Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate,sold under the brand namesRitalin(/ˈrɪtəlɪn/RIT-ə-lin) andConcerta(/kənˈsɜːrtə/kən-SUR-tə) among others, is acentral nervous system(CNS)stimulantused medically to treatattention deficit hyperactivity disorder(ADHD) and, to a lesser extent,narcolepsy.It is afirst-line treatmentfor ADHD (e.g. in theUK[16]); it may be takenby mouthor applied to the skin, and different formulations have varying durations of effect.[4]For ADHD, the effectiveness of methylphenidate is comparable toatomoxetine[17][18][19][20]but modestly lower thanamphetamines,[21][22][23][24]alleviating theexecutive functioningdeficits of sustained attention, inhibition, working memory, reaction time[25]and emotional self-regulation.[26][27]
Common adverse reactions of methylphenidate includeeuphoria,dilated pupils,tachycardia,palpitations,headache,insomnia,anxiety,hyperhidrosis,weight loss,decreased appetite,dry mouth,nausea,andabdominal pain.[10]Withdrawal symptomsmay includechills,depression,drowsiness,dysphoria,exhaustion,headache,irritability,lethargy,nightmares,restlessness,suicidal thoughts,andweakness.[4]
Methylphenidate is believed to work by blocking thereuptakeofdopamineandnorepinephrinebyneurons.[28][29]It is acentral nervous system(CNS) stimulant of thephenethylamineandpiperidineclasses. It is available as ageneric medication.[30]In 2022, it was the 32nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 17million prescriptions.[31][32]
Etymology
[edit]The word methylphenidate is aportmanteauof the chemical name,Methyl-2-phenyl-2-(piperidin-2-yl) acetate.
The name "Ritalin" derives from Marguerite "Rita" Panizzon, the wife of Leandro Panizzon, who first synthesized the drug in 1944. Rita was the first person to take methylphenidate, and described its effects to her husband.[33]
Uses
[edit]Methylphenidate is most commonly used to treatADHDandnarcolepsy.[34]
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
[edit]Methylphenidate is used for the treatment ofattention deficit hyperactivity disorder(ADHD).[35]The dosage may vary and istitratedto effect, with some guidelines recommending initial treatment with a low dose.[36]Methylphenidate is available in both immediate-release and extended-release (XR) formulations to provide a sustained release of the drug.[37][38]Methylphenidate is not approved for children under six years of age.[39][40]
The International Consensus Statement on ADHD shows that the results fromsystematic reviews,meta-analysesand large scale studies are clear: methylphenidate is safe and efficacious, but also among the most efficacious drugs in all of medicine; treatment in the long-term significantly reduces or eliminates the elevated risks for obesity, accidental injuries, traumatic brain injury, substance abuse, cigarette smoking, educational underachievement, bone fractures, sexually transmitted infections, depression, suicide, criminal activity, teenage pregnancy, vehicle crashes, burn injuries and overall-cause mortality.[41]
One committee from theWorld Health Organization(WHO) responsible for theWorld Health Organization Essential Medicines Listrejected an application in 2019, and a second application endorsed by 51 professional medical groups in 2021, for methylphenidate's inclusion due to uncertainty about its efficacy and safety.[42][43]However, in November 2023, the WHO Mental Health Gap Action Programme Guidelines for mental, neurological, and substance use disorders makes a clear recommendation that methylphenidate should be considered for children aged 6 years and older who have ADHD, noting specifically that, "methylphenidate treatment shows substantial effects on symptom reduction",[44]in addition to other WHO publications.[45]In 2024, theEuropean Society for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry(ESCAP) and theAmerican Academy of Paediatrics(AAP) endorsed the inclusion of methylphenidate in the WHO EML.[46][47]
Safety and efficacy data have been reviewed extensively by medical regulators (e.g., the US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency), the developers of evidence-based national guidelines (e.g., the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the American Academy of Pediatrics), and government agencies who have endorsed these guidelines (e.g., the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council). These professional groups unanimously conclude, based on the scientific evidence, that methylphenidate is safe and effective and should be considered as a first-line treatment for ADHD.[41]
Since ADHD diagnosis has increased around the world, methylphenidate may be misused as a "study drug" by some populations, which may be harmful.[48]This also applies to people who may be experiencing a different issue and aremisdiagnosedwith ADHD.[48]People in this category can then experience negative side-effects of the drug, which worsen their condition.[48]
Long-term meta-analyses and systematic reviews show that the medications used to treat ADHD are not associated with observed deficits in brain structure, but with improved brain development and functioning, most prominently in inferior frontal and striatal regions.[41]The most comprehensive meta-analysis available (19 studies with over 3.9 million participants) found "no statistically significant association between ADHD medications [including methylphenidate] and the risk of cardiovascular event among children and adolescents, young and middle-aged adults, or older adults";[49]as do other systematic reviews and meta-analyses.[50][51][52]
Narcolepsy
[edit]Narcolepsy,achronicsleep disordercharacterized by overwhelming daytime drowsiness and uncontrollable sleep, is treated primarily with stimulants. Methylphenidate is considered effective in increasingwakefulness,vigilance, and performance.[53]Methylphenidate improves measures ofsomnolenceonstandardized tests,such as theMultiple Sleep Latency Test(MSLT), but performance does not improve to levels comparable to healthy people.[54]
Other medical uses
[edit]Methylphenidate may also be prescribed foroff-label useintreatment-resistant casesofbipolar disorderandmajor depressive disorder.[55]It can also improve depression in several groups, includingstroke,cancer,andHIV-positivepatients.[56]There is weak evidence in favor of methylphenidate's effectiveness for depression,[57]including providing additional benefit in combination withantidepressants.[58]In individuals withterminal cancer,methylphenidate can be used to counteractopioid-inducedsomnolence,to increase theanalgesiceffects of opioids, to treat depression, and to improve cognitive function.[59]A 2021 systematic review and meta-analysis found that all studies on geriatric depression reported positive results of methylphenidate use; the review recommended short-term use in combination withcitalopram.[60]A 2018 review found low-quality evidence supporting its use to treat apathy as seen inAlzheimer's disease,in addition to slight benefits for cognition and cognitive performance.[61]
Enhancing performance
[edit]Methylphenidate's efficacy as anathletic performance enhancer,cognitive enhancer,aphrodisiac,andeuphoriantis supported by research.[62][63][64][65][66][67][68][69][70]However, the manner in which methylphenidate is used for these purposes (high dosages, alternate routes of administration, during sleep deprivation, etc.) can result in severe unintended side effects.[71][72][70] A 2015 review found that therapeutic doses ofamphetamineand methylphenidate result in modest improvements incognition,includingworking memory,episodic memory,andinhibitory control,in normal healthy adults;[73][a][74][b] the cognition-enhancing effects of these drugs are known to occur through theindirect activationof bothdopamine receptor D1andadrenoceptor α2in theprefrontal cortex.[73]Methylphenidate and other ADHD stimulants also improve tasksaliencyand increase arousal.[75][76]Stimulants such as amphetamine and methylphenidate can improve performance on difficult and boring tasks,[75][c][76][77]and are used by some students as a study and test-taking aid.[48][78]Based upon studies of self-reported illicit stimulant use, performance-enhancing use rather than use as arecreational drug,is the primary reason that students use stimulants.[79]
Excessive doses of methylphenidate, above the therapeutic range, can interfere with working memory andcognitive control.[75][76]Like amphetamine andbupropion,methylphenidate increases stamina andendurancein humans primarily throughreuptake inhibitionof dopamine in the central nervous system.[80]Similar to the loss of cognitive enhancement when using large amounts, large doses of methylphenidate can induceside effectsthat impair athletic performance, such asrhabdomyolysisandhyperthermia.[13]While literature suggests it might improve cognition, most authors agree that using the drug as a study aid when an ADHD diagnosis is not present does not actually improveGPA.[48]Moreover, it has been suggested that students who use the drug for studying may be self-medicating for potentially deeper underlying issues.[48]
Contraindications
[edit]Methylphenidate iscontraindicatedfor individuals with agitation,tics,glaucoma,heart defectsor ahypersensitivityto any ingredients contained in methylphenidate pharmaceuticals.[13]
Pregnant women are advised to only use the medication if the benefits outweigh the potential risks.[81]Not enough human studies have been conducted to conclusively demonstrate an effect of methylphenidate onfetal development.[82]In 2018, a review concluded that it has not beenteratogenicin rats and rabbits, and that it "is not a major human teratogen".[83]
Adverse effects
[edit]
The most common side effects associated with methylphenidate (in standard and extended-release formulations) areappetite loss,dry mouth,anxiety/nervousness,nausea,andinsomnia.[85]Gastrointestinaladverse effects may includeabdominal painandweight loss.Nervous systemadverse effects may includeakathisia(agitation/restlessness),irritability,dyskinesia(tics),lethargy(drowsiness/fatigue), anddizziness.Cardiacadverse effects may includepalpitations,changes inblood pressure,andheart rate(typically mild), andtachycardia(rapid heart rate).[86]Ophthalmologicadverse effects may includeblurred visioncaused by pupil dilatation and dry eyes, with less frequent reports ofdiplopiaandmydriasis.[contradictory][87][88]
Results from a 2024 systematic review showed that methylphenidate significantly improves ADHD symptoms and broadband measures but can cause appetite suppression and other adverse events in children and adolescents.[89]Smokers with ADHD who take methylphenidate may increase theirnicotinedependence, and smoke more often than before they began using methylphenidate, with increased nicotine cravings and an average increase of 1.3cigarettesper day.[90]
There is some evidence of mild reductions in height with prolonged treatment in children.[91]This has been estimated at 1 centimetre (0.4 in) or less per year during the first three years with a total decrease of 3 centimetres (1.2 in) over 10 years.[92][93]
Hypersensitivity(includingskin rash,urticaria,andfever) is sometimes reported when using transdermal methylphenidate. TheDaytranapatch has a much higher rate of skin reactions than oral methylphenidate.[94]
Methylphenidate can worsenpsychosisin people who are psychotic, and in very rare cases it has been associated with the emergence of new psychotic symptoms.[95]It should be used with extreme caution in people withbipolar disorderdue to the potential induction ofmaniaorhypomania.[96]There have been very rare reports ofsuicidal ideation,but some authors claim that evidence does not support a link.[91]Logorrheais occasionally reported and visualhallucinationsare very rarely reported.[87]Priapismis a very rare adverse event that can be potentially serious.[97]
U.S. Food and Drug Administration-commissioned studies in 2011 indicate that in children, young adults, and adults, there is no association between serious adversecardiovascular events(sudden death,heart attack,andstroke) and the medical use of methylphenidate or other ADHD stimulants.[98]
Because some adverse effects may only emerge during chronic use of methylphenidate, a constant watch for adverse effects is recommended.[99]
A 2018Cochrane reviewfound that methylphenidate might be associated with serious side effects such as heart problems, psychosis, and death. The certainty of the evidence was stated as very low.[100]
The same review found tentative evidence that it may cause both serious and non-serious adverse effects in children.[100][d]
Overdose
[edit]The symptoms of a moderate acute overdose on methylphenidate primarily arise fromcentral nervous systemoverstimulation; these symptoms include:vomiting,nausea,agitation,tremors,hyperreflexia,muscle twitching,euphoria,confusion, hallucinations,delirium,hyperthermia,sweating,flushing,headache,tachycardia,heart palpitations,cardiac arrhythmias,hypertension,mydriasis,and dryness ofmucous membranes.[13][101]A severe overdose may involve symptoms such ashyperpyrexia,sympathomimetic toxidrome,convulsions,paranoia,stereotypy(a repetitive movement disorder),rhabdomyolysis,coma,andcirculatory collapse.[13][101][102][e] A methylphenidate overdose is rarely fatal with appropriate care.[102]Following injection of methylphenidate tablets into anartery,severe toxic reactions involvingabscessformation andnecrosishave been reported.[103]
Treatment of a methylphenidate overdose typically involves the administration ofbenzodiazepines,withantipsychotics,α-adrenoceptoragonists andpropofolserving as second-line therapies.[102]

Addiction and dependence
[edit]Methylphenidate is a stimulant with an addiction liability and dependence liability similar toamphetamine.It has moderate liability amongaddictive drugs;[104][105]accordingly,addictionandpsychological dependenceare possible and likely when methylphenidate is used at high doses as a recreational drug.[105]When used above the medical dose range, stimulants are associated with the development ofstimulant psychosis.[106]
Biomolecular mechanisms
[edit]Methylphenidate has the potential to induceeuphoriadue to itspharmacodynamiceffect (i.e.,dopamine reuptake inhibition) in the brain'sreward system.At therapeutic doses, ADHD stimulants do not sufficiently activate the reward system; consequently, when taken as directed in doses that are commonly prescribed for the treatment of ADHD, methylphenidate use lacks the capacity to cause anaddiction.[105]
Interactions
[edit]Methylphenidate may inhibit the metabolism ofvitamin K anticoagulants,certainanticonvulsants,and some antidepressants (tricyclic antidepressants,andselective serotonin reuptake inhibitors).Concomitant administrationmay require dose adjustments, possibly assisted by monitoring ofplasmadrug concentrations.[12]There are several case reports of methylphenidate inducingserotonin syndromewith concomitant administration of antidepressants.[107][108][109][110]
When methylphenidate is coingested withethanol,a metabolite calledethylphenidateis formed viahepatictransesterification,[111][112]not unlike the hepatic formation ofcocaethylenefromcocaineand ethanol. The reduced potency of ethylphenidate and its minor formation means it does not contribute to the pharmacological profile at therapeutic doses and even in overdose cases ethylphenidate concentrations remain negligible.[113][112]
Coingestion ofalcoholalso increases the blood plasma levels of d-methylphenidate by up to 40%.[114]
Liver toxicityfrom methylphenidate is extremely rare, but limited evidence suggests that intake ofβ-adrenergic agonistswith methylphenidate may increase the risk of liver toxicity.[115]
Pharmacology
[edit]Pharmacodynamics
[edit]| Neurotransmitter transporter |
Measure (units) |
dl-MPH | d-MPH | l-MPH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAT | Ki(nM) | 121 | 161 | 2250 |
| IC50(nM) | 20 | 23 | 1600 | |
| NET | Ki(nM) | 788 | 206 | >10000 |
| IC50(nM) | 51 | 39 | 980 | |
| SERT | Ki(nM) | >10000 | >10000 | >6700 |
| IC50(nM) | — | >10000 | >10000 | |
| GPCR | Measure (units) |
dl-MPH | d-MPH | l-MPH |
| 5-HT1A | Ki(nM) | 5000 | 3400 | >10000 |
| IC50(nM) | 10000 | 6800 | >10000 | |
| 5-HT2B | Ki(nM) | >10000 | 4700 | >10000 |
| IC50(nM) | >10000 | 4900 | >10000 |
Methylphenidate acts primarily as a strongnorepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor(NDRI). It is abenzylpiperidineandphenethylaminederivativewhich also shares part of its basic structure withcatecholamines.
