Tornadoes of 2024
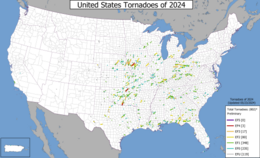 A map of 2024 United States tornado paths from the results of preliminary surveys. | |
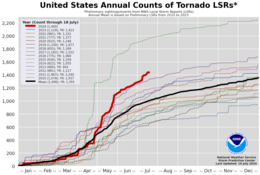 A chart of the 2024 United States tornadolocal storm reportcount compared to years 2010 through 2023, and the 2010–2023 mean. | |
| Timespan | January 3 – ongoing |
|---|---|
| Maximum rated tornado | EF4tornado
|
| Fatalities (U.S.) | 40 |
| Fatalities (worldwide) | 74 |
This page documentsnotable tornadoesandtornado outbreaksworldwide in 2024. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in theUnited States,Argentina,Southern Brazil,theBengalregion andChina,but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southernCanadaduring summer in theNorthern Hemisphereand somewhat regularly at other times of the year acrossEurope,South Africa,Japan,AustraliaandNew Zealand.Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms ofsevere weather,includingthunderstorms,strongwindsandhail.
Worldwide, at least 74 tornado-related deaths have been confirmed – 40 in theUnited States,14 inChina,12 inSouth Africa,5 inIndia,2 inMexico,and 1 inIndonesia.
Events[edit]
United States[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 119 | 355 | 540 | 114 | 32 | 3 | 0 | 1,163 |
There have been 1,163 confirmed tornadoes in theUnited States.
Approximate touchdown location of deadly tornadoes in 2024 Summary of tornadoes[1]
|
Europe[edit]
According to theEuropean Severe Storms Laboratory,there have been 357 confirmed tornadoes in Europe in 2024 (to date July 11), resulting in 13 injuries.[2]
January[edit]
January 3 (Belgium)[edit]
A tornado struck the communities ofOnze-Lieve-Vrouw-WaverandPutteinBelgium.Multiple houses had roofing material torn off, one of which sustained collapse of a gable. Garages, outbuildings, and greenhouses were destroyed, and gravestones were damaged at a cemetery. Trees and fences were toppled over as well. One person and several horses were injured. TheEuropean Severe Storms Laboratoryrated the tornado IF1.5.[2][3][4]
January 8–10 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16 | 15 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 |

During the evening of January 8 through January 9, a severe weather outbreak brought damaging winds and numerous tornadoes to theSoutheasternandEastern United States.On January 7, theStorm Prediction Centerissued an enhanced risk for severe weather in the states ofTexas,Louisiana,Mississippi,Alabama,andFlorida,including a 10% hatched risk for tornadoes. The outbreak began with several brief EF0 tornadoes touching down in Louisiana and Mississippi on January 8. Later that night, multiple tornadic supercell thunderstorms formed over theGulf of Mexicoand began moving toward theGulf CoastandFlorida Panhandle.In the early morning hours of January 9, a powerfultornadic waterspoutformed offshore ofPanama City Beach, Floridaand moved inland at EF3 intensity, causing major damage in theLower Grand Lagooncommunity. Multiple homes, condominiums, apartment buildings, and businesses were severely damaged or destroyed, and large boat storage warehouses sustained significant damage at the Pirate's Cove Marina. The tornado continued to cause lesser damage in the western part ofPanama Citybefore it dissipated. A high-end EF2 tornado also touched down inLynn Haven, Florida,causing significant damage along the shores of Deer Point Lake to dozens of mobile and frame homes. A brief but strong EF2 tornado significantly damaged a few houses inCallaway,and an EF1 tornado caused moderate damage inSanta Rosa Beachas well.[5][6]
Another strong EF2 tornado impacted the outskirts ofMarianna,where many RVs were thrown and destroyed at an RV park, and dozens of frame homes were badly damaged or destroyed in subdivisions. The longest-tracked and widest tornado of the outbreak touched down southwest ofGraceville, Floridabefore it crossed into Alabama and struckCottonwoodat EF2 strength, unroofing homes, collapsing the walls of a brick business, and completely destroying aMoose Lodgebuilding. One person was killed near Cottonwood when the tornado destroyed a mobile home. Several more EF1 tornadoes also touched down inGeorgia,South Carolina,andNorth Carolina,including a tornado that struck the eastern edge ofClaremont, North Carolinaand rolled a manufactured home, resulting in another fatality. The final significant tornado of the day was an EF2 tornado that struckBamberg, South Carolina,where multiple historic brick buildings were destroyed, and a barrel factory suffered major damage. In all, 35 tornadoes were confirmed, resulting in two fatalities. Four additional fatalities unrelated to tornadoes occurred during the event as well.[5]The system responsible for this tornado outbreak also produced heavy snow and blizzard conditions in parts of thePacific Northwest,theMidwest,and theNortheastern United States.[5][7][6]
January 18 (Indonesia)[edit]
A damaging tornado struck the villages ofWalidonoandCangkringinEast Java,damaging 253 homes and 10 public buildings. Nineteen people were injured, two of them seriously.[8][9]
February[edit]
February 4 (Indonesia)[edit]
A tornado damaged or destroyed at least 300 homes and numerous other buildings as it moved through the villages ofKedung Wonokerto,Bendo Tretek,andWatutuliswithin thePrambon DistrictinEast Java.Sheet metal debris was scattered throughout the damage path and trees were downed. A man was killed by flying debris when the shop he was in was destroyed by the tornado, and at least one other person was injured.[10]
February 4 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

