Prostacyclin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Flolan, Veletri |
| AHFS/Drugs | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokineticdata | |
| Eliminationhalf-life | 42 seconds |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChemCID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H32O5 |
| Molar mass | 352.471g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Prostacyclin(also calledprostaglandin I2orPGI2) is aprostaglandinmember of theeicosanoidfamily oflipidmolecules.It inhibits platelet activation and is also an effective vasodilator.
When used as a drug, it is also known asepoprostenol.[1]The terms are sometimes used interchangeably.[2]
Function[edit]
Prostacyclin chiefly prevents formation of theplatelet pluginvolved in primaryhemostasis(a part ofblood clotformation). It does this by inhibiting platelet activation.[3]It is also an effectivevasodilator.Prostacyclin's interactions contrast with those ofthromboxane(TXA2), another eicosanoid. Both molecules are derived fromarachidonic acid,and work together with opposite platelet aggregatory effects. These strongly suggest a mechanism of cardiovascularhomeostasisbetween these two hormones in relation tovasculardamage.
Medical uses[edit]
It is used to treatpulmonary arterial hypertension(PAH),[4][5]pulmonary fibrosis,[6]as well asatherosclerosis.[6]Specifically, epoprostenol is given to patients with class III or class IV PAH.[citation needed]
Degradation[edit]
Prostacyclin, which has ahalf-lifeof 42 seconds,[7]is broken down into 6-keto-PGF1,which is a much weaker vasodilator. A way to stabilize prostacyclin in its active form, especially during drug delivery, is to prepare prostacyclin in alkaline buffer. Even at physiological pH, prostacyclin can rapidly form the inactive hydration product6-keto-prostaglandin F1α.[8]
Mechanism[edit]
Prostacyclin effect Mechanism Cellular response Classical
functionsVessel tone ↑cAMP, ↓ET-1
↓Ca2+,↑K+↓SMC proliferation
↑VasodilationAntiproliferative ↑cAMP
↑PPARgamma↓Fibroblast growth
↑ApoptosisAntithrombotic ↓Thromboxane-A2
↓PDGF↓Platelet aggregation
↓Platelet adherence to vessel wallNovel
functionsAntiinflammatory ↓IL-1, IL-6
↑IL-10↓Proinflammatory cytokines
↑Antiinflammatory cytokinesAntimitogenic ↓VEGF
↓TGF-β↓Angiogenesis
↑ECM remodeling
As mentioned above, prostacyclin (PGI2) is released by healthy endothelial cells and performs its function through aparacrinesignaling cascade that involvesG protein-coupled receptorson nearby platelets and endothelial cells. The platelet Gs protein-coupled receptor (prostacyclin receptor) is activated when it binds to PGI2.This activation, in turn, signals adenylyl cyclase to producecAMP.cAMP goes on to inhibit any undue platelet activation (in order to promote circulation) and also counteracts any increase in cytosolic calcium levels that would result fromthromboxane A2(TXA2) binding (leading to platelet activation and subsequentcoagulation). PGI2also binds to endothelialprostacyclin receptors,and in the same manner, raises cAMP levels in the cytosol. This cAMP then goes on to activateprotein kinase A(PKA). PKA then continues the cascade by promoting the phosphorylation of themyosin light chain kinase,which inhibits it and leads tosmooth musclerelaxation andvasodilation.It can be noted that PGI2and TXA2work as physiological antagonists.
Members[9][edit]
| PROSTACYCLINS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Flolan (epoprostenol sodium) for Injection |
Continuously infused | 2 ng/kg/min to start, increased by 2 ng/kg/min every 15 minutes or longer until suitable efficacy/tolerability balance is achieved | Class III Class IV |
| Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection |
Continuously infused | 2 ng/kg/min to start, increased by 2 ng/kg/min every 15 minutes or longer until suitable efficacy/tolerability balance is achieved | Class III Class IV |
| Remodulin SC§ (treprostinilsodium) Injection |
Continuously infused | 1.25 ng/kg/min to start, increased by up to 1.25 ng/kg/min per week for 4 weeks, then up to 2.5 ng/kg/min per week until suitable efficacy/tolerability balance is achieved | Class II Class III Class IV |
| Ventavis (iloprost) Inhalation Solution |
Inhaled 6–9 times daily | 2.5 μg 6–9 times daily to start, increased to 5.0 μg 6–9 times daily if well tolerated | Class III Class IV |
Pharmacology[edit]

Synthetic prostacyclin analogues (iloprost,cisaprost) are used intravenously, subcutaneously or by inhalation:
- as avasodilatorin severeRaynaud's phenomenonorischemiaof a limb;
- inpulmonary hypertension.
