Rostock
Rostock | |
|---|---|
|
From top: Rostock skyline,St. Mary's Church,St. Peter's Church,seaside resortWarnemünde,city hall, Warnemünde beach | |
| Coordinates:54°5′N12°8′E/ 54.083°N 12.133°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Mecklenburg-Vorpommern |
| District | Urban district |
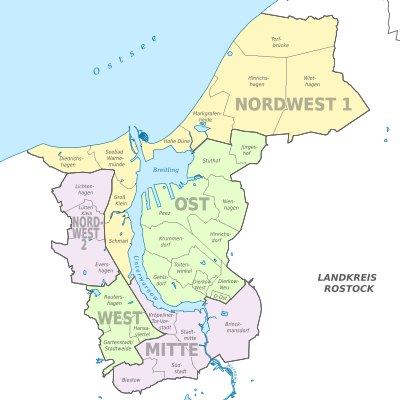
| Subdivisions | 21 boroughs |
| Government | |
| •Lord mayor(2023–30) | Eva-Maria Kröger(Left) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 181.44 km2(70.05 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 13 m (43 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 209,920 |
| • Density | 1,200/km2(3,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00(CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00(CEST) |
| Postal codes | 18001–18147 |
| Dialling codes | 0381 |
| Vehicle registration | HRO |
| Website | rostock.de |

Rostock(German:[ˈʁɔstɔk];Polabian:Roztoc), officially theHanseaticand University City of Rostock(German:Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the GermanstateofMecklenburg-Vorpommernand lies in theMecklenburgianpart of the state, close to the border withPomerania.[a]With around 210,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city on the GermanBalticcoast afterKielandLübeck,the eighth-largest city in the area of formerEast Germany,as well as the39th-largest cityof Germany. Rostock was the largest coastal and most important port city in East Germany.
Rostock stands on the estuary of theRiver Warnowinto theBay of Mecklenburgof the Baltic Sea. The city stretches for about 16 km (10 mi) along the river. The river flows into the sea in the very north of the city, between the boroughs ofWarnemündeand Hohe Düne. The city center lies further upstream, in the very south of the city. Most of Rostock's inhabitants live on the western side of the Warnow; the area east of the river is dominated by the port, industrial estates, and the forestedRostock Heath.The city's coastline east and west of the river mouth is relatively undeveloped, with long sandy beaches prevailing. The name of the city is ofSlavicorigin.
Rostock is the economic center of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and the state's onlyregiopolis(a city outside the core of a metropolitan area). The port of Rostock is the fourth largest port in Germany after theNorth Seaports ofHamburg,Bremen/Bremerhaven,andWilhelmshaven,and the largest port on the German Baltic coast. The ferry routes between Rostock toGedserin Denmark and toTrelleborgin Southern Sweden are among the busiest between Germany andScandinavia.Rostock–Laage Airportlies in arural regionsoutheast of the city.
The city is home to the oldest university in theBaltic regionand one of theoldest universities in the world,theUniversity of Rostock,founded in 1419. The university's hospital,Universitätsmedizin Rostock,is one of two university hospitals in the state, along withUniversitätsmedizin Greifswaldof theUniversity of GreifswaldinWestern Pomerania.
History[edit]
Early history[edit]
In the 11th centuryPolabian Slavsfounded a settlement at the Warnow river calledRoztoc(*ras-tokŭ,Slavic for "fork of a river" ); the name Rostock is derived from that designation.
The Danish kingValdemar Iset the town on fire in 1161. Afterwards the place was settled by German traders. Initially there were three separate cities:
- Altstadt(Old Town) around theAlter Markt(Old Market), which hadSt. Petri(St. Peter's Church),
- Mittelstadt(Middle Town) around theNeuer Markt(New Market), with St. Marien (St. Mary's Church) and

- Neustadt(New Town) around theHopfenmarkt(Hop Market, now University Square), with St. Jakobi (St. James's Church, demolished after World War II).
In 1218, Rostock was grantedLübeck lawcity rights byHeinrich Borwin,prince of Mecklenburg.
Hanseatic League[edit]

During thefirst partition of Mecklenburgfollowing the death ofHenry Borwin II of Mecklenburgin 1226, Rostock became the seat of theLordship of Rostock,which survived for almost a century. In 1251, the city became a member of theHanseatic League.In the 14th century it was a powerful seaport town with 12,000 inhabitants and the largest city inMecklenburg.Shipsfor cruising theBaltic Seawere constructed in Rostock. The formerly independent fishing village ofWarnemündeat the Baltic Sea became a part of Rostock in 1323, to secure the city's access to the sea.
In 1419, theUniversity of Rostockwas founded, the oldest university in continental northern Europe and theBaltic Seaarea.
15th to 18th centuries[edit]


At the end of the 15th century, the dukes ofMecklenburgsucceeded in enforcing their rule over the town of Rostock, which had until then been only nominally subject to their rule and essentially independent. They took advantage of a riot known asDomfehde,a failed uprising of theimpoverishedpopulation. Subsequent quarrels with the dukes and persistent plundering led ultimately to a loss of the city's economic and political power.