Several tornadoes on touched down inGeorgiaandFloridaon February 4, including an EF1 tornado that caused damage at the historic Seminole Plantation nearBoston, Georgia.Cottages sustained roof, chimney, and structural damage, and some open-air barns on the property were also damaged. Dozens of trees were downed as well, one of which landed on a building. The strongest tornado of the day produced EF2 damage nearValdosta,destroying two manufactured homes and injuring two people. An outbuilding was also destroyed, a metal building was severely damaged, and several other homes sustained less intense damage elsewhere along the path. A few weak tornadoes caused minor damage in Florida, including an EF0 tornado that touched down in the western outskirts ofJacksonville,damaging trees and fences and overturning a dumpster. A total of six tornadoes were confirmed.[5]
February 8 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A localized severe weather weather event inIllinoisandWisconsinproduced multiple supercells. One supercell produced the first recorded February tornado in Wisconsin nearJuda,which heavily damaged a frail prefabricated house at high-end EF1 intensity, caused more minor damage to two other homes, destroyed outbuildings, and rolled several campers. The same supercell spawned a strong, long-tracked EF2 tornado that touched down nearEvansville, Wisconsinand moved through the rural community ofPorter,causing significant damage to numerous farmsteads. Multiple houses were heavily damaged and had large portions of their roofs torn off, and many barns, sheds, and metal farm buildings were completely destroyed with debris scattered long distances across fields. Farming equipment was tossed around, trees and power poles were snapped, and one person was injured when the tornado blew their car off a road into a ditch. Less severe damage occurred in and aroundAlbionandBusseyvillebefore the tornado dissipated.[11]TheNational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administrationpublished the tornado caused more than $2.5 million in damage.[12]An EF1 tornado that destroyed farm buildings, damaged a metal garage, and overturned a semi-truck nearMcNabb, Illinoiswas also confirmed.[5]
February 14 (Cyprus and Turkey)[edit]
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
An IF1.5 tornado struck populated areas inGermasogeia,Limassol,Cypruson the night of February 14. Roughly 200 homes and apartment buildings sustained roof damage, some of which had a considerable amount of their roof tiles removed. Trees, signs, and fences were downed, and a crane at a construction site collapsed. Dozens of cars were damaged by flying debris as well. One person was injured and multiple families were displaced from their homes. Additionally, an IF0.5 tornado touched down inTece,Mersin Province,Turkey,damaging trees.[2]
February 21 (Indonesia)[edit]
A tornado caused significant damage and was caught on video from multiple angles as it struckRancaekek,Bandung Regencyand parts ofSumedang Regency.It injured 22 people and damaged or destroyed more than 500 structures. Large trucks were overturned and trees were blown over as well.[13]The tornado was given a rating of F2 on theFujita scale.[14][15]
February 22 (Brazil)[edit]
A rare northern Brazil tornado hitEstrela de Alagoas,Alagoas.According to MetSul Meteorologia, the damage caused by the tornado was rated F1.[16]
February 27–28 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 12 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A severe weather outbreak produced numerous tornadoes across theGreat LakesandOhio Valleyregions in late February.[17][18]The Storm Prediction Center outlined two separate enhanced risk areas on February 27; one in northernIllinois,and the other along theOhio River.Severe storms developed later that evening and moved through theChicago metropolitan area,producing straight-line wind damage and multiple EF0 and EF1 tornadoes throughout the region, including three parallel tornadoes that moved in tandem through the towns ofInverness,Hoffman Estates,Palatine,andSouth Barrington.[5][17][19][20]BothO'HareandMidway International Airportsissued ground stops as the system moved through the area, and travelers were encouraged to seek shelter in interior locations and in underground tunnels.[21][22]InMichigan,a low-end EF2 tornado struckGrand Blanc,where warehouses were significantly damaged at an industrial park, trees and power poles were snapped, and gas leaks were reported.[23][24][25][26][27][28]The storms moved intoOhioduring the early morning hours of February 28, producing several tornadoes in and around theDaytonandColumbusmetro areas.[29][30][5][31]An EF1 tornado moved through the Dayton suburbs ofRiversideandFairborn,damaging airplanes and a hangar atWright-Patterson Air Force Base,before damaging apartment buildings and trees nearWright State University.A high-end EF2 tornado severely damaged or destroyed multiple homes and unroofed a church as it passed nearSpringfield,then destroyed a hangar and tossed small planes at the Madison County Airport nearLondon.In southeastern Ohio, two EF2 tornadoes damaged multiple houses and destroyed outbuildings nearGahannaandMiltonsburg.Overall, a total of 24 tornadoes were confirmed as a result of this outbreak, which resulted in three injuries.[5]
March[edit]
March 2 (India and Pakistan)[edit]
A tornado touched down nearMoga,Punjab,causing significant damage.[32][33]Shortly after the Moga tornado, another tornado touched down and caused damage inJhelum, Punjab, Pakistan.[34][35][36][37]
March 5 (Turkey and France)[edit]
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Several tornadoes and waterspouts touched down in Europe.[2]One waterspout hitDemre,Turkey,causing IF1 damage to 175 decares of greenhouses and electricity poles.[38]A second IF1 tornado affectedGöksu,Hacıveliler,Yenimahalle,KumlucaandToptaşin Antalya Province, along a 12 km long and 80 meter wide path. Weak greenhouses were damaged, a mobile construction trailer was shifted, roofs were damaged and trees were downed. Six people sustained injuries.[39][40]Another IF1 tornado hitPayallar,causing near complete destruction of a weak greenhouse facility, and tossing a container into the greenhouse facility, causing one injury. A total of three people were injured.[41]Two unrated tornadoes touched down inFrance.[42][43][44]
March 9 (Spain)[edit]
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
An IF2 rated tornado struck the town ofCórdobaduring the early hours of the night. Wind speeds are calculated to be around 200 km/h and several structures sustained light to severe damage. No fatalities or injuries were reported. Another IF1.5 struck the thermosolar plant in the nearby town ofPosadas.[45][46]
March 9 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A small severe weather event impacted the states ofAlabama,Georgia,andFlorida,producing multiple tornadoes. In the early morning hours, a high-end EF1 tornado touched down east ofOzark, Alabama,causing tree damage and impacting several homes and outbuildings. Later that morning, another EF1 tornado occurred north ofMiccosukee, Florida,resulting in tree damage only.[47]Another tornado formed northeast ofArgyle, Georgia,damaging two structures and numerous trees and receiving a rating of EF1.[48]During the early afternoon, a significant tornado touched down southeast ofNahunta, Georgia.This tornado caused significant damage, including the roof of a home being severely damaged and the destruction of a travel trailer. Additionally, a double-wide manufactured home was completely destroyed, with its undercarriage thrown into trees and bent. Five people sustained injuries, and the tornado received a high-end EF2 rating, with wind speeds up to 130 mph (210 km/h). In total, four tornadoes were confirmed during this event.[5]
March 13–15 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 11 | 11 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 |

From the evening of March 13 through March 15, a severe weather and tornado outbreak impacted the Central, Midwestern, and Southern United States. On March 13, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk for severe weather across Kansas and Missouri. Two tornadoes touched down that day in Kansas, nearAlta VistaandRossville,both of which caused EF2 damage.[49]On March 14, the Storm Prediction Center issued another enhanced risk area for parts ofTexas,Oklahoma,Arkansas,andMissouri,including a 10% risk area for tornadoes. However, the most intense supercells formed northeast of that area in theOhio Valley.[50]That afternoon, a low-end EF2 tornado touched down inHanover, Indiana,tearing the roofs off a few homes, before crossing into Kentucky and striking the town ofMilton,destroying numerous trailers and causing damage to many homes. The tornado then re-entered Indiana and destroyed more trailers nearBrooksburgbefore lifting. Two people were injured by this tornado.[5][51]That evening, a long-tracked supercell produced numerous tornadoes inIndianaandOhio.The first tornado spawned by this supercell was a brief EF1 tornado nearCelina,[52][53]before another EF1 tornado directly struck Celina and the nearby community ofSt Marys.[54]The supercell then spawned a multiple-vortex, high-end EF3 tornado that impacted the towns ofWapakonetaandLakeview,destroying manufactured homes, uprooting and partially debarking trees, and obliterating RVs at a trailer park where a site-built structure was also destroyed. Three people were killed, and 26 others were injured by this tornado.[55]Shortly thereafter, a separate supercell to the north of the Lakeview supercell produced an EF2 tornado that completely destroyed a manufactured home and damaged trees, homes, and outbuildings nearPlymouth.[56]After the Lakeview EF3 tornado dissipated, the storm produced an EF2 tornado that caused major damage to homes, outbuildings, and trees as it passed nearRaymond,throughBroadway,and nearOstrander.[57]The final tornado from the Lakeview supercell was a long-tracked EF1 tornado that passed nearDelaware,Sunbury,Galena,andSt. Louisville.[58]Just south of the Lakeview supercell, another supercell spawned an EF2 tornado that impactedSelma, Indiana.[59][60]Later, the storm spawned another strong tornado nearFarmland, Indiana,which tore the roofs off numerous homes as it moved eastward. The tornado then struckWinchesterat high-end EF3 intensity, destroying many homes, a church, and a Taco Bell restaurant. The tornado then crossed the border intoOhio,causing EF1-EF2 damage to farmsteads as it moved throughDarkeandMiamicounties before dissipating nearBradford.The tornado injured 40 people with one person dying from their injuries about a month later.[5][59][61][62]Further south, a low-end EF2 tornado destroyed a metal structure and snapped many trees inHot Springs Village, Arkansasas well.[63]Only isolated, weak tornadic activity occurred on March 15 before the outbreak came to an end.[64]In total, 33 tornadoes were confirmed from this outbreak along with four fatalities and 69 injuries.[5]
March 27 (Italy and France)[edit]
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A weak unrated tornado occurred just north-east of downtownVerona,Italywithin the north-eastern suburb ofBorgo Venezia.Another IF2 tornado hitPort-Joinville,France, damaging 60 roofs and downing trees. One person sustained injuries.[2][65][66][67]
March 31 (India)[edit]
A tornado, accompanied by anor'wester,struck the city ofJalpaiguri,West Bengal,killing five people and injuring over 100 others. More than 100 houses were destroyed by the tornado.[68]
March 31 (China)[edit]
An EF2 tornado was confirmed from an overnight extremeQLCSevent inNanchang,Jiangxi Province.The tornado sucked three people out of high-rise buildings and caused four fatalities in total.[69][70]
April[edit]
April 1–3 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 | 52 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

