Human mouth
| Human mouth | |
|---|---|
 Photograph of the closed mouth of a male | |
 Head and neck | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | os, oris[1] |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.010 |
| TA2 | 119 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Inhuman anatomy,themouthis the first portion of thealimentary canalthat receivesfoodand producessaliva.[2]Theoral mucosais the mucous membraneepitheliumlining the inside of the mouth.
In addition to its primary role as the beginning of thedigestive system,the mouth also plays a significant role incommunication.While primary aspects of thevoiceare produced in thethroat,thetongue,lips,andjaware also needed to produce the range of sounds included inspeech.
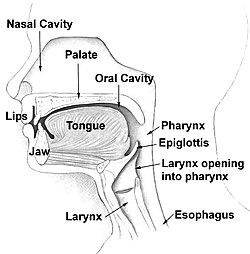
The mouth consists of two regions, thevestibuleand theoral cavity proper.The mouth, normally moist, is lined with amucous membrane,and contains theteeth.The lips mark the transition from mucous membrane toskin,which covers most of thebody.
Structure[edit]
Oral cavity[edit]


The mouth consists of two regions: the vestibule and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule is the area between the teeth, lips and cheeks.[3]The oral cavity is bounded at the sides and in front by thealveolar process(containing theteeth) and at the back by theisthmus of the fauces.Its roof is formed by thehard palate.The floor is formed by themylohyoid musclesand is occupied mainly by the anterior two-thirds of thetongue.Amucous membrane– theoral mucosa,lines the sides and under surface of the tongue to thegums,and lines the inner aspect of the jaw (mandible). It receives secretions from thesubmandibularandsublingualsalivary glands.The posterior border of the oral cavity (ie, junction between the oral cavity and theoropharynx) includes the junction of thehard palateand thesoft palatesuperiorly, thecircumvallate papillaeof thetongueinferiorly, and theretromolar trigone.
Lips[edit]

Thelipscome together to close the opening of the mouth, forming a line between the upper and lower lip. Infacial expression,thismouth lineis iconically shaped like an up-openparabolain asmile,and like a down-open parabola in afrown.Adown-turned mouthmeans a mouth line forming a down-turned parabola, and when permanent can be normal. Also, adown-turned mouthcan be part of the presentation ofPrader–Willi syndrome.[4]
Nerve supply[edit]
The teeth and theperiodontium(thetissuesthat support the teeth) are innervated by themaxillaryandmandibular nerves– divisions of thetrigeminal nerve.Maxillary (upper) teeth and their associatedperiodontal ligamentare innervated by the superior alveolar nerves, branches of the maxillary division, termed theposterior superior alveolar nerve,anterior superior alveolar nerve,and the variably presentmiddle superior alveolar nerve.These nerves form thesuperior dental plexusabove the maxillary teeth. The mandibular (lower) teeth and their associated periodontal ligament are innervated by theinferior alveolar nerve,a branch of the mandibular division. This nerve runs inside the mandible, within theinferior alveolar canalbelow the mandibular teeth, giving off branches to all the lower teeth (inferior dental plexus).[5][6]Theoral mucosaof the gingiva (gums) on thefacial(labial) aspect of the maxillaryincisors,caninesandpremolarteeth is innervated by the superior labial branches of theinfraorbital nerve.The posterior superior alveolar nerve supplies the gingiva on the facial aspect of the maxillarymolarteeth. The gingiva on thepalatalaspect of the maxillary teeth is innervated by thegreater palatine nerveapart from in the incisor region, where it is thenasopalatine nerve(long sphenopalatine nerve). The gingiva of thelingualaspect of the mandibular teeth is innervated by the sublingual nerve, a branch of thelingual nerve.The gingiva on the facial aspect of the mandibular incisors and canines is innervated by themental nerve,the continuation of the inferior alveolar nerve emerging from themental foramen.The gingiva of the buccal (cheek) aspect of the mandibular molar teeth is innervated by thebuccal nerve(long buccal nerve).[7]
Development[edit]
Thephiltrumis the vertical depression formed between thephiltral ridgesbetween the upper lip and the nasal septum, formed where thenasomedialandmaxillaryprocesses meet duringembryo development.When these processes fail to fuse fully, acleft lip,cleft palate,or both can result.
