Route (gridiron football)
Arouteis a pattern or path that areceiveringridiron footballruns to get open for aforward pass.[1]Routes are usually run by wide receivers, running backs and tight ends, but other positions can act as a receiver given the play.
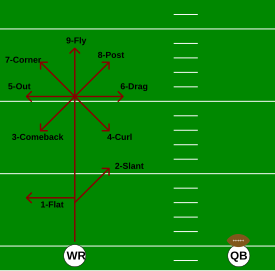
One popular way to organize routes is with a "route tree". A route tree is a way to show all the various routes with one diagram.[2]
Routes
[edit]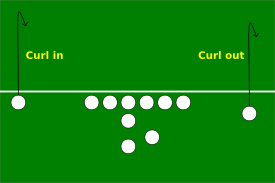
Curl
[edit]A curl route, also called a hitch or hook (sometimes a button hook), is a route where the receiver appears to be running aflypattern but after a set number of steps or yards will quickly stop and turn around, looking for a pass.[3]This generally works best when the defendingcornerorsafetycommits himself to guarding the fly and is unable to stop quickly enough to defend the pass. A "curl out" on the sideline is often referred to as a comeback route.[4]
The curl is a pattern used frequently by theWest Coast offensive scheme,where quick and accurate passes are favored.
This route can also be used in what is called ascreen,where while the receiver is receiving the pass, one or morelinemen,tight ends,orrunning backswill run in the direction of the receiver in order to block the initial pursuing defenders so that the receiver has time and space to be able to run after the catch.
Drag
[edit]
A drag route (also known as an in route or a dig route) is arouterun by areceiver,where the receiver runs a few yards downfield, then turns 90° towards the center of the field and runs parallel to theline of scrimmage.[5][6]This type of route is relatively safe and is thrown to an agile receiver who can make a play after the catch. Alternatively, a drag route may be used as a second option if the principal receiver on a play is covered.
The use of two crossing drag routes can also be used to try to create an open receiver by using the other receiver to block the path of a defensive back in a man coverage scheme. Out and in routes are the most difficult routes to cover in man-to-man coverage, but can be dangerous plays to run because, if the defender intercepts the pass, he will often have a clear path to theend zone.
Corner
[edit]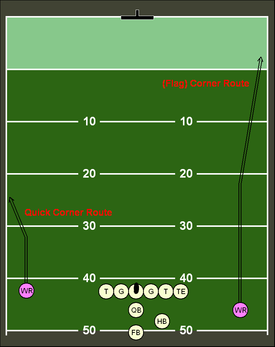
A corner route is apatternrun by areceiver,where the receiver runs up the field and then turns at approximately a 45-degree angle, heading away from thequarterbacktowards the sideline.[7]Usually, the pass is used when thedefensive backis playing towards the inside shoulder of the receiver, thus creating a one on one vertical matchup.[7]The corner route is less likely to be intercepted when compared to theslant route,because it is thrown away from the middle of the field. The pass is used frequently in theWest Coast offensive scheme,where quick, accurate throwing is key.[8]The pass may also be used closer to the goal line in what is called a "fade". The quarterback will lob the ball over a beaten defender to a wide receiver at the back corner of the end zone.
Fly
[edit]
A fly route, also called a streak route or go route, is apatternrun where the receiver runs straight upfield towards the endzone.[9]The goal of the pattern is to outrun any defensive backs and get behind them, catching an undefended pass while running untouched for a touchdown.[10]Generally, the fastest receiver on the team or any receiver faster than the man covering him would be the one to run these routes. When run down the sidelines, a fly can be called a fade route.[11]
Fly patterns can also be used to clear out space for other receivers. Generally, a fly pattern will draw the attention of both the cornerback assigned to the receiver as well as "over the top" help from a safety. This can create a large gap in coverage, allowing another receiver to run a shorter route, but then gain many yards after the catch because the safety committed to the deep receiver.
The famed "Hail Mary"play generally involves between three and five receivers all running fly routes in order to have the most chance of one of them catching the ball and scoring or at least gaining significant yardage.