From April 1 through April 3, aderecho[71][72]and significant tornado outbreak occurred primarily in theCentral Plains,Mississippi Valley,Ohio Valley,andMid-Atlantic.On April 1, a moderate risk for severe weather was issued across parts ofOklahomaandTexas,including a 10% hatched area for tornadoes. On April 1, several weak tornadoes occurred acrossOklahoma,Arkansas,andMissouri,including an EF0 tornado that overturned a tractor trailer nearLenapah.Two non-tornadic injuries were reported due to high winds toppling trees inKentuckyandIndiana.Tornadic activity continued into the early morning hours of April 2 across theOhio RiverValley. An EF2 tornado touched down nearLake of Egypt,Illinois, downing numerous trees, power lines, and causing damage to a few outbuildings. Another EF2 tornado damaged a metal building and rolled a mobile home nearEldorado,injuring two people. An EF2 tornado caused considerable damage to several buildings nearUniontownin Kentucky. EF2 tornadoes also impacted the towns ofNew HarmonyandCynthianain Indiana. On the afternoon of April 2, an EF2 tornado downed numerous trees and damaged the roof of a home inCannonsburg, Kentucky.Hundreds of hardwood trees were downed by an EF2 tornado nearFayetteville, West Virginia.Another EF2 tornado damaged several homes inJeffersonville, Indianabefore crossing theOhio Riverand strikingProspect,Kentucky resulting in 22 injuries. Further south in Georgia, an EF2 tornado struck the city ofConyers,causing considerable damage and two injuries.[5]In total, 86 tornadoes were confirmed causing over 37 injuries.
Widespread flooding occurred as a part of the storm system, with hourly rainfall rates of 1.5 in (38 mm) inTulsa, Oklahomaon April 1. Severe storms across theNortheastern United Stateson April 3 produced a daily rainfall record of 1.75 in (44 mm) of precipitation atLaGuardia AirportinNew York City.[73]The storm system left roughly 123,000 customers without power in West Virginia.[74]While no tornado-related fatalities occurred, at least five people were killed as a result of the storm system and several others were injured.[citation needed]
April 9–11 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 6 | 24 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A small severe weather outbreak produced numerous tornadoes along theGulf Coast.On April 9, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk of severe weather fromCentral Texasthrough westernLouisiana,including a 10% risk for tornadoes. On April 10, the Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk for south-central Louisiana into southern Mississippi, with a 15% risk for strong tornadoes. During the very early morning of April 10, a squall line produced an brief EF1 tornado inKaty, Texasand another, stronger EF2 tornado in downtownPort Arthur.Afterwards, aquasi-linear convective system(QLCS) formed in eastern Texas, producing twin EF1 tornadoes south ofLake Charlesand a damaging EF2 tornado nearMcNeese State University.The final significant tornado of the outbreak touched down nearLake Pontchartrain,causing EF2 damage on the southern side ofSlidelland injuring several people in the area before it dissipated northwest ofPearlingtonas the tornado was absorbed by an EF1 tornado that moved through NorthernSlidellbefore occluding intoStennis Space Center.Simultaneously, a long-track high-end EF1 tornado touched down in the southern side ofPearl Riverbefore strikingGainesville, Mississippiand theStennis Space Center,causing moderate damage. In addition to the tornadoes that day, flooding nearPittsburghled to aflash flood emergency.[75]In total, 35 tornadoes were confirmed from the outbreak, with no fatalities and several injuries, as well as $1.5 billion in damages.[76][5]
April 15–18 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 18 | 18 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

A moderately severe weather outbreak produced numerous tornadoes across theCentral Plainsinto theMidwest.On April 15, the Storm Prediction Center issued an enhanced risk intoKansas,NebraskaandSouth Dakota,with a 10% hatched tornado risk. On April 16, another enhanced risk was issued forIowa,Illinois,andMissouri,with an additional 30% hatched risk for large hail. On the morning of April 16, multiple supercells from the previous day produced several tornadoes across Iowa and Missouri. A long-lived EF1 tornado passed through the southeastern side ofEureka, Kansas,causing significant damage to barns. After this tornado dissipated, a supercell to the north produced three weak but long-tracked tornadoes southwest ofOverbrook.The same cell produced a stronger EF2 tornado south ofVirgil,which caused significant damage to barns and telephone poles. The final and strongest tornado of the outbreak was a long-tracked, high-end EF2 tornado that touched down nearHoughtonbefore moving through rural areas nearNew London.This strong tornado caused severe damage at several houses farmsteads nearYarmouthand uprooted numerous trees atPort Louisa National Wildlife Refugebefore dissipating nearToolesboro.In total, 45 tornadoes were confirmed from this outbreak, causing no injuries or fatalities.[5]
April 19 (Alaska)[edit]

A very rare EFU tornado occurred near Rusty Point, just outside ofAnchorage, Alaska,marking the fifth officially recorded tornado to occur in the state. It remained over remote areas and caused no damage.[5]This was also the first Alaskan tornado recorded since 2005.[77][78]
April 26–28 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 41 | 65 | 16 | 8 | 1 | 0 |

A devastatingtornado outbreakoccurred across the centralUnited Statesat the end of April. On April 26, a large EF3 wedge tornado, touched down nearElba, Nebraska.Another large EF3 wedge tornado touched down nearYutan, Nebraskaand tracked through theNorthwestern Omaha MetroandBlair, Nebraska,prompting a tornado emergency for theOmaha, Nebraskaarea. Significant damage was observed inElkhorn, Nebraskafrom the tornado, with houses sustaining loss of roofs, collapsed walls, or were completely leveled, along with debarked trees.[79][80]More than 100 homes were destroyed and several people were injured, though exact numbers are not known as of April 26.[81]TheOmaha Public Power Districtreported that the tornado outbreak left more than 10,000 homes without power, though half of those affected had power return by the following morning.[82]Omaha's airport,Eppley Airfield,was struck directly and sustained damage to itsgeneral aviationbuilding.[83][84]InLancaster County,a tornado struck an industrial building while 70 people were inside, resulting in the building's collapse and at least three non-fatal injuries.[85]Another long-tracked and strong tornado was documented derailing a train nearLincoln, Nebraskabefore hitting a highway. Another tornado was documented by multiple surveillance cameras while passing throughCouncil Bluffs, Iowa.A strong tornado struckMinden, IowaandTennant, Iowa,prompting a tornado emergency. A large wedge high-end EF2 tornado[86]tracked nearRedding, Iowa,as it later prompted another PDS warning forPleasant Hill, Iowa.[87]At least 100 tornado reports were filed.[88]An estimated 40–50 homes were destroyed inMinden, Iowa,and at least two people were injured.[85]

