Hyperrectangle
It has been suggested that this article bemergedwithK-cell (mathematics).(Discuss)Proposed since July 2024. |
| Hyperrectangle Orthotope | |
|---|---|
 A rectangularcuboidis a 3-orthotope | |
| Type | Prism |
| Faces | 2n |
| Edges | n× 2n−1 |
| Vertices | 2n |
| Schläfli symbol | {}×{}×···×{} = {}n[1] |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [2n−1],order2n |
| Dual polyhedron | Rectangularn-fusil |
| Properties | convex,zonohedron,isogonal |
Ingeometry,ahyperrectangle(also called abox,hyperbox,ororthotope[2]), is the generalization of arectangle(aplane figure) and therectangular cuboid(asolid figure) tohigher dimensions. Anecessary and sufficient conditionis that it iscongruentto theCartesian productof finiteintervals.If all of the edges are equal length, it is ahypercube. A hyperrectangle is a special case of aparallelotope.
Types
[edit]A four-dimensional orthotope is likely a hypercuboid.[3]
The special case of ann-dimensional orthotope where all edges have equal length is then-cubeor hypercube.[2]
By analogy, the term "hyperrectangle" can refer to Cartesian products oforthogonalintervals of other kinds, such as ranges of keys indatabase theoryor ranges ofintegers,rather thanreal numbers.[4]
Dual polytope
[edit]| n-fusil | |
|---|---|
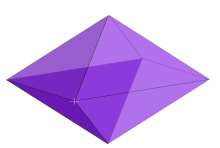 Example: 3-fusil | |
| Type | Prism |
| Faces | 2n |
| Vertices | 2n |
| Schläfli symbol | {}+{}+···+{} =n{}[1] |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [2n−1],order2n |
| Dual polyhedron | n-orthotope |
| Properties | convex,isotopal |
Thedual polytopeof ann-orthotope has been variously called a rectangularn-orthoplex,rhombicn-fusil,orn-lozenge.It is constructed by2npoints located in the center of the orthotope rectangular faces.
Ann-fusil'sSchläfli symbolcan be represented by a sum ofnorthogonal line segments:{ } + { } +... + { }orn{ }.
A 1-fusil is aline segment.A 2-fusil is arhombus.Its plane cross selections in all pairs of axes arerhombi.
| n | Example image |
|---|---|
| 1 | Line segment { } |
| 2 |  Rhombus { } + { } = 2{ } |
| 3 |  Rhombic 3-orthoplex inside3-orthotope { } + { } + { } = 3{ } |
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^abN.W. Johnson:Geometries and Transformations,(2018)ISBN978-1-107-10340-5Chapter 11:Finite symmetry groups,11.5 Spherical Coxeter groups, p.251
- ^abCoxeter, 1973
- ^Hirotsu, Takashi (2022). "Normal-sized hypercuboids in a given hypercube".arXiv:2211.15342.
- ^See e.g.Zhang, Yi; Munagala, Kamesh; Yang, Jun (2011),"Storing matrices on disk: Theory and practice revisited"(PDF),Proc. VLDB,4(11): 1075–1086,doi:10.14778/3402707.3402743.
References
[edit]- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald (1973).Regular Polytopes(3rd ed.). New York: Dover. pp.122–123.ISBN0-486-61480-8.