Methylphenidate is apsychostimulantand increases the activity of thecentral nervous systemthrough inhibition on reuptake of the neurotransmittersnorepinephrineanddopamine.As models of ADHD suggest, it is associated with functional impairments in some of the brain'sneurotransmitter systems,particularly those involving dopamine in themesocorticalandmesolimbicpathways and norepinephrine in theprefrontal cortexandlocus coeruleus.[119]Psychostimulants like methylphenidate and amphetamine may be effective in treating ADHD because they increase neurotransmitter activity in these systems. When reuptake of those neurotransmitters is halted, its concentration and effects in thesynapseincrease and last longer, respectively. Therefore, methylphenidate is called a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor.[113]By increasing the effects of norepinephrine and dopamine, methylphenidate increases the activity of the central nervous system and produces effects such as increased alertness, reducedfatigue,and improved attention.[119][120]
Methylphenidate is most active at modulating levels of dopamine (DA) and to a lesser extent norepinephrine (NE).[121]Methylphenidate binds to and blocksdopamine transporters(DAT) andnorepinephrine transporters(NET).[122]Variability exists between DAT blockade, and extracellular dopamine, leading to the hypothesis that methylphenidate amplifiesbasaldopamine activity, leading to nonresponse in those with low basal DA activity.[123]On average, methylphenidate elicits a 3–4 times increase in dopamine and norepinephrine in thestriatumandprefrontal cortex.[2]Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) studies suggest that long-term treatment with ADHD stimulants (specifically,amphetamineand methylphenidate) decreases abnormalities inbrainstructure and function found in subjects with ADHD.[124][125][126][f]
Bothamphetamineand methylphenidate are predominantlydopaminergicdrugs, yet theirmechanisms of actionare distinct. Methylphenidate acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, while amphetamine is both areleasing agentandreuptake inhibitorof dopamine and norepinephrine. Methylphenidate's mechanism of action in the release of dopamine and norepinephrine is fundamentally different from most otherphenethylamine derivatives,as methylphenidate is thought to increase neuronalfiring rate,[127][128][129]whereasamphetaminereduces firing rate, but causesmonoaminerelease by reversing the flow of the monoamines throughmonoamine transportersvia a diverse set of mechanisms, includingTAAR1activation and modulation ofVMAT2function, among other mechanisms.[130][131][g][132][h] The difference in mechanism of action between methylphenidate and amphetamine results in methylphenidate inhibiting amphetamine's effects on monoamine transporters when they are co-administered.[130][better source needed]
Methylphenidate has bothdopamine transporterandnorepinephrine transporterbinding affinity,with thedextromethylphenidateenantiomersdisplaying a prominent affinity for thenorepinephrine transporter.[133]Both thedextrorotaryandlevorotaryenantiomers displayedreceptor affinityfor theserotonergic5HT1Aand5HT2Bsubtypes, though direct binding to theserotonin transporterwas not observed.[118]A later study confirmed the d-threo-methylphenidate (dexmethylphenidate) binding to the 5HT1Areceptor, but no significant activity on the 5HT2Breceptor was found.[134]
There exist some paradoxical findings that oppose the notion that methylphenidate acts as silent antagonist of the DAT (DAT inhibitor).[135]80% occupancy of the DAT is necessary for methylphenidate's euphoriant effect, but re-administration of methylphenidate beyond this level of DAT occupancy has been found to produce similarly potent euphoriant effects (despite DAT occupancy being unchanged with repeated administration).[135]By contrast, other DAT inhibitors such asbupropionhave not been observed to exhibit this effect.[136]These observations have prompted the hypothesis that methylphenidate may act as a "DAT inverse agonist" or "negative allosteric modifier of the DAT" by reversing the direction of the dopamine efflux by the DAT at higher dosages.[137]
Methylphenidate mayprotect neuronsfrom the neurotoxic effects ofParkinson's diseaseandmethamphetamineuse disorder.[138]The hypothesized mechanism of neuroprotection is through inhibition of methamphetamine–DAT interactions, and through reducing cytosolic dopamine, leading to decreased production of dopamine-relatedreactive oxygen species.[138]
The dextrorotary enantiomers are significantly more potent than the levorotary enantiomers, and some medications therefore only contain dexmethylphenidate.[121]The studied maximized daily dosage of OROS methylphenidate appears to be 144 mg/day.[139]
Pharmacokinetics
[edit]Methylphenidate taken by mouth has abioavailabilityof 11–52% with a duration of action around 2–4 hours for instant-release (i.e. Ritalin), 3–8 hours forsustained-release(i.e. Ritalin SR), and 8–12 hours for extended-release (i.e. Concerta). Thehalf-lifeof methylphenidate is 2–3 hours, depending on the individual. The peak plasma time is achieved at about 2 hours.[14]Methylphenidate has a low plasma protein binding of 10–33% and a volume of distribution of 2.65 L/kg.[11]
Dextromethylphenidate is much more bioavailable than levomethylphenidate when administered orally, and is primarily responsible for the psychoactivity ofracemicmethylphenidate.[14]
The oralbioavailabilityand speed of absorption for immediate-release methylphenidate is increased when administered with a meal.[140]The effects of a high fat meal on the observedCmaxdiffer between someextended-releaseformulations, with combined IR/ER andOROSformulations showing reduced Cmaxlevels[141]while liquid-basedextended-releaseformulations showed increased Cmaxlevels when administered with a high-fat meal, according to some researchers.[142]A 2003 study, however, showed no difference between a high-fat meal administration and a fasting administration of oral methylphenidate.[143]
Methylphenidate ismetabolizedintoritalinic acidbyCES1A1enzymes in the liver. Dextromethylphenidate is selectively metabolized at a slower rate than levomethylphenidate.[144]97% of the metabolised drug is excreted in the urine, and between 1 and 3% is excreted in the faeces. A small amount, less than 1%, of the drug is excreted in the urine in its unchanged form.[11]
Chemistry
[edit]Despite the claim made by some urban legends, it is not acocainederivative nor analog, however both compounds contain a methyl piperidinylcarboxylate moiety with 2-carbondistance betweennitrogenandmethanoate,methylphenidate containing methyl (piperidin-2-yl)-ethanoate and cocaine containing methyl (piperidin-3-yl)-methanoate. Cocaine is alocal anestheticand ligand channel blocker withSNDRIaction, while methylphenidate is anNDRIwith 2–3 fold selectivity for thedopamine transporter(DAT) over thenorepinephrine transporter(NET). Cocaine is also more potent inserotonin transporters(SERTs) than NDRI sites.[145][146]
Fourisomersof methylphenidate are possible, since the molecule has twochiral centers.One pair ofthreoisomers and one pair oferythroare distinguished, from which primarilyd-threo-methylphenidateexhibits the pharmacologically desired effects.[121][147]The erythrodiastereomersarepressoramines, a property not shared with the threo diastereomers. When the drug was first introduced it was sold as a 4:1 mixture of erythro:threo diastereomers, but it was later reformulated to contain only the threo diastereomers. "TMP" refers to a threo product that does not contain any erythro diastereomers, i.e. (±)-threo-methylphenidate. Since the threo isomers are energetically favored, it is easy toepimerizeout any of the undesired erythro isomers. The drug that contains onlydextrorotatorymethylphenidate is sometimes called d-TMP, although this name is only rarely used and it is much more commonly referred to asdexmethylphenidate,d-MPH, or d-threo-methylphenidate. A review on the synthesis ofenantiomerically pure(2R,2'R)-(+)-threo-methylphenidate hydrochloride has been published.[148]
Detection in biological fluids
[edit]The concentration of methylphenidate orritalinic acid,its majormetabolite,may be quantified in plasma, serum or whole blood in order to monitor compliance in those receiving the drug therapeutically, to confirm the diagnosis in potential poisoning victims or to assist in the forensic investigation in a case of fatal overdosage.[151]
History
[edit]Methylphenidate was firstsynthesizedin 1944 and was approved for medical use in the United States in 1955.[152][153][154]It was synthesized by chemist Leandro Panizzon and sold by Swiss companyCIBA(nowNovartis).[152]He named the drug after his wife Margarita, nicknamed Rita, who used Ritalin to compensate for low blood pressure.[155]Methylphenidate was not reported to be a stimulant until 1954.[156][157]The drug was introduced for medical use in the United States in 1957.[158]Originally, it was marketed as amixtureof tworacemates,80% (±)-erythro and 20% (±)-threo, under the brand name Centedrin.[156]Subsequent studies of the racemates showed that the central stimulant activity is associated with the threo racemate and were focused on the separation and interconversion of the erythro isomer into the more active threo isomer.[156][159][160][161]The erythro isomer was eliminated, and now modern formulations of methyphenidate contain only the threo isomer in a 50:50 mixture ofd- andl-isomers.[156]
Methylphenidate was first used to allaybarbiturate-induced coma, narcolepsy and depression.[162]It was later used to treat memory deficits in the elderly.[163]Beginning in the 1960s, it was used to treat children with ADHD based on earlier work, starting with the studies by American psychiatristCharles Bradley[164]on the use of psychostimulant drugs, such asBenzedrine,with then called "maladjusted children".[165]Production and prescription of methylphenidate rose significantly in the 1990s, especially in the United States, as the ADHD diagnosis came to be better understood and more generally accepted within the medical and mental health communities.[166]
In 2000,Alza Corporationreceived US FDA approval to market Concerta, an extended-release form of methylphenidate.[12][167][168]
It was estimated that the number of doses of methylphenidate used globally in 2013 increased by 66% compared to 2012.[169]In 2022, it was the 32nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 17million prescriptions.[32]It is available as ageneric medication.[4]
Society and culture
[edit]Names
[edit]-
Swiss "Ritalin" brand methylphenidate
-
Indian "AddWize" branded instant-release and extended-release formulations costing US$1.9 for a strip of instant-release and US$2.9 for a strip of AddWize extended-release
-
Clockwise from top: Concerta 18 mg, Medikinet 5 mg, Methylphenidat TAD 10 mg, Ritalin 10 mg, Medikinet XL 40 mg
Methylphenidate is sold in the majority of countries worldwide.[170]: 8–9 Brand names for methylphenidate include Ritalin (in honor of Rita, the wife of the molecule discoverer), Rilatine (in Belgium to avoid a conflict of commercial name with the RIT pharmaceutical company), Concerta,[12]Medikinet, Adaphen, Addwize, Inspiral, Methmild, Artige, Attenta, Cognil, Konsenidat, Equasym, Foquest,[171]Methylin, Penid, Phenida, Prohiper, and Tradea.[170]: 8–9
Available forms
[edit]The dextrorotary enantiomer of methylphenidate, known as dexmethylphenidate, is sold as a generic and under the brand names Focalin and Attenade in both an immediate-release and an extended-release form. There is some evidence that dexmethylphenidate has better bioavailability and a longer duration of action than methylphenidate.[133]
Immediate-release
[edit]-
Structural formulafor the substance among Ritalin tablet series. (Ritalin, Ritalin LA, Ritalin SR.) The volume of distribution was 2.65±1.11 L/kg for d-methylphenidate and 1.80±0.91 L/kg for l-methylphenidate subsequent to swallow of Ritalin tablet.[10]
-
Structural formula for the substance inside Concerta tablet. Following administration of Concerta, plasma concentrations of the l-isomer were approximately1/40the plasma concentrations of the d-isomer.[12]Note that the substance is the same as for Concerta - the differences lies in other aspects of the individual pills.