The next day, a major outbreak broke out across parts ofTexas,Oklahoma,Kansas,andMissouri.[89]The strongest tornadoes struck Southern Oklahoma during the nighttime hours. A high-end EF3 tornado struckSulphur,severely damaging or destroying homes and killing one person. Later, another EF3 tornado passed through or nearSpaulding,Holdenville,andBearden,causing major damage and killing two people.[90]Another large, violent EF4 tornado struckMarietta,causing major damage to aDollar Treedistribution center, and killing one person. The next day, multiple tornadoes struck eastern Texas and southeastern Oklahoma.[91]Although all the tornadoes were weak, one brief EF1 tornado impacted a subdivision ofTrinity, Texas,destroying a mobile home. Both occupants were injured, with one of them later dying from his injuries. The tornado also damaged trees and vehicles.[92][93]Overall, 148 tornadoes, six fatalities, and more than 150 injuries were confirmed during the outbreak.[5]
April 27 (China)[edit]
A significant tornado moved through several villages in theBaiyun DistrictofGuangzhou,killing five people, and injuring dozens of others. More than 140 factory buildings sustained a certain degree of damage.[94]
April 30 – May 4 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
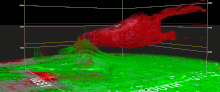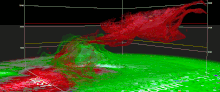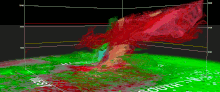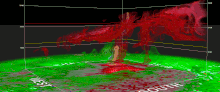
On April 30, the Storm Prediction Center issued an Enhanced risk for severe weather in the states ofKansas,Missouri,andNebraska,including a 5% risk for tornadoes. During the mid-afternoon, alow-precipitation supercellspawned an intense,multiple-vortextornado that struckWestmoreland, Kansas,causing extensive damage to homes and businesses. Two poorly constructed frame homes were destroyed, and as a result, a low-end EF3 rating was applied, with wind speeds estimated at 140 mph (230 km/h). One fatality occurred in a destroyed mobile home as well.[95]A photogenic tornado struck south ofVermillion, Kansas,heavily damaging one home at high-end EF1 intensity. In the early evening, a high-end EF1 tornado directly struckNew Cordell, Oklahoma,damaging numerous homes and businesses. Later in the evening, a powerful supercell displayed an intensetornado vortex signatureeast ofHollister, Oklahoma.Given this tornado occurred in a rural area, the lack of damage indicators for it to hit led to a high-end EF1 rating. The same supercell spawned an anticyclonic EF1 tornado southeast ofLoveland.[96][97]On May 1, multiple weak tornadoes touched down in and aroundSpearman, Texas;an unrelated EF0 tornado also occurred inPuerto Rico.On May 2, the Storm Prediction Center issued an Enhanced risk for severe weather in the state of Texas, with a 5% risk for tornadoes. Numerous tornadoes touched down, the strongest being a "drill bit" high-end EF3 tornado that struck west ofHawley, Texas.Power poles and outbuildings sustained significant damage near the start of its path. As the tornado deviated south, it struck a poorly-constructed home, sweeping it clean off its foundation. Another home, more well-constructed, was struck as the tornado continued to move south. All of its walls collapsed, with debris partially swept off the foundation. All four occupants sustained injuries.[98]Vehicles were thrown and severely damaged as well. On May 3, the Storm Prediction Center issued yet another Enhanced risk for severe weather. Several tornadoes touched down throughout the day, including an EF2 tornado south ofSilver, Texasand a deviant high-end EF1 wedge tornado south ofRobert Lee.[99]The storms have also been associated with severe flooding inTexas,which resulted in at least 224 people being rescued from their homes and vehicles inHarris Countyby May 3.[100]BNSF's Fort Worth Subdivision was closed for a few days after severe flooding caused awashoutnearClifton;[101]it was later closed again when the first train to go over the line after it reopened derailed.[102]Amtrak'sTexas Eaglewas forced to operate a bus bridge betweenSan AntonioandFort Worth, Texasand later betweenTempleand Fort Worth.[103]
May[edit]
May 6–10 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 62 | 79 | 14 | 3 | 1 | 0 |

Another large and deadly tornado outbreak occurred across theGreat Plains,Mississippi Valley,and theOhio Valleyfrom May 6–10. On May 6, a tornado-drivenhigh riskwas issued by theStorm Prediction Centeracross central, north central, and, later, northeasternOklahomaand south centralKansas.However, throughout the day, only weak tornadoes occurred across the Plains. A separate system also spawned severe thunderstorms inTennessee,including one that produced an EF1 tornado that moved throughSmithville.Later that night, a powerfulsupercellspawned a violent EF4 tornado southeast ofHominy, Oklahoma.The tornado moved northeastward and struck the community ofBarnsdall,prompting the issuance of atornado emergency.Two people were killed within the town, and many homes and other structures were heavily damaged or destroyed, including some that were leveled. The tornado continued northeast and moved intoBartlesville, Oklahoma,causing additional severe damage before dissipating northeast of the town.[104][105][106]Through the overnight hours into May 7, a squall line produced widespread damaging winds and isolated weak tornadoes across all ofMissouri.[107]On May 7, a tornado-driven Enhanced risk was issued across theOhio Valleyby theStorm Prediction Center.That afternoon, a strong, high-end EF2 tornado caused severe damage inPortage, Michigan.Later, a large EF2 tornado along with a satellite EF1 tornado prompted the issuance of a tornado emergency forUnion CityandSherwood,the first tornado emergency ever issued in the state of Michigan. Other tornadoes were reported acrossMichiganalong withOhio,West Virginia,Indiana,Arkansas,andPennsylvaniathrough the overnight hours into May 8.[108]Later on May 8, more severe weather and tornadoes impacted much of theMiddle MississippiandTennessee Valleyswith many areas experiencing multiple rounds of storms. PDS tornado warnings were issued for EF1 tornadoes nearEquality, IllinoisandAurora, Missouri.A tornado emergency was issued for a large, low-end EF3 tornado east ofColumbia, Tennessee;a fatality and four injuries have been confirmed with this tornado.[109]Later in the evening, an intense, low-end EF3 tornado crossedWheeler Lakesoutheast ofRogersville, Alabamaand came ashore in the Bridgadoon subdivision. It damaged several homes, including one large home that sustained significant damage. That night, another PDS tornado warning was issued when the same storm that produced the Brigadoon tornado spawned a strong EF2 tornado inHuntsville, Alabama;the same storm later produced another destructive low-end EF3 tornado that prompted the issuance of another tornado emergency forHenagar,Hammondville,andMentone.Strong straight-line winds blew a tree down on a car east ofLone Mountain, Tennessee,killing the driver.[110]Severe storms also forced aMajor League Baseballgame atBusch Stadiumto be postponed until August 5.[111]More isolated tornadic activity occurred on May 9, but widespread reports of wind damage and large to very large hail were recorded throughout theDeep South.Through the overnight hours into May 10, a severe MCS moved through the southern Gulf Coast, producing scattered wind damage.[112]The MCS would produce an EF2 tornado northeast ofPensacola, Floridabefore spawning three large tornadoes that simultaneously impactedLeon County, Florida.The two northern-most tornadoes, which were both rated low-end EF2, moved directly throughTallahassee,inflicting major damage to the downtown area as well as on the campuses ofFlorida State UniversityandFlorida A&M University.To the south of these tornadoes, a swath of significant straight-line winds of around 100 mph (160 km/h) caused damage in the southern part of Tallahassee and points east. The third tornado, which was rated high-end EF1, passed south of Tallahassee, producing widespread tree damage.[112][113]Tornadic activity then ceased, but severe weather continued to impact the Southeastern United States until the system finally pushed offshore early on May 11.[114]In all, 169 tornadoes, three tornadic fatalities, and three non-tornadic fatalities were confirmed from this outbreak.[115]
May 10 (Australia)[edit]
An EF2 tornado struck the town ofBunbury,damaging around 100 homes, including seven that were declared uninhabitable, and injuring two people.[116][117]
May 13 (United States)[edit]

| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Severe storms produced damaging winds, large hail, and isolated tornadoes across mainly theGulf Coast.The strongest tornadoes were spawned in association with an MCS that moved through theAcadianaregion ofLouisiana.[118]An EF2 tornado impacted the eastern part ofSulphur,destroying warehouses and damaging homes, other structures, trees, and power lines.[119]As that tornado dissipated, an EF1 tornado developed inWestlakeand moved through DowntownLake Charles,damaging homes, businesses, trees and power lines.[120]Later, another EF2 tornado crossed overI-10and moved throughHenderson,damaging homes and businesses, rolling mobile homes and RV, destroying outbuildings, and damaging trees and power lines. The tornado killed one person and injured another person.[121]
May 16 (Italy)[edit]
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A rain-wrapped IF0.5 tornado touched down nearGualtieri,causing minor damage to the roof of a cemetery. Several weak trees were downed, crops were flattened and a truck was moved. The tornado may have reached IF1 intensity. It tracked 2.2 km and reached 50 meters in width.[2][122][123]A second rain-wrapped IF2 tornado touched down atVilla Poma1 hour and 10 minutes later, tracking 2.6 km and reaching 110 meters in width. Seventank carsfrom afreight trainwere blown over and a steel tower collapsed. Sporadic patterns in the grass was also observed together with a downed steel fence. Additional damage was observed to greenhouses and roofs.[2]
May 16 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |

Apowerful derechoaffected areas fromSoutheast TexastoFlorida,producing three EF1 tornadoes.[124]Two of these tornadoes were reported in theHoustonarea, the first inCypressand the second inWaller County.The third tornado struck the towns ofRomevilleandConvent, Louisiana,damaging the roofs of several frame houses and manufactured homes in addition to snapping trees and power poles.[125]Although these tornadoes caused no casualties, the event overall killed eight people.[126]
May 19–27 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 65 | 106 | 21 | 12 | 1 | 0 |

