Oi language
Appearance
(Redirected fromSok language)
| Oy | |
|---|---|
| The | |
| Native to | Laos |
| Ethnicity | Oy, Jeng, Sok, Sapuan |
Native speakers | 24,000 (2015 census)[1] plus 8,000 Sok, Sapuan and Jeng (1981–2007)[2][3] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:oyb– Oyspu–Sapuan |
| Glottolog | oyyy1238Oysapu1247Sapuan–Sokjeng1241Jeng |
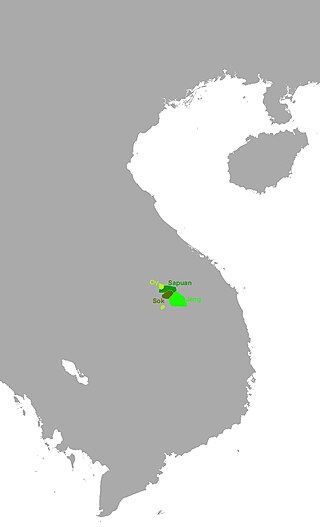 | |
Oi(Oy, Oey;[4]also known asThe,Thang Ong,Sok) is anAustroasiaticdialect clusterofAttapeu Province,southernLaos.The dominant variety is Oy proper, with 11,000 speakers who are 80% monolinguals. The Jeng (Cheng) speak the same language but are ethnically distinct (Sidwell 2003). Speakers follow traditional religions.[1]
Distribution
[edit]Some locations where Oi is spoken in include (Sidwell 2003:26):
- Ban Sok, 40 km north ofAttapeu
- Ban Lagnao, 10 km northwest ofAttapeu
- Ban Inthi, 25 km southwest ofAttapeu;speakers claim to have migrated from theBolaven Plateauabout 80 years ago, around the time of theOng KommandamRebellion.
- Ban Mai, at the southern slope of the Bolaven Plateau
- Ban Champao, at the southern slope of the Bolaven Plateau
- Sepian forest, as far as the Khampo River
The Jeng live mostly along the banks of the Sekaman River, in and around Ban Fandeng (Phandɛŋ).
According to Daniell (2020), there are about 20 Oy villages inAttapeu Province,Laos. The following villages are ordered roughly from west to east, and are located along or near theSekong River,in an area ofAttapeu Provinceto the west ofAttapeuTown.[5]
|
|
References
[edit]- ^abOyatEthnologue(18th ed., 2015)(subscription required)
SapuanatEthnologue(18th ed., 2015)(subscription required) - ^SokatEthnologue(18th ed., 2015)(subscription required)
- ^JengatEthnologue(18th ed., 2015)(subscription required)
- ^"Mon-Khmer Classification (draft)".Retrieved24 June2016.
- ^Daniell, Jennifer. 2020.Phonological Variation in Oy: A Comparison of Four Varieties.M.A. dissertation. Chiang Mai: Payap University.
External links
[edit]- Sidwell, Paul (2003).A Handbook of comparative Bahnaric, Vol. 1: West Bahnaric.Pacific Linguistics, 551. Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University.
- http://projekt.ht.lu.se/rwaaiRWAAI (Repository and Workspace for Austroasiatic Intangible Heritage)
- http://hdl.handle.net/10050/00-0000-0000-0003-903F-3@viewOi in RWAAI Digital Archive
- http://hdl.handle.net/10050/00-0000-0000-0003-9041-C@viewSapuar in RWAAI Digital Archive
