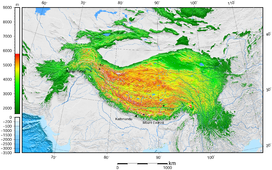
Tibetan Plateau
| Tibetan Plateau | |
|---|---|
| Cao nguyên Thanh Tạng(Qīng–Zàng Gāoyuán,Qinghai–Tibet Plateau) | |
 The Tibetan Plateau lies between theHimalayanrange to the south and theTaklamakan Desertto the north. (Composite image) | |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 2,500 km (1,600 mi) |
| Width | 1,000 km (620 mi) |
| Area | 2,500,000 km2(970,000 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
| Location | |
| Range coordinates | 33°N88°E/ 33°N 88°E |
 | |
TheTibetan Plateau,[a]also known asQinghai–Tibet Plateau[b]andQing–Zang Plateau,[c]is a vast elevatedplateaulocated at the intersection ofCentral,South,andEast Asia[d]covering most of theTibet Autonomous Region,most ofQinghai,western half ofSichuan,SouthernGansuprovinces inWestern China,southernXin gian g,Bhutan,theIndian regionsofLadakhandLahaul and Spiti(Himachal Pradesh) as well asGilgit-BaltistaninPakistan,northwesternNepal,easternTajikistanand southernKyrgyzstan.It stretches approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) north to south and 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) east to west. It is the world's highest and largestplateauabove sea level, with an area of 2,500,000 square kilometres (970,000 sq mi) (about five times the size ofMetropolitan France).[13]With an average elevation exceeding 4,500 metres (14,800 ft)[citation needed]and being surrounded by imposingmountain rangesthat harbor the world's two highest summits,Mount EverestandK2,the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "theRoof of the World".
The Tibetan Plateau contains theheadwatersof thedrainage basinsof most of thestreamsandriversin surroundingregions.This includes the three longest rivers inAsia(the Yellow,Yangtze,andMekong). Its tens of thousands ofglaciersand other geographical and ecological features serve as a "water tower"storing water and maintainingflow.It is sometimes termed theThird Polebecause itsice fieldscontain the largest reserve of fresh water outside the polar regions. The impact ofclimate changeon the Tibetan Plateau is of ongoing scientific interest.[14][15][16][17]
Description
[edit]The Tibetan Plateau is surrounded by the massive mountain ranges[18]ofhigh-mountain Asia.The plateau is bordered to the south by theinner Himalayan range,to the north by theKunlun Mountains,which separate it from theTarim Basin,and to the northeast by theQilian Mountains,which separate the plateau from theHexi CorridorandGobi Desert.To the east and southeast the plateau gives way to the forested gorge and ridge geography of the mountainous headwaters of theSalween,Mekong,andYangtzerivers in northwestYunnanand westernSichuan(theHengduan Mountains). In the west, the curve of the ruggedKarakoramrange of northernKashmirembraces the plateau. TheIndus Riveroriginates in the western Tibetan Plateau in the vicinity ofLake Manasarovar.
The Tibetan Plateau is bounded in the north by a broad escarpment where the altitude drops from around 5,000 metres (16,000 ft) to 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) over a horizontal distance of less than 150 kilometres (93 mi). Along the escarpment is a range of mountains. In the west, theKunlun Mountainsseparate the plateau from the Tarim Basin. About halfway across the Tarim the bounding range becomes theAltyn-Taghand the Kunluns, by convention, continue somewhat to the south. In the 'V' formed by this split is the western part of theQaidam Basin.The Altyn-Tagh ends near the Dangjin pass on theDunhuang–Golmudroad. To the west are short ranges called the Danghe, Yema, Shule, and Tulai Nanshans. The easternmost range is the Qilian Mountains. The line of mountains continues east of the plateau as theQinling,which separates theOrdos Plateaufrom Sichuan. North of the mountains runs the Gansu orHexi Corridorwhich was the main silk-road route fromChina properto the West.
The plateau is a high-altitude aridsteppeinterspersed with mountain ranges and largebrackishlakes. Annual precipitation ranges from 100 to 300 millimetres (3.9 to 11.8 in) and falls mainly ashail.The southern and eastern edges of the steppe have grasslands that can sustainably support populations of nomadic herdsmen, although frost occurs for six months of the year.Permafrostoccurs over extensive parts of the plateau. Proceeding to the north and northwest, the plateau becomes progressively higher, colder, and drier, until reaching the remoteChangtangregion in the northwestern part of the plateau. Here the average altitude exceeds 5,000 metres (16,000 ft) and winter temperatures can drop to −40 °C (−40 °F). As a result of this extremely inhospitable environment, the Changtang region (together with the adjoining Kekexili region) is the least populous region in Asia and the third least populous area in the world after Antarctica and northern Greenland.
