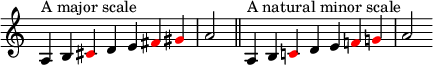
Minor scale
Inmusic theory,theminor scalehas threescalepatterns – thenatural minor scale(orAeolian mode), theharmonic minor scale,and themelodic minor scale(ascending or descending)[1]– mirroring themajor scale,with itsharmonicandmelodicforms.



In each of these scales, the first, third, and fifthscale degreesform aminor triad(rather than amajor triad,as in a major scale). In some contexts,minor scaleis used to refer to anyheptatonic scalewith this property[2](seeRelated modesbelow).
Natural minor scale[edit]
Relationship to relative major[edit]
Anatural minor scale(orAeolian mode) is adiatonic scalethat is built by starting on the sixthdegreeof itsrelativemajor scale.For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale:
Because of this, the key ofA minoris called therelative minorofC major.Every major key has a relative minor, which starts on the 6th scale degree or step. For instance, since the 6th degree ofF majoris D, the relative minor of F major isD minor.
Relationship to parallel major[edit]
A natural minor scale can also be constructed by altering a major scale withaccidentals.In this way, a natural minor scale is represented by the following notation:
- 1, 2,♭3, 4, 5,♭6,♭7, 8
This notation is based on the major scale, and represents each degree (each note in the scale) by a number, starting with the tonic (the first, lowest note of the scale). By making use of flat symbols (♭) this notation thus represents notes by how they deviate from the notes in the major scale. Because of this, we say that a number without a flat represents a major (or perfect) interval, while a number with a flat represents a minor interval. In this example, the numbers mean:
- 1 =(perfect) unison
- 2 =major second
- ♭3 =minor third
- 4 =perfect fourth
- 5 =perfect fifth
- ♭6 =minor sixth
- ♭7 =minor seventh
- 8 =(perfect) octave
Thus, for instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by lowering the third, sixth, and seventh degrees of the A major scale by one semitone:
Because they share the same tonic note of A, the key of A minor is called theparallel minorofA major.
Intervals[edit]

Theintervalsbetween the notes of a natural minor scale follow the sequence below:
- whole, half, whole, whole, half, whole, whole
where "whole" stands for awhole tone(a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for asemitone(a red angled line in the figure).
The natural minor scale ismaximally even.
Harmonic minor scale[edit]
Construction[edit]

