Huizhou
Huizhou
Huệ Châu thị | |
|---|---|
 Top: He gian g Tower, Huizhou West Lake, Middle: Jiangbei skyline,Huicheng Districtat night Bottom: Shuangyue Bay | |
| Motto: A city to benefit people (Huệ dân chi châu) | |
 | |
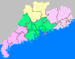
 Location of Huizhou in Guangdong | |
| Coordinates (Huizhou government):23°06′43″N114°24′58″E/ 23.112°N 114.416°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guangdong |
| City | 1988 |
| Municipal seat | Huicheng District |
| Government | |
| •CPC Secretary | Li Yiwei (Lý di vĩ) |
| •Mayor | Liu Ji (Lưu cát) |
| Area | |
| •Prefecture-level city | 10,922 km2(4,217 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,672 km2(1,032 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,488.5 km2(574.7 sq mi) |
| •Coastline | 223.6 km2(86.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 15 m (49 ft) |
| Population (2020 census[1]) | |
| •Prefecture-level city | 6,042,852 |
| • Density | 550/km2(1,400/sq mi) |
| •Urban | 3,494,715 |
| • Urban density | 1,300/km2(3,400/sq mi) |
| •Metro | 2,090,578 |
| • Metro density | 1,400/km2(3,600/sq mi) |
| GDP[2] | |
| •Prefecture-level city | CN¥497.7 billion US$77.2 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 82,113 US$ 12,728 |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00(China Standard) |
| Postal code | 516000 |
| Area code | 0752 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GD-13 |
| Licence Plate | Việt L |
| Website | www |
| Huizhou | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"Huizhou", as written in Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | Huệ Châu | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Waichow | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Huizhou(Chinese:Huệ Châu) is a city in central-eastGuangdongProvince, China, forty-three miles north ofHong Kong.Huizhou borders the provincial capital ofGuangzhouto the west,ShenzhenandDongguanto the southwest,Shaoguanto the north,Heyuanto the northeast,Shanweito the east, andDaya Bayof theSouth China Seato the south. As of the 2020 census, the city has about 6,042,852 inhabitants and is administered as aprefecture-level city.[3]Huizhou's core metropolitan area, which is within Huicheng and Huiyang Districts, is home to around 2,090,578 inhabitants.[4]
History
[edit]During theSong dynasty,Huizhou was a prefectural capital of the Huiyang prefecture and the cultural center of the region.[5]
The West Lake in Huizhou was formerly known as Feng Lake. At the age of 59,Su Shiwas exiled to Huizhou by the imperial government of Song. When he visited Feng Lake in Huizhou, he found it located in the west of the city and was as beautiful asWest Lake in Hangzhou.Therefore, he renamed it the West Lake. In order to solve the traffic problems on both sides of West Lake, he invested to help build two bridges. Later generations named bridges as the bridge Su Di to commemorate his achievements. And the two bridges in the West Lake becomes one of the eight scenic spots in the West Lake, called "Su Di Play Moon".[6]
Huizhou used to be a prosperous region, specializing in commerce and trading, which changed during the 20th century due towars.[7]After the 1980s, Huizhou developed as a manufacturing base.
Demographics
[edit]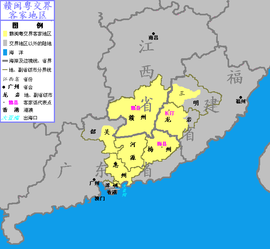
Historical demographics
[edit]In ancient China, Huizhou andHeyuanwere a part of the remoteLingnanregion. In pre-Tangtimes, the population includedBaiyuepeoples (Zhuang,Yao,Hmong,Tanka,andShe) but very fewHan Chineseaside from imperial Chinese soldiers.[8]According to the Huiyang County annals (2003), during the lateYuan dynasty(14th century), what is now Huizhou had only 45,410 inhabitants in 9,545 households.[8]That corresponds to one household or five people per square kilometer.[8]Most of the 6 million inhabitants in Huizhou and Heyuan are descended from people who migrated during the late Yuan and earlyMingdynasties and during theQing dynastyafter theGreat Clearance.[8]
Population
[edit]According to the2020 census,the city's permanent population was 6,042,852,[9]representing an increase of 1,444,450 people, or 31.43%, from the2010 census.Between 2000 and 2010, the average annual increase over that 10-year period was 3.64%. As of 2010, the population included 2,419,258 males (52.63%) and 2,177,744 females (47.37%), for a sex ratio of 111.09 males for every 100 females. There were 809,270 children aged 0–14 (17.6%); 3,517,928 people aged 15–64 (76.53%), and 269,804 people aged 65 and older (5.87%).