Out
[edit]
An out route (or down and out or jet route) is apatternrun by areceiver.On an out route, the receiver will start running aflypattern (i.e., running straight down the field toward the end zone) but, after a certain number of steps, will cut hard 90 degrees "to the outside", or toward the sideline, away from thequarterback.[12]If the cut comes very quickly, usually after only a few steps, it is called a "quick out". Out routes generally allow a one-on-one match-up between the receiver and thedefensive backwho is guarding him, assafetiesgenerally are concerned with helping out on long routes downfield or the center of the field.
This route is used much more frequently near the end of each half, or when a team is running theirtwo-minute drillto preserve time on the clock, because, as soon as the receiver catches the ball or after a short run after the catch, he should be able to get out of bounds, stopping the clock. It is a quick execution play; if the ball is thrown correctly usually a defensive player can't respond quickly enough to interfere. It is also often called in a 3rd-down situation where the full ten yards are needed. Out andinroutes are the most difficult routes to cover in man-to-man coverage, but can be dangerous plays to run because, if the defender intercepts the pass, he will often have a clear path to theend zone.
Post
[edit]
A post route is a moderate to deeppassing routein which areceiverruns 10–20 yards from theline of scrimmagestraight down the field, then cuts toward the middle of the field (towards the facinggoalposts,hence the name) at a 45-degree angle.[13]
It is designed to stretch the opposing secondary deep down the field, opening holes in the coverage over the middle. It works particularly well against secondaries that don't have more than onesafetywho is effective in coverage, or against safeties with 2 or 4 deep zone players, attacking the void in the middle of the field. It tends to induce the opposing defense to play a deeper field and drop more defenders into deep coverage, but this may still open up the run.Cover 3packages can be effective against it, if the defender in middle deep coverage is perceptive enough.
To run the route effectively, a wide receiver must be adept at catching the ball in traffic, and have the vertical ability and strength to rise above the top of a safety to catch the ball.
A variant of the post pattern, in which the receiver cuts infield at a shallower angle, is called a skinny post.[14]It is designed to find a hole in deep coverage, cutting shallow inside the deep sideline defender, but not far enough to draw the middle defender.
Slant
[edit]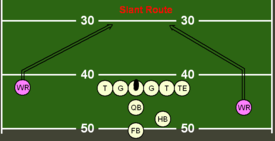
A slant route is apattern,where the receiver runs up the field at approximately a 45-degree angle, heading to the gap between thelinebackersand thelinemen.[15]Usually, the pass is used when thecornerornickelbackare playing farther away from the receiver, so a quick pass is able to be completed before the defender has time to try to break up the pass. The pass is used frequently in theWest Coast system,where quick, accurate throwing is key. This route is most commonly used to exploit thecover 2defense. Usually throwing in the seam between thesafetyand the cornerback is the key to getting a completion using this route.
Flat
[edit]
A flat route is usually run by arunning backor afullback.When run by a receiver it can be known as a speed out or arrow route. The eligiblereceiverruns parallel to theline of scrimmagetill near thesidelines(in theflat) and turns toward thequarterbackto wait for thepass.[16]The QB's pass should arrive when he has not yet passed the line of scrimmage. The receiver will then turn upfield at the sideline and run straight down the field.
The route is used withlong post,long cornerorfly routes,so thesafetiesand thecornerbacksshould be upfield when the pass is caught by the RB or FB. There should be alinebackercovering the RB/FB on these kinds of plays, which is likely to be an easy match for an elusive runner like therunning back.
Wheel
[edit]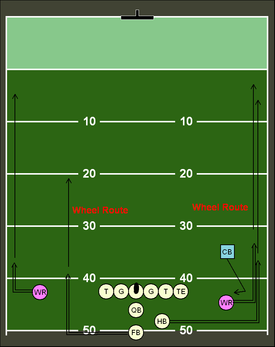
A wheel route can be run by areceiverorrunning backinAmerican football.If a receiver runs it, they will immediately run a quickout pattern,then proceed to turn upfield in a curved pattern.[17]Typically this route is run by an inside receiver, with the number one receiver heading inside to exploit coverage in the defense. When run from the running back position the player will run towards the sideline while looking back at thequarterbackas if about to receive a pass on aflare route.The running back will then turn upfield at the sideline and run straight down the field.