Methylphenidate was originally available as an immediate-release racemic mixture formulation under the Novartis brand name Ritalin, although a variety of generics are available, some under other brand names. Generic brand names include Ritalina, Rilatine, Attenta, Medikinet, Metadate, Methylin, Penid, Tranquilyn, and Rubifen.[citation needed]
Extended-release
[edit]Extended-releasemethylphenidate products include:
| Brand name(s) | Generic name(s)[172][173][174][175] | Duration | Dosage form |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aptensio XR (US); Biphentin (CA) |
Currently unavailable | 12 hours[176][177] | XR capsule |
| Concerta (US/CA/AU); Concerta XL (UK) |
methylphenidate ER (US/CA);[i] methylphenidate ER‑C (CA)[ii] |
12 hours[178] | OROS tablet |
| Quillivant XR (US) | Currently unavailable | 12 hours[178] | oral suspension |
| Daytrana (US) | methylphenidate film, extended release;transdermal (US)[iii] | 11 hours[179] | transdermal patch |
| Metadate CD (US); Equasym XL (UK) |
methylphenidate ER (US)[iv] | 8–10 hours[178] | CD/XL capsule |
| QuilliChew ER (US) | Currently unavailable | 8 hours[180] | chewable tablet |
| Jornay PM (US) | Currently unavailable | 6 hours (following 10 hour delay)[181] | DR/ER capsule |
| Ritalin LA (US/AU); Medikinet XL (UK) |
methylphenidate ER (US)[v] | 8 hours[178] | ER capsule |
| Ritalin SR (US/CA/UK); Rubifen SR (NZ) |
Metadate ER (US);[vi] Methylin ER (US);[vii] methylphenidate SR (US/CA)[viii] |
5–8 hours[178] | CR tablet |
| |||
Concerta tablets are marked with the letters "ALZA" and followed by: "18", "27", "36", or "54", relating to the dosage strength in milligrams. Approximately 22% of the dose is immediate-release,[182]and the remaining 78% of the dose is released over 10–12 hours post-ingestion, with an initial increase over the first 6–7 hours, and subsequent decline in the released drug.[183]
Ritalin LA capsules are marked with the letters "NVR" (abbrev.: Novartis) and followed by: "R20", "R30", or "R40", depending on the (mg) dosage strength. Ritalin LA[86]provides two standard doses – half the total dose being released immediately and the other half released four hours later. In total, each capsule is effective for about eight hours.
Metadate CD capsules contain two types of beads: 30% are immediate-release, and the other 70% are evenly sustained release.[184]
Medikinet Retard/CR/Adult/Modified Release tablets are an extended-release oral capsule form of methylphenidate. It delivers 50% of the dosage as IR MPH and the remaining 50% in 3–4 hours.[185][186]
Jornay PM is a delayed release formulation that is taken at bedtime. An outer polymer coating delays the initial release of the drug until 8 hours after administration, after which an inner coating regulates the rate of drug absorption. Peak plasma concentration occurs 14 hours following administration.[181]This formulation was motivated by the need for a pediatric ADHD medication that is active immediately after morning waking, as most long-acting formulations exhibit a delay between administration and absorption that leads to inadequate therapeutic effect in the early morning.[187]
Skin patch
[edit]A methylphenidateskin patchis sold under the brand name Daytrana in the United States. It was developed and marketed by Noven Pharmaceuticals and approved in the US in 2006.[13]It is also referred to as methylphenidatetransdermalsystem (MTS). It is approved as a once-daily treatment in children with ADHD aged 6–17 years. It is mainly prescribed as a second-line treatment when oral forms are not well tolerated, or if people have difficulty with compliance. Noven's original FDA submission indicated that it should be used for 12 hours. When the FDA rejected the submission, they requested evidence that a shorter time period was safe and effective; Noven provided such evidence, and it was approved for a 9-hour period.[188]
Orally administered methylphenidate is subject tofirst-pass metabolism,by which the levo-isomeris extensively metabolized. By circumventing this first-pass metabolism, the relative concentrations of ℓ-threo-methylphenidate are much higher with transdermal administration (50–60% of those ofdexmethylphenidateinstead of about 14–27%).[189]
A 39 nanograms/mL peak serum concentration of methylphenidate has been found to occur between 7.5–10.5 hours after administration.[13]However, the onset to peak effect is 2 hours, and the clinical effects remain up to 2 hours after the patch has been removed. The absorption is increased when the transdermal patch is applied onto inflamed skin or skin that has been exposed to heat. The absorption lasts for approximately 9 hours after application (onto normal, unexposed to heat and uninflamed skin). 90% of the medication is excreted in the urine as metabolites and unchanged drug.[13]
Parenteral formulation
[edit]When it was released in the United States, methylphenidate was available from CIBA in a parenteral form for use by medical professionals. It came in 10mL multiple-dose vials containing 100 mg methylphenidate HCl and 100 mg lactose in lyophilized (freeze-dried) form. It was also available as single-dose ampoules containing 20 mg methylphenidate HCl. Instructions were to reconstitute with 10mL sterile solvent (water). The indication was 10 to 20 mg (1.0mL from MDV's, up to one full single-use ampoule) to produce a focused, talkative state that could help certain patients breakdown the resistance to therapy. Parenteral methylphenidate was discontinued out of a concern for the actual benefit and of inducing a psychic dependence. This is not truth serum in the normal sense, as it does not impair the ability to control the flow of information like a barbiturate agent (Pentothal) or similar might.[citation needed]
Cost
[edit]
Brand-name andgenericformulations are available.[4]
Legal status
[edit]
Internationally, methylphenidate is a Schedule II drug under theConvention on Psychotropic Substances.[190]
Legal
|
Controlled Substance
|
Illegal
|
| Country/Territory | Status | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Schedule 8" controlled substance. Such drugs must be kept in a lockable safe until dispensed and possession without prescription is punishable by fines and imprisonment. | [191] | ||
| Schedule III of theControlled Drugs and Substances Actand is illegal to possess without a prescription, with unlawful possession punishable by up to three years imprisonment, or (viasummary conviction) by up to one year imprisonment and/or fines of up to two thousand dollars. Unlawful possession for the purpose of trafficking is punishable by up to ten years imprisonment, or (via summary conviction) by up to eighteen months imprisonment. | [192] | ||
| Schedule 1 Illicit Drug under the Illicit Drugs Control Act 2004 | [193] | ||
| Covered by the "narcotics" schedule, prescription and distribution conditions are restricted, with hospital or city specialist-only (pediatrician for children, psychiatrist or neurologist for adults) prescription for the initial treatment and yearly consultations.[194] | |||
| Controlled under the schedule 1 of the Dangerous Drugs Ordinance (cap. 134). | [195] | ||
| Methylphenidate is aschedule Xdrug and is controlled by theDrugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945.It is dispensed only by physician's prescription. Legally, 2 grams of methylphenidate is classified as a small quantity, and 50 grams as a large or commercial quantity. | [196][197] | ||
| In New Zealand, methylphenidate is a "class B2 controlled substance". Unlawful possession is punishable by six-month prison sentence and distribution by a 14-year sentence. | |||
| List I controlled psychotropic substance without recognized medical value. The Constant Committee for Drug Control of the Russian Ministry of Health has put methylphenidate and its derivatives on the National List of Narcotics, Psychotropic Substances and Their Precursors, and the Government banned methylphenidate for any use on 25 October 2014. | [198] | ||
| List II controlled substance with recognized medical value. Possession without a prescription is punishable by up to three years in prison. | [199] | ||
| Controlled "Class B" substance. Possession without prescription carries a sentence up to 5 years or an unlimited fine, or both; supplying methylphenidate is 14 years or an unlimited fine, or both. | [200] | ||
| Classified as aSchedule IIcontrolled substance,the designation used for substances that have a recognized medical value but present a high potential for misuse. | [201] |
Controversy
[edit]Methylphenidate has been the subject of controversy in relation to its use in the treatment of ADHD. The prescription of psychostimulant medication to children to reduce ADHD symptoms has been a major point of criticism.[202][need quotation to verify]The contention that methylphenidate acts as agateway drughas been discredited by multiple sources,[203]according to which abuse is statistically very low and "stimulant therapy in childhood does not increase the risk for subsequent drug and alcohol abuse disorders later in life".[204]A study found that ADHD medication was not associated with an increased risk of cigarette use, and in fact, stimulant treatments such as Ritalin seemed to lower this risk.[205]People treated with stimulants such as methylphenidate during childhood were less likely to havesubstance use disordersin adulthood.[206]
Among countries with the highest rates of use of methylphenidate medication is Iceland,[207]where research shows that the drug was the most commonly used substance amongpeople who inject drugs.[208]The study involved 108 people who inject drugs and 88% of them had injected methylphenidate within the last 30 days and for 63% of them, methylphenidate was the most preferred substance.