Ethnicity
[edit]The majority of Huizhou's residents areHan Chinese,with a population of 3,617,800, 97.69% of Huizhou's population. There are 85,500 residents of minority ethnic groups, includingYaoandShe,representing 2.31% of the population.[10]The Han population includesHakkaandHoklopeople. The Hakka are distributed widely in each district and county of the prefecture-level city, and Huizhou hasHakka walled villages.The Hoklo are concentrated in Boluo County and Huidong County. In Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan, there are more than 800,000 people of Huizhou ancestry.
Economy
[edit]Located in the Pearl River Delta, Huizhou is one of the 9 prefecture-level cities in thePearl River Delta Economic Zone(include Huizhou urban area, Huiyang, Huidong and Boluo only).TCL,a major TV and multinational consumer electronics company is headquartered in Huizhou.[11]
Development zones
[edit]Huizhou Dayawan Economic and Technological Development Zone
[edit]TheHuizhou Daya Bay Economic and Technological Development Zone(DBETDZ) was approved by the State Council in 1993. It had an initial area of 9.98 km2(3.85 sq mi), and in 2006, the State Council expanded the zone to 23.6 km2(9.1 sq mi) in three phases.
Industries encouraged in the zone include Automobile Production/Assembly, Chemical Production and Processing and Electronics Assembly & Manufacturing.[12]
Huizhou Export Processing Zone
[edit]The Huizhou Export Processing Zone was approved by Guangdong Provincial Government as a subzone of DBETDZ in June 2005. The planned area was 3 km2(1.2 sq mi) in size. The zone was considered suitable for companies focusing on electronics, auto parts, textiles and chemicals.[13]
Huizhou Zhongkai High-tech Industrial Development Zone
[edit]The Huizhou Zhongkai High-tech Industrial Development Zone is connected with Shenzhen, Guangzhou and Dongguan by the Huizhou-Shenzhen Highway, Guangzhou-Huizhou Highway and Dongguan-Huizhou Highway. The Beijing-Kowloon Railway and Huizhou-Aotou Railway also run through the zone, linking it withBeijing,Hong Kong,and other cities along the railway. Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport is a one-and-a-half hour drive from the zone.
The Huizhou Zhongkai HIDZ has also established electronics, information technology and optical-, mechanical- and electronic-integration as its major industries. It also encourages investment in new materials, telecommunications, and other high-tech industries. The zone is one of the National Electronic Information Industry Bases and National Video and Audio Products Parks in China.[11]
Administration
[edit]Theprefecture-level cityof Huizhou administers 5county-level divisions,including 2districtsand 3counties.


| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010 census) |
Area (km2) |
Density (/km2) |
| Huicheng District | Huệ thành nội | Huìchéng Qū | 1,579,818 | 1,488.45 | 1,061 |
| Huiyang District | Huệ dương khu | Huìyáng Qū | 764,816 | 1,205.44 | 664 |
| Boluo County | Bác la huyện | Bóluó Xiàn | 1,038,198 | 2,855.11 | 364 |
| Huidong County | Huệ đông huyện | Huìdōng Xiàn | 908,390 | 3,526.73 | 258 |
| Longmen County | Long Môn huyện | Lóngmén Xiàn | 307,180 | 2,267.2 | 135 |
Transport
[edit]Huicheng,the urban center of Huizhou, is served by theJingjiu Railway(also known as theGuangmeishan Railwayin Guangdong) with two stations:Huizhou WestandHuizhou.Huizhou itself is vast asLos Angeles Countywith sparse rail service as compared with bay peer cities.
