Khoshut
This article has multiple issues.Please helpimprove itor discuss these issues on thetalk page.(Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
 The Khoshuts with theOirat Confederation | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Languages | |
| Oirat dialect | |
| Religion | |
| Tibetan Buddhism,Mongolian shamanism | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Mongols,especiallyOirats |
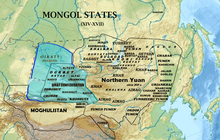
TheKhoshut(Mongolian:Хошууд,ᠬᠤᠱᠤᠳ,qoşūd,Chinese:Cùng thạc đặc;literally "bannermen," fromMiddle Mongolianqosighu"flag, banner" ) are one of the four major tribes of theOiratpeople. They established theKhoshut Khanatein the area ofQinghaiin 1642–1717.
History[edit]
Originally, Khoshuuds were one of theKhorchintribes in southeasternMongolian Plateau,but in the mid-15th century they migrated to western Mongolian Plateau to become an ally of the Oirats to counter the military power in central Mongolian Plateau. Their ruling family Galwas was theHasarid-Khorchinswho were deported by the Western Mongols.
The Khoshuts first appeared in the 1580s and by the 1620s were the most powerful Oirat tribe. They led others in converting toBuddhism.In 1636Güshi Khanled many Khoshuds to occupy Kokenuur (Qinghai). TheKhoshut Khanatewas established in 1642. Some time after 1645, his brother Kondeleng Ubashi migrated to theVolga,joining theKalmyks.However, many Khoshuts remained in the Oirat homelandDzungariaunder Ochirtu Setsen.
After theDzungarleaderGaldan Boshogtu Khankilled Ochirtu, the Khoshut chief Khoroli submitted to theQing dynastywith his people in 1686 and resettled inAlashan.
The Khoshuts of theDzungar Khanateremained influential until the Qingannihilated them in 1755.In 1771 the Volga Khoshuts fled back to Dzungaria with theKalmyksand were resettled by the Qing aroundBosten Lake.Their small remnants under a Tumen family inKalmykiawere influential until 1917. Another part of them was formed into a separate banner inBulgan Province,Khovd Province;but they were counted asTorghutwho migrated with them in much larger numbers.
20th century[edit]
The Khoshuts in Alashan numbered 36,900 in 1990.
The Khoshuts around Bosten Lake numbered more than 12,000 in 1999.
See also[edit]
- Lha-bzang Khan,Khoshut chief and King of Tibet
- Upper Mongols
References[edit]
- Санчиров В. П.О Происхождении этнонима торгут и народа, носившего это название // Монголо-бурятские этнонимы: cб. ст. — Улан-Удэ: БНЦ СО РАН, 1996. C. 31—50. - in Russian
- Ovtchinnikova O., Druzina E., Galushkin S., Spitsyn V., Ovtchinnikov I.An Azian-specific 9-bp deletion in region V of mitochondrial DNA is found in Europe // Medizinische Genetic. 9 Tahrestagung der Gesellschaft für Humangenetik, 1997, p. 85.
- Haines, R Spencer (2018). "Charismatic Authority in Context: An Explanation of Guushi Khan's Swift Rise to Power in the Early 17th Century".Mongolica: An International Journal of Mongolian Studies.52.International Association of Mongolists: 24–31.
- Galushkin S.K., Spitsyn V.A., Crawford M.H.Genetic Structure of Mongolic-speaking Kalmyks // Human Biology, December 2001, v.73, no. 6, pp. 823–834.
- Хойт С.К.Генетическая структура европейских ойратских групп по локусам ABO, RH, HP, TF, GC, ACP1, PGM1, ESD, GLO1, SOD-A // Проблемы этнической истории и культуры тюрко-монгольских народов. Сборник научных трудов. Вып. I. Элиста: КИГИ РАН, 2009. с. 146-183. - in Russian
- [hamagmongol.narod.ru/library/khoyt_2008_r.htmХойт С.К.Антропологические характеристики калмыков по данным исследователей XVIII-XIX вв. // Вестник Прикаспия: археология, история, этнография. No. 1. Элиста: Изд-во КГУ, 2008. с. 220-243.]
- Хойт С.К.Кереиты в этногенезе народов Евразии: историография проблемы. Элиста: Изд-во КГУ, 2008. – 82 с.ISBN978-5-91458-044-2(Khoyt S.K. Kereits in enthnogenesis of peoples of Eurasia: historiography of the problem. Elista: Kalmyk State University Press, 2008. – 82 p. (in Russian))
- [hamagmongol.narod.ru/library/khoyt_2012_r.htmХойт С.К.Калмыки в работах антропологов первой половины XX вв. // Вестник Прикаспия: археология, история, этнография. No. 3, 2012. с. 215-245.]
- Boris Malyarchuk, Miroslava Derenko, Galina Denisova, Sanj Khoyt, Marcin Wozniak, Tomasz Grzybowski and Ilya ZakharovY-chromosome diversity in the Kalmyks at theethnical and tribal levels // Journal of Human Genetics (2013), 1–8.
- Хойт С.К.Этническая история ойратских групп.Элиста, 2015. 199 с. (Khoyt S.K. Ethnic history of oyirad groups. Elista, 2015. 199 p. in Russian)
- video about khoshuuds
- Хойт С.К.Данные фольклора для изучения путей этногенеза ойратских групп// Международная научная конференция «Сетевое востоковедение: образование, наука, культура», 7-10 декабря 2017 г.: материалы. Элиста: Изд-во Калм. ун-та, 2017. с. 286-289. (in Russian)