Geology and geological history
[edit]
This sectionneeds expansion.You can help byadding to it.(January 2011) |
The geological history of the Tibetan Plateau is closely related to that of the Himalayas. The Himalayas belong to theAlpine Orogenyand are therefore among the younger mountain ranges on the planet, consisting mostly of upliftedsedimentaryandmetamorphic rock.Their formation is a result of acontinental collisionororogenyalong theconvergent boundarybetween theIndo-Australian Plateand theEurasian Plate.
The collision began in theUpper Cretaceousperiod about 70 million years ago, when the north-movingIndo-Australian Plate,moving at about 15 cm (6 in) per year, collided with theEurasian Plate.About 50 million years ago, this fast-moving Indo-Australian plate had completely closed theTethys Ocean,the existence of which has been determined bysedimentary rockssettled on the ocean floor, and thevolcanoesthat fringed its edges. Since these sediments were light, they crumpled into mountain ranges rather than sinking to the floor. During this early stage of its formation in the Late Palaeogene, Tibet consisted of a deep palaeovalley bounded by multiple mountain ranges rather than the more topographically uniform elevated flatland that it is today.[20]The Tibetan Plateau's mean elevation continued to vary since its initial uplift in the Eocene; isotopic records show the plateau's altitude was around 3,000 metres above sea level around the Oligocene-Miocene boundary and that it fell by 900 metres between 25.5 and 21.6 million years ago, attributable to tectonic unroofing from east–west extension or to erosion from climatic weathering. The plateau subsequently rose by 500 to 1,000 metres between 21.6 and 20.4 million years ago.[21]

Palaeobotanicalevidence indicates that the Nu gian g Suture Zone and the Yarlung-Zangpo Suture Zone remained tropical or subtropicallowlandsuntil the latestOligoceneorEarly Miocene,enabling biotic interchange across Tibet.[22]The age of east–west grabens in the Lhasa and Himalaya terranes suggests that the plateau's elevation was close to its modern altitude by around 14 to 8 million years ago.[23]Erosion rates in Tibet decreased significantly around 10 million years ago.[24]The Indo-Australian plate continues to be driven horizontally below the Tibetan Plateau, which forces the plateau to move upwards; the plateau is stillrisingat a rate of approximately 5 mm (0.2 in) per year (although erosion reduces the actual increase in height).[25]
Much of the Tibetan Plateau is of relatively low relief. The cause of this is debated among geologists. Some argue that the Tibetan Plateau is an upliftedpeneplainformed at low altitude, while others argue that the low relief stems fromerosionandinfillof topographic depressions that occurred at already high elevations.[26]The current tectonics of the plateau are also debated. The best-regarded explanations are provided by the block model and the alternative continuum model. According to the former, the crust of the plateau is formed of several blocks with little internal deformation separated by majorstrike-slip faults.In the latter, the plateau is affected by distributed deformation resulting from flow within the crust.[27]
Environment
[edit]
The Tibetan Plateau supports a variety of ecosystems, most of them classified asmontanegrasslands. While parts of the plateau feature analpine tundra-like environment, other areas feature monsoon-influenced shrublands and forests.Species diversityis generally reduced on the plateau due to the elevation and low precipitation. The Tibetan Plateau hosts theTibetan wolf,[28]and species ofsnow leopard,wild yak,wild ass,cranes, vultures, hawks, geese, snakes, andwater buffalo.One notable animal is thehigh-altitude jumping spider,that can live at elevations of over 6,500 metres (21,300 ft).[29]
Ecoregionsfound on the Tibetan Plateau, as defined by theWorld Wide Fund for Nature,are as follows:
- ThePamir alpine desert and tundracovers the western end of the Tibetan Plateau where it transitions to thePamir Mountains
- TheNorth Tibetan Plateau–Kunlun Mountains alpine desertcovers the northwestern limits of the Tibetan Plateau along theKunlun Mountains
- TheKarakoram–West Tibetan Plateau alpine steppecovers the westernmost parts of the Tibetan Plateau andLadakh
- TheNorthwestern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadowson the edges mountains bordering the extreme west of the Tibetan Plateau
- TheCentral Tibetan Plateau alpine steppecovers most of the central portions of the Tibetan Plateau and the easternChangtang
- TheWestern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadowscovers the southwestern plateau in theGaruda Valleyregion