Huizhou Pingtan Airportreopened in 2015.[14]Additionally the town is about a one and one half-hour drive by bus fromShenzhen Bao'an International Airport.[15]There are also coach bus services connecting Huizhou withHong Kong International Airport.[16]
A mass rapid transit linking it to Shenzhen was under construction as of 2011[update].
In April 2018, theChina Dailyannounced that the world's first automatic railroad was currently under construction between Dongguan and Huizhou. As a pilot project, it would contain ten railway stations, driverless trains and robotic assistance for passengers with luggage and tickets.[17]
Language
[edit]The main languages spoken in Huizhou areHakka Chinese(Huiyang dialect),Huizhou dialect,Hokkiendialect, andCantonese.
Military
[edit]Huizhou is the headquarters of the42nd Group Armyof thePeople's Liberation Army,one of the two group armies that comprise theGuangzhou Military Regionresponsible for the defense of China's southern coast and its border withVietnam.
Education
[edit]Educational facilities in Huizhou include:
- Huizhou University[18]
- Huizhou Radio and Television University
- Huizhou Nanshan School
- Medi's International school
Sport
[edit]Huizhou is a well-known city of sports in China with the opening ofHuizhou Olympic Stadiumin 2010.
Climate
[edit]Huizhou has ahumid subtropical climate(Köppen climate classification:Cwa). Summers are long, hot and humid. Winters are short, mild and dry.
| Climate data for Huizhou (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.3 (84.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.2 (88.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
20.4 (68.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
11.7 (53.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
19.2 (66.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.0 (75.2) |
20.7 (69.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
11.6 (52.9) |
18.8 (65.9) |
| Averageprecipitationmm (inches) | 37.3 (1.47) |
62.8 (2.47) |
87.0 (3.43) |
202.0 (7.95) |
226.7 (8.93) |
323.6 (12.74) |
255.1 (10.04) |
276.1 (10.87) |
173.0 (6.81) |
66.6 (2.62) |
28.2 (1.11) |
33.4 (1.31) |
1,771.8 (69.75) |
| Average precipitation days(≥ 0.1 mm) | 6.3 | 10.6 | 12.6 | 14.5 | 18.3 | 18.7 | 17.2 | 18.4 | 13.0 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 146.1 |
| Source:Weather China | |||||||||||||
Tourism
[edit]
Daya Bay
[edit]Daya Bay is located to the southeast of Huizhou City, on the South China Sea, with waters covering an area of nearly 500 km2(190 sq mi). There are nearly 100 islands and reefs in the bay. The climate is described as a typical subtropicaloceanic climate,with temperatures averaging 21.8 °C (71.2 °F) over the year. Historically, Daya Bay had whales and turtles.[19][20]The bay was one of the breeding grounds along the southern coast of China for Asian population ofgray whaleswhich are now one of the most endangered whale population in the world. They migrated here to calve in the winter-spring seasons. Other species, such ashumpback whalesalso migrated here historically. All of these were wiped out by Japanese whalers established whaling stations on various sites on Chinese coasts including at nearby Daya Bay.[21][22]Critically endangeredChinese white dolphinsand occasional whales such as humpbacks have been confirmed in the bay recent years.[23]
International relations
[edit]Twin towns – sister cities
[edit] Hallstatt,Austria
Hallstatt,Austria North Vancouver,Canada
North Vancouver,Canada Milpitas,United States
Milpitas,United States
Friendly cities
[edit]Notable people
[edit]- Zeng Jingsheng(born 1954) - painter
References
[edit]- ^"China: Administrative Division of Guăngdōng / Quảng Đông tỉnh".Retrieved26 February2016.
