy.3(3). Johns Hopkins University Press: 154–157. July 1992.doi:10.1353/jod.1992.0042.Archived fromthe originalon 25 April 2006.
- ^Ayers, Bert (2015).Bridging the Gap.Lulu. p. 28.ISBN978-1-329-64683-4.[self-published source]
- ^Alì, Maurizio (2003).L'attività di peacekeeping della Forza Multinazionale di Protezione in Albania(report) (in Italian). Rome, Italy: Università Roma Tre – Facoltà di Scienze Politiche – via HAL.
- ^"Oberation Alba".United Nations Website.Permanent Mission of Slovenia to the UN. Archived fromthe originalon 21 October 2008.Retrieved4 January2013.
- ^"Ahmetaj: Premtimi për 300 mijë vende punë është mbajtur | Gazeta SHQIP Online".Archived fromthe originalon 26 January 2017.
- ^"Presidenti Nishani e dekreton: 25 qershori data e zgjedhjeve parlamentare".gsh.al(in Albanian). 21 May 2017.
- ^"Shqipëri: Dështimi i tretë për zgjedhjen e presidentit".Radio Evropa e Lirë(in Albanian). 22 April 2017.
- ^"Ilir Meta, president i ri i Shqipërisë".Telegrafi(in Albanian). 28 April 2017.
- ^"Albania's Socialists win ruling majority in parliamentary elections | DW | 27.06.2017".Deutsche Welle.
- ^"Albania PM hails 'most difficult but sweetest' election win".
- ^"Albania court overturns president's impeachment".The Independent.17 February 2022.
- ^"Albanian parliament elects Bajram Begaj new president".aa.tr.
- ^Taylor, Alice (25 July 2022)."Albania swears in ninth president amid political division".euractiv.
- ^"'Historic moment': EU negotiations open for Albania, North Macedonia ".euronews.19 July 2022.
- ^"EU Western Balkans Summit in Tirana: shared responsibilities and values for a future together | EEAS".eeas.europa.eu.
Sources[edit]
- Ducellier, Alain (1999). "24(b) – Eastern Europe: Albania, Serbia and Bulgaria". In Abulafia, David (ed.).The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 5, c.1198 – c.1300.Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 779–795.ISBN978-0-52-136289-4.
- Elsie, Robert(2010).Historical Dictionary of Albania.Scarecrow Press.ISBN978-0-8108-7380-3.
- Ellis, Steven G.; Klusáková, Lud'a (2007).Imagining Frontiers, Contesting Identities.Edizioni Plus. pp. 134–.ISBN978-88-8492-466-7.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr.(1994) [1987].The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest.Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press.ISBN0472082604.
- Gjon Marku, Ndue (2017).Mirdita House of Gjomarku Kanun.CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.ISBN978-1542565103.
- The American Slavic and East European Review 1952.1952.ASIN1258092352.
- Varzos, Konstantinos (1984).Η Γενεαλογία των Κομνηνών[The Genealogy of the Komnenoi]. Centre for Byzantine Studies, University of Thessaloniki.
- Lazaridis, Iosif; Alpaslan-Roodenberg, Songül; et al. (26 August 2022)."The genetic history of the Southern Arc: A bridge between West Asia and Europe".Science.377(6609): eabm4247.doi:10.1126/science.abm4247.PMC10064553.PMID36007055.S2CID251843620.
- Govedarica, Blagoje (2016)."The Stratigraphy of Tumulus 6 in Shtoj and the Appearance of the Violin Idols in Burial Complexes of the South Adriatic Region".Godišnjak Centra za balkanološka ispitivanja(45).ISSN0350-0020.Retrieved7 January2023.
- Kyle, B.; Schepartz, L. A.; Larsen, C. S. (2016). "Mother City and Colony: Bioarchaeological Evidence of Stress and Impacts of Corinthian Colonisation at Apollonia, Albania".International Journal of Osteoarchaeology.26(6). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: 1067–1077.doi:10.1002/oa.2519.
- Gori, Maja; Recchia, Giulia; Tomas, Helen (2018)."The Cetina phenomenon across the Adriatic during the 2nd half of the 3rd millennium BC: new data and research perspectives".38° Convegno Nazionale Sulla Preistoria, Protostoria, Storia della Daunia.
Bibliography[edit]
- Abrahams, Fred CModern Albania: From Dictatorship to Democracy in Europe(2015)
- Bernd Jürgen Fischer.Albania at war, 1939-1945(Purdue UP, 1999)
- Elsie, Robert.Historical Dictionary of Albania(2010)online
- Elsie, Robert.The Tribes of Albania: History, Society and Culture(I.B. Tauris, 2015)
- Fischer, Bernd J., and Oliver Jens Schmitt.A Concise History of Albania(Cambridge University Press, 2022).
- Hall, Richard C.War in the Balkans: An Encyclopedic History from the Fall of the Ottoman Empire to the Breakup of Yugoslavia(2014)excerpt
- Najbor, Patrice.Histoire de l'Albanie et de sa maison royale(5 volumes), JePublie, Paris, 2008, (ISBN978-2-9532382-0-4).
- Rama, Shinasi A.The end of communist rule in Albania: political change and the role of the student movement(Routledge, 2019)
- Reci, Senada, and Luljeta Zefi. "Albania-Greece sea issue through the history facts and the future of conflict resolution."Journal of Liberty and International Affairs7.3 (2021): 299–309.
- Sette, Alessandro.From Paris to Vlorë. Italy and the Settlement of the Albanian Question (1919–1920),inThe Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920) and Its Aftermath: Settlements, Problems and Perceptions,eds. S. Arhire, T. Rosu, (2020).
- 2003 U.S. Department of State Background Noteof Albania
- Vickers, Miranda.The Albanians: A Modern History(I.B. Tauris, 2001)
- Winnifrith, Tom, ed.Perspectives on Albania.(Palgrave Macmillan, 1992).
- Winnifrith, T. J.Nobody's Kingdom: A History of Northern Albania(2021).
External links[edit]
- History of Albania: Primary Documents
- Library of Congress Country Studyof Albania
- Famille royale d'Albanie, site officiel en langue anglaiseEnglish version
- L'Albanie et le sauvetage des Juifs
- Books about Albania and the Albanian people(scribd )Reference of books (and some journal articles) about Albania and the Albanian people; their history, language, origin, culture, literature, etc. Public domain books, fully accessible online.