This route is useful when run from the wide receiver position because thedefensive backwill expect the ball to be thrown as the receiver makes his first turn and will bite (go for the fake) underneath the receiver (run between the quarterback and the receiver to try to prevent, block, or intercept the pass) to defend the pass and be unable to recover as the receiver turns upfield. In this respect the route is very similar to an Out-and-Up orChair route,but without the vertical release that the Out-and-Up utilizes. The route is useful when run from the running back position because the defender will assume the ball is going to be thrown to the running back behind the line of scrimmage (the quarterback can use a pump fake to further "sell" this), and will bite underneath the running back only to have the running back turn upfield.
Swing
[edit]A swing route or a flare route is run by therunning back,and is like a wheel route thrown before the turn up the sideline,[18]i. e. release toward the sideline, and then bend or arc upfield ever so slightly,[19]and look for a short pass.[20]It can be combined with ascreen pass.It is distinguished from aflat routeby approaching theline of scrimmagemore gradually, on a curved path.[21]
Seam
[edit]The seam route[22][23][24]is a route, usually played against azone defense in American football,in which the receiver runs at the edges of a defender's coverage (for example, between thelinebackerandsafety), thus, on the "Seam" between two or more coverages. It is not a route on its own, but the location of another route (typicallyfly routeorpost route). The Seam[25]is the area where two defenders' areas of responsibility meet. The concept behind this is that the ability to complete a pass is increased because the defenders may be confused about which one of them is responsible for defending the player on the Seam or; the defenders are trying to cover their area of responsibility which creates an open space equidistant between the defenders.
Stop-and-go
[edit]A stop-and-go, pump-and-go or a hitch-and-go is a route run by areceiver.It is a combination of a fakecurl(or hitch) followed by a go (orfly route).[citation needed]
Jerk
[edit]A jerk route is run by a receiver. In essence, it is a shallowcrossing routewith a stutter step.[26] The idea is to isolate the receiver on a linebacker. One stops as if he is receiving a pass on acurlor going to retrace his steps, then he has the option to continue across the field, or change direction at an angle.[27]
Double Out
[edit]A double out is when a receiver runs 5-8 yards down field cuts outside, then cuts vertically upfield once more then cuts outside again. This route is very difficult to run and to defend due to all of the drastic changes in momentum, this route is also rarely used due to the time taken to correctly complete.
Angle route
[edit]Typically run by a running back, fullback, or tight end, the player will run out at a 45-degree angle for a few steps, then cut 90 degrees back inside.
Sail route
[edit]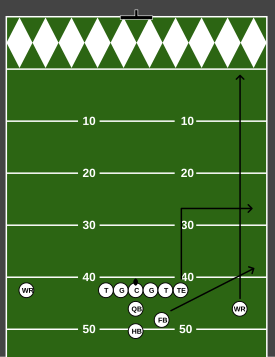
The sail route is not a route, but a combinations of routes. The sail concept is a three-level passing scheme that overloads one side of the defense while stretching the coverage vertically. Typically, the sail concept is a combination of a deep vertical route from the outside receiver, an intermediate out or christopher crossing route from the inside receiver, and a short flat route ‒ often a quick out or a swing route ‒ by the running back. This sets up a three-level read for the quarterback, with a receiver at 25-, 15- and 5- yard depths vertically.[28]
Pivot
[edit]A pivot route, also known as a shark route or a zig route, is similar to an out route, except the receiver will cut one direction, then spin 180 degrees towards the line of scrimmage then continue in the opposite direction.