- ^Quảng Đông tỉnh thống kê cục, quốc gia thống kê cục Quảng Đông điều tra tổng đội (August 2016).《 Quảng Đông thống kê niêm giám -2016》.Trung Quốc thống kê nhà xuất bản.ISBN978-7-5037-7837-7.Archived fromthe originalon 22 December 2017.
- ^"Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area - Map(Huizhou)".bayarea.gov.hk.Retrieved28 February2021.
- ^"China: Guăngdōng (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- ^Ezra F. Vogel (October 1990).One Step Ahead in China: Guangdong Under Reform.Harvard University Press. pp. 225–226.ISBN978-0-674-63911-9.
- ^Hoàng kiến bình (1997).Đông Pha nơi nơi có Tây Hồ.Giang Tô hội nghị hiệp thương chính trị(3): 32.
- ^Poon, Linda (5 January 2015)."China's Villages Are Dying. A New Film Asks If They Can Be Saved".NPR.
- ^abcdPhan gia ý, lâm luân luân ( 2011 ), khu đông Lưỡng Quảng huệ hà phiến Mân Nam ngữ phân bố và địa lý hoàn cảnh đặc trưng, 《 Đài Loan ngữ văn nghiên cứu 》 đệ 6 cuốn đệ 2 kỳ,2011, p.16
- ^"China: Guăngdōng".City Population.
- ^"Huệ Châu thị 2005 năm cả nước 1% dân cư lấy mẫu điều tra chủ yếu số liệu công báo".Huệ Châu thị thống kê cục. 12 July 2010.Archivedfrom the original on 27 August 2018.Retrieved12 July2017.
- ^abhttp:// bayarea/gov.hk/aboutHuizhou/Guangdong-Hongkong-Macao Greater Bay Area Huizhou
- ^"Huizhou Dayawan Economics Technology Development Zone".Retrieved26 February2016.
- ^"Guangdong Huizhou Export Processing Zone".Retrieved26 February2016.
- ^"Huệ Châu sân bay đem với 2 nguyệt 5 ngày phục hàng -- 24 giờ lăn lộn tin tức - nhân dân võng".cpc.people.cn(in Chinese).Retrieved28 October2020.
- ^"Guangdong TrafficArchived26 April 2018 at theWayback Machine."Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport.Retrieved on May 9, 2018.
- ^"Mainland Coaches."Hong Kong International Airport.Retrieved on May 8, 2018.
- ^nan, Zhong (2 May 2018)."Automated railways being tested".China Daily.Retrieved2 May2018.
- ^Huizhou University.ResearchGate.Retrieved 22 February 2021.
- ^Dredging in China under strict environment controlArchived2016-04-06 at theWayback Machine
- ^Đại cay giáp đảo hải vực hiện tử vong cá voi nguyên nhân chết không rõ
- ^Jefferson A.T., Hung K.S., 2007,An updated, annotated checklist of the marine mammals of Hong Kong,Mammalia (2007) – DOI 10.1515/MAMM.2007.021, pp.105–114
- ^Rockwell D.H., 2009,When in Rome, Do as the Whales Do!Archived4 May 2014 at theWayback Machine
- ^Đại Á loan phát hiện cá heo trắng Trung Quốc chuyên gia: Ứng bảo trì trăm mét an toàn khoảng cách
- ^"Huệ Châu thành thị bằng hữu vòng tân tăng bạn tốt Lô Châu".xinhuanet(in Chinese). Xinhua News. 17 April 2017. Archived fromthe originalon 26 November 2021.Retrieved9 February2021.
- ^"Samoa signs MOU with China's Huizhou City".loopsamoa.co.Loop News. 17 November 2015. Archived fromthe originalon 29 July 2021.Retrieved9 February2021.
- ^"중국 후이저우시".seongnam.go.kr(in Korean). Seongnam.Retrieved9 February2021.
- ^"Come and invest in Worcestershire, say county-decision makers back from China mission".worcesternews.co.uk.Worcester News.21 November 2014.Retrieved9 February2021.
External links
[edit]- Government website of HuizhouArchived30 April 2019 at theWayback Machine