In 1565 there were further clashes with Schwerin that had far-reaching consequences. Among other things, the nobility introduced a beerexcisethat favoured the dukes.John Albert Iadvanced on the city with 500 horsemen, after Rostock had refused to take the formal oath of allegiance, and had the city wall razed (slighted) to have a fortress built. The conflict did not end until the firstRostock Inheritance Agreementof 21 September 1573, in which the state princes were guaranteed hereditary rule over the city for centuries and recognizing them as the supreme judicial authority; this bound Rostock for a long time. The citizens razed (or slighted) the fortress the following spring.
From 1575 to 1577 the city walls were rebuilt, as was theLagebuschtower and theSteinGate, in the Dutch Renaissance style. The inscriptionsit intra te concordia et publica felicitas( "Let there be harmony and public happiness within you" ), can still be read on the gate, and refers directly to the conflict with the Duke. In 1584 the Second Rostock Inheritance Agreement was enforced, which resulted in a further loss of former city tax privileges. At the same time, these inheritance contracts put paid to Rostock's ambition of achievingimperial immediacy,asLübeckhad done in 1226.
The strategic location of Rostock provoked the envy of its rivals.Danesand Swedes occupied the city twice, first during theThirty Years' War(1618–48) and again from 1700 to 1721. Later in the early 19th century, theFrench,underNapoleon,occupied the town for about a decade until 1813. In nearbyLübeck-Ratekau,Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher,who was born in Rostock and who was one of few generals to fight on after defeat at theBattle of Jena,surrendered to the French in 1806. This was only after furious street fighting in theBattle of Lübeck,in which he led some of thecavalry chargeshimself. By the time of the surrender, the exhaustedPrussianshad neither food nor ammunition.
19th century[edit]

In the first half of the 19th century, Rostock regained much of its economic importance, due at first to the wheat trade, then, from the 1850s, to industry, especially its shipyards. The first propeller-driven steamers in Germany were constructed here.
The city grew in area and population, with new quarters developing in the south and west of the ancient borders of the city. Two notable developments were added to house the increasing population at around 1900:
- Steintor-Vorstadtin the south, stretching from the old city wall to the facilities of the newLloydbahnhof(Lloyd Railway Station, nowRostock Hauptbahnhof), was designed as a living quarter. It consisted mostly of large single houses, once inhabited by wealthy citizens.
- Kröpeliner-Tor-Vorstadtin the west, was designed to house the working population as well as to provide smaller and larger industrial facilities, such as the Mahn & Ohlerich's Brewery (now Hanseatische Brauerei Rostock). The main shipyard,Neptun,was nearby at the shore of the river.
20th century[edit]
In the 20th century, important aircraft manufacturing facilities were situated in the city, such as theArado FlugzeugwerkeinWarnemündeand theHeinkelWorks with facilities at various places, including their secondaryHeinkel-Südfacility in Schwechat, Austria,as the original Heinkel firm's Rostock facilities had been renamedHeinkel-Nord.The world's firstairworthy jet plane prototypemade its test flights at their facilities in what used to be named theRostock-Marieneheneighborhood (today'sRostock-Schmarlcommunity, along the west bank of theUnterwarnowestuary).
In the early 1930s, the Nazi Party gained in popularity among Rostock's voters, many of whom had suffered economic hardship during the 1920s. Inelectionsin the summer of 1932, when the Nazis achieved 37.3 percent, their greatest national showing in a free election, they polled 40.3 percent in Rostock. A year later, after theNazi seizure of powerand the suppression of other political parties, the Rostock city council (Stadtrat) was composed entirely of Nazis. DuringKristallnachton 10 November 1938, the synagogue in Rostock's Augustenstrasse was destroyed by arson and dozens of Jews were beaten and imprisoned.
Feverish rearmament by the Nazi regime boosted Rostock's industrial importance in the late 1930s, and employment soared at theHeinkelandAradofactories, and at the Neptunwerft shipyard. The city's population grew from 100,000 in 1935 to 121,192 in 1939.
DuringWorld War II,Rostock was subjected to repeated and increasingly heavy bombing attacks, especially by the BritishRoyal Air Force.Targets included the Heinkel and Arado plants and the shipyard, but churches and other historic structures in the city centre were also heavily damaged, among them the 14th-century Nikolaikirche (St Nicholas Church) and Jakobikirche (St Jacob's Church). The ruins of the latter were pulled down in 1960.
The city was eventually captured by the Soviet2nd Belorussian Fronton 2 May 1945 during theStettin-Rostock offensive operation.
After the war, Rostock – now in theGerman Democratic Republic– became East Germany's largest seaport. The state expanded the national shipyards in the district ofWarnemünde.The city's population, boosted in part by resettled ethnic German refugees who had been expelled from territories in the east, increased in the GDR years to a peak of 260,000. Following thereunificationof Germany in 1990, Rostock lost its privileged position as the No. 1 port of the GDR, and the city's population declined to about 200,000. However, after 2006, the population increased again. Today, Rostock and Warnemünde are significant tourist destinations on the Baltic Sea.
Since the late 20th century migrants have come to Germany from Turkey and Africa seeking work. In response to high rates of joblessness and increased levels of crime, some Germans took part in theRostock-Lichtenhagen riotswhich occurred from 22 to 24 August 1992.
-
Depiction of Rostock in 1845
-
Rostock bomb damage, 1942
-
City hall, Market Square after war
-
Rostock in 2011
-
The 16th-centurySteintorcity gate
-
St. Mary's Church (Marienkirche), 2011
Population[edit]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1378 | 10,785 | — |
| 1773 | 9,000 | −16.6% |
| 1871 | 30,980 | +244.2% |
| 1900 | 54,713 | +76.6% |
| 1910 | 65,383 | +19.5% |
| 1919 | 67,953 | +3.9% |
| 1925 | 77,669 | +14.3% |
| 1933 | 90,150 | +16.1% |
| 1935 | 104,585 | +16.0% |
| 1939 | 121,315 | +16.0% |
| 1950 | 133,109 | +9.7% |
| 1955 | 150,004 | +12.7% |
| 1960 | 158,630 | +5.8% |
| 1965 | 184,204 | +16.1% |
| 1970 | 198,636 | +7.8% |
| 1975 | 213,475 | +7.5% |
| 1980 | 232,506 | +8.9% |
| 1985 | 244,444 | +5.1% |
| 1990 | 248,088 | +1.5% |
| 1995 | 227,535 | −8.3% |
| 2000 | 200,506 | −11.9% |
| 2005 | 199,288 | −0.6% |
| 2010 | 202,735 | +1.7% |
| 2015 | 206,011 | +1.6% |
| 2019 | 209,191 | +1.5% |
| Population size may be affected by changes in administrative divisions.[2][circular reference] | ||
Rostock has a population of about 210,000 people and is the largest city inMecklenburg-Vorpommernstate. Rostock became a member ofHanseatic Leaguein 15th century, which made Rostock a larger city. Rostock reached its peak of over 100,000 in 1935. In theEast Germanyera, Rostock was the largest and most important port of East Germany where many sailors and boatmen moved to this city. It also brought many harbour and other industiries to Rostock. Rostock reached its historical peak of population in 1988 with population of about 254,000. After theGerman Reunification,population Rostock decline due to many people who moved to former West Germany. Since 2003, Rostock's population starts to grow again due to students and new companies.
| Rank | Nationality | Population (31.12.2022) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2,816 | |
| 2 | 2,439 | |
| 3 | 1,574 | |
| 4 | 1,382 | |
| 5 | 1,033 | |
| 6 | 794 | |
| 7 | 714 | |
| 8 | 545 | |
| 9 | 465 | |
| 10 | 385 |
Politics[edit]
Districts[edit]
Symbols[edit]