Sluggo
[edit]A sluggo is run by areceiver.[29]The word was coined byBill Walshas an apparent compression of "slantandgo".[30]
Hot route
[edit]A hot route is used to escape a potential sack from ablitzing defense.A hot route is a variation on the regular running route for a running back. It results usually from an audible called by aquarterback,and is based on a read of a blitzing defense. If the defense does not blitz, the running back runs the regular route. If the defense does blitz, the running back will, instead of blocking the blitzing defensive player, run a short route, such as abubble screen,and catch the ball which the quarterback dumps off quickly.[31]
Crossing
[edit]A crossing route or crossing pattern refers to either adrag[32]orslant[33]routewhere areceivercrosses across the field.
Chair
[edit]The chair route or out-and-up was pioneered byDon Hutson.[34]It is anout routefollowed by afly route,like awheel routewith a quicker vertical release; or astop-and-gowith an out rather than a curl.[35]
References
[edit]- ^"Glossary".NFL-360.Retrieved13 April2016.
- ^Nogle, Kevin (June 20, 2016)."Football 101: The route tree".The Phinsider.
- ^"10 Football Passing Routes Explained".9 November 2015.
- ^"American Football Passing Patterns".
- ^"500(FUMBLE!) - Sporting Charts".sportingcharts.
- ^Staff, Xs Os (28 May 2015)."Pass Routes 101 | Football".
- ^abBass, Tom (2004).Football skills & drills.Human Kinetics. p.96.ISBN978-0-7360-5456-0.
- ^Henderson, Frank; Olson, Mel (1997).Football's West Coast offense.Human Kinetics. p. 55.ISBN978-0-88011-662-6.
- ^"500(FUMBLE!) - Sporting Charts".sportingcharts.
- ^Williams, Travis (May 12, 2014)."Understanding the Route Tree, Part II".Field Gulls.
- ^Bowen, Matt."NFL 101: Breaking Down the Basics of the Route Tree".Bleacher Report.
- ^"How to Run an Out Route - top wide receiver training".topwrtraining.Archived fromthe originalon 2015-09-20.
- ^"WR Basics: Routes and the Passing Tree".Shakin The Southland.March 22, 2010.
- ^"Chalk Talk: Skinny-Post versus Traditional-Post Route | MidValleySports.Com".
- ^"Slant Route - top wide receiver training".topwrtraining.Archived fromthe originalon 2016-03-13.
- ^"500(FUMBLE!) - Sporting Charts".sportingcharts.
- ^"500(FUMBLE!) - Sporting Charts".sportingcharts.
- ^Mallory, Bill; Nehlen, Don; Association, American Football Coaches (1 January 2006).Football Offenses and Plays.Human Kinetics.ISBN9780736062619– via Google Books.
- ^Kirby, Alex (10 August 2015).New England vs Seattle.Alex Kirby.ISBN9781516846740– via Google Books.
- ^Staff, Xs Os."Pass Routes 101 - Football".
- ^"ITP Glossary: Swing Route - Inside The Pylon".19 February 2016.
- ^"Playoff Anatomy: Saints' seam route".NFL.
- ^"Seam Route Definition - Sporting Charts".
- ^"Learning Seams And Soft Spots Against Zone Coverage - Football Tutorials".Football Tutorials.10 October 2011.
- ^"Prepqb".prepqb.
- ^Neumann, David (September 24, 2014)."All-22 of the 49ers new 5-WR sets".Niners Nation.
- ^"Anatomy of a Play: Royal times two".NFL.Archived fromthe originalon September 18, 2016.
- ^"ITP Glossary: Sail Concept".24 November 2015.
- ^"Pass Routes 101 - Football".xsosfootball.
- ^Brown, Chris B. (17 August 2012)."Matt Barkley and USC's" Sluggo Seam "Play".
- ^Olson, Mel; Henderson, Frank (1997).Football's West Coast offense.Champaign: Human Kinetics. p. 28.ISBN9780880116626.
- ^George, Thomas (25 January 1997)."The Passing Matchup: Quick Slant vs. Cross".The New York Times.
- ^"Route Breakdown: Crossing Routes | PFF News & Analysis | PFF".
- ^Goldberg, Dave (6 November 2008)."Wacky Wideouts not new".USAtoday.
- ^"Wide receiver patterns".The Football Times.9 November 2005. Archived fromthe originalon 5 April 2016.
