MaRisk
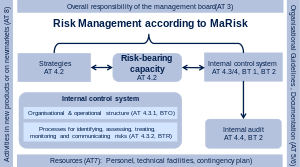
MaRiskis an acronym referring to theminimum requirements for risk management[1](German:Mindestanforderungen an das Risikomanagement), a circular by the GermanFederal Financial Supervisory Authority(Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht,BaFin) providing concepts for risk management of banks, insurances and other companies financially trading in Germany. The primary legal background for MaRisk is theKreditwesengesetz(KWG), the secondary legal background is theSolvabilitätsverordnung SolvV.
MaRisk implements the qualitative requirements ofBasel IIandBasel IIIinto German law. Strictly speaking, MaRisk is not a law, but anorm-interpreting administrative regulation(German:normeninterpretierende Verwaltungsvorschrift), nevertheless it is de facto binding for all financial institutes and insurance companies with business in Germany.
Details
[edit]One core principle of MaRisk is that the risk control department has to be set up to be organisationally independent from those departments performing business transactions. This separation should prevail throughout the organisation up to and including the management board.
Related
[edit]- The primary legal background for MaRisk is theKreditwesengesetz(KWG).
- TheKonTraG(German:Gesetz zur Kontrolle und Transparenz im Unternehmensbereich,i.e. law for control and transparency for businesses) is another legal requirement to be fulfilled by companies financially trading in Germany.
- TheSarbanes–Oxley Actcan be seen as the US equivalent of MaRisk.
References
[edit]- ^"Minimum Requirements for Risk Management"(PDF).Bundesbank.Bundesanstalt für Finanzdiensleistungsaufsicht.Retrieved9 December2015.