- TheQaidam Basin semi-desertlocated in theQaidam Basinon the northern Tibetan Plateau
- TheQilian Mountains subalpine meadowscovering theQilian Mountainsin the northernmost portions of the plateau
- TheQilian Mountains conifer forestscovering parts of the mountain ranges in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau
- TheTibetan Plateau alpine shrublands and meadowscovering a swath of the central and northeastern Tibetan Plateau
- TheYarlung Tsangpo arid steppein theYarlung Tsangporiver Valley, where most of the permanent human population on the Tibetan Plateau lives
- TheEastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadowscover the southern Tibetan Plateau on the north side of theHimalayas

- TheSoutheast Tibet shrub and meadowscover the southeastern and eastern parts of the plateau and are generally rainier than the other high-altitude Tibetan Plateau regions
- TheNortheastern Himalayan subalpine conifer forestsreach up mountain valleys in the southern plateau and contain some of the highest altitude forests in the world
- TheNu gian g Lancang Gorge alpine conifer and mixed forestscover the mountain valleys that reach 500 km (310 mi) into the southeastern Tibetan Plateau
- TheHengduan Mountains subalpine conifer forestscover the southeasternmost mountain valleys on the plateau
- TheQionglai–Minshan conifer forestscover the eastern edges of the plateau and are the densest forests to be found anywhere on the Tibetan Plateau
Human history
[edit]
Extinct humans (Denisovans) lived on the Tibetan plateau from around 200,000 to 40,000 years ago. this is according to a study published inNature.[30]
Nomadson the Tibetan Plateau and in theHimalayasare the remainders of nomadic practices historically once widespread in Asia and Africa.[31]Pastoral nomads constitute about 40% of the ethnicTibetanpopulation.[32]The presence of nomadic peoples on the plateau is predicated on their adaptation to survival on the world'sgrasslandby raising livestock rather than crops, which are unsuitable to the terrain. Archaeological evidence suggests that the earliest human occupation of the plateau occurred between 30,000 and 40,000 years ago.[33]Since colonization of the Tibetan Plateau, Tibetan culture has adapted and flourished in the western, southern, and eastern regions of the plateau. The northern portion, theChangtang,is generally too high and cold to support permanent population.[34]One of the most notable civilizations to have developed on the Tibetan Plateau is theTibetan Empirefrom the 7th century to the 9th century AD.
Impact on other regions
[edit]
Role in monsoons
[edit]Monsoons are caused by the different amplitudes of surface temperature seasonal cycles between land and oceans. This differential warming occurs because heating rates differ between land and water. Ocean heating is distributed vertically through a "mixed layer" that may be 50 meters deep through the action of wind and buoyancy-generatedturbulence,whereas the land surface conducts heat slowly, with the seasonal signal penetrating only a meter or so. Additionally, thespecific heat capacityof liquid water is significantly greater than that of most materials that make up land. Together, these factors mean that the heat capacity of the layer participating in the seasonal cycle is much larger over the oceans than over land, with the consequence that the land warms and cools faster than the ocean. In turn, air over the land warms faster and reaches a higher temperature than does air over the ocean.[35]The warmer air over land tends to rise, creating an area oflow pressure.The pressure anomaly then causes a steady wind to blow toward the land, which brings the moist air over the ocean surface with it. Rainfall is then increased by the presence of the moist ocean air. The rainfall is stimulated by a variety of mechanisms, such as low-level air being lifted upwards by mountains, surface heating, convergence at the surface, divergence aloft, or from storm-produced outflows near the surface. When such lifting occurs, the air cools due to expansion in lower pressure, which in turn producescondensationand precipitation.

In winter, the land cools off quickly, but the ocean maintains the heat longer. The hot air over the ocean rises, creating a low-pressure area and a breeze from land to ocean while a large area of drying high pressure is formed over the land, increased by wintertime cooling.[35]Monsoons are similar tosea and land breezes,a term usually referring to the localized,diurnal cycleof circulation near coastlines everywhere, but they are much larger in scale, stronger and seasonal.[36]The seasonal monsoon wind shift and weather associated with the heating and cooling of the Tibetan plateau is the strongest such monsoon on Earth.