Rostock has had three different coats of arms, known as theSignum,theSecretumand theSigillum.The Signum, which can be traced back to 1367, was developed last and is to this day the coat of arms of the city.
The Signum depicts a goldengriffinon a blue background, with bars of silver and red, the colours of theHanseatic League,below. It can be seen not only on flags and houses, and at bus stops, but also on bridges, gullies, fences, ships and restaurants.
Administration[edit]

Since the 13th century, the governing body of the city has been the city council (Rat), first consisting of ten, later of 24 electedaldermen(Ratsherren). The chairman of the city council was the city mayor. In the 19th century there were three mayors. Since 1925, the head of the city has borne the title ofLord Mayor.Having been elected by the city council for centuries, since 2002 this position is now elected directly by the citizens of Rostock, following a reform. If a candidate does not achieve an absolute majority in the first round, the two candidates with the most votes stand in a second round.
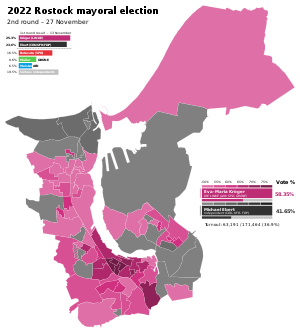
The current Lord Mayor of Rostock is Eva-Maria Kröger ofThe Left,who was elected mayor in 2022 and took office on 1 February 2023.[3]She won in the second round with 58.4% of votes against senior police officer Michael Ebert, anindependentbacked by theChristian Democratic Union,Independent Citizens for Rostock, andFree Democratic Party.[4]
The most recent mayoral election was held on 13 November 2022, with a runoff held on 27 November, and the results were as follows:
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Eva-Maria Kröger | The Left | 18,885 | 25.3 | 36,546 | 58.4 | |
| Michael Ebert | Independent(CDU/UFR/FDP) | 17,598 | 23.6 | 26,082 | 41.6 | |
| Carmen-Alina Botezatu | Social Democratic Party | 12,339 | 16.5 | |||
| Claudia Müller | Alliance 90/The Greens | 6,414 | 8.6 | |||
| Michael Meister | Alternative for Germany | 4,812 | 6.5 | |||
| Jörg Kibellus | Independent | 3,836 | 5.1 | |||
| Jens Kaufmann | Independent | 3,007 | 4.0 | |||
| Robert Uhde | Independent | 1,807 | 2.4 | |||
| Karol Langnickel | Independent | 1,442 | 1.9 | |||
| Holger Luckstein | Independent | 1,182 | 1.6 | |||
| Niels Burmeister | Independent | 1,109 | 1.5 | |||
| Rebecca Thoß | German Beer Drinkers Union | 669 | 0.9 | |||
| Niklas Zimathis | Independent | 453 | 0.6 | |||
| Roland Ulrich | Independent | 369 | 0.5 | |||
| Matthias Bräuer | Independent | 312 | 0.4 | |||
| Kai Oppermann | Independent | 196 | 0.3 | |||
| Alina Kreis | Independent | 155 | 0.2 | |||
| Valid votes | 71,585 | 99.4 | 62,628 | 99.1 | ||
| Invalid votes | 476 | 0.6 | 563 | 0.9 | ||
| Total | 75,061 | 100.0 | 63,191 | 100.0 | ||
| Electorate/voter turnout | 171,884 | 43.7 | 171,464 | 36.9 | ||
| Source: City of Rostock (1st round,2nd round) | ||||||


