Jafarabad State
| Jafarabad State Jafrabad State જાફરાબાદ રિયાસત | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely StateofBritish India In union withJanjira(1759–1948) | |||||||
| c. 1650–1948 | |||||||
|
Flag | |||||||
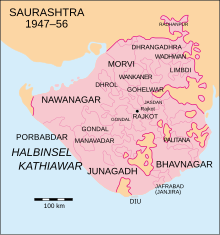 Location of Jafrabad State in Saurashtra | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• 1901 | 68 km2(26 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1901 | 12,097 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | 30 August | ||||||
| 1948 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Gujarat,India | ||||||
Jafarabad,orJafrabad State,[1]was a tributaryprincely stateinIndiaduring theBritish Raj.It was located in theKathiawar Peninsulaon theGujaratcoast. The state had formerly been part of theBaroda Agencyand later of theKathiawar Agencyof theBombay Presidency.
Jafrabad State was a dependency of theNawabofJanjira State,[2]located 320 km to theSSEon theKonkan coast.
Jafrabadtown, the capital and only municipality, is located 275 km south ofAhmedabadand 240 southwest ofBaroda.The state was formed by the city and 11 villages and initially consisted of two districts located on both sides of the estuary of the Ranai river. Jafrabad state had an area of 68 km2and a population in 1881 of 4,746 and in 1901 of 6,038 inhabitants. The majority of the population were Muslims (80%) and the rest Hindus. The state and the town took their name from Sultan Muzaffar Jafar from Gujarat who built fortifications.[citation needed]
History
[edit]Jafarabad State was founded around 1650. On 6 December 1733 the ruler of Jafarabad State signed a defensive and offensive treaty with theBritish East India Company.In 1759, the Jafarabad and Janjira states entered into apersonal union.Finally in 1834 Jafarabad State became aBritish protectorate.
Around 1731 when theMughal Empirerule was relaxed in Gujarat, the localThanedar(ruler) who was an ally in the Muslim Mughal garrison became independent. Thereafter theThanedarand the localKoliswere devoted to piracy, repeatedly attacking ships and disturbing commercial traffic fromSurat.Sidi Hilal,the prince of the dynasty ofJanjirawhich was then ruling Surat, attacked the Kolis, destroyed their boats and captured them demanding a hefty fine.[3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^Vadivelu, A. (1915).The Ruling Chiefs, Nobles & Zamindars of India.Vol. One. Madras: G. C. Loganadham Bros. p. 325.
- ^Chisholm, Hugh,ed. (1911)..Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 15 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 125.
- ^Robbins, Kenneth X.; McLeod, John (2006).African elites in India: Habshi Amarat.Mapin. pp. 272 Pages.ISBN1890206970.