Glaciology: the Ice Age and at present
[edit]

Today, Tibet is an important heating surface of the atmosphere. However, during theLast Glacial Maximum,an approximately 2,400,000 square kilometres (930,000 sq mi) ice sheet covered the plateau.[37][38][39]Due to its great extent, this glaciation in the subtropics was an important element ofradiative forcing.With a much lower latitude, the ice in Tibet reflected at least four times more radiation energy per unit area into space than ice at higherlatitudes.Thus, while the modern plateau heats the overlying atmosphere, during the Last Ice Age it helped to cool it.[40]
This cooling had multiple effects on regional climate. Without thethermal lowpressure caused by the heating, there was nomonsoonover theIndian subcontinent.This lack of monsoon causedextensive rainfallover theSahara,expansion of theThar Desert,more dust deposited into theArabian Sea,and a lowering of thebiotic life zoneson the Indian subcontinent. Animals responded to this shift in climate, with theJavan rusamigrating into India.[41]
In addition, the glaciers in Tibet createdmeltwater lakesin theQaidam Basin,theTarim Basin,and theGobi Desert,despite the strong evaporation caused by the low latitude.Siltand clay from the glaciers accumulated in these lakes; when the lakes dried at the end of the ice age, the silt and clay wereblownby thedownslope windoff the Plateau. These airborne fine grains produced the enormous amount ofloessin the Chinese lowlands.[41]
Frozen biological samples
[edit]
Ice of the plateau provides a valuable window to the past. In 2015, researchers studying the Plateau reached the top of the Guliyaglacier,with ice thickness of 310 m (1,020 ft), and drilled to a depth of 50 m (160 ft) in order to recoverice coresamples. Due to the extremely lowbiomassin those 15,000-year-old samples, it had taken around 5 years of research to extract 33 viruses, of which 28 were new to science. None had survived the extraction process.Phylogeneticanalysis suggests those viruses infectedplantsor other microorganisms.[42][43]
Climate change
[edit]The Tibetan Plateau contains the world's third-largest store of ice. Qin Dahe, the former head of theChina Meteorological Administration,issued the following assessment in 2009:
Temperatures are rising four times faster than elsewhere in China, and the Tibetan glaciers are retreating at a higher speed than in any other part of the world. In the short term, this will cause lakes to expand and bring floods and mudflows. In the long run, the glaciers are vital lifelines for Asian rivers, including theIndusand theGanges.Once they vanish, water supplies in those regions will be in peril.[44]
The Tibetan Plateau contains the largest area of low-latitudeglaciers and is particularly vulnerable to global warming. Over the past five decades, 80% of the glaciers in the Tibetan Plateau have retreated, losing 4.5% of their combined areal coverage.[45]
This region is also liable to suffer damages from permafrost thaw caused by climate change.

See also
[edit]
- Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China
- Bayan Har block
- Central Tibetan Administration
- Geography of Tibet
- Geology of the Himalaya
- Tibet (1912–1951)
- Tibetan culture
- Tibetan sovereignty debate
- Tibetan diaspora
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^Wang, Zhaoyin; Li, Zhiwei; Xu, Mengzhen; Yu, Guoan (30 March 2016).River Morphodynamics and Stream Ecology of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.CRC Press.
- ^Jones, J.A.; Liu, Changming; Woo, Ming-Ko; Kung, Hsiang-Te (6 December 2012).Regional Hydrological Response to Climate Change.Springer Science & Business Media. p. 360.
- ^"हिमालयी क्षेत्र में जीवन यापन पर रिसर्च करेंगे अमेरिका और भारत".
- ^"In Little Tibet, a story of how displaced people rebuilt life in a distant land".18 February 2020.
- ^Illustrated Atlas of the World(1986) Rand McNally & Company.ISBN0-528-83190-9pp. 164–65
- ^Atlas of World History(1998 ) HarperCollins.ISBN0-7230-1025-0p. 39
- ^"The Tibetan Empire in Central Asia (Christopher Beckwith)".Retrieved19 February2009.
- ^Hopkirk 1983, p. 1
- ^Peregrine, Peter Neal & Melvin Ember, etc. (2001).Encyclopedia of Prehistory: East Asia and Oceania, Volume 3.Springer.p. 32.ISBN978-0-306-46257-3.