The city parliament (Bürgerschaft) represents the citizens. Representative are elected for five years. The number of representatives is currently 53. The city parliament is presided by thePräsident der Bürgerschaft,who heads and prepares the sessions and, together with the Lord Mayor, represents the city. The most recent city council election was held on 26 May 2019, and the results were as follows:
| Party | Votes | % | +/- | Seats | +/- | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Left(Die Linke) | 58,405 | 19.9 | 11 | |||
| Alliance 90/The Greens(Grüne) | 55,616 | 19.0 | 10 | |||
| Christian Democratic Union(CDU) | 42,422 | 14.5 | 8 | |||
| Social Democratic Party(SPD) | 42,269 | 14.4 | 8 | |||
| Alternative for Germany(AfD) | 28,294 | 9.6 | 5 | |||
| Independent Citizens for Rostock (UFR) | 21,483 | 7.3 | 4 | ±0 | ||
| Rostock Alliance (RB) | 12,086 | 4.1 | 2 | |||
| Free Democratic Party(FDP) | 9,645 | 3.3 | 2 | |||
| Die PARTEI(PARTEI) | 7,373 | 2.5 | New | 1 | New | |
| Free Voters(FW) | 3,790 | 1.3 | New | 1 | New | |
| New Start 09 (A'09) | 2,897 | 1.0 | 1 | ±0 | ||
| The Grays - For All Generations (Graue) | 1,869 | 0.6 | 0 | |||
| Pirate Party Germany(Piraten) | 1,714 | 0.6 | New | 0 | New | |
| National Democratic Party(NPD) | 1,633 | 0.6 | 0 | |||
| Independents | 3,779 | 1.3 | 0 | ±0 | ||
| Valid votes | 293,275 | 98.6 | ||||
| Invalid votes | 4,179 | 1.4 | ||||
| Total | 102,304 | 100.0 | 53 | ±0 | ||
| Electorate/voter turnout | 173,650 | 58.9 | ||||
| Source:City of Rostock | ||||||

Regiopolis Rostock[edit]
Rostock is the first city region that defines itself not only as a city in its boundaries, but as aregiopolis,with a supra-regional sphere of influence. A regiopolis can be compared to ametropolis,but on a smaller scale. This is a sign for the inter-regional cooperation and economic dynamics that can be found in the Rostock area. A taskforce with different actors such as the hanseatic city of Rostock, the administrativedistrict of Rostock,theRegional Planning Association Middle Mecklenburg/Rostockand the local business organisations are working on the promotion and advancement of the concept.[5]
Geography[edit]
Geographic location[edit]
Rostock is located nearly centrally onMecklenburg-Vorpommern'sBaltic Seacoast. The city is crossed by theWarnow.
The seaside part of Rostock, Rostock-Warnemünde,is about 16 km (10 mi) to the north of the historic city centre. The west and the southeast are the most densely populated parts of town. The overseas port is to the east of Rostock. Rostock stretches 21.6 km (13.4 mi) from theBaltic Seato the south and 19.4 km (12.1 mi) from east to west.
Climate[edit]
Rostock has anoceanic climate(Köppen:Cfb) with strong influence of theBaltic Sea,more similar toDenmarkand far southernSwedenthan to the rest of Germany. The main difference with lower Scandinavia is that the continuous landmass to the south and east enables stronger bursts of heat during summer. In spite of this, theWarnemündestation is generally less warm on the average summer day than on the northern side of the sea. In addition, the maritime influence of the Baltic Sea tempers any Arctic blasts, ensuring slightly milder winters. The Warnemünde station is located on the open sea and thus has a stronger maritime influence and slightly smaller variations than the downtown that is further inland.
| Climate data for Rostock (Warnemünde), 1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.0 (57.2) |
17.0 (62.6) |
22.3 (72.1) |
29.5 (85.1) |
32.8 (91.0) |
35.0 (95.0) |
35.5 (95.9) |
36.9 (98.4) |
32.4 (90.3) |
26.1 (79.0) |
19.5 (67.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
36.9 (98.4) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 10.1 (50.2) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.7 (60.3) |
22.0 (71.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
28.9 (84.0) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.6 (87.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
10.7 (51.3) |
32.5 (90.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.8) |
4.4 (39.9) |
7.3 (45.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
19.7 (67.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
8.0 (46.4) |
4.9 (40.8) |
12.7 (54.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.9 (35.4) |
2.2 (36.0) |
4.4 (39.9) |
8.4 (47.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.4 (65.1) |
15.0 (59.0) |
10.5 (50.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
3.0 (37.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −0.2 (31.6) |
0.1 (32.2) |
1.8 (35.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
9.0 (48.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
15.0 (59.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
1.1 (34.0) |
6.9 (44.4) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | −7.7 (18.1) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
0.4 (32.7) |
4.3 (39.7) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
11.1 (52.0) |
7.7 (45.9) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.8 (0.0) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
−15.1 (4.8) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
0.0 (32.0) |
2.5 (36.5) |
7.3 (45.1) |
6.5 (43.7) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
−15.6 (3.9) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
| Averageprecipitationmm (inches) | 46.2 (1.82) |
38.2 (1.50) |
39.2 (1.54) |
34.2 (1.35) |
49.7 (1.96) |
67.8 (2.67) |
69.8 (2.75) |
68.5 (2.70) |
56.1 (2.21) |
48.1 (1.89) |
45.7 (1.80) |
50.9 (2.00) |
614.3 (24.19) |
| Average precipitation days(≥ 1.0 mm) | 16.6 | 14.8 | 13.5 | 11.3 | 12.5 | 13.5 | 14.0 | 14.8 | 13.4 | 15.1 | 15.9 | 17.4 | 171.9 |
| Average snowy days(≥ 1.0 cm) | 5.9 | 6.0 | 3.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 19.4 |
| Averagerelative humidity(%) | 84.5 | 82.1 | 79.1 | 74.4 | 74.4 | 74.2 | 74.7 | 74.8 | 77.4 | 80.7 | 84.5 | 85.5 | 78.9 |
| Mean monthlysunshine hours | 49.2 | 67.7 | 133.3 | 207.8 | 260.3 | 250.4 | 252.1 | 224.8 | 168.7 | 109.1 | 53.6 | 37.1 | 1,813.9 |
| Source 1:World Meteorological Organization[6] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Météo Climat[7][8]Infoclimat[9] | |||||||||||||
Main sights[edit]
Rostock[edit]