Treatment of ADHD by way of methylphenidate has led to legal actions, includingmalpracticesuits regardinginformed consent,inadequate information on side effects, misdiagnosis, and coercive use of medications byschool systems.[209]
Research
[edit]Apathy
[edit]Methylphenidate may be effective as a treatment forapathyinAlzheimer's diseaseand other conditions.[210][211][212][213]It may also be useful in the treatment of more severedisorders of diminished motivation,likeabuliaandakinetic mutism.[213][214]
Addiction
[edit]Methylphenidate has shown some benefits as areplacement therapyfor individuals who areaddictedto anddependentuponmethamphetamine.[215]Methylphenidate andamphetaminehave been investigated as a chemical replacement for the treatment ofcocaine addiction.[216][217]Its effectiveness in treatment of cocaine or psychostimulant addiction or psychological dependence has not been proven.[218]
Social anxiety
[edit]Methylphenidate has been reported to be effective in the treatment ofsocial anxiety disorderin people who arecomorbidfor both this condition andattention deficit hyperactivity disorder(ADHD) in small preliminaryclinical studiesandcase reports.[219][220][221][222][223][224]
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ The procognitive actions of psychostimulants are only associated with low doses... cognition-enhancing effects of psychostimulants involve the preferential elevation of catecholamines in the PFC and the subsequent activation of norepinephrine α2 and dopamine D1 receptors.... This differential modulation of PFC-dependent processes across dose appears to be associated with the differential involvement of noradrenergic α2 versus α1 receptors.[73]
- ^ The results of this meta-analysis... do confirm the reality of cognitive enhancing effects for normal healthy adults in general, while also indicating that these effects are modest in size.[74]
- ^ Therapeutic (relatively low) doses of psychostimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamine, improve performance on working memory tasks both in normal subjects and those with ADHD... [It] is now believed that dopamine and norepinephrine, but not serotonin, produce the beneficial effects of stimulants on working memory. At abused (relatively high) doses, stimulants can interfere with working memory and cognitive control... stimulants act not only on working memory function, but also on general levels of arousal and, within the nucleus accumbens, improve the saliency of tasks. Thus, stimulants improve performance on effortful but tedious tasks... through indirect stimulation of dopamine and norepinephrine receptors.[75]
- ^ "Our findings suggest that methylphenidate may be associated with a number of serious adverse events as well as a large number of non-serious adverse events in children" "Concerning adverse events associated with the treatment, our systematic review of randomised clinical trials (RCTs) demonstrated no increase in serious adverse events, but a high proportion of participants suffered a range of non-serious adverse events."[100]
- ^ The management of amphetamine, dextroamphetamine, and methylphenidate overdose is largely supportive, with a focus on interruption of the sympathomimetic syndrome with judicious use of benzodiazepines. In cases where agitation, delirium, and movement disorders are unresponsive to benzodiazepines, second-line therapies include antipsychotics such as ziprasidone or haloperidol, central Alpha -adrenoreceptor agonists such as dexmedetomidine, or propofol.... However, fatalities are rare with appropriate care.[102]
- ^ Basal ganglia regions like the right globus pallidus, the right putamen, and the nucleus caudatus are structurally affected in children with ADHD. These changes and alterations in limbic regions like ACC and amygdala are more pronounced in non-treated populations and seem to diminish over time from child to adulthood. Treatment seems to have positive effects on brain structure.[126]
- ^ VMAT2 is the CNS vesicular transporter for not only the biogenic amines DA, NE, EPI, 5-HT, and HIS, but likely also for the trace amines TYR, PEA, and thyronamine (THYR)... AMPH release of DA from synapses requires both an action at VMAT2 to release DA to the cytoplasm and a concerted release of DA from the cytoplasm via "reverse transport" through DAT.[131]
- ^ Despite the challenges in determining synaptic vesicle pH, the proton gradient across the vesicle membrane is of fundamental importance for its function. Exposure of isolated catecholamine vesicles to protonophores collapses the pH gradient and rapidly redistributes transmitter from inside to outside the vesicle.... Amphetamine and its derivatives like methamphetamine are weak base compounds that are the only widely used class of drugs known to elicit transmitter release by a non-exocytic mechanism. As substrates for both DAT and VMAT, amphetamines can be taken up to the cytosol and then sequestered in vesicles, where they act to collapse the vesicular pH gradient.[132]
References
[edit]- ^Concerta, "Consumer Medicine Information".New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority.Retrieved17 September2024.
{{cite web}}:Check|url=value (help) - ^abHodgkins P, Shaw M, Coghill D, Hechtman L (September 2012)."Amfetamine and methylphenidate medications for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: complementary treatment options".European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.21(9): 477–492.doi:10.1007/s00787-012-0286-5.PMC3432777.PMID22763750.
- ^Stahl SM (April 2024). "Methylphenidate (D,L)".Prescriber's Guide: Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology(8th ed.). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. pp. 503–510.ISBN9781108228749.
- ^abcde"Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals".Drugs.AHFS.Archivedfrom the original on 19 December 2018.Retrieved19 December2018.
- ^"FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)".nctr-crs.fda.gov.FDA.Retrieved22 October2023.
- ^Anvisa(31 March 2023)."RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial"[Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese).Diário Oficial da União(published 4 April 2023).Archivedfrom the original on 3 August 2023.Retrieved3 August2023.
- ^"Ritalin Product information".Health Canada.25 April 2012.Archivedfrom the original on 11 June 2022.Retrieved11 June2022.
- ^"Controlled Drugs and Substances Act".Justice Laws Website.31 March 2022.Archivedfrom the original on 21 August 2021.Retrieved11 June2022.
- ^"Mental health".Health Canada.9 May 2018.Retrieved13 April2024.
- ^abc"Ritalin- methylphenidate hydrochloride tablet".DailyMed.26 June 2021.Archivedfrom the original on 20 March 2017.Retrieved26 March2022.
- ^abc"Ritalin LA- methylphenidate hydrochloride capsule, extended release".DailyMed.26 June 2021.Archivedfrom the original on 26 March 2017.Retrieved26 March2022.
- ^abcde"Concerta- methylphenidate hydrochloride tablet, extended release".DailyMed.1 July 2021.Archivedfrom the original on 26 March 2017.Retrieved26 March2022.
- ^abcdefgh"Daytrana- methylphenidate patch".DailyMed.15 June 2021.Archivedfrom the original on 19 March 2022.Retrieved26 March2022.
- ^abcKimko HC, Cross JT, Abernethy DR (December 1999). "Pharmacokinetics and clinical effectiveness of methylphenidate".Clinical Pharmacokinetics.37(6): 457–470.doi:10.2165/00003088-199937060-00002.PMID10628897.S2CID397390.
- ^ab"Methylphenidate".Pubchem.Archivedfrom the original on 6 January 2014.Retrieved4 September2017.
- ^"Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Treatment".National Health Service (NHS).24 December 2021.Retrieved18 October2022.
- ^Bushe C, Day K, Reed V, Karlsdotter K, Berggren L, Pitcher A, et al. (May 2016). "A network meta-analysis of atomoxetine and osmotic release oral system methylphenidate in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adult patients".Journal of Psychopharmacology.30(5): 444–458.doi:10.1177/0269881116636105.PMID27005307.S2CID104938.
- ^Hazell PL, Kohn MR, Dickson R, Walton RJ, Granger RE, Wyk GW (November 2011). "Core ADHD symptom improvement with atomoxetine versus methylphenidate: a direct comparison meta-analysis".Journal of Attention Disorders.15(8): 674–683.doi:10.1177/1087054710379737.PMID20837981.S2CID43503227.
- ^Hanwella R, Senanayake M, de Silva V (November 2011)."Comparative efficacy and acceptability of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis".BMC Psychiatry.11(1): 176.doi:10.1186/1471-244X-11-176.PMC3229459.PMID22074258.
- ^Rezaei G, Hosseini SA, Akbari Sari A, Olyaeemanesh A, Lotfi MH, Yassini M, et al. (10 February 2016)."Comparative efficacy of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis".Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.30:325.PMC4898838.PMID27390695.
- ^Stuhec M, Lukić P, Locatelli I (February 2019). "Efficacy, Acceptability, and Tolerability of Lisdexamfetamine, Mixed Amphetamine Salts, Methylphenidate, and Modafinil in the Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis".The Annals of Pharmacotherapy.53(2): 121–133.doi:10.1177/1060028018795703.PMID30117329.S2CID52019992.
- ^Faraone SV, Pliszka SR, Olvera RL, Skolnik R, Biederman J (June 2001). "Efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a reanalysis using drug-placebo and drug-drug response curve methodology".Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology.11(2): 171–180.doi:10.1089/104454601750284081.PMID11436957.ProQuest204600452.
- ^Faraone SV, Biederman J, Roe C (October 2002). "Comparative efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis".Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.22(5): 468–473.doi:10.1097/00004714-200210000-00005.PMID12352269.S2CID19726926.
- ^Faraone SV, Buitelaar J (April 2010). "Comparing the efficacy of stimulants for ADHD in children and adolescents using meta-analysis".European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.19(4): 353–364.doi:10.1007/s00787-009-0054-3.PMID19763664.S2CID9447892.
- ^Isfandnia F, El Masri S, Radua J, Rubia K (July 2024)."The effects of chronic administration of stimulant and non-stimulant medications on executive functions in ADHD: A systematic review and meta-analysis".Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews.162:105703.doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105703.PMID38718988.
- ^Faraone SV, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Zheng Y, Biederman J, Bellgrove MA, et al. (September 2021)."The World Federation of ADHD International Consensus Statement: 208 Evidence-based conclusions about the disorder".Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews.128:789–818.doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.01.022.PMC8328933.PMID33549739.
- ^Kamradt JM, Ullsperger JM, Nikolas MA (2014). "Executive function assessment and adult attention-deficit/Hyperactivity disorder: Tasks versus ratings on the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale".Psychological Assessment.26(4): 1095–1105.doi:10.1037/pas0000006.PMID24885846.
- ^Arnsten AF, Li BM (June 2005). "Neurobiology of executive functions: catecholamine influences on prefrontal cortical functions".Biological Psychiatry.57(11): 1377–1384.doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.08.019.PMID15950011.S2CID22992765.
- ^Stahl SM (11 April 2013).Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical applications(4th ed.). Cambridge University Press.ISBN978-1-107-68646-5.
- ^"Methylphenidate Monograph for Professionals".Drugs.American Society of Health-System Pharmacists.Archivedfrom the original on 3 February 2019.Retrieved2 February2019.
- ^"The Top 300 of 2022".ClinCalc.Archivedfrom the original on 30 August 2024.Retrieved30 August2024.
- ^ab"Methylphenidate Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022".ClinCalc.Retrieved30 August2024.
- ^Tappy B."Every molecule tells a story: Ritalin - Chronique - Corpore Sano - InVivo".invivomagazine.Retrieved12 March2024.
- ^"Methylphenidate".DrugBank.Archived fromthe originalon 31 January 2019.Retrieved30 January2019.
- ^Fone KC, Nutt DJ (February 2005). "Stimulants: use and abuse in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder".Current Opinion in Pharmacology.5(1): 87–93.doi:10.1016/j.coph.2004.10.001.PMID15661631.
- ^Huss M, Duhan P, Gandhi P, Chen CW, Spannhuth C, Kumar V (2 June 2021)."Methylphenidate dose optimization for ADHD treatment: review of safety, efficacy, and clinical necessity".Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.13:1741–1751.doi:10.2147/NDT.S130444.PMC5505611.PMID28740389.
- ^Wolraich M, Brown L, Brown RT, DuPaul G, Earls M, Feldman HM, et al. (November 2011)."ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents".Pediatrics.128(5): 1007–1022.doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2654.PMC4500647.PMID22003063.
- ^Neinstein L (2009).Handbook of Adolescent Health Care.Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health / Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.ISBN978-0-7817-9020-8.OCLC226304727.: 722
- ^Vitiello B (October 2001). "Psychopharmacology for young children: clinical needs and research opportunities".Pediatrics.108(4): 983–989.doi:10.1542/peds.108.4.983.PMID11581454.S2CID33417584.
- ^Hermens DF, Rowe DL, Gordon E, Williams LM (May 2006). "Integrative neuroscience approach to predict ADHD stimulant response".Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics.6(5): 753–763.doi:10.1586/14737175.6.5.753.PMID16734523.S2CID15971025.
- ^abcFaraone SV, Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Zheng Y, Biederman J, Bellgrove MA, et al. (September 2021)."The World Federation of ADHD International Consensus Statement: 208 Evidence-based conclusions about the disorder".Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews.128:789–818.doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.01.022.PMC8328933.PMID33549739.