An extended period of significant tornado outbreaks and tornado activity along with two derechos rounded out the very active month of May starting on May 19. On May 19, severe weather produced destructive hurricane-force straight-line winds, very large hail, and numerous tornadoes across mainlyKansasandOklahoma.One large EF2 tornado prompted the issuance of atornado emergencyforCuster City, Oklahomawhile another EF2 tornado passed nearYukon.[127][128]On May 21, the Storm Prediction Center issued a Moderate risk for severe weather in the states ofIowa,Missouri,Minnesota,Wisconsin,andIllinois,including a 15% hatched risk for significant, long-track tornadoes.[129]As a result, aParticularly Dangerous Situationtornado watch was issued.[130]A few tornadoes occurred nearMacedoniaandRed Oak.One long-tracked and violent tornado touched down nearVillisca, Iowa.Continuing northeast, it toppled and crumpled several wind turbines.[131]The tornado then approachedGreenfield,where it intensified to EF4 intensity[132][133]Numerous homes were damaged or destroyed with some of them being reduced to their foundations or swept clean. Vehicles sustained severe damage as well and multiple trees were severely debarked. Four people were killed in Greenfield. Another fatality occurred near the town ofCorning,about 30 miles southwest of Greenfield when the tornado blew a vehicle off the road. At least 35 people sustained injuries to some degree.[134]ADoppler on Wheelsmeasured 309–318 mph (497–512 km/h) winds in a small area between 30–50 m (98–164 ft) above the surface near Greenfield making this one of the highest windspeeds ever recorded in a tornado.[135]

Tornadic activity continued over the next several days. During the overnight hours of May 25 into May 26, several destructive tornadoes touched down in northern Texas from an isolated supercell. One destructive and intense low-end EF3 tornado caused severe damage nearValley ViewandPilot Point, Texas,killing at least seven people and injuring 100 others.[136][137][138]Further to the north, supercell clusters formed and moved eastward across southeastern Kansas and northeastern Oklahoma as well as northern Arkansas and southernMissouri,causing widespread destruction from both tornadoes and damaging straight-line winds of up to 100 mph (160 km/h). Another destructive EF3 tornado struckClaremoreand nearPryor, Oklahoma,killing two people.[139]An EF3 tornado nearDecatur, Arkansasbecame the largest tornado ever recorded in the state while secondary circulation spawned a damaging anticyclonic EF2 tornado.[140]A strong EF2 tornado also struckRogers,causing major damage. A total of four people were killed by an EF3 tornado neatOlveyandPyatt,[140][141]another tornadic fatality occurred when a low-end EF3 tornado struckBriarcliff(which was also struck by an EF2 satellite tornado),[142]and another one confirmed with a low-end EF3 tornado that moved throughSikeston, Missouri.In the evening hours of May 26, a large and destructive high-end EF3 tornado prompted four tornado emergencies as it impactedCrider,Charleston,andBarnsley,causing significant damage and a fatality. In all, 222 tornadoes and 21 tornadic fatalities were confirmed from the outbreak sequence, along with 10 additional non-tornadic fatalities.[5]
May 23 (Mexico)[edit]
Two people were killed after a fence fell onto them during a tornado inToluca,State of Mexico.[143][144]
May 30 (United States)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |

A small, but significant outbreak of tornadoes impactedTexasandLouisiana.The SPC issued an enhanced risk of severe weather over part ofWest Texasmainly for the threat of damaging winds and large hail, however, a 5% tornado risk was also included.[145]That evening, numerous tornadoes touched down in Texas, including an EF2 tornado that prompted atornado emergencyfor areas to the south ofMidland,damaging power poles and RVs. This was the first issuance of a tornado emergency by theNational Weather Serviceoffice in Midland. An EF3 tornado damaged heavy oil equipment and caused ground scouring nearMidkiff.[146][147]Further east, multiple EF1 tornadoes touched down near the Texas-Louisiana border, including a tornado nearStonewall, Louisianathat tossed a metal building.[148]This outbreak produced 13 tornadoes but no casualties.
June[edit]
June 2 (United States)[edit]

| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Severe thunderstorms developed across a broad portion of the Central United States with tornadoes reported in the Dakotas and Texas.[149]Two tornadoes, rated low-end EF3 and high-end EF1, struckSanderson, Texas.The EF3 tornado caused significant damage to houses, destroyed a mobile home, and debarked trees, injuring 12 people. The EF1 tornado damaged roofs, snapped power poles, and destroyed a wooden building.[150]An EF2 tornado snapped power poles and uprooted trees east ofMaurine, South Dakota.[151]Two EF0 tornadoes damaged vegetation atLake MeredithnearSanford, Texas[5]and two EFU tornadoes moved over remote terrain north ofSilverton, Texas.[152]
June 3 (Bosnia)[edit]
A very brief but significant tornado hitMišin Han,Bosnia,damaging over 20 homes and crossing the M4 road. While it only tracked 0.5 km, it managed to cause IF2 damage to a home, heavily deroofing a brick home. Other homes and outbuildings also sustained some sort of damage, and trees and powerlines were downed.[2][153][154][155]
June 3 (South Africa)[edit]
On June 3 around 4 pm local time, a large EF3wedge tornadostruck the small coastal town ofoThongathi(Tongaat) 40 km north ofDurban.The tornado caused significant damage to hundreds of homes, businesses, schools and the surrounding area. Several homes collapsed in the neighborhoods of Magwaveni and Sandfields, while trees were uprooted and vehicle damage occurred. The storm also knocked out power lines, leaving many parts ofeThekwiniwithout electricity. The tornado displaced at least 1,200 people, leaving 12 people dead and no less than 120 others injured. It also caused R481.7 million in damages.[156][157]Gift of the Giversjoined relief efforts.[158][159][160]
June 5–6 (United States)[edit]

| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
An EF1 tornado struck nearPlymouthandLivoniainMichigan,snapping and uprooting trees, and inflicting roof damage to homes. A toddler was killed, and another person was injured due to an uprooted tree. No tornado warning was issued for this storm.[161][162][163]Another tornado, rated EF0, downed trees nearEldorado, Michigan.[164]The highest concentration of tornadoes occurred in the Mid-Atlantic region with nine tornadoes touching down inMarylandand four others inWest Virginiaand far northernVirginia.An EF1 tornado moved throughGaithersburg, Maryland,where several homes were damaged by falling trees with five people being injured in one of them. Another EF1 tornado caused damage inColumbiawhile yet another EF1 tornado struckArbutusandHalethorpenearBaltimore.[164][165]Other tornadoes impactedIllinois,Ohio,Mississippi,andAlabamaas well,[164][5]including an EF2 tornado that struckFrazeysburg, Ohioshortly after midnight on June 6, injuring eight people.[166]
June 13 (China)[edit]
A tornado caused roof damage to a few houses inCangzhou,Hebei Province.[167][168]
June 18–19 (Europe)[edit]
| IFU | IF0 | IF0.5 | IF1 | IF1.5 | IF2 | IF2.5 | IF3 | IF4 | IF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
A severe weather outbreak in Europe spawned multiple tornadoes across the continent. On June 18, a significant tornado touched down inCarlepont,France.The tornado was filmed from multiple angles and damaged 34 buildings. A weak barn was completely destroyed, giving it an IF2 rating. Later into the evening, a damaging tornado was observed causing heavy roof damage inBockenem,Lower Saxony,Germany.The tornado has not been rated yet as damage survey is still underway. The next day, a weak tornado struck a forest and nearby roads in a ski resort nearChalmazel,inFrance,injuring one person. Later, several tornadoes were observed inRussia,with one IF1.5 occurring in Pereboevo, causing roof damage along a 9 km long path and with one IF1 damaging roofs and downing trees near Dubishno.[2]
June 25 (Georgia)[edit]
A rare IF2 tornado struck theAlaverdi Monastery,near the town ofAkhmetain theKakhetiregion of easternGeorgia.The tornado damaged the roof of the monastery and uprooted trees. Cars were lifted into the air, injuring two people. The tornado was the strongest in the country since 2005.[169]
June 25–26 (United States)[edit]

| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Multiple days of significant severe weather occurred from June 25–26, resulting in at least 16 tornadoes. In the early morning of June 25, an EF1 tornado struck nearKeshena, Wisconsin,snapping and uprooting trees and causing minor damage to homes and utility poles. Later in the day, a few weaklandspouttornadoes occurred in central and easternIowa,producing minor damage to trees and outbuildings.[5]In the evening, a powerful supercell developed in northwesternCherry County, Nebraska,and continued south-southeast intoGrant County,where it produced an intense tornado that impacted the community ofWhitman.EF1 damage was observed in Whitman, with trees being snapped and uprooted. Further south, the tornado struck a large farmstead, completely destroying two poorly constructed homes and injuring one person. A newly built home nearby sustained severe damage to its exterior walls, with most interior walls still standing. The tornado continued further south, enteringHooker Countyand producing EF1 damage to grain bins and pivot irrigation systems. It then continued intoMcPherson County,lifting after tracking for nearly 40 mi (64 km). As a result of the damage, a preliminary high-end EF3 rating was applied, with wind speeds estimated at 160 mph (260 km/h).[170]Notably, the National Weather Service office inNorth Plattefailed to issue a tornado warning before the tornado hit Whitman, causing controversy among citizens.[171]On June 26, multiple tornadoes impacted thePittsburgh, Pennsylvania metropolitan area,including an EF2 tornado nearNew Alexandria.Two EF1 tornadoes also touched down in theProvidence, Rhode Island metropolitan area.[5]Nearby, aMajor League Baseballgame atFenway Parkbetween theBoston Red SoxandToronto Blue Jayswas postponed until August 26.[172]The associated severe weather in the Northeast resulted in two fatalities and 300,000 power outages.[173]
July[edit]
July 4–5 (China)[edit]
On the afternoon of July 4, a tornado struckDongtai,Jiangsu Province,destroying some farm houses. The next day, a tornado killed five people and injured 83 others after travelling through the downtown ofDongming,Shandong.This tornado destroyed an industrial estate, directly struck high-rise apartments and damaged 2820 houses.[174][175][176][177][178][179]Two more tornadoes hitYunchengandJuancheng,both inShandong,causing damage.[180][181][user-generated source]Later, a damaging tornado touched down inZibo,Shandong.[182][user-generated source]
July 8–10 (Hurricane Beryl)[edit]
| EFU | EF0 | EF1 | EF2 | EF3 | EF4 | EF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 13 | 39 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
A damaging tornado outbreak spawned byHurricane Berylstruck EasternTexas,westernLouisiana,and southernArkansason July 8. Tornadoes have been confirmed in several locations, including EF2 tornadoes nearJasper, Texas,and inPleasant Hill, Louisiana.An EF1 tornado east ofBenton, Louisianakilled a person when a tree fell on a mobile home; two people were also injured by this tornado.[5][183][184][185]The outbreak continued into July 9 with more tornadoes being confirmed,[186]including a low-end EF3 tornado nearMt. Vernon, Indiana,[187]before impacting the interiorNortheastern United Stateson July 10, where a low-end EF2 tornado destroyed multiple farm buildings nearEden, New York.[188]
See also[edit]
- Weather of 2024
- Meteorology in the 21st century
- Tornado
- History of tornado research#2024
- List of tornado outbreaks
- List of tornado outbreaks by outbreak intensity score
- List of F5 and EF5 tornadoes
- List of F4 and EF4 tornadoes
- List of North American tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of 21st-century Canadian tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of European tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks in Asia
- List of Southern Hemisphere tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
- List of tornadoes striking downtown areas of large cities
- List of tornadoes with confirmed satellite tornadoes
- List of case studies on tornadoes (2020–present)
- Tornado intensity
Notes[edit]
References[edit]
- ^"Annual U.S. Killer Tornado Statistics".Storm Prediction Center.National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on January 14, 2023.RetrievedJanuary 17,2024.
- ^abcdefghiStaff of theEuropean Severe Storms Laboratory(2024)."European Severe Weather Database"(Interactive mapanddatabase).ESWD.European Severe Storms Laboratory.Archivedfrom the original on 2022-09-20.Retrieved2024-01-04.
- ^"LIVE. Windhoos laat spoor van vernieling achter in oosten van regio Mechelen - Steeds meer huizen onder water in Vlaams-Brabant".GVA.Gazet van Antwerpen.3 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 4 January 2024.Retrieved4 January2024.
- ^Additional references listed by the European Severe Storms Laboratory:
- "03/01/2024 – Tornade F2 à Putte".3 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2024.Retrieved10 March2024.
- "LIVE. Hevige regenval veroorzaakt wateroverlast in Vlaanderen".3 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 4 January 2024.Retrieved10 March2024.
- ""Oh my god!": waanzinnige beelden tonen hoe bewoners maar nipt kunnen vluchten voor rondvliegend puin door windhoos ".3 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2024.Retrieved10 March2024.
- "Muur ingestort, dak verdwenen, tuinhuis in puin: dronebeelden tonen ravage in Putte na doortocht windhoos".4 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 10 March 2024.Retrieved10 March2024.
- ^abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwBranches of theNational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration;National Weather Service;National Severe Storms Laboratory(2024)."Damage Assessment Toolkit".DAT.United States Department of Commerce.Archivedfrom the original on 2020-04-23.Retrieved2024-01-20.
- ^abNWS Damage Survey for 1/9/24 Tornado Event – Update #1(Public Information Statement). Tallahassee, Florida: National Weather Tallahassee, FL. January 11, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on January 11, 2024.RetrievedJanuary 11,2024– via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
- ^National Weather ServiceinColumbia, South Carolina(10 January 2024)."Bamberg EF-2 Tornado in Bamberg County, SC"(Public Information Statement).Iowa Environmental Mesonet.National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 11 January 2024.Retrieved11 January2024.
- ^"Amukan Puting Beliung Rusak 60 Rumah di Prajekan Bondowoso".18 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 24 January 2024.Retrieved24 January2024.
- ^"Kerusakan Akibat Puting Beliung di Bondowoso Terus Bertambah".20 January 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 24 January 2024.Retrieved24 January2024.
- ^"Satu Warga Tewas Tertimpa Seng Akibat Puting Beliung di Sidoarjo"(News article)(in Indonesian).Surabaya,East Java,Indonesia:Ngopibareng.id. 4 February 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 5 February 2024.Retrieved5 February2024.
- ^"NWS Damage Survey for 02/08/2024 Tornado Event"(Public Information Statement). Sullivan, Wisconsin: National Weather Service Sullivan, Wisconsin. February 9, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on March 18, 2024.RetrievedFebruary 9,2024– via Iowa Environmental Mesonet.
- ^The finalized damage survey by theNational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administrationby county impacted by the tornado:
- National Centers for Environmental Information;National Weather Service(16 May 2024)."Wisconsin Event Report: EF2 Tornado (Rock County)"(Press release).Storm Events Database.Asheville, North CarolinaandDousman, Wisconsin:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 16 May 2024.Retrieved17 May2024.
- National Centers for Environmental Information; National Weather Service (16 May 2024)."Wisconsin Event Report: EF1 Tornado (Dane County)"(Press release).Storm Events Database.Asheville, North CarolinaandDousman, Wisconsin:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 16 May 2024.Retrieved17 May2024.
- National Centers for Environmental Information; National Weather Service (16 May 2024)."Wisconsin Event Report: EF1 Tornado (Jefferson County)"(Press release).Storm Events Database.Asheville, North CarolinaandDousman, Wisconsin:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 16 May 2024.Retrieved17 May2024.
- ^COSTA, FABIO MARIA LOPES (2024-02-22)."Tornado in Bandung-Sumedang causes 706 buildings to be damaged".kompas.id(in Indonesian).Archivedfrom the original on 2024-02-22.Retrieved2024-02-22.
- ^"Bandung Experiences First F2 Tornado in Indonesia, Sign of Climate Change Extremes".Social Expat.2024-02-22.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-02-22.Retrieved2024-02-22.
