Telephone numbers in Europe
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(August 2014) |
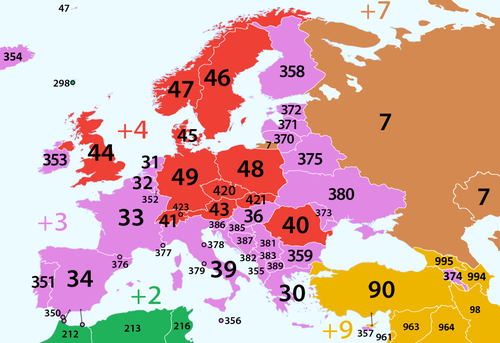
Telephone numbers in Europeare managed by the national telecommunications authorities of each country. Mostcountry codesstart with3and4,but some countries that by theCopenhagen criteriaare considered part of Europe have country codes starting on numbers most common outside of Europe (e.g. Faroe Islands ofDenmarkhave a code starting on number 2, which is most common in Africa).
Theinternational access code(dial out code) has been standardized as00,as recommended by theInternational Telecommunication Union(ITU).
European Economic Area
[edit]| Country | Country code | National number length | Dialing plan* | International access code | National trunk prefix | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 4 to 13 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 32 | 8 to 10 | fixed with 0 | 00 | 0 | |||
| 359 | 7 to 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 385 | 8 or 9 (some mobile) | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 357 | 8 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 420 | 9 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 45 | 8 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 372 | 7 (fixed or mobile), 8 (mobile) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 358 | 5 to 12 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 33 | 9 | fixed with 0 | 00 | 0 | |||
| 49 | 3 to 12 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 30 | 4 to 5 (company numbers) 10 (fixed and mobile) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 36 | 8 (landline) or 9 (mobile) | variable | 00 | 06 | |||
| 354 | 7 (mobile and landline) or 9 (for 3xxxxxxxx) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 353 | 7 to 9; 10 (mobile voicemail and Northern Ireland) | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 39 | 6 to 12 (generally 10) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 371 | 8 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 423 | up to 12 (generally is 7) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 370 | 8 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 352 | 8 (fixed new numbering plan); 9 (mobile); 12 (mobile telematic); 4-11 (historic numbers still active)[1] | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 356 | 8 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 31 | 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 47 | 4-12 (generally 8) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 48 | 9 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 351 | 9 | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 40 | 9 | fixed with 0 | 00 | 0 | |||
| 421 | 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 386 | 8 | variable | 00 | 0 | |||
| 34 | 9 (3 for emergency services, 4 for phone companies, 5 and starting with 118 for telephonic information, 6 and starting with 116 for social interest and 5 or 6 with starting with other numbers that are not listed before for premium services) | fixed | 00 | – | |||
| 46 | 6 to 9 | 00 | 0 | ||||
| All European Economic Area member states apply theEuropean Union roaming regulations.The regulation eventually led to the abolition of all roaming charges for temporary roaming when traveling within the EEA as of June 15, 2017. TheEuropean Union international calls regulationsregulate prices of calls (and text messages) when calling from your home country to anotherEEAcountry. | |||||||
Other European countries/territories
[edit]| Country | Country code | National number length | Dialing plan | International access code | National trunk prefix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 840 (landline) / 7 940 (mobile) | 7 | variable | 8~10 | 8 | |
| 355 | 8 (fixed), 9 (mobile) | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 376 | 6 or 9 (in special cases) | fixed | 00 | – | |
| 374 | 8 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 375 | 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 387 | 8 to 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 298 | 6 | fixed | 00 | – | |
| 995 | 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 350 | 8 | fixed | 00 | – | |
| 383 | 8 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 389 | 8 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 373 | 8 | fixed with 0[2] | 00 | 0 | |
| 377 | 8 to 9 | fixed (?) | 00 | – | |
| 382 | 8 | fixed | 00 | 0 | |
| 7 (shared with Kazakhstan) | 10 | variable | 8~10 | 8 | |
| 378 | 6 to 12 | fixed | 00 | – | |
| 381 | 8 to 10 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 7 850 (fixed), 7 929 (mobile) | 5 to 7 | variable | 8~10 | 8 | |
| 41 | 9 | fixed with 0 | 00 | 0 | |
| 373 5 / 373 2 (Moldova codes used) | 7 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 90 | 10 | fixed | 00 | 0 | |
| 90 392 (fixed), 90 533 / 90 542 (mobile) | 7 | fixed | 00 | 0 | |
| 44 | 9 or 10 digits (geographic); 7, 9 or 10 (non-geographic) | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 380 | 9 | variable | 00 | 0 | |
| 379 (not activated) |
† = Disputed state, may not be recognized as an independent state by some or all European Union members.
*A variable dialing plan has different dialing procedures for local and long-distance telephone calls. A call within the same city or within an area is dialed only by the subscriber number, while for calls outside the area, the telephone number must be prefixed with the destination area code. A fixed dialing plan requires to dial all digits of the complete telephone number, including any area codes.
Harmonized service numbers
[edit]The following service numbers are harmonized across the European Union:
- 112foremergency services[5][6]
- 116xxxfor (other)harmonized services of social value
Single numbering plan (1996 proposal)
[edit]In 1996, theEuropean Commissionproposed the introduction of a single telephone numbering plan, in which allEuropean Unionmember states would use the country code 3. Calls between member states would no longer require the international access code 00. Instead the digit 1 was proposed for these calls, replaced by the country code 3 for calls from outside the EU. Each country would have a two-digit country code after the 1 or the 3. Calls within each country would not be affected.
This proposal would have required states such as Germany, the United Kingdom, Denmark and others, whose country codes began with the digit '4', to return these to theInternational Telecommunication Union.
A Green Paper on the proposal was published, but the disruption and inconvenience of the change was deemed to outweigh any advantages.
A disadvantage would have been that every local number beginning with "1" would have had to be changed (except emergency number which would be kept).
Another disadvantage would be that people wanting to call France (e.g.Southeast France using +33 4...) using an old number would connect another country like Spain, or people wanting to callSpain(e.g. +34 9...) would end up in e.g. Germany if they use an old number.
The EU proposal should not be confused with theEuropean Telephony Numbering Space(ETNS), which uses the country code 388, and was intended to complement, rather than replace, existing national numbering plans.
See also
[edit]- Telephone numbering plan
- National conventions for writing telephone numbers
- European Union roaming regulations
- List of country calling codes
- List of international call prefixes
- Category:Telephone numbers by country
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^"E.164 Number Ranges in use in Luxembourg"(PDF).Institut Luxembourgeois de Régulation.October 2017.
- ^"Moldova Switches over to" Closed "Type Numbering Plan for Fixed Telephone Subscribers | ANRCETI".
- ^"Абонентам ДНР и ЛНР выделен телефонный код российской системы нумерации".Rossiyskaya Gazeta(in Russian). 7 May 2022.Retrieved7 May2022.
- ^Petrenko, Roman (7 May 2022)."Russia switches mobile operators of certain areas of occupied territories to its +7 telephone code".Ukrayinska Pravda.Retrieved7 May2022.
- ^"112 – The European emergency number".European Commission – Information Society.Retrieved31 January2011.
- ^"SOS 112 Europe".Retrieved31 January2011.