- ^"eEML - Electronic Essential Medicines List".list.essentialmeds.org.Archivedfrom the original on 26 March 2020.Retrieved26 March2020.
- ^"A.21 Methylphenidate – attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder – EML and EMLc".who.int.Retrieved1 May2024.
- ^"Mental Health Gap Action Programme (mhGAP) guideline for mental, neurological and substance use disorders".who.int.Retrieved1 May2024.
- ^https://applications.emro.who.int/docs/EMRPUB_leaflet_2019_mnh_214_en.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^Cortese S, Coghill D, Fegert JM, Mattingly GW, Rohde LA, Wong IC, et al. (May 2024). "ESCAP endorses the inclusion of methylphenidate in the WHO model lists of essential medicines and in the Union list of critical medicines".European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.33(5): 1605–1608.doi:10.1007/s00787-024-02443-5.PMID38662057.
- ^Cortese S, Coghill D, Mattingly GW, Rohde LA, Thom RP, Wilens TE, et al. (July 2024). "AACAP Endorses the Inclusion of Methylphenidate in the WHO Model Lists of Essential Medicines".Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.63(7): 663–665.doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2024.02.008.PMID38428579.
- ^abcdefAbelman DD (October 2017)."Mitigating risks of students use of study drugs through understanding motivations for use and applying harm reduction theory: a literature review".Harm Reduction Journal.14(1): 68.doi:10.1186/s12954-017-0194-6.PMC5639593.PMID28985738.
- ^Zhang L, Yao H, Li L, Du Rietz E, Andell P, Garcia-Argibay M, et al. (November 2022)."Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases Associated With Medications Used in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis".JAMA Network Open.5(11): e2243597.doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.43597.PMC9685490.PMID36416824.
- ^Liang EF, Lim SZ, Tam WW, Ho CS, Zhang MW, McIntyre RS, et al. (August 2018)."The Effect of Methylphenidate and Atomoxetine on Heart Rate and Systolic Blood Pressure in Young People and Adults with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression".International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.15(8): 1789.doi:10.3390/ijerph15081789.PMC6121294.PMID30127314.
- ^Liu H, Feng W, Zhang D (October 2019). "Association of ADHD medications with the risk of cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis".European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry.28(10): 1283–1293.doi:10.1007/s00787-018-1217-x.PMID30143889.
- ^Habel LA, Cooper WO, Sox CM, Chan KA, Fireman BH, Arbogast PG, et al. (December 2011)."ADHD medications and risk of serious cardiovascular events in young and middle-aged adults".JAMA.306(24): 2673–2683.doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1830.PMC3350308.PMID22161946.
- ^Fry JM (February 1998). "Treatment modalities for narcolepsy".Neurology.50(2 Suppl 1): S43–S48.doi:10.1212/WNL.50.2_Suppl_1.S43.PMID9484423.S2CID36824088.
- ^Mitler MM (December 1994)."Evaluation of treatment with stimulants in narcolepsy".Sleep.17(8 Suppl): S103–S106.doi:10.1093/sleep/17.suppl_8.S103.PMID7701190.
- ^Dell'Osso B, Dobrea C, Cremaschi L, Arici C, Altamura AC (December 2014). "Wake-promoting pharmacotherapy for psychiatric disorders".Current Psychiatry Reports.16(12): 524.doi:10.1007/s11920-014-0524-2.PMID25312027.S2CID26314915.
- ^Leonard BE, McCartan D, White J, King DJ (April 2004). "Methylphenidate: A review of its neuropharmacological, neuropsychological, and adverse clinical effects".Human Psychopharmacology.19(3): 151–180.doi:10.1002/hup.579.PMID15079851.S2CID21173346.
- ^Bahji A, Mesbah-Oskui L (September 2021). "Comparative efficacy and safety of stimulant-type medications for depression: A systematic review and network meta-analysis".Journal of Affective Disorders.292:416–423.doi:10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.119.PMID34144366.
- ^Pary R, Scarff JR, Jijakli A, Tobias C, Lippmann S (April 2015)."A Review of Psychostimulants for Adults With Depression".Federal Practitioner.32(Suppl 3): 30S–37S.PMC6375494.PMID30766117.
- ^Rozans M, Dreisbach A, Lertora JJ, Kahn MJ (January 2002). "Palliative uses of methylphenidate in patients with cancer: a review".Journal of Clinical Oncology.20(1): 335–339.doi:10.1200/JCO.20.1.335.PMID11773187.
- ^Smith KR, Kahlon CH, Brown JN, Britt RB (September 2021). "Methylphenidate use in geriatric depression: A systematic review".International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.36(9): 1304–1312.doi:10.1002/gps.5536.PMID33829530.S2CID233184870.
- ^Ruthirakuhan MT, Herrmann N, Abraham EH, Chan S, Lanctôt KL (May 2018)."Pharmacological interventions for apathy in Alzheimer's disease".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.5(6): CD012197.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012197.pub2.PMC6494556.PMID29727467.
- ^"Treatment".nhs.uk.Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). 1 June 2018.Retrieved24 October2022.
- ^Robison LS, Ananth M, Hadjiargyrou M, Komatsu DE, Thanos PK (May 2017)."Chronic oral methylphenidate treatment reversibly increases striatal dopamine transporter and dopamine type 1 receptor binding in rats".Journal of Neural Transmission.124(5): 655–667.doi:10.1007/s00702-017-1680-4.PMC5400672.PMID28116523.
- ^Spencer RC, Devilbiss DM, Berridge CW (June 2015)."The cognition-enhancing effects of psychostimulants involve direct action in the prefrontal cortex".Biological Psychiatry.77(11): 940–950.doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.09.013.PMC4377121.PMID25499957.
- ^Ilieva IP, Hook CJ, Farah MJ (June 2015)."Prescription Stimulants' Effects on Healthy Inhibitory Control, Working Memory, and Episodic Memory: A Meta-analysis".Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.27(6): 1069–1089.doi:10.1162/jocn_a_00776.PMID25591060.S2CID15788121.Archivedfrom the original on 26 May 2022.Retrieved12 June2022.
- ^Busardò FP, Kyriakou C, Cipolloni L, Zaami S, Frati P (2016)."From Clinical Application to Cognitive Enhancement: The Example of Methylphenidate".Current Neuropharmacology.14(1): 17–27.doi:10.2174/1570159x13666150407225902.PMC4787280.PMID26813119.
- ^Carlier J, Giorgetti R, Varì MR, Pirani F, Ricci G, Busardò FP (January 2019). "Use of cognitive enhancers: methylphenidate and analogs".European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences.23(1): 3–15.doi:10.26355/eurrev_201901_16741.PMID30657540.S2CID58643522.
- ^Repantis D, Bovy L, Ohla K, Kühn S, Dresler M (February 2021)."Cognitive enhancement effects of stimulants: a randomized controlled trial testing methylphenidate, modafinil, and caffeine".Psychopharmacology.238(2): 441–451.doi:10.1007/s00213-020-05691-w.PMC7826302.PMID33201262.
- ^Montgomery KA (June 2008)."Sexual desire disorders".Psychiatry.5(6): 50–55.PMC2695750.PMID19727285.
- ^abBerezanskaya J, Cade W, Best TM, Paultre K, Kienstra C (January 2022)."ADHD Prescription Medications and Their Effect on Athletic Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis".Sports Medicine - Open.8(1): 5.doi:10.1186/s40798-021-00374-y.PMC8755863.PMID35022919.
- ^Thoenes MM (1 March 2011). "Heat-related illness risk with methylphenidate use".Journal of Pediatric Health Care.25(2): 127–132.doi:10.1016/j.pedhc.2010.07.006.PMID21320685.
- ^Docherty JR, Alsufyani HA (July 2021)."Cardiovascular and temperature adverse actions of stimulants".British Journal of Pharmacology.178(13): 2551–2568.doi:10.1111/bph.15465.PMID33786822.S2CID232431910.
- ^abcSpencer RC, Devilbiss DM, Berridge CW (June 2015)."The cognition-enhancing effects of psychostimulants involve direct action in the prefrontal cortex".Biological Psychiatry.77(11): 940–950.doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.09.013.PMC4377121.PMID25499957.
- ^abIlieva IP, Hook CJ, Farah MJ (June 2015)."Prescription Stimulants' Effects on Healthy Inhibitory Control, Working Memory, and Episodic Memory: A Meta-analysis".Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience.27(6): 1069–1089.doi:10.1162/jocn_a_00776.PMID25591060.S2CID15788121.Archivedfrom the original on 19 September 2018.Retrieved14 November2018.
- ^abcdMalenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Higher cognitive function and behavioral control". In Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.).Molecular Neuropharmacology: A foundation for clinical neuroscience(2nd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 318.ISBN978-0-07-148127-4.
- ^abcWood S, Sage JR, Shuman T, Anagnostaras SG (January 2014)."Psychostimulants and cognition: a continuum of behavioral and cognitive activation".Pharmacological Reviews.66(1): 193–221.doi:10.1124/pr.112.007054.PMC3880463.PMID24344115.
- ^Agay N, Yechiam E, Carmel Z, Levkovitz Y (July 2010). "Non-specific effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) on cognitive ability and decision-making of ADHD and healthy adults".Psychopharmacology.210(4): 511–519.doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1853-4.PMID20424828.S2CID17083986.
- ^Twohey M (26 March 2006)."Pills become an addictive study aid".JS Online.Archived fromthe originalon 15 August 2007.Retrieved2 December2007.
- ^Teter CJ, McCabe SE, LaGrange K, Cranford JA, Boyd CJ (October 2006)."Illicit use of specific prescription stimulants among college students: prevalence, motives, and routes of administration".Pharmacotherapy.26(10): 1501–1510.doi:10.1592/phco.26.10.1501.PMC1794223.PMID16999660.
- ^Roelands B, de Koning J, Foster C, Hettinga F, Meeusen R (May 2013). "Neurophysiological determinants of theoretical concepts and mechanisms involved in pacing".Sports Medicine.43(5): 301–311.doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0030-4.PMID23456493.S2CID30392999.
- ^"Methylphenidate: Use During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding".Drugs.Archived fromthe originalon 2 January 2018.
- ^Humphreys C, Garcia-Bournissen F, Ito S, Koren G (July 2007)."Exposure to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder medications during pregnancy".Canadian Family Physician.53(7): 1153–1155.PMC1949295.PMID17872810.
- ^Ornoy A (February 2018). "Pharmacological Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder During Pregnancy and Lactation".Pharmaceutical Research.35(3): 46.doi:10.1007/s11095-017-2323-z.PMID29411149.S2CID3663423.
- ^Nutt D, King LA, Saulsbury W, Blakemore C (March 2007). "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse".Lancet.369(9566): 1047–1053.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60464-4.PMID17382831.S2CID5903121.
- ^Coghill D, Banaschewski T, Zuddas A, Pelaz A, Gagliano A, Doepfner M (September 2013)."Long-acting methylphenidate formulations in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review of head-to-head studies".BMC Psychiatry.13(1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 237.doi:10.1186/1471-244x-13-237.PMC3852277.PMID24074240.
- ^ab"Ritalin LA (methylphenidate hydrochloride) extended-release capsules"(PDF).Novartis. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 20 July 2011.
- ^abde Sousa A, Kalra G (January 2012)."Drug therapy of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: current trends".Mens Sana Monographs.10(1): 45–69.doi:10.4103/0973-1229.87261(inactive 30 March 2024).PMC3353606.PMID22654382.
{{cite journal}}:CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of March 2024 (link) - ^Jaanus SD (1992). "Ocular side effects of selected systemic drugs".Optometry Clinics.2(4): 73–96.PMID1363080.
- ^Peterson BS, Trampush J, Maglione M, Bolshakova M, Rozelle M, Miles J, et al. (April 2024). "Treatments for ADHD in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review".Pediatrics.153(4).doi:10.1542/peds.2024-065787.PMID38523592.