- ^"BPBD Establishes Refugee Tents In 3 Bandung Districts Affected By Puting Beliung".VOI - Waktunya Merevolusi Pemberitaan.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-02-22.Retrieved2024-02-22.
- ^"RARO TORNADO PROVOCA ESTRAGOS NO INTERIOR DO NORDESTE DO BRASIL".22 February 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 23 February 2024.Retrieved23 February2024.
- ^abUS Department of Commerce, NOAA."February 27, 2024: Record Warmth Culminates in Evening Severe Storms With Large Hail and Several Tornadoes".weather.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-03-08.Retrieved2024-03-10.
- ^US Department of Commerce, NOAA."Severe Storms, High Winds, and Tornadoes - February 27, 2023".weather.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 2023-04-05.Retrieved2024-03-10.
- ^National Weather Service Chicago Illinois."NWS Damage Survey for 2/27/2024 Tornado Event Final Update".mesonet.agron.iastate.edu.Archivedfrom the original on 8 March 2024.Retrieved10 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Detroit/Pontiac Michigan."NWS Damage Survey for 02/28/24 Tornado Event".mesonet.agron.iastate.edu.Archivedfrom the original on 28 February 2024.Retrieved10 March2024.
- ^Kleist, Mary Kay; Terry, Jermont; Curran, Ed (February 28, 2024)."Severe storms bring tornadoes, hail to Chicago area and beyond as cold front pounds through - CBS Chicago".cbsnews.Archivedfrom the original on March 9, 2024.RetrievedMarch 9,2024.
- ^US Department of Commerce, NOAA."February 27, 2024: Record Warmth Culminates in Evening Severe Storms With Large Hail and Several Tornadoes".weather.gov.Archivedfrom the original on March 8, 2024.RetrievedMarch 9,2024.
- ^Powers, Sara (February 28, 2024)."National Weather Service confirms EF-2 tornado hit Grand Blanc - CBS Detroit".cbsnews.Archivedfrom the original on March 9, 2024.RetrievedMarch 9,2024.
- ^Erwin, Alyssa (March 4, 2024)."Waretech Industrial Park in Grand Blanc 'total loss' after tornado".ABC 12 WJRT-TV.Archivedfrom the original on March 9, 2024.RetrievedMarch 9,2024.
- ^Bowling, Erin (February 28, 2024)."Tornado in Marshall shocks residents, causing considerable damage".WILX.Archivedfrom the original on March 9, 2024.RetrievedMarch 9,2024.
- ^"'Sounded like a freight train': Cleanup continues after EF-2 tornado hits Grand Blanc, taking down trees and utility lines ".audacy.2024-02-28.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-03-10.Retrieved2024-03-10.
- ^Powers, Sara (2024-02-28)."National Weather Service confirms EF-2 tornado hit Grand Blanc - CBS Detroit".cbsnews.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-03-09.Retrieved2024-03-10.
- ^"National Weather Service confirms 11 tornadoes in Illinois, NW Indiana".ABC7 Chicago.2024-02-28.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-03-10.Retrieved2024-03-10.
- ^"NWS confirms 2 tornadoes in Dayton area following severe weather".28 February 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"Tornado damages homes, ruptures gas lines as rare February storm hits Michigan".28 February 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 28 February 2024.Retrieved28 February2024.
- ^"Sixth Ohio tornado now confirmed. See the paths they took during Wednesday's storms".The Columbus Dispatch.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-03-08.Retrieved2024-03-09.
- ^https://x /paulofdbarros/status/1764405870366986398
- ^https://x /1kGc9/status/1765066864219324838
- ^https://x /DisasterTrackHQ/status/1763970657430183968
- ^https:// youtube /watch?v=KTm2DgkXlrc
- ^https:// youtube /watch?v=TIqexoxaR1w
- ^https:// youtube /watch?v=FXwAEzbgM_A
- ^"Antalya'da hortum! Korku dolu anlar kamerada".Ensonhaber(in Turkish). 8 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 8 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"Antalya'da hortum felaketi! Tarım alanları zarar gördü".CNN(in Turkish). 5 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"Antalya'da hortum her yeri dağıttı! Zarar büyük".Milliyet(in Turkish). 5 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"Alanya'da hortum dehşeti!".Yeni Alanya(in Turkish). 6 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"Des vents de 115km/h font de nombreux dégâts à Villeneuve-sur-Lot".La Dépêche(in French). 5 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"TEMOIGNAGE." On s'est planqué sous la table, c'était d'une violence inouïe ": le passage d'une tornade à Cahors a fait de nombreux dégâts".La Dépêche(in French). 6 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^"Toitures envolées, tôles sur la voie ferrée, poteau tombé... Une tornade fait des dégâts au sud de Cahors".La Dépêche(in French). 6 March 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 9 March 2024.Retrieved9 March2024.
- ^Larrea, Manuel Á (April 5, 2024)."Radiografía del tornado de Córdoba: 220 km/h, 14 kilómetros de recorrido y doble trayectoria".Diario Córdoba.Archivedfrom the original on April 17, 2024.RetrievedApril 17,2024.
- ^Soriano Romero, J. de D., & Gutiérrez Rubio, D. (n.d.).Informe preliminar sobre la posibilidad de ocurrencia de tornado en municipios de Córdoba entre el 8 y el 9 de marzo de 2024.SINOBAS AEMET. https://sinobas.aemet.es/subidos/pdfs/1894-d16a76bea02a6082b6d4.pdf
- ^National Weather Service Tallahassee, Florida."NWS Damage Survey for 03/09/2024 Tornado Event".mesonet.agron.iastate.edu.Archivedfrom the original on 11 March 2024.Retrieved17 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Jacksonville, Florida."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/09/24 TORNADO EVENT IN NORTHWEST CLINCH AND NORTHWEST WARE COUNTIES (GA)".mesonet.agron.iastate.edu.Archivedfrom the original on 20 March 2024.Retrieved20 March2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Wednesday March 13, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 9 May 2024.Retrieved14 May2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Thursday March 14, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 10 May 2024.Retrieved14 May2024.
- ^National Weather Service Louisville, Kentucky."NWS Damage Survey for 3/14/24 Tornado Event".Archivedfrom the original on 24 March 2024.Retrieved24 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Wilmington, Ohio."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/14/2024 TORNADO EVENT".Archivedfrom the original on 17 March 2024.Retrieved17 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Northern Indiana."NWS Damage Survey for 03/14/2024 Tornado Event".Archivedfrom the original on 17 March 2024.Retrieved17 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Wilmington, Ohio."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/14/2024 TORNADO EVENT".Archivedfrom the original on 17 March 2024.Retrieved17 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Wilmington, Ohio."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/14/2024 TORNADO EVENT".Archivedfrom the original on 20 March 2024.Retrieved19 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Cleveland, Ohio."NWS Damage Survey for 03/14/2024 Tornado Event - Update #1".Archivedfrom the original on 15 March 2024.Retrieved15 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Wilmington, Ohio."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/14/2024 TORNADO EVENT".Archivedfrom the original on 20 March 2024.Retrieved19 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Wilmington, Ohio."NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 03/14/2024 TORNADO EVENT".Archivedfrom the original on 20 March 2024.Retrieved19 March2024.
- ^ab"Summary of March 14th 2024 Severe Storms (Updated 3/27: 2 Tornadoes)".weather.gov.National Weather Service Indianapolis IN.Archivedfrom the original on 27 March 2024.Retrieved11 April2024.
- ^"...NWS Damage Survey for 03/14/24 Tornado Event Update 3..."Iowa Environment Mesonet.National Weather Service Indianapolis IN.Archivedfrom the original on 14 May 2024.Retrieved14 May2024.
- ^National Weather Service Indianapolis, Indiana."...NWS Damage Survey for 03/14/24 Tornado Event Update 4..."Archivedfrom the original on 29 April 2024.Retrieved15 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Wilmington, Ohio."EF-2 Tornado Confirmed in Darke and Miami Counties in Ohio".Archivedfrom the original on 15 March 2024.Retrieved15 March2024.
- ^National Weather Service Little Rock, Arkansas."NWS Damage Survey for 3/14/24 Tornado Event".Archivedfrom the original on 15 March 2024.Retrieved15 March2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Friday March 15, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 16 March 2024.Retrieved14 May2024.
- ^"Phénomène venteux violent sur l'Ile d'Yeu".
- ^"Tempête Nelson: une blessée légère sur l'île d'Yeu et des forts coups de vent en Vendée".France 3 Pays de la Loire.March 28, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on March 29, 2024.RetrievedMarch 29,2024.