Thenasolabial foldsare the deep creases of tissue that extend from the nose to the sides of the mouth. One of the first signs of age on the human face is the increase in prominence of the nasolabial folds.
Function[edit]
The mouth plays an important role ineating,drinking,and speaking.Mouth breathingrefers to the act of breathing through the mouth (as a temporary backup system) if there is an obstruction tobreathing through the nose,which is the designated breathing organ for the human body.[8]
Infantsare born with asucking reflex,by which theyinstinctivelyknow to suck for nourishment using their lips andjaw. The mouth also helps inchewingandbitingfood.
For some disabled people, especially many disabled artists, who through illness, accident or congenital disability have lost dexterity, their mouths take the place of their hands, when typing, texting, writing, makingdrawings,paintingsand other works of art by maneuvering brushes and other tools, in addition to the basic oral functions.Mouth paintershold the brush in their mouth or between their teeth and maneuver it with their tongue and cheek muscles, but mouth painting can be strenuous for neck and jaw muscles since the head has to perform the same back and forth movement as a hand does when painting.[9][10]
Amalemouth can hold, on average, 71.2 ml (2.51 imp fl oz; 2.41 US fl oz), while afemalemouth holds 55.4 ml (1.95 imp fl oz; 1.87 US fl oz).[11]
See also[edit]
- Head and neck anatomy
- Index of oral health and dental articles
- List of basic dentistry topics
- Mouth breathing
Further reading[edit]
- Nestor, James (2020).Breath: The New Science of a Lost Art.Riverhead Books. p. 304.ISBN978-0735213616.
References[edit]
- ^Schröder, Hannsjörg; Moser, Natasha; Huggenberger, Stefan (2020).Neuroanatomy of the Mouse: An Introduction.Springer International Publishing. p. 105.ISBN978-3-03019-898-5.RetrievedDecember 24,2023.
- ^Maton, Anthea; Jean Hopkins; Charles William McLaughlin; Susan Johnson; Maryanna Quon Warner; David LaHart; Jill D. Wright (1993).Human Biology and Health.Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, USA: Prentice Hall.ISBN0-13-981176-1.
- ^Pocock, Gillian (2006).Human Physiology(Third ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 382.ISBN978-0-19-856878-0.
- ^Cassidy, Suzanne B.; Dykens, Elisabeth; Williams, Charles A. (2000). "Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes: Sister imprinted disorders".American Journal of Medical Genetics.97(2): 136–46.doi:10.1002/1096-8628(200022)97:2<136::AID-AJMG5>3.0.CO;2-V.PMID11180221.
- ^Susan Standring, ed. (2008).Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice(40th ed.). [Edinburgh]: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier.ISBN978-0443066849.
- ^Lindhe, Jan; Lang, Niklaus P; Karring, Thorkild, eds. (2008) [2003].Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry 5th edition.Oxford, UK: Blackwell Munksgaard. p. 48.ISBN9781405160995.
- ^Lindhe, Jan; Lang, Niklaus P; Karring, Thorkild, eds. (2008) [2003].Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry 5th edition.Oxford, UK: Blackwell Munksgaard.ISBN9781405160995.
- ^Turowski, Jason (2016-04-29)."Should I Breathe Through My Mouth or Through My Nose?".Cleveland Clinic.Archivedfrom the original on Jun 30, 2020.Retrieved2020-06-28.
- ^"Squeezable Paint Brushes (Howard University)".RESNA.Rehabilitation Engineering and Assistive Technology Society of North America.31 May 2014. Archived fromthe originalon 1 March 2016.Retrieved18 January2020.
- ^Winchester, Levi (10 July 2014)."Watch: Woman born without fully-formed limbs creates stunning artwork using her mouth".express.co.uk.Daily Express.
- ^Nascimento, Weslania Viviane; Cassiani, Rachel Aguiar; Dantas, Roberto Oliveira (September 2012)."Gender effect on oral volume capacity".Dysphagia.27(3): 384–389.doi:10.1007/s00455-011-9379-4.ISSN1432-0460.PMID22120835.S2CID22688382.
External links[edit]
 Media related toHuman mouthsat Wikimedia Commons
Media related toHuman mouthsat Wikimedia Commons Quotations related toMouthsat Wikiquote
Quotations related toMouthsat Wikiquote