- ^Bron TI, Bijlenga D, Kasander MV, Spuijbroek AT, Beekman AT, Kooij JJ (June 2013). "Long-term relationship between methylphenidate and tobacco consumption and nicotine craving in adults with ADHD in a prospective cohort study".European Neuropsychopharmacology.23(6): 542–554.doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.06.004.PMID22809706.S2CID23148548.
- ^abCortese S, Holtmann M, Banaschewski T, Buitelaar J, Coghill D, Danckaerts M, et al. (March 2013). "Practitioner review: current best practice in the management of adverse events during treatment with ADHD medications in children and adolescents".Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines.54(3): 227–246.doi:10.1111/jcpp.12036.PMID23294014.
- ^Poulton A (August 2005)."Growth on stimulant medication; clarifying the confusion: a review".Archives of Disease in Childhood.90(8): 801–806.doi:10.1136/adc.2004.056952.PMC1720538.PMID16040876.
- ^Hinshaw SP, Arnold LE (January 2015)."ADHD, Multimodal Treatment, and Longitudinal outcome: Evidence, paradox, and challenge".Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Cognitive Science.6(1): 39–52.doi:10.1002/wcs.1324.PMC4280855.PMID25558298.
- ^Findling RL, Dinh S (March 2014)."Transdermal therapy for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with the methylphenidate patch (MTS)".CNS Drugs.28(3): 217–228.doi:10.1007/s40263-014-0141-y.PMC3933749.PMID24532028.
- ^Kraemer M, Uekermann J, Wiltfang J, Kis B (July 2010). "Methylphenidate-induced psychosis in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: report of 3 new cases and review of the literature".Clinical Neuropharmacology.33(4): 204–206.doi:10.1097/WNF.0b013e3181e29174.PMID20571380.S2CID34956456.
- ^Wingo AP, Ghaemi SN (2008). "Frequency of stimulant treatment and of stimulant-associated mania / hypomania in bipolar disorder patients".Psychopharmacology Bulletin.41(4): 37–47.PMID19015628.
- ^"Methylphenidate ADHD medications: Drug safety communication – risk of long-lasting erections".U.S.Food and Drug Administration(FDA).17 December 2013. Archived fromthe originalon 17 December 2013.Retrieved17 December2013.
- ^"FDA drug safety communication: Safety review update of medications used to treat attention-ceficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and young adults".U.S.Food and Drug Administration(FDA).20 December 2011.Archivedfrom the original on 30 October 2013.Retrieved4 November2013. Cooper WO, Habel LA, Sox CM, Chan KA, Arbogast PG, Cheetham TC, et al. (November 2011)."ADHD drugs and serious cardiovascular events in children and young adults".The New England Journal of Medicine.365(20): 1896–1904.doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1110212.PMC4943074.PMID22043968. "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Safety Review Update of Medications used to treat Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults".U.S.Food and Drug Administration(FDA).15 December 2011.Archivedfrom the original on 30 October 2013.Retrieved4 November2013. Habel LA, Cooper WO, Sox CM, Chan KA, Fireman BH, Arbogast PG, et al. (December 2011)."ADHD medications and risk of serious cardiovascular events in young and middle-aged adults".JAMA.306(24): 2673–2683.doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1830.PMC3350308.PMID22161946.
- ^Gordon N (1999). "Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Possible causes and treatment".International Journal of Clinical Practice.53(7): 524–528.doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.1999.tb11794.x.PMID10692738.S2CID27462347.
- ^abcStorebø OJ, Pedersen N, Ramstad E, Kielsholm ML, Nielsen SS, Krogh HB, et al. (May 2018)."Methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents - assessment of adverse events in non-randomised studies".The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews(Systematic Review).5(5): CD012069.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012069.pub2.PMC6494554.PMID29744873.
- ^abHeedes G, Ailakis J."Methylphenidate hydrochloride (PIM 344)".INCHEM.International Programme on Chemical Safety.Archivedfrom the original on 23 June 2015.Retrieved23 June2015.
- ^abcdSpiller HA, Hays HL, Aleguas A (July 2013)."Overdose of drugs for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Clinical presentation, mechanisms of toxicity, and management".CNS Drugs.27(7): 531–543.doi:10.1007/s40263-013-0084-8.PMID23757186.S2CID40931380.
- ^Bruggisser M, Bodmer M, Liechti ME (2011)."Severe toxicity due to injected but not oral or nasal abuse of methylphenidate tablets".Swiss Medical Weekly.141:w13267.doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13267.PMID21984207.
- ^Morton WA, Stockton GG (October 2000)."Methylphenidate Abuse and Psychiatric Side Effects".Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.2(5): 159–164.doi:10.4088/PCC.v02n0502.PMC181133.PMID15014637.
- ^abcMalenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 15: Reinforcement and addictive disorders". In Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.).Molecular Neuropharmacology: A foundation for clinical neuroscience(2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 368.ISBN978-0-07-148127-4.
- ^Auger RR, Goodman SH, Silber MH, Krahn LE, Pankratz VS, Slocumb NL (June 2005)."Risks of high-dose stimulants in the treatment of disorders of excessive somnolence: A case-control study".Sleep.28(6): 667–672.doi:10.1093/sleep/28.6.667.PMID16477952.
- ^Ishii M, Tatsuzawa Y, Yoshino A, Nomura S (April 2008)."Serotonin syndrome induced by augmentation of SSRI with methylphenidate".Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences.62(2): 246.doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2008.01767.x.PMID18412855.S2CID5659107.
- ^Türkoğlu S (2015). "Serotonin syndrome with sertraline and methylphenidate in an adolescent".Clinical Neuropharmacology.38(2): 65–66.doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000075.PMID25768857.S2CID38523209.
- ^Park YM, Jung YK (May 2010). "Manic switch and serotonin syndrome induced by augmentation of paroxetine with methylphenidate in a patient with major depression".Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry.34(4): 719–720.doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.03.016.PMID20298736.S2CID31984813.
- ^Bodner RA, Lynch T, Lewis L, Kahn D (February 1995). "Serotonin syndrome".Neurology.45(2): 219–223.doi:10.1212/wnl.45.2.219.PMID7854515.S2CID35190429.
- ^Patrick KS, González MA, Straughn AB, Markowitz JS (January 2005). "New methylphenidate formulations for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder".Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2(1): 121–143.doi:10.1517/17425247.2.1.121.PMID16296740.S2CID25026467.
- ^abMarkowitz JS, DeVane CL, Boulton DW, Nahas Z, Risch SC, Diamond F, et al. (June 2000). "Ethylphenidate formation in human subjects after the administration of a single dose of methylphenidate and ethanol".Drug Metabolism and Disposition.28(6): 620–624.PMID10820132.
- ^abMarkowitz JS, Logan BK, Diamond F, Patrick KS (August 1999). "Detection of the novel metabolite ethylphenidate after methylphenidate overdose with alcohol coingestion".Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.19(4): 362–366.doi:10.1097/00004714-199908000-00013.PMID10440465.
- ^Patrick KS, Straughn AB, Minhinnett RR, Yeatts SD, Herrin AE, DeVane CL, et al. (March 2007)."Influence of ethanol and gender on methylphenidate pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics".Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.81(3): 346–353.doi:10.1038/sj.clpt.6100082.PMC3188424.PMID17339864.
- ^Roberts SM, DeMott RP, James RC (1997). "Adrenergic modulation of hepatotoxicity".Drug Metabolism Reviews.29(1–2): 329–353.doi:10.3109/03602539709037587.PMID9187524.
- ^Markowitz JS, Patrick KS (June 2008). "Differential pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methylphenidate enantiomers: Does chirality matter?".Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.28(3 Suppl 2): S54–S61.doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181733560.PMID18480678.
- ^Williard RL, Middaugh LD, Zhu HJ, Patrick KS (February 2007). "Methylphenidate and its ethanol transesterification metabolite ethylphenidate: brain disposition, monoamine transporters and motor activity".Behavioural Pharmacology.18(1): 39–51.doi:10.1097/fbp.0b013e3280143226.PMID17218796.S2CID20232871.
- ^abMarkowitz JS, DeVane CL, Pestreich LK, Patrick KS, Muniz R (December 2006). "A comprehensive in vitro screening of d-, l-, and dl-threo-methylphenidate: an exploratory study".Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology.16(6): 687–698.doi:10.1089/cap.2006.16.687.PMID17201613.S2CID22895177.
- ^abMalenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 6: Widely projecting systems: Monoamines, acetylcholine, and orexin". In Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.).Molecular Neuropharmacology: A foundation for clinical neuroscience(2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. pp. 154–157.ISBN978-0-07-148127-4.
- ^Steele M, Weiss M, Swanson J, Wang J, Prinzo RS, Binder CE (2006)."A randomized, controlled effectiveness trial of OROS-methylphenidate compared to usual care with immediate-release methylphenidate in attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder".The Canadian Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.13(1): e50–e62.PMID16456216.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 15 December 2011.
- ^abcHeal DJ, Pierce DM (2006). "Methylphenidate and its isomers: their role in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder using a transdermal delivery system".CNS Drugs.20(9): 713–738.doi:10.2165/00023210-200620090-00002.PMID16953648.S2CID39535277.
- ^Iversen L (January 2006)."Neurotransmitter transporters and their impact on the development of psychopharmacology".British Journal of Pharmacology.147(Suppl 1): S82–S88.doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706428.PMC1760736.PMID16402124.
- ^Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang G, Ding Y, Gatley SJ (1 January 2002). "Mechanism of action of methylphenidate: insights from PET imaging studies".Journal of Attention Disorders.6(Suppl 1): S31–S43.doi:10.1177/070674370200601s05.PMID12685517.S2CID9132302.
- ^Hart H, Radua J, Nakao T, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K (February 2013)."Meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of inhibition and attention in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: exploring task-specific, stimulant medication, and age effects".JAMA Psychiatry.70(2): 185–198.doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.277.PMID23247506.
- ^Spencer TJ, Brown A, Seidman LJ, Valera EM, Makris N, Lomedico A, et al. (September 2013)."Effect of psychostimulants on brain structure and function in ADHD: a qualitative literature review of magnetic resonance imaging-based neuroimaging studies".The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.74(9): 902–917.doi:10.4088/JCP.12r08287.PMC3801446.PMID24107764.
- ^abFrodl T, Skokauskas N (February 2012)."Meta-analysis of structural MRI studies in children and adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder indicates treatment effects".Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica.125(2): 114–126.doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01786.x.PMID22118249.S2CID25954331.
- ^Viggiano D, Vallone D, Sadile A (2004)."Dysfunctions in dopamine systems and ADHD: evidence from animals and modeling".Neural Plasticity.11(1–2): 97–114.doi:10.1155/NP.2004.97.PMC2565441.PMID15303308.
- ^"Focalin XR".RxList.Archivedfrom the original on 6 August 2020.Retrieved5 February2020.
- ^"Concerta XL 18 mg – 54 mg prolonged release tablets".eMC.Archived fromthe originalon 17 October 2017.
- ^abMiller GM (January 2011)."The emerging role of trace amine-associated receptor 1 in the functional regulation of monoamine transporters and dopaminergic activity".Journal of Neurochemistry.116(2): 164–176.doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07109.x.PMC3005101.PMID21073468.
- ^abEiden LE, Weihe E (January 2011)."VMAT2: a dynamic regulator of brain monoaminergic neuronal function interacting with drugs of abuse".Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.1216(1): 86–98.Bibcode:2011NYASA1216...86E.doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05906.x.PMC4183197.PMID21272013.
- ^abSulzer D, Cragg SJ, Rice ME (August 2016)."Striatal dopamine neurotransmission: regulation of release and uptake".Basal Ganglia.6(3): 123–148.doi:10.1016/j.baga.2016.02.001.PMC4850498.PMID27141430.
- ^abLiu F, Minami H, Silva RR (December 2006)."Dexmethylphenidate hydrochloride in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder".Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment.2(4): 467–473.doi:10.2147/nedt.2006.2.4.467.PMC2671958.PMID19412495.