- in primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH)
The production of prostacyclin is inhibited by the action ofNSAIDsoncyclooxygenaseenzymes COX1 and COX2. These convertarachidonic acidtoprostaglandin H2(PGH2), the immediate precursor of prostacyclin. Since thromboxane (aneicosanoidstimulator of platelet aggregation) is also downstream of COX enzymes, one might think that the effect of NSAIDs would act to balance. However, prostacyclin concentrations recover much faster than thromboxane levels, so aspirin administration initially has little to no effect but eventually prevents platelet aggregation (the effect of prostaglandins predominates as they are regenerated). This is explained by understanding the cells that produce each molecule, TXA2and PGI2.Since PGI2is primarily produced in a nucleated endothelial cell, the COX inhibition by NSAID can be overcome with time by increased COX gene activation and subsequent production of more COX enzymes tocatalyzethe formation of PGI2.In contrast, TXA2is released primarily by anucleated platelets, which are unable to respond to NSAID COX inhibition with additionaltranscriptionof the COX gene because they lackDNAmaterial necessary to perform such a task. This allows NSAIDs to result in PGI2dominance that promotes circulation and retardsthrombosis.
In patients withpulmonary hypertension,inhaled epoprostenol reduces pulmonary pressure, and improves right ventricularstroke volumein patients undergoing cardiac surgery. A dose of 60 μg is hemodynamically safe, and its effect is completely reversed after 25 minutes. No evidence ofplateletdysfunction or an increase in surgical bleeding after administration of inhaled epoprostenol has been found.[10]The drug has been known to cause flushing, headaches and hypotension.[11]
Synthesis[edit]
Biosynthesis[edit]
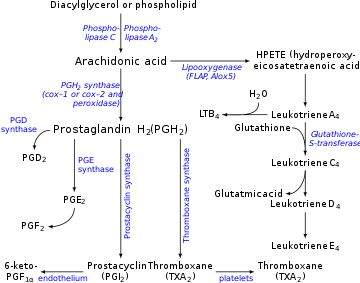
Prostacyclin is produced inendothelialcells,which line the walls of arteries and veins,[12]fromprostaglandin H2(PGH2) by the action of theenzymeprostacyclin synthase.Although prostacyclin is considered an independent mediator, it is calledPGI2(prostaglandin I2) in eicosanoid nomenclature, and is a member of theprostanoids(together with theprostaglandinsandthromboxane). PGI2,derived primarily from COX-2 in humans, is the major arachidonate metabolite released from the vascular endothelium. This is a controversial point, some assign COX 1 as the major prostacyclin producing cyclooxygenase in the endothelial cells of the blood vessels.[13]
The series-3 prostaglandin PGH3also follows the prostacyclin synthase pathway, yielding another prostacyclin,PGI3.[14]The unqualified term 'prostacyclin' usually refers to PGI2.PGI2is derived from the ω-6arachidonic acid.PGI3is derived from the ω-3EPA.
Artificial synthesis[edit]
Prostacyclin can besynthesizedfrom themethylesterofprostaglandin F2α.[15]After its synthesis, the drug is reconstituted in saline and glycerin.[16]
Because prostacyclin is so chemically labile, quantitation of their inactive metabolites, rather than the active compounds, is used to assess their rate of synthesis.[17]
History[edit]
During the 1960s, a UK research team, headed by ProfessorJohn Vane,began to explore the role ofprostaglandinsin anaphylaxis and respiratory diseases. Working with a team from theRoyal College of Surgeons,Vane discovered that aspirin and other oral anti-inflammatory drugs work by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins. This critical finding opened the door to a broader understanding of the role of prostaglandins in the body.
A team at The Wellcome Foundation led by Salvador Moncada had identified a lipid mediator they called "PG-X," which inhibits platelet aggregation. PG-X, later known as prostacyclin, is 30 times more potent than any other then-known anti-aggregatory agent. They did this while searching for an enzyme that generates a fellow unstable prostanoid,Thromboxane A2[18]
In 1976, Vane and fellow researchersSalvador Moncada,Ryszard Gryglewski,andStuart Buntingpublished the first paper on prostacyclin inNature.[19]The collaboration produced a synthesized molecule, which was named epoprostenol. But, as with native prostacyclin, the epoprostenol molecule is unstable in solution and prone to rapid degradation.[citation needed]This presented a challenge for both in vitro experiments and clinical applications.