Theharmonic minor scale(or Aeolian♯7 scale) has the same notes as the natural minor scale except that the seventh degree is raised by onesemitone,creating anaugmented secondbetween the sixth and seventh degrees.
Thus, a harmonic minor scale is represented by the following notation:
- 1, 2,♭3, 4, 5,♭6, 7, 8
A harmonic minor scale can be built by lowering the 3rd and 6th degrees of the parallel major scale by one semitone.
Because of this construction, the 7th degree of the harmonic minor scale functions as aleading toneto thetonicbecause it is asemitonelower than the tonic, rather than awhole tonelower than the tonic as it is in natural minor scales.
Intervals[edit]
Theintervalsbetween the notes of a harmonic minor scale follow the sequence below:
- whole, half, whole, whole, half, augmented second, half
Uses[edit]
While it evolved primarily as a basis for chords, the harmonic minor with its augmented second is sometimes used melodically. Instances can be found inMozart,Beethoven(for example, the finale of hisString Quartet No. 14), andSchubert(for example, in the first movement of theDeath and the Maiden Quartet). In this role, it is used while descending far more often than while ascending. A familiar example of the descending scale is heard in aRing of bells.A ring of twelve is sometimes augmented with a 5♯ and 6♭ to make a 10 note harmonic minor scale from bell 2 to bell 11 (for example, Worcester Cathedral).[4]
TheHungarian minor scaleis similar to the harmonic minor scale but with a raised 4th degree. This scale is sometimes also referred to as "Gypsy Run", or alternatively "Egyptian Minor Scale", as mentioned byMiles Daviswho describes it in his autobiography as "something that I'd learned at Juilliard".[5]
In popular music, examples of songs in harmonic minor includeKaty B's "Easy Please Me",Bobby Brown's "My Prerogative",andJazmine Sullivan's "Bust Your Windows".The scale also had a notable influence on heavy metal, spawning a sub-genre known asneoclassical metal,with guitarists such asChuck Schuldiner,Yngwie Malmsteen,Ritchie Blackmore,andRandy Rhoadsemploying it in their music.[6]
Melodic minor scale[edit]
Construction[edit]
The distinctive sound of the harmonic minor scale comes from theaugmented secondbetween its sixth and seventh scale degrees. While some composers have used this interval to advantage in melodic composition, others felt it to be an awkward leap, particularly invocal music,and preferred awhole stepbetween these scale degrees for smooth melody writing. To eliminate the augmented second, these composers either raised the sixth degree by asemitoneor lowered the seventh by a semitone.
Themelodic minor scaleis formed by usingbothof these solutions. In particular, the raised sixth appears in the ascending form of the scale, while the lowered seventh appears in the descending form of the scale. Traditionally, these two forms are referred to as:
- theascending melodic minor scaleorjazz minor scale(also known as the Ionian♭3 or Dorian♯7): This form of the scale is also the 5th mode of theacoustic scale.
- thedescending melodic minor scale:This form is identical to the natural minor scale.
The ascending and descending forms of the A melodic minor scale are shown below:
The ascending melodic minor scale can be notated as
- 1, 2,♭3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
while the descending melodic minor scale is
- 8,♭7,♭6, 5, 4,♭3, 2, 1
Using these notations, the two melodic minor scales can be built by altering the parallel major scale.
Intervals[edit]
The intervals between the notes of an ascending melodic minor scale follow the sequence below:
- whole, half, whole, whole, whole, whole, half
The intervals between the notes of a descending melodic minor scale are the same as those of a descending natural minor scale.
Uses[edit]
![\relative c''' {
\set Staff.midiInstrument = #"violin"
\set Score.tempoHideNote = ##t \tempo 4 = 120
\key g \dorian
\time 4/4
g8^\markup \bold "Allegro"
f16 es d c bes a g a bes c d e fis g
fis8[ d]
}](https://upload.wikimedia.org/score/8/o/8owojgeebkd9l92qc54i7cs1s19knkd/8owojgee.png)
Composers have not been consistent in using the two forms of the melodic minor scale. Composers frequently require the lowered 7th degree found in the natural minor in order to avoid the augmented triad (III+) that arises in the ascending form of the scale.
Examples of the use of melodic minor inrockandpopular musicincludeElton John's "Sorry Seems to Be the Hardest Word",which makes," a nod to the common practice... by the use of F♯[theleading tonein G minor] as the penultimate note of the finalcadence."[7]The Beatles' "Yesterday"also partly uses the melodic minor scale.[citation needed]
Key signature[edit]
In modern notation, thekey signaturefor music in aminor keyis typically based on theaccidentalsof thenaturalminor scale, not on those of the harmonic or melodic minor scales. For example, a piece in E minor will have one sharp in its key signature because the E natural minor scale has one sharp (F♯).
Major and minor keys that share the samekey signaturearerelativeto each other. For instance, F major is the relative major of D minor since both have key signatures with one flat. Since the natural minor scale is built on the 6th degree of the major scale, the tonic of the relative minor is amajor sixthabove the tonic of the major scale. For instance, B minor is the relative minor of D major because the note B is a major sixth above D. As a result, the key signatures of B minor and D major both have two sharps (F♯and C♯).
Related modes[edit]
Sometimes scales whose root, third, and fifth degrees form aminor triadare considered "minor scales". In the Western system, derived from theGreek modes,the principal scale that includes the minor third is theAeolian mode(the natural minor scale), with the minor third also occurring in theDorian modeand thePhrygian mode.The Dorian mode is a minor mode with a major sixth, while the Phrygian mode is a minor mode with a minor second. TheLocrian mode(which isveryrarely used) has a minor third but not the perfect fifth, so its rootchordis adiminished triad.
Although varioushemitonic[clarification needed]pentatonic scalesmight be calledminor,the term is most commonly applied to the relative minor pentatonic scale, derived as a mode of the major pentatonic scale, using scale tones 1, 3, 4, 5, and 7 of the natural minor scale.[8]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Kostka, Stefan;Payne, Dorothy (2004).Tonal Harmony(5th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 12.ISBN0-07-285260-7.
- ^Prout, Ebenezer(1889).Harmony: Its Theory and Practice,pp. 15, 74, London, Augener.
- ^abForte, Allen(1979).Tonal Harmony,p. 13. Third edition. Holt, Rinhart, and Winston.ISBN0-03-020756-8.
- ^"Dove's Guide"
- ^Davis, Miles; Troupe, Quincy (1990).Miles, the Autobiography.Simon & Schuster. pp.64.ISBN0-671-72582-3.
- ^"Neo-Classical Metal Music Genre Overview | AllMusic".AllMusic.Retrieved2018-11-26.
- ^Stephenson, Ken (2002).What to Listen for in Rock: A Stylistic Analysis.Yale University Press. p. 41.ISBN9780300128239.
- ^Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003),Music: In Theory and Practice,seventh edition (Boston: McGraw Hill), vol. I, p. 37.ISBN978-0-07-294262-0.
Further reading[edit]
- Hewitt, Michael. 2013.Musical Scales of the World.The Note Tree.ISBN978-0-9575470-0-1.
- Yamaguchi, Masaya. 2006.The Complete Thesaurus of Musical Scales,revised edition. New York: Masaya Music Services.ISBN0-9676353-0-6.