- ^Markowitz JS, DeVane CL, Ramamoorthy S, Zhu HJ (February 2009). "The psychostimulant d-threo-(R,R)-methylphenidate binds as an agonist to the 5HT(1A) receptor".Die Pharmazie.64(2): 123–125.PMID19322953.
- ^abVolkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Gatley SJ, Ding YS, Logan J, et al. (September 1996)."Relationship between psychostimulant-induced" high "and dopamine transporter occupancy".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.93(19): 10388–10392.Bibcode:1996PNAS...9310388V.doi:10.1073/pnas.93.19.10388.PMC38394.PMID8816810.
- ^Shoptaw S, Heinzerling KG, Rotheram-Fuller E, Steward T, Wang J, Swanson AN, et al. (August 2008)."Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of bupropion for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence".Drug and Alcohol Dependence.96(3): 222–232.doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.03.010.PMC3652530.PMID18468815.
- ^Heal DJ, Gosden J, Smith SL (December 2014). "Dopamine reuptake transporter (DAT)" inverse agonism "– a novel hypothesis to explain the Enigma tic pharmacology of cocaine".Neuropharmacology.87:19–40.doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.06.012.PMID24953830.S2CID4660652.
- ^abVolz TJ (December 2008)."Neuropharmacological mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective effects of methylphenidate".Current Neuropharmacology.6(4): 379–385.doi:10.2174/157015908787386041.PMC2701286.PMID19587858.
- ^"Concerta".Drugs.1 October 2018.Archivedfrom the original on 29 September 2018.Retrieved11 March2019.
- ^Chan YP, Swanson JM, Soldin SS, Thiessen JJ, Macleod SM, Logan W (July 1983)."Methylphenidate hydrochloride given with or before breakfast: II. Effects on plasma concentration of methylphenidate and ritalinic acid".Pediatrics.72(1): 56–59.doi:10.1542/peds.72.1.56.PMID6866592.S2CID28806553.Archivedfrom the original on 17 December 2021.Retrieved12 December2021.
- ^"Cotempla XR-ODT- methylphenidate tablet, orally disintegrating".DailyMed.1 July 2021.Archivedfrom the original on 26 May 2022.Retrieved25 May2022.
- ^"Quillivant XR- methylphenidate hydrochloride suspension, extended release".DailyMed.30 June 2021.Archivedfrom the original on 26 May 2022.Retrieved26 May2022.
- ^Lee L, Kepple J, Wang Y, Freestone S, Bakhtiar R, Wang Y, et al. (September 2003). "Bioavailability of modified-release methylphenidate: influence of high-fat breakfast when administered intact and when capsule content sprinkled on applesauce".Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition.24(6): 233–243.doi:10.1002/bdd.358.PMID12973820.S2CID29609987.
- ^Sun Z, Murry DJ, Sanghani SP, Davis WI, Kedishvili NY, Zou Q, et al. (August 2004). "Methylphenidate is stereoselectively hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase CES1A1".The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.310(2): 469–476.doi:10.1124/jpet.104.067116.PMID15082749.S2CID24233422.
- ^Preedy VR (2016).Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse.Vol. 3: General processes and mechanisms, prescription medications, caffeine and areca, polydrug misuse, emerging addictions, and non-drug addictions. Academic Press. p. 651.ISBN978-0-12-800677-1.Archivedfrom the original on 29 August 2021.Retrieved19 December2018.
- ^Bagot KS, Kaminer Y (April 2014)."Efficacy of stimulants for cognitive enhancement in non-attention deficit hyperactivity disorder youth: A systematic review".Addiction.109(4): 547–557.doi:10.1111/add.12460.PMC4471173.PMID24749160.
- ^Froimowitz M, Patrick KS, Cody V (October 1995). "Conformational analysis of methylphenidate and its structural relationship to other dopamine reuptake blockers such as CFT".Pharmaceutical Research.12(10): 1430–1434.doi:10.1023/A:1016262815984.PMID8584475.S2CID26097197.
- ^Prashad M (2001). "Approaches to the Preparation of Enantiomerically Pure (2R,2′R)-(+)-threo-Methylphenidate Hydrochloride ".Adv. Synth. Catal.343(5): 379–392.doi:10.1002/1615-4169(200107)343:5<379::AID-ADSC379>3.0.CO;2-4.
- ^Axten JM, Krim L, Kung HF, Winkler JD (1998). "A Stereoselective Synthesis ofdl-threo-Methylphenidate: Preparation and Biological Evaluation of Novel Analogues".The Journal of Organic Chemistry.63(26): 9628–9629.doi:10.1021/jo982214t.
- ^Singh S (March 2000). "Chemistry, design, and structure-activity relationship of cocaine antagonists".Chemical Reviews.100(3): 925–1024.doi:10.1021/cr9700538.PMID11749256.
- ^Baselt R, ed. (2011).Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man(9th ed.). Seal Beach, CA: Biomedical Publications. pp. 1091–1093.
- ^abLange KW, Reichl S, Lange KM, Tucha L, Tucha O (December 2010)."The history of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder".Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders.2(4): 241–255.doi:10.1007/s12402-010-0045-8.PMC3000907.PMID21258430.
- ^Wenthur CJ (August 2016). "Classics in chemical neuroscience: Methylphenidate".ACS Chem Neurosci.7(8): 1030–1040.doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00199.PMID27409720.
- ^Panizzon L (1944). "La preparazione di piridile piperidil-arilacetonitrili e di alcuni prodotti di trasformazione (Parte Ia)".Helvetica Chimica Acta.27:1748–1756.doi:10.1002/hlca.194402701222.
- ^Myers RL (1 January 2007).The 100 Most Important Chemical Compounds: A reference guide.ABC-CLIO. p. 178.ISBN978-0-313-33758-1.Archivedfrom the original on 2 February 2017.Retrieved24 September2016– via Google Books.
- ^abcdHeal DJ, Pierce DM (2006). "Methylphenidate and its isomers: their role in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder using a transdermal delivery system".CNS Drugs.20(9): 713–738.doi:10.2165/00023210-200620090-00002.PMID16953648.S2CID39535277.
- ^Meier R, Gross F, Tripod J (May 1954). "Ritalin, eine neuartige synthetische Verbindung mit spezifischer zentralerregender Wirkungskomponente" [Ritalin, a new synthetic compound with specific analeptic components].Klinische Wochenschrift(in German).32(19–20): 445–450.doi:10.1007/BF01466968.PMID13164273.S2CID24516999.
- ^Wood S, Sage JR, Shuman T, Anagnostaras SG (2014)."Psychostimulants and cognition: A continuum of behavioral and cognitive activation".Pharmacol Rev.66(1): 193–221.doi:10.1124/pr.112.007054.PMC3880463.PMID24344115.
- ^US 2507631,Hartmann, M.; Panizzon, L., "Pyridine and piperidine compounds and process of making same", issued 16 May 1950, assigned to CIBA Pharmaceutical Products, Inc
- ^US 2838519,Rouietscji, R., "Process for the conversion of stereoisomers", issued 10 June 1958, assigned to CIBA Pharmaceutical Products, Inc
- ^US 2957880,Rouietscji, R., "Process for the conversion of stereoisomers", issued 25 October 1960, assigned to CIBA Pharmaceutical Products, Inc
- ^Myers RL (August 2007).The 100 Most Important Chemical Compounds: A reference guide.ABC-CLIO. p.178.ISBN978-0-313-33758-1.Retrieved10 September2010.
... named ritalin after his wife...
- ^Stolerman I (2010).Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology.Berlin, DE / London, UK: Springer. p. 763.ISBN978-3-540-68698-9.
- ^McCrossin S (1995).Ritalin and attention deficit disorder: History of its use, effects, and side effects(PDF)(Report). Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 24 August 2012.Retrieved22 July2014.
- ^Bradley C (January 1950). "Benzedrine and dexedrine in the treatment of children's behavior disorders".Pediatrics.5(1): 24–37.doi:10.1542/peds.5.1.24.PMID15404645.S2CID45655000.
- ^Woodworth T (16 May 2000).DEA Congressional Testimony(Report). U.S.Drug Enforcement Administration.Archived fromthe originalon 12 October 2007.Retrieved2 November2007.
- ^"Drug Approval Package: Concerta (methylphenidate HCI) NDA #21-121".fda.gov.24 December 1999.Archivedfrom the original on 27 March 2022.Retrieved26 March2022.
- ^"Newly Approved Drug Therapies (637) Concerta, Alza".CenterWatch.Archived fromthe originalon 16 December 2010.Retrieved30 April2011.
- ^"Narcotics monitoring board reports 66% increase in global consumption of methylphenidate".The Pharmaceutical Journal.294(7853). Royal Pharmaceutical Society. 4 March 2015.doi:10.1211/PJ.2015.20068042.Archivedfrom the original on 19 December 2018.Retrieved19 December2018.
- ^abMoscibrodzki P, Katz C (8 December 2018).Application for inclusion to the 22nd expert committee on the selection and use of essential medicines: Methylphenidate hydrochloride(PDF)(Report).World Health Organization.Archived(PDF)from the original on 6 August 2020.Retrieved16 November2019.
- ^Foquest: Methylphenidate hydrochloride controlled release capsules(PDF)(vers. E). Product Monograph. Pickering, Ontario, Canada: Purdue Pharma. 1 March 2019. Submission Control Nr 214860.Retrieved14 December2022– via caddra.ca.
- ^
"Education / training".Illinois DocAssist.Clinical resources. Chicago, IL:University of Illinois.Archived fromthe originalon 1 January 2013.Retrieved26 July2012.
Ritalin‑SR, methylphenidate SR, Methylin ER, and Metadate ER are the same formulation and have the same drug delivery system
- ^ "Comparative bioavailability".Apo‑methylphenidate SR(PDF)(product monograph). Apotex Inc. 31 March 2005.Retrieved26 July2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^
"New product: Sandoz methylphenidate SR 20 mg"(PDF)(Press release). Sandoz Canada Inc. 5 May 2009.Archived(PDF)from the original on 3 December 2012.Retrieved26 July2012.
An alternative to Ritalin‑SR from Novartis
- ^ "FDA approved drug products".Drugs@FDA.USFood and Drug Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 2 October 2016.Retrieved1 October2016.[failed verification]
- ^ Hosenbocus S, Chahal R (November 2009)."A review of long-acting medications for ADHD in Canada".Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.18(4): 331–339.PMC2765387.PMID19881943.
- ^ "Aptensio XR Prescribing Information"(PDF).Archived(PDF)from the original on 2 February 2017.Retrieved15 April2017.
- ^abcdeMoses S (26 July 2009)."Methylphenidate".Family Practice Notebook.Archivedfrom the original on 14 September 2012.Retrieved7 August2012.
- ^"Daytrana transdermal".WebMD.Archivedfrom the original on 11 June 2015.Retrieved11 June2015.
- ^"Quillichew ER (methylphenidate HCl extended-release chewable tablets CII)".Pfizer Medical Information (pfizermedicalinformation )(Press release). U.S.: Pfizer. Archived fromthe originalon 16 April 2017.Retrieved16 April2017.
- ^ab"Jornay PM Full Prescribing Information"(PDF).accessdata.fda.gov.FDA.Retrieved27 April2024.
- ^"Concerta for Kids with ADHD".Pediatrics.about.1 April 2003. Archived fromthe originalon 7 January 2011.
- ^"Concerta (methylphenidate extended-release tablets)".RxList.Drug information: User reviews, side effects, drug interactions, and dosage. Archived fromthe originalon 26 March 2011.Retrieved30 April2011.
- ^"Metadate CD".Archived fromthe originalon 10 July 2011.
- ^Coghill D, Banaschewski T, Zuddas A, Pelaz A, Gagliano A, Doepfner M (September 2013)."Long-acting methylphenidate formulations in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review of head-to-head studies".BMC Psychiatry.13:237.doi:10.1186/1471-244X-13-237.PMC3852277.PMID24074240.
- ^"UK Report on Ritalin".p. 9.Retrieved9 January2024.