To overcome this challenge, the research team that discovered prostacyclin continued the research. The research team synthesized nearly 1,000 analogues.[citation needed]
References[edit]
- ^"epoprostenol"atDorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^Kermode J, Butt W, Shann F (August 1991)."Comparison between prostaglandin E1 and epoprostenol (prostacyclin) in infants after heart surgery".British Heart Journal.66(2): 175–178.doi:10.1136/hrt.66.2.175.PMC1024613.PMID1883670.
- ^Pathologic Basis of Disease,Robbins and Cotran, 8th ed. Saunders Philadelphia 2010
- ^"Epoprostenol Sodium Monograph for Professionals".Drugs.AHFS. 6 April 2020.Retrieved22 October2020.
- ^"Flolan- epoprostenol sodium injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution Diluent- water solution".DailyMed.15 November 2019.Retrieved22 October2020.
- ^abStitham J, Midgett C, Martin KA, Hwa J (13 May 2011)."Prostacyclin: an inflammatory paradox".Frontiers in Pharmacology.2.Frontiers Media S.A.: 24.doi:10.3389/fphar.2011.00024.PMC3108482.PMID21687516.
- ^Cawello W, Schweer H, Müller R, Bonn R, Seyberth HW (1994). "Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of prostaglandin E1 administered by intravenous infusion in human subjects".European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.46(3): 275–277.doi:10.1007/BF00192562.PMID8070511.S2CID25410558.
- ^Lewis PJ, Dollery CT (July 1983). "Clinical pharmacology and potential of prostacyclin".British Medical Bulletin.39(3): 281–4.doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071834.PMID6354353.
- ^^ REM_RefGuideWC_AUG07v.1
- ^Haché M, Denault A, Bélisle S, Robitaille D, Couture P, Sheridan P, et al. (March 2003)."Inhaled epoprostenol (prostacyclin) and pulmonary hypertension before cardiac surgery".The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery.125(3): 642–649.doi:10.1067/mtc.2003.107.PMID12658208.
- ^ Nickson, C. (2015, October 28). Prostacyclin or Epoprostenol. Retrieved November 16, 2015, fromhttp://lifeinthefastlane /ccc/prostacyclin-or-epoprostenol/
- ^prostacyclin. (n.d.) Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. (2003). Retrieved November 17, 2015 fromhttp://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary /prostacyclin
- ^Kirkby NS, Lundberg MH, Harrington LS, Leadbeater PD, Milne GL, Potter CM, et al. (October 2012)."Cyclooxygenase-1, not cyclooxygenase-2, is responsible for physiological production of prostacyclin in the cardiovascular system".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.109(43): 17597–17602.Bibcode:2012PNAS..10917597K.doi:10.1073/pnas.1209192109.PMC3491520.PMID23045674.
- ^Fischer S, Weber PC (September 1985). "Thromboxane (TX)A3 and prostaglandin (PG)I3 are formed in man after dietary eicosapentaenoic acid: identification and quantification by capillary gas chromatography-electron impact mass spectrometry".Biomedical Mass Spectrometry.12(9): 470–476.doi:10.1002/bms.1200120905.PMID2996649.
- ^Johnson RA, Lincoln FH, Nidy EG, Schneider WP, Thompson JL, Axen U (1978). "Synthesis and characterization of prostacyclin, 6-ketoprostaglandin F1. Alpha., prostaglandin I1, and prostaglandin I3".Journal of the American Chemical Society.100(24): 7690–7705.doi:10.1021/ja00492a043.
- ^ Nickson C (15 October 2015)."Prostacyclin or Epoprostenol".Life in the Fast Lane.Archived fromthe originalon 28 March 2015.Retrieved16 November2015.
- ^Collins PW, Djuric SW (1993). "Synthesis of therapeutically useful prostaglandin and prostacyclin analogs".Chemical Reviews.03(4): 1533–1564.doi:10.1021/cr00020a007.
- ^Kermode J, Butt W, Shann F (August 1991)."Comparison between prostaglandin E1 and epoprostenol (prostacyclin) in infants after heart surgery".British Heart Journal.66(2): 175–178.doi:10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80377-4.PMC1024613.PMID1883670.
- ^Moncada S, Gryglewski R, Bunting S, Vane JR (October 1976). "An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation".Nature.263(5579): 663–665.Bibcode:1976Natur.263..663M.doi:10.1038/263663a0.PMID802670.S2CID4279030.
External links[edit]
- "Epoprostenol".Drug Information Portal.U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Epoprostenol sodium".Drug Information Portal.U.S. National Library of Medicine.