One of the most picturesque places in Rostock is theNeuer Markt(New Market Square), with the Town Hall – that was originally built in the 13th century inBrick Gothicstyle, but extensively transformed in the 18th century, with the addition of aBaroquefaçade and a banqueting hall. The square also preserved six original, carefully restored gable houses from the 15th and 16th centuries. The other historical houses in Hanseatic style that once bordered the square were destroyed in an Allied air-raid in 1942, and rebuilt in a simplified manner.[10]
The 15th-centuryKerkhofhaus(at Große Wasserstraße, behind the Town Hall) is considered the best-preserved brick Gothic house in Rostock.[citation needed]
St. Mary's ChurchMarienkirche,on Ziegenmarkt, is an imposingBrick Gothicchurch. Built in the 13th century, it was enlarged and modified at the end of the 14th century into the present cross-shaped basilica. The huge tower was not completed until the end of the 18th century. Inside there is anastronomical clockerected in 1472 by Hans Düringer.

The main pedestrian precinct isKröpeliner Straße,which runs east from the Neuer Markt to the 14th-centuryKröpeliner Tor,a former town gate. The main buildings ofRostock Universitylie at Universitätsplatz, near the middle of the street, in front of the lively fountain ofzest for life (Brunnen der Lebensfreude),known colloquially as Pornobrunn (fountain of pornography), for its nude sculptures.
TheKloster St Katharinen(Convent of St. Catherine), is an oldFranciscanmonasteryfounded in 1243, and extended several times during the 14th and 15th centuries. Now used as the seat of the Academy of Music and Theatre (HMT-Rostock).
The Brick GothicNikolaikirche(St. Nicholas Church), which is the oldest church in Rostock, was built in the mid-13th century. Heavily damaged duringWorld War IIand subsequently restored, the building is now used as an exhibition centre and concert hall, due to its outstanding acoustics.
Some parts of the medievalcity wall,with fourcity gates,have survived to the present day. The city has a large population of herring gulls that squawk loudly most days throughout the year.
Warnemünde[edit]



Warnemündeis the seaside part of Rostock and a major attraction of the city. Locals and tourists alike enjoy the maritime flair of old houses, a large beach, alighthouseand the old fisherman's port.
Economy[edit]
The economy is mainly characterised by maritime industries (especiallyshipbuilding), high-tech industries (IT,biotechnology/life sciences,medical engineering), theUniversity of Rostock,tourismand the service sector. Major companies include:
- Maritime Industry
- Caterpillar Inc.,manufacturer of diesel engines for ships
- Deutsche Seereederei Rostock, transport, cruises, property and tourism holding
- F. Laeisz
- Neptun Werft,shipyard belonging toMeyer Neptun Group
- Nordic Yards Warnemünde, shipyard
- Schiffselektronik Rostock
- Tamsen Maritim shipyard
- AIDA Cruises[11]
- Other engineering
- Nordex SE,a major producer ofwind turbines
- Suzlon,world's 5th largest wind turbine manufacturer
- Liebherr,manufacturer of cranes
- Tourism industry
- AIDA Cruises,German company for cruises
- Scandlines,German-Danish ferry operator (byScandferries Holding)
- Others
- Hanseatische Brauerei Rostock, German brewery belonging to theOetker-Gruppe
- Rostock University Hospital (Universitätsmedizin)
- Yara International,supplier of plant nutrients
Education[edit]