- ^Morris, Neil (2007).North and East Asia.Heinemann-Raintree Library. p.11.ISBN978-1-4034-9898-4.
- ^Webb, Andrew Alexander Gordon (2007).Contractional and Extensional Tectonics During the India-Asia Collision.ProQuestLLC. p. 137.ISBN978-0-549-50627-0.
- ^Marston, Sallie A.; Paul L. Knox, Diana M. Liverman (2002).World regions in global context: peoples, places, and environments.Prentice Hall.p.430.ISBN978-0-13-022484-2.
- ^"Natural World: Deserts".National Geographic.Archived fromthe originalon 12 January 2006.
- ^Leslie Hook (30 August 2013)."Tibet: life on the climate front line".Financial Times.Archived fromthe originalon 10 December 2022.Retrieved1 September2013.
- ^Liu, Xiaodong; Chen (2000). "Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades".International Journal of Climatology.20(14): 1729–1742.Bibcode:2000IJCli..20.1729L.CiteSeerX10.1.1.669.5900.doi:10.1002/1097-0088(20001130)20:14<1729::aid-joc556>3.0.co;2-y– via Academia.edu.
- ^Ni, Jian (2000)."A Simulation of Biomes on the Tibetan Plateau and Their Responses to Global Climate Change".Mountain Research and Development.20(1): 80–89.doi:10.1659/0276-4741(2000)020[0080:ASOBOT]2.0.CO;2.S2CID128916992.
- ^Cheng, Guodong; Wu (8 June 2007)."Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau".Journal of Geophysical Research.112(F2): F02S03.Bibcode:2007JGRF..112.2S03C.doi:10.1029/2006JF000631.S2CID14450823.
- ^Yang, Qinye; Zheng, Du (2004).A Unique Geographical Unit.Năm châu truyền bá nhà xuất bản. p. 6.ISBN978-7-5085-0665-4.
- ^Petra Seibert and Lorne Stockman."The Yamdrok Tso Hydropower Plant in Tibet: A Multi-facetted and Highly Controversial Project".Archived fromthe originalon 5 August 2007.Retrieved29 June2007.
- ^Su, T.; Farnsworth, A.; Spicer, R. A.; Huang, J.; Wu, F.-X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.-F.; Xing, Y.-W.; Huang, Y.-J.; Deng, W.-Y.-D.; Tang, H.; Xu, C.-L.; Zhao, F.; Strivastava, G.; Valdes, P. J.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Z.-K. (6 March 2019)."No high Tibetan Plateau until the Neogene".Science Advances.5(3): eaav2189.Bibcode:2019SciA....5.2189S.doi:10.1126/sciadv.aav2189.PMC6402856.PMID30854430.
- ^Jia, Guodong; Bai, Yang; Ma, Yongjia; Sun, Jimin; Peng, Ping'an (March 2015)."Paleoelevation of Tibetan Lunpola basin in the Oligocene–Miocene transition estimated from leaf wax lipid dual isotopes".Global and Planetary Change.126:14–22.Bibcode:2015GPC...126...14J.doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.12.007.Retrieved24 December2022.
- ^Liu, Jia; Su, Tao; Spicer, Robert A.; Tang, He; Deng, Wei-Yu-Dong; Wu, Fei-Xiang; Srivastava, Gaurav; Spicer, Teresa; Do, Truong Van; Deng, Tao; Zhou, Zhe-Kun (15 June 2019)."Biotic interchange through lowlands of Tibetan Plateau suture zones during Paleogene".Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology.524:33–40.Bibcode:2019PPP...524...33L.doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.02.022.S2CID135460949.Retrieved6 November2022.
- ^Xu, Qiang; Ding, Lin; Zhang, Liyun; Cai, Fulong; Lai, Qingzhou; Yang, Di; Liu-Zeng, Jing (15 January 2013)."Paleogene high elevations in the Qiangtang Terrane, central Tibetan Plateau".Earth and Planetary Science Letters.362:31–42.Bibcode:2013E&PSL.362...31X.doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.11.058.Retrieved13 December2022.
- ^Tremblay, Marissa M.; Fox, Matthew; Schmidt, Jennifer L.; Tripathy-Lang, Alka; Wielicki, Matthew M.; Harrison, T. Mark; Zeitler, Peter K.; Shuster, David L. (14 September 2015)."Erosion in southern Tibet shut down at ~10 Ma due to enhanced rock uplift within the Himalaya".Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.112(39): 12030–12035.Bibcode:2015PNAS..11212030T.doi:10.1073/pnas.1515652112.PMC4593086.PMID26371325.