- ^Steingard R, Taskiran S, Connor DF, Markowitz JS, Stein MA (June 2019)."New Formulations of Stimulants: An Update for Clinicians".J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol.29(5): 324–339.doi:10.1089/cap.2019.0043.PMC7207053.PMID31038360.
- ^Methylphenidate transdermal system (MTS)(PDF)(safety summary). Noven Pharmaceuticals. 24 October 2005.NDA No. 21-514,Appendix 3. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 30 September 2007.Retrieved17 January2022– via U.S.Food and Drug Administration.
- ^Heal DJ, Pierce DM (2006). "Methylphenidate and its isomers: their role in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder using a transdermal delivery system".CNS Drugs.20(9): 713–738.doi:10.2165/00023210-200620090-00002.PMID16953648.S2CID39535277. Anderson VR, Scott LJ (2006). "Methylphenidate transdermal system: In attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children".Drugs.66(8): 1117–1126.doi:10.2165/00003495-200666080-00007.PMID16789796.S2CID46975783.
- ^Green List: Annex to the annual statistical report on psychotropic substances (form P)(PDF)(Report) (23rd ed.). Vienna International Centre, Austria: International Narcotics Board. August 2003.(1.63 MB).Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 31 August 2012.Retrieved2 March2006.
- ^"Poisons Standard 2012 as amended made under paragraph 52D(2)(a) of the Therapeutic Goods Act 1989".Therapeutic Goods Administration. 27 November 2014.Archivedfrom the original on 1 July 2015.Retrieved28 June2015.
- ^Controlled Drugs and Substances Act(Report). Laws. Department of Justice, Government of Canada. 25 April 2017. S.C. 1996, c. 19.Archivedfrom the original on 3 April 2011.Retrieved26 April2017.
- ^"FIJI ISLANDS ILLICIT DRUGS CONTROL ACT 2004"(PDF).health.gov.fj.Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 13 July 2018.Retrieved5 August2023.
- ^"TDAH: la prescription de méthylphénidate peut désormais être initiée en villexxxxxxxxx".VIDAL(in French).
- ^"Dangerous Drugs Ordinance".Hong Kong e-Legislation.1438402701417-001.Archivedfrom the original on 28 August 2021.Retrieved20 March2019.
- ^The Drugs and Cosmetics Rules(Report). Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. Government of India. 15 August 2013 [1945]. pp. 729–730.Archivedfrom the original on 8 August 2016.Retrieved5 December2016.
- ^Mehta R (26 February 2014).Drug Law Enforcement Field Officers' Hand Book(PDF)(Report). Narcotics Control Bureau, Ministry of Home Affairs. Government of India. p. 145. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 5 March 2017.Retrieved5 December2016.
- ^"Decree of the Government of Russian Federation on 25 October 2014"(PDF).No. 1102.Archived(PDF)from the original on 26 March 2015.Retrieved17 October2019.
- ^"Narkotikastrafflag (1968:64)".Ministry of Justice.Archivedfrom the original on 6 October 2013.Retrieved15 January2014.
- ^"Schedule 2: Controlled Drugs".Misuse of Drugs Act (c. 38) (Report). Office of Public Sector Information. 1971.Archivedfrom the original on 28 August 2021.Retrieved15 June2009.
- ^Finlator J (28 October 1971)."Phenmetrazine and its salts, and Methylphenidate"(PDF).Isomer Design.Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs.Archived(PDF)from the original on 3 March 2022.Retrieved16 January2023.
- ^Lakhan SE, Hagger-Johnson GE (October 2007)."The impact of prescribed psychotropics on youth".Clinical Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health.3(1): 21.doi:10.1186/1745-0179-3-21.PMC2100041.PMID17949504.
- ^"New research helps explain ritalin's low abuse potential when taken as prescribed".NIH.gov.29 September 1998. Archived fromthe originalon 28 May 2010.Retrieved30 April2011.
- ^"Stimulant ADHD medications: Methylphenidate and amphetamines".Drugabuse.gov.NIDA InfoFacts. Archived fromthe originalon 26 March 2010.Retrieved30 April2011.
- ^Schoenfelder EN, Faraone SV, Kollins SH (June 2014)."Stimulant treatment of ADHD and cigarette smoking: A meta-analysis".Pediatrics.133(6): 1070–1080.doi:10.1542/peds.2014-0179.PMC4531271.PMID24819571.
- ^Wilens TE, Faraone SV, Biederman J, Gunawardene S (January 2003). "Does stimulant therapy of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder beget later substance abuse? A meta-analytic review of the literature".Pediatrics.111(1): 179–185.doi:10.1542/peds.111.1.179.PMID12509574.S2CID29956425.
- ^Karlstad Ø, Zoëga H, Furu K, Bahmanyar S, Martikainen JE, Kieler H, et al. (December 2016)."Use of drugs for ADHD among adults-a multinational study among 15.8 million adults in the Nordic countries".European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.72(12): 1507–1514.doi:10.1007/s00228-016-2125-y.PMC5110707.PMID27586399.
- ^Bjarnadottir GD, Haraldsson HM, Rafnar BO, Sigurdsson E, Steingrimsson S, Johannsson M, et al. (29 November 2016)."Prevalent intravenous abuse of methylphenidate among treatment-seeking patients with substance abuse disorders: a descriptive population-based study".Journal of Addiction Medicine.9(3): 188–194.doi:10.1097/ADM.0000000000000115.PMC4450903.PMID25748561.
- ^Ouellette EM (1991). "Legal issues in the treatment of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder".Journal of Child Neurology.6(Suppl): S68–S75.doi:10.1177/0883073891006001S08.PMID2002217.S2CID1773939.
- ^Ruthirakuhan MT, Herrmann N, Abraham EH, Chan S, Lanctôt KL (May 2018)."Pharmacological interventions for apathy in Alzheimer's disease".Cochrane Database Syst Rev.5(5): CD012197.doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012197.pub2.PMC6494556.PMID29727467.
- ^Lee CW, Chen JY, Ko CC, Chuang MH, Tsai WW, Sun CK, et al. (December 2022). "Efficacy of methylphenidate for the treatment of apathy in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies".Psychopharmacology (Berl).239(12): 3743–3753.doi:10.1007/s00213-022-06261-y.PMID36243827.
- ^Theleritis C, Siarkos K, Katirtzoglou E, Politis A (January 2017). "Pharmacological and Nonpharmacological Treatment for Apathy in Alzheimer Disease: A systematic review across modalities".Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology.30(1): 26–49.doi:10.1177/0891988716678684.PMID28248559.S2CID24642197.
- ^abSpiegel DR, Warren A, Takakura W, Servidio L, Leu N (January 2018)."Disorders of diminished motivation: What they are, and how to treat them"(PDF).Current Psychiatry.17(1): 10–18, 20.
- ^Arnts H, van Erp WS, Lavrijsen JC, van Gaal S, Groenewegen HJ, van den Munckhof P (May 2020)."On the pathophysiology and treatment of akinetic mutism".Neurosci Biobehav Rev.112:270–278.doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.02.006.hdl:2066/225901.PMID32044373.
- ^Elkashef A, Vocci F, Hanson G, White J, Wickes W, Tiihonen J (2008)."Pharmacotherapy of methamphetamine addiction: an update".Substance Abuse.29(3): 31–49.doi:10.1080/08897070802218554.PMC2597382.PMID19042205.
- ^Grabowski J, Roache JD, Schmitz JM, Rhoades H, Creson D, Korszun A (December 1997). "Replacement medication for cocaine dependence: methylphenidate".Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.17(6): 485–488.doi:10.1097/00004714-199712000-00008.PMID9408812.
- ^"Understanding drug abuse and addiction: What science says".US National Institute on Drug Addiction. 1 February 2019.Retrieved11 February2023.
- ^Shearer J (May 2008)."The principles of agonist pharmacotherapy for psychostimulant dependence".Drug and Alcohol Review.27(3): 301–308.doi:10.1080/09595230801927372.PMID18368612.
- ^Villas-Boas CB, Chierrito D, Fernandez-Llimos F, Tonin FS, Sanches AC (March 2019). "Pharmacological treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder comorbid with an anxiety disorder: a systematic review".Int Clin Psychopharmacol.34(2): 57–64.doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000243.PMID30422834.
In a retrospective analysis of a case series, the monotherapy with extendedrelease methylphenidate was seen to be effective in reducing ADHD and social AD symptoms evaluated by the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) and Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale (LSAS) (Koyuncu et al., 2017).
- ^Koyuncu A, İnce E, Ertekin E, Tükel R (2019)."Comorbidity in social anxiety disorder: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges".Drugs Context.8:212573.doi:10.7573/dic.212573.PMC6448478.PMID30988687.
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), another childhood disorder that extends over adulthood, is an overlooked condition that has high rates of comorbidity with SAD.31 Only recently increasing evidence suggests that the relationship between the two disorders is closer than that was thought before. Several studies found high rates (up to 60–70%) of childhood ADHD comorbidity, especially predominantly inattentive type, in adults with SAD.67,157,158 In addition, follow-up studies showed that the lifetime prevalence of SAD among ADHD patients is higher compared to healthy controls.159 In treatment studies investigating patients with SAD plus ADHD comorbidity found that ADHD medications such as methylphenidate or atomoxetine could effectively improve symptoms of both disorders at the same time.160–163 According to a developmental hypothesis, SAD may be etiologically linked to ADHD in a subgroup of patients, and thus SAD may develop secondary to ADHD.31
- ^Pelissolo A, Abou Kassm S, Delhay L (December 2019). "Therapeutic strategies for social anxiety disorder: where are we now?".Expert Rev Neurother.19(12): 1179–1189.doi:10.1080/14737175.2019.1666713.PMID31502896.
Recently, clinical studies have found high rates of Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in SAD children (up to 60-%), but also in adults [98]. Koyuncu et al. proposed a "developmental hypothesis", suggesting that SAD may be etiologically linked to ADHD in a subgroup of patients. The impact of this association on response to treatment still needs investigations, but preliminary studies showed that atomoxetine and methylphenidate can be effective in treating both ADHD and comorbid SAD [99,100].
- ^Golubchik P, Sever J, Weizman A (July 2014)."Methylphenidate treatment in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and comorbid social phobia".Int Clin Psychopharmacol.29(4): 212–215.doi:10.1097/YIC.0000000000000029.PMC4047304.PMID24448460.
- ^Koyuncu A, Çelebi F, Ertekin E, Kahn DA (May 2015). "Extended-release Methylphenidate Treatment and Outcomes in Comorbid Social Anxiety Disorder and Attention-deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: 2 Case Reports".J Psychiatr Pract.21(3): 225–231.doi:10.1097/PRA.0000000000000070.PMID25955266.
- ^Koyuncu A, Çelebi F, Ertekin E, Kök BE, Tükel R (November 2017)."Extended-release methylphenidate monotherapy in patients with comorbid social anxiety disorder and adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: retrospective case series".Ther Adv Psychopharmacol.7(11): 241–247.doi:10.1177/2045125317714193.PMC5638159.PMID29090087.
External links
[edit]- Methylphenidate
- 2-Benzylpiperidines
- 2-Piperidinyl compounds
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management
- Biology of bipolar disorder
- Carboxylate esters
- CYP2D6 inhibitors
- Ergogenic aids
- Euphoriants
- Drugs developed by Novartis
- Methyl esters
- Nootropics
- Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors
- Pro-motivational agents
- Sigma agonists
- Stimulants
- Vasoconstrictors
- Wakefulness-promoting agents
- World Anti-Doping Agency prohibited substances

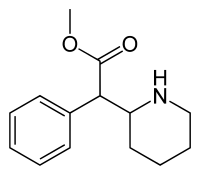





![Structural formula for the substance among Ritalin tablet series. (Ritalin, Ritalin LA, Ritalin SR.) The volume of distribution was 2.65±1.11 L/kg for d-methylphenidate and 1.80±0.91 L/kg for l-methylphenidate subsequent to swallow of Ritalin tablet.[10]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/30/Structural_formula_for_Concerta.jpg)