Rostock is home to one of the oldest universities in the world. Founded in 1419, theUniversity of Rostockis the third oldest university in Germany in continuous operation, and one of theoldest universities of the world. It also maintains abotanical garden,theBotanischer Garten Universität Rostock.
The Academy of Music and Theatre (Hochschule für Musik und Theater) offers graduate degrees in artistic fields. Founded in 1994, the institution combinedErnst Busch,the former drama school, and the outpost school of theHanns Eisler Music School Berlin.Today, the combined school is a member of the Association of Baltic Academies of Music (ABAM), a union of 17 music conservatories at the Baltic Sea and Israel. Unique in Europe is the postgraduate degree in piano duo performance. The school possesses a large opera stage (Katharinensaal) and two chamber music halls. There are concerts every day throughout the year.
Rostock also hosts theMax Planck Institute for Demographic Researchand the Leibniz Institute for Catalysis, as well as two branches of Fraunhofer Institutes, one for Computer Graphics and one for Large Structures in Production Technology.
Culture[edit]

Theatre[edit]
The municipal theatre is theVolkstheater Rostockwhere theNorddeutsche Philharmonie Rostockplays.
Events[edit]
The city is home to the annualHanse Sailfestival, during which many large sailing ships and museum vessels are brought out to sea, drawing over 1.5 million visitors.
An annual jazz festival,Ostsee-Jazz( "Baltic Sea Jazz" ), takes place in June.
Cinemas[edit]
The Lichtspieltheater Wundervoll is theart housecinema of Rostock. It opened in 1993 and offers a daily programme in two venues, the Metropol and the Frieda 23 with three cinemas. At Frieda 23 is the Institut für neue Medien (IFNM), Rostock's Institute for New Media, which includes a media workshop. Both Liwu and IFNM are active members of theLandesverband Filmkommunikation Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.Special screenings for schools, educational programmes and special programmes are offered as well. It is the central venue for Rostock's Film Festival, the Festival im Stadthafen (FISH), the German Federal Festival for Young German Film.
Museums and zoo[edit]

- Rostock Art Gallery(Kunsthalle Rostock)
- Museum of Cultural History(Kulturhistorisches Museum)
- Stasi Museum (Dokumentations- und Gedenkstätte der Bundesbeauftragten für die Unterlagen des Staatssicherheitsdienstes der ehemaligen Deutschen Demokratischen Republik)
- Warnemünde Local History Museum (Heimatmuseum Warnemünde)
- Shipbuilding and Shipping Museum (Schiffbau- und Schifffahrtsmuseum)
- Rostock Zoo
- Walter Kempowski Archive
- Max-Samuel-Haus,Rostock Jewish Heritage Centre
Food and drink[edit]
Rostock manufactures its own local beer, called Rostocker Pilsner, manufactured at the Hanseatische Brauerei Rostock GmbH (Rostock Hanseatic Brewery Ltd.). The beer is well known throughout the city and is also sold in cities nearby. To celebrate Rostock's 800th birthday, a special light beer called Heller Freude was brewed to commemorate the occasion.
Sport[edit]


| Club | Sport | Founded | League | Venue | Head Coach | Website |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hansa Rostock | Football | 1965 | 2. Bundesliga | Ostseestadion | Alois Schwartz | [1] |
| Rostock Seawolves | Basketball | 1994 | Basketball Bundesliga | Stadthalle Rostock | Christian Held | [2] |
| Rostocker FC 1895 | Football | 1895 | NOFV-Oberliga Nord(5th division) | Sportpark am Damerower Weg | Jan Kistenmacher | [3] |
| HC Empor Rostock | Team handball | 1946 | 3. Bundesliga | Rostocker Stadthalle | Maik Handschke | [4] |
| SV Warnemünde | Volleyball | 1990 | 3rd league (men and women team) | Sporthalle Gerüstbauerring | [5] | |
| Piranhas Rostock | Ice hockey | 1953 | Oberliga(3rd division) | Eishalle Rostock | Henry Thom | [6] |
| Rostocker Nasenbären | Skater hockey | 2005 | Inline-Skaterhockey-Bundesliga (1st league) | OSPA-Arena | Dimitri Kramarenko[12] | [7] |
| HSG Warnemünde | Water polo | 1971 | Oberliga SH-MV (3rd league) | Neptun-Schwimmhalle | [8] |
Transport[edit]