- ^Sanyal, Sanjeev (10 July 2013).Land of the seven rivers: a brief history of India's geography.Penguin Books.ISBN978-0-14-342093-4.OCLC855957425.
- ^Lia, Jijun; Ma, Zhenhua; Li, Xiaomiao; Peng, Ting gian g; Guo, Benhong; Zhang, Jun; Song, Chunhui; Liu, Jia; Hui, Zheng giường; Yu, Hao; Ye, Xiyan; Liu, Shanpin; Wang Xiuxi (2017). "Late Miocene-Pliocene geomorphological evolution of the Xiaoshuizi peneplain in the Maxian Mountains and its tectonic significance for the northeastern Tibetan Plateau".Geomorphology.295:393–405.Bibcode:2017Geomo.295..393L.doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.07.024.
- ^Shi, F.; He, H.; Densmore, A.L.; Li, A.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. (2016)."Active tectonics of the Ganzi–Yushu fault in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau"(PDF).Tectonophysics.676:112–124.Bibcode:2016Tectp.676..112S.doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2016.03.036.
- ^Werhahn, Geraldine; Senn, Helen; Ghazali, Muhammad; Karmacharya, Dibesh; Sherchan, Adarsh Man; Joshi, Jyoti; Kusi, Naresh; López-Bao, José Vincente; Rosen, Tanya; Kachel, Shannon; Sillero-Zubiri, Claudio; MacDonald, David W. (2018)."The unique genetic adaptation of the Himalayan wolf to high-altitudes and consequences for conservation".Global Ecology and Conservation.16:e00455.doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2018.e00455.hdl:10651/50748.
- ^"Wild China: The Tibetan Plateau".The Nature of Things.Canadian Broadcasting Corporation.Retrieved21 March2013.
- ^"Extinct humans survived on the Tibetan plateau for 160,000 years".ScienceDaily.Retrieved6 July2024.
- ^David Miller."Nomads of Tibet and Bhutan".asinart.Retrieved10 February2008.
- ^In pictures: Tibetan nomadsBBC News
- ^Zhang, X. L.; Ha, B. B.; Wang, S. J.; Chen, Z. J.; Ge, J. Y.; Long, H.; He, W.; Da, W.; Nian, X. M.; Yi, M. J.; Zhou, X. Y. (30 November 2018)."The earliest human occupation of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau 40 thousand to 30 thousand years ago".Science.362(6418): 1049–1051.Bibcode:2018Sci...362.1049Z.doi:10.1126/science.aat8824.ISSN0036-8075.PMID30498126.
- ^Ryavec, Karl (2015).A Historical Atlas of Tibet.University of Chicago Press.ISBN9780226732442.
- ^abOracle Thinkquest Education Foundation.monsoons: causes of monsoons.Archived16 April 2009 at theWayback MachineRetrieved on 22 May 2008.
- ^"The Asian Monsoon".BBCWeather. Archived fromthe originalon 1 November 2004.
- ^Kuhle, Matthias (1998). "Reconstruction of the 2.4 Million km2Late Pleistocene Ice Sheet on the Tibetan Plateau and its Impact on the Global Climate ".Quaternary International.45/46: 71–108.Bibcode:1998QuInt..45...71K.doi:10.1016/S1040-6182(97)00008-6.
- ^Kuhle, M (2004). "The High Glacial (Last Ice Age and LGM) ice cover in High and Central Asia". In Ehlers, J.; Gibbard, P.L. (eds.).Development in Quaternary Science 2c (Quaternary Glaciation – Extent and Chronology, Part III: South America, Asia, Africa, Australia, Antarctica).pp. 175–99.
- ^Kuhle, M. (1999). "Tibet and High Asia V. Results of Investigations into High Mountain Geomorphology, Paleo-Glaciology and Climatology of the Pleistocene".GeoJournal.47(1–2): 3–276.doi:10.1023/A:1007039510460.S2CID128089823. See chapter entitled: "Reconstruction of an approximately complete Quaternary Tibetan Inland Glaciation between the Mt. Everest and Cho Oyu Massifs and the Aksai Chin. – A new glaciogeomorphological southeast-northwest diagonal profile through Tibet and its consequences for the glacial isostasy and Ice Age cycle".