Car[edit]
Rostock can be reached by motorway (Autobahn)A 1fromHamburgviaLübeckonA 20and byA 19fromBerlinand A 20 fromSzczecinin Poland.
Public transport[edit]
Rostock Hauptbahnhofoffers fast rail connections toHamburgandBerlinand from there to almost any other European city.
Rostock is served by theRostock tramway network,with six tram lines that serve the inner city as well as the suburbs. The city is also served by an extensive bus fleet, as well as a handful of ferries that cross the Warnow.
Ferry/ship[edit]
Rostock is Germany's largest Baltic port. Rostock is also home to a large ferry port. It is a main base for ferry operatorsScandlinesandTT-Line,which both connect Rostock with major Scandinavian destinations. Furthermore, Rostock receives the highest number of cruise tourists in Germany every year.
Ferries leave for
- Helsinki,Finland
- Gedser,Denmark
- Trelleborg,Sweden
- Nynäshamn,Sweden
- Visby,Sweden
Air[edit]
TheRostock–Laage Airportoffers connections to major German and international destinations; regular flights to e.g.Munichare offered. The nearest larger international airports are inHamburgandBerlin.There are also a number of airfields for smaller aircraft, such as Purkshof.
Twin towns - sister cities[edit]
 Szczecin,Poland (1957)
Szczecin,Poland (1957) Turku,Finland (1959)
Turku,Finland (1959) Dunkirk,France (1960)
Dunkirk,France (1960) Riga,Latvia (1961)
Riga,Latvia (1961) Antwerp,Belgium (1963)
Antwerp,Belgium (1963) Aarhus,Denmark (1964)
Aarhus,Denmark (1964) Gothenburg,Sweden (1965)
Gothenburg,Sweden (1965) Bergen,Norway (1965)
Bergen,Norway (1965) Rijeka,Croatia (1966)
Rijeka,Croatia (1966) Varna,Bulgaria (1966)
Varna,Bulgaria (1966) Bremen,Germany (1987)
Bremen,Germany (1987) Dalian,China (1988)
Dalian,China (1988) Raleigh,United States (2001)
Raleigh,United States (2001) Guldborgsund,Denmark (2014)
Guldborgsund,Denmark (2014)
Notable people[edit]




Public service & thinking[edit]
- Henry Borwin I, Lord of Mecklenburg(??–1227), Lord of Mecklenburg
- Carl Friedrich Behrens(1701-1750), a German sailor and soldier, landed inEaster Island
- Franz Aepinus(1724–1802), German-Russian natural philosopher.[14]
- Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher(1742–1819), Prussian field marshal.[15]
- Moritz Wiggers(1816–1894), politician, lawyer and notary
- Rudolph Sohm(1841–1917), jurist, Church historian and theologian
- Mathilde Mann(1859–1925), prominent German translator and editor
- Carl Brockelmann(1868–1956),semiticistand orientalist
- Hans Paasche(1881–1920), politician and pacifist
- Ernst Heinkel(1888–1958), aviation pioneer, worked inWarnemünde
- Erika Fuchs(1906–2005), translator
- Duchess Woizlawa Feodora of Mecklenburg(1918–2019), member of the House of Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- Berndt von Staden(1919–2014), diplomat, Ambassador to the United States 1973–1979
- Peter Schulz(1930–2013), politician (SPD) and firstMayor of Hamburg1971–1974
- Klaus Kilimann(born 1938), politician (SPD), physicist and Mayor of Rostock 1990–1993
- Joachim Gauck(born 1940), politician, civil rights activist and President of Germany 2012–2017
- Heinz Eggert(born 1946), theologian and CDU politician
- Eva-Maria Kröger(born 1982), politician, Mayor of Rostock since February 2023.
Science and academia[edit]
- Simon Paulli(1603–1680), Danish physician and naturalist
- Matthias Christian Sprengel(1746–1803), geographer and historian
- Christian Martin Frähn(1782–1851), German-Russian numismatist and historian.[16]
- Sir Ferdinand Jacob Heinrich von Mueller(1825–1896), German-Australian physician, geographer and botanist.[17]
- Clara Wehl(1833–1901), Australian botanist.
- Johann Georg Noel Dragendorff(1836–1898), pharmacist and chemist
- Hermann von Maltzan(1843–1891),malacologist,worked in the field ofconchology
- Albrecht Kossel(1853–1927), biochemist and pioneer in genetics, recipient of 1910Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicinefor determining the chemical composition of nucleic acids
- Paul Walden(1863–1957), Latvian-German chemist, lived and worked in Rostock
- Gustav Mie(1868–1957), physicist, worked on electromagnetic waves
- Karl Leo Heinrich Lehmann(1894–1960), American art historian, archaeologist and professor
- Arthur R. von Hippel(1898–2003), German-American materials scientist and physicist
- Hans von Ohain(1911–1998), physicist and engineer, worked inWarnemünde
- Egbert Brieskorn(1936–2013), mathematician who introducedBrieskorn spheres
- Sibylle Günter(born 1964), theoretical physicist, since 2011 heads theMax Planck Institute for Plasma Physics


The Arts[edit]
- Francis Cleyn(ca.1582 – 1658), painter and tapestry designer.[18]
- Johann Heinrich Bartholomäus Walther(1734–1802), Baltic-German architect, worked inTartu
- John Brinckman(1814–1870), poet and short story writer inLow German
- brothersFriedrich Eggers(1819-1872, art historian &Karl Eggers(1826–1900), lyric poet.
- Paul Tischbein(1820–1874), illustrator and painter primarily of landscapes; part of theTischbein family
- Adolf Wilbrandt(1837–1911), a German novelist and dramatist.[19]
- Edvard Munch(1863–1944), Norwegian painter, lived in Rostock 1907/08.[20]
- Heinrich Tessenow(1876–1950), architect, professor and urban planner
- Paul Wallat(1879–1964), landscape artist, draftsman and sculptor
- Margarete Scheel(1881–1969), artist, specializing in sculpture and ceramics
- Bruno Gimpel, (DE Wiki)(1886–1943), painter and illustrator.
- Egon Tschirch(1889–1948), painter and illustrator.
- Dörte Helm(1898–1941),Bauhausartist, painter and graphic designer.
- Jessie Rindom(1903–1981), a Danish film actress.
- Marianne Hoppe(1909–2002), actress
- Peter Borgelt(1927–1994), actor
- Jo Jastram(1928–2011), sculptor
- Walter Kempowski(1929–2007), writer
- Erik Smith(1931–2004), British record producer, pianist and harpsichordist.
- Mario Frank(born 1958), writer, CEO ofDer Spiegel2007/8; now a political biographer
- Franziska Knuppe(born 1974), fashion model
- Hinnerk Schönemann(born 1974), actor
- Marteria(born 1982), hip hop artist

Sports[edit]
- Friedrich Wilhelm Rahe(1888–1949), tennis and field hockey player
- Siegfried Brietzke(born 1952), a German rower and Olympic team gold medallist
- Hansjörg Kunze(born 1959), track and field athlete, bronze medallist at the1988 Summer Olympics
- Frank Rohde(born 1960), footballer and coach, played over 250 games and 42 forEast Germany
- Martina Proeber(born 1963), diver, silver medallist at the1980 Summer Olympics
- Christian Schenk(born 1965), decathlete, gold medallist at the1988 Summer Olympics
- Ramona Portwich(born 1967), canoe sprinter and multiple team medallist at three Summer Olympics
- Andreas Tews(born 1968), flyweight boxer, won two medals at two Summer Olympics
- Jörn Lenz(born 1969), footballer who played over 430 games
- Jan Quast(born 1970), light flyweight boxer, bronze medallist at the1992 Summer Olympics
- Steffen Baumgart(born 1972), football manager and former player who played 535 games
- Rolf Kohnert(born 1938), cyclist, 3 times Australian Masters Champion
- Jan Ullrich(born 1973), cyclist,Tour de Francewinner, won two medals at the2000 Summer Olympics
- Dörte Lindner(born 1974), diver, bronze medallist at the2000 Summer Olympics
- Annika Walter(born 1975), diver silver medallist at the1996 Summer Olympics
- Britta Kamrau(born 1979), long-distance swimmer
- André Greipel(born 1982), road bicycle racer
- Jennifer Zietz(born 1983), footballer, played 278 games and 15 for Germany women
- Hannes Ocik(born 1991), rower, three-time world champion, twice an Olympic team silver medallist
Notes[edit]
- ^Closest border point with Pomerania from Rostock inRibnitz-Damgartenbetween Ribnitz (Mecklenburg) and Damgarten (Pomerania). Border constituted byRiver Recknitz.
References[edit]
- ^"Bevölkerungsstand der Kreise, Ämter und Gemeinden 2022"(XLS)(in German).Statistisches Amt Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.2023.
- ^Link
- ^"Rostock: New Mayor Eva-Maria Kröger takes office".Norddeutscher Rundfunk(in German). 1 February 2023.
- ^"Left's Eva-Maria Kröger becomes the new mayor of Rostock".Der Spiegel(in German). 27 November 2022.
- ^Regiopole RostockArchived26 April 2014 at theWayback Machine(German)
- ^"World Meteorological Organization Climate Normals for 1991–2020".World Meteorological Organization Climatological Standard Normals (1991–2020).National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived fromthe originalon 12 October 2023.Retrieved12 October2023.
- ^"Climate normals for Germany 1981–2010"(in French). Météo Climat.Retrieved15 January2019.
- ^"Weather extremes for Rostock"(in French). Météo Climat.Retrieved15 January2019.
- ^"Climatologie de l'année à Rostock-Warnemuende"(in French). Infoclimat.Retrieved18 October2023.
- ^Bomben auf Rostock; H.-W. Bohl, B. Keipke, k. Schröder; Konrad Reich Verlag 1995
- ^"Impressum".AIDA Cruises.Retrieved14 June2023.
- ^"Verein Rostock - Die Nasenbaeren - Der Hockey Verein Rostocks".rostocker-nasenbaeren.de.
- ^"Partnerstädte".rathaus.rostock.de(in German). Rostock.
- ^.Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 1 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 258.
- ^.Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 4 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 90.
- ^.Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 10 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 773.
- ^.Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 18 (11th ed.). 1911.
- ^Cust, Lionel(1887)..Dictionary of National Biography.Vol. 11. pp. 26–27.
- ^.Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 28 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 631–632.
- ^"Munch Haus".rostock.de(in German).Retrieved23 April2023.
Bibliography[edit]
See also[edit]
External links[edit]
- Official Website
- Official tourism site
- European Route of Brick Gothic: Rostock
- .Encyclopædia Britannica.Vol. 23 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 754.
- Cities in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
- Rostock
- Cities and towns in Mecklenburg
- Denmark–Germany border crossings
- Members of the Hanseatic League
- Port cities and towns in Germany
- Port cities and towns of the Baltic Sea
- Populated coastal places in Germany (Baltic Sea)
- 1218 establishments in Europe
- Populated places established in the 11th century
- Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- Holocaust locations in Germany
- Urban districts of Germany