- ^Kuhle, M. (1988). "The Pleistocene Glaciation of Tibet and the Onset of Ice Ages – An Autocycle Hypothesis".GeoJournal.17(4): 581–96.doi:10.1007/BF00209444.S2CID129234912.Tibet and High-Asia I. Results of the Sino-German Joint Expeditions (I).
- ^abKuhle, Matthias (2001). "The Tibetan Ice Sheet; its Impact on the Palaeomonsoon and Relation to the Earth's Orbital Variations".Polarforschung.71(1/2): 1–13.
- ^Zhong, Zhi-Ping; Tian, Funing; Roux, Simon; Gazitúa, M. Consuelo; Solonenko, Natalie E.; Li, Yueh-Fen; Davis, Mary E.; Van Etten, James L.; Mosley-Thompson, Ellen; Rich, Virginia I.; Sullivan, Matthew B.; Thompson, Lonnie G. (20 July 2021)."Glacier ice archives nearly 15,000-year-old microbes and phages".Microbiology.9(1): 160.doi:10.1186/s40168-021-01106-w.PMC8290583.PMID34281625.
- ^"15,000-year-old viruses discovered in Tibetan glacier ice".ScienceDaily.20 July 2021.Retrieved14 August2023.
- ^"Global warming benefits to Tibet: Chinese official".Agence France-Presse. 18 August 2009. Archived fromthe originalon 23 January 2010.
- ^Liu, Yongqin; Ji, Mukan; Yu, Tao; Zaugg, Julian; Anesio, Alexandre M.; Zhang, Zhihao; Hu, Songnian; Hugenholtz, Philip; Liu, Keshao; Liu, Pengfei; Chen, Yuying; Luo, Yingfeng; Yao, Tandong (September 2022)."A genome and gene catalog of glacier microbiomes".Nature Biotechnology.40(9): 1341–1348.doi:10.1038/s41587-022-01367-2.ISSN1546-1696.PMID35760913.S2CID250091380.
- ^abRan, Youhua; Cheng, Guodong; Dong, Yuanhong; Hjort, Jan; Lovecraft, Amy Lauren; Kang, Shichang; Tan, Meibao; Li, Xin (13 October 2022). "Permafrost degradation increases risk and large future costs of infrastructure on the Third Pole".Communications Earth & Environment.3(1): 238.Bibcode:2022ComEE...3..238R.doi:10.1038/s43247-022-00568-6.S2CID252849121.
- ^Hjort, Jan; Streletskiy, Dmitry; Doré, Guy; Wu, Qingbai; Bjella, Kevin; Luoto, Miska (11 January 2022)."Impacts of permafrost degradation on infrastructure".Nature Reviews Earth & Environment.3(1): 24–38.Bibcode:2022NRvEE...3...24H.doi:10.1038/s43017-021-00247-8.hdl:10138/344541.S2CID245917456.
Sources
[edit]- Hopkirk, Peter(1983).Trespassers on the Roof of the World: The Secret Exploration of Tibet.J. P. Tarcher.ISBN978-0-87477-257-9.
- Brantingham, P. J. & Xing, G. (2006). "Peopling of the northern Tibetan Plateau".World Archaeology.38(3): 387–414.doi:10.1080/00438240600813301.S2CID13534630.
External links
[edit]- ON THINNER ICE như đi trên băng mỏng (by GRIP, Asia Society and MediaStorm)
- The Third Pole: Understanding Asia's Water Crisis
- The End of Earth's Summer
- Long Rivers and Distant Sources
- "Roof of the Earth" Offers Clues About How Our Planet Was ShapedArchived31 October 2012 at theWayback Machine
- Plateau Perspectives (international NGO)
- Leaf morphology and the timing of the rise of the Tibetan Plateau
- "Weather in the eastern Chang Tang".Archived from the original on 19 March 2006.Retrieved9 May2006.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - Protected areas of the Tibetan Plateau region
- "North Tibetan Plateau-Kunlun Mountains alpine desert".Terrestrial Ecoregions.World Wildlife Fund.
- Photos of Tibetan nomads
- "Roof of the Earth" Offers Clues About How Our Planet Was Shaped
- Contemporary lifestyle and language learning center from Tibet lhasa, the official language of Tibetan. podcast.
- Tibetan History-The true history of any region cannot be fully understood without knowing the basic characteristics of a region and of its inhabitants