- ^"Tempête Nelson: une" mini-tornade "à l'île d'Yeu a touché une soixantaine de maisons".actu.fr.March 28, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on May 6, 2024.RetrievedApril 28,2024.
- ^Kumari, Sweety (31 March 2024)."IMD warns of more tornadoes in northern Bengal after 5 killed and over 100 injured in Jalpaiguri".The Indian Express.Archivedfrom the original on 1 April 2024.Retrieved1 April2024.
- ^"Archived copy".Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-17.Retrieved2024-04-13.
{{cite web}}:CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^Loh, Matthew (April 2, 2024)."3 people died after being ripped from their high-rise apartments by freak wind storms in China, local reports say".businessinsider.Business Insider.Archivedfrom the original on May 23, 2024.RetrievedMay 23,2024.
- ^Rukavina, Jennifer (6 April 2024)."NWS confirms at least 17 tornadoes touched down during national radar outage"(Newsarticle).The Paducah Sun.Paducah, Kentucky:Paxton Media Group&WPSD-TV.Archivedfrom the original on 6 April 2024.Retrieved6 April2024.
The Storm Prediction Center said this storm system was significant enough to be classified as a Derecho event: a type of severe weather event defined by a bowing line of damaging winds over a far distance.
- ^National Weather Service(April 2024)."Information for April 2nd Tornadoes and Wind Damage (Additional Surveys will be Conducted This Week)"(Historiograpicalweb page).Charleston, West Virginia:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 11 April 2024.Retrieved11 April2024.
A historic severe weather outbreak occurred on Tuesday, April 2nd, 2024…
- ^Marlene Lenthang; Kathryn Prociv (4 April 2024)."Deadly April storm batters Northeast, snarling travel and knocking out power to half a million".NBC News.Archivedfrom the original on 9 April 2024.Retrieved9 April2024.
- ^Appalachian Power Company (2 April 2024)."Storm and Outage Details: Appalachian Power Storm Response Update #1".Appalachian Power.Archivedfrom the original on 4 April 2024.
- ^"Major storm brings flash flooding, damaging winds to East Coast".ABC News.April 12, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on April 20, 2024.RetrievedApril 20,2024.
- ^National Centers for Environmental Information(April 2024)."U.S. Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters"(Press release).Events.Asheville, North Carolina,United States:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 15 April 2024.Retrieved15 April2024.
- ^"Landspout tornado spotted near Rusty Point on April 19th! These events, while not rare, go mostly unnoticed due to our topographically diverse area. Credit to Geremy Clarion who captured these pictures".National Weather Service.Archivedfrom the original on 26 April 2024.Retrieved26 April2024.
- ^Sistek, Scott (25 April 2024)."Rare tornado spotted in Alaska's Chugach State Park may only be state's 5th on record".FOX Weather.Archivedfrom the original on 26 April 2024.Retrieved26 April2024.
- ^National Weather Service(26 April 2024)."A violent tornado continues to impact areas south of Blair, just northwest of the Blair airport"(Post on𝕏).𝕏(FormerlyTwitter).National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 27 April 2024.Retrieved27 April2024.
- ^""Many houses are flattened" in Elkhorn as large tornado sweeps trough ".1011NOW. 26 April 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 27 April 2024.Retrieved27 April2024.
- ^"Clean-up, damage assessment underway in Omaha after major tornado outbreak".Yahoo News.2024-04-27.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-27.Retrieved2024-04-27.
- ^Press, Associated (2024-04-27)."Midwest tornadoes demolish homes, businesses in Nebraska and Iowa".New York Daily News.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-27.Retrieved2024-04-27.
- ^Parsons, McKenzy (April 26, 2024)."Eppley Airfield suffers major damage from tornado, no one was injured".KETVOmaha.RetrievedApril 27,2024.
- ^Writer, Marjie Ducey World-Herald Staff (2024-04-26)."'I was praying': Passenger looks outside airplane to see tornado at Eppley Airfield ".Omaha World-Herald.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-27.Retrieved2024-04-27.
- ^ab"Residents begin going through the rubble after tornadoes hammer parts of Nebraska and Iowa".AP News.2024-04-27.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-27.Retrieved2024-04-27.
- ^"The National Weather Service says six EF-2 tornadoes swept through Iowa Friday night".27 April 2024.Retrieved27 April2024.
- ^"PDS Tornado Warning for Pleasant Hill, IA as a large and dangerous tornado confirmed".twitter.26 April 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 3 May 2024.Retrieved26 April2024.
- ^"Storm Prediction Center Today's Reports".Storm Prediction Center. 26 April 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 27 April 2024.Retrieved27 April2024.
- ^"240427's Storm Reports".Storm Prediction Center.Archivedfrom the original on April 28, 2024.RetrievedApril 27,2024.
- ^"Tornado in Sulphur, Oklahoma".Mint News.2024-04-27.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-28.Retrieved2024-04-27.
- ^"NWS primarily tornado ratings".weather.gov.2024-05-02.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-04-27.Retrieved2024-05-02.
- ^Terry, Christian (2024-04-29)."Confirmed Trinity County tornado with 100mph winds and path the size of two football fields".KPRC.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-03.Retrieved2024-05-04.
- ^Sistek, Scott (2024-05-04)."Texas police officer dies from injuries sustained in Sunday tornado strike".FOX Weather.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-04.Retrieved2024-05-04.
- ^"Aerial photos show devastation left by a deadly tornado in China".NBC News. Associated Press. April 29, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on May 14, 2024.RetrievedMay 14,2024.
- ^Jones, Shayndel (April 30, 2024)."Extensive damage, 1 confirmed death from Westmoreland tornado".WIBW13.Archivedfrom the original on May 1, 2024.RetrievedMay 1,2024.
- ^"Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports".spc.noaa.gov.2024-04-30.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-01.Retrieved2024-04-30.
- ^"Tornadoes ripping through parts of Oklahoma".2024-04-30.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-01.Retrieved2024-04-30.
- ^"Powerful tornado was spotted north of Abilene".foxweather.2024-05-02.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-03.Retrieved2024-05-02.
- ^"Massive Tornado Ripping Through Southern Coke County".2024-05-03.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-04.Retrieved2024-05-03.
- ^Gilbert, Mary; Sutton, Joe (May 3, 2024)."Texas severe weather: At least 178 people rescued as rivers flood to Hurricane Harvey levels, with more rain forecasted".CNN.Archivedfrom the original on May 4, 2024.RetrievedMay 5,2024.
- ^Villasana, Joe (5 May 2024).""Clifton is an island": Strong storms overnight lead to widespread flooding in Bosque County ".KWTX.Archivedfrom the original on 7 May 2024.Retrieved7 May2024.
- ^"Update Report: Train Derailment near Clifton, TX (Ft Worth Subdivision) | Customer Notifications | BNSF".BNSF Railway.Archivedfrom the original on 8 May 2024.Retrieved8 May2024.
- ^"Service Adjustment: As of 8:25 PM CT, Texas Eagle Train 21/421 will terminate at Ft. Worth (FTW) due to severe weather conditions in the area. Bus transportation will be provided between Ft. Worth and San Antonio".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024."UPDATE: As of 11:58 pm CT, Due to severe weather conditions, Texas Eagle Train 22 is canceled between San Antonio (SAS) and Ft. Worth (FTW) and will originate at Ft. Worth. Bus transportation will be provided between San Antonio and Ft. Worth".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024."UPDATE: As of 11:33 pm CT, Texas Eagle Train 21, which departed Chicago (CHI) on 5/6, will operate a bus bridge between Ft. Worth (FTW) and Temple (TPL) due to previous weather events".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024."UPDATE: As of 11:45 pm CT, Texas Eagle Train 22, which departed San Antonio (SAS) on 5/7, will operate a bus bridge between Temple (TPL) and Ft. Worth (FTW) due to previous weather events".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024."UPDATE: As of 11:46 pm CT, Texas Eagle Train 422, which departed Los Angeles (LAX) on 5/5, will operate a bus bridge between Temple (TPL) and Ft. Worth (FTW) due to previous weather events".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024."Service Adjustment: As of 10:25 pm CT, due to previous weather events, Train 21/421 which departed Chicago (CHI) on 5/7, will have bus transportation provided between Ft. Worth (FTW) and Temple (TPL), at which operation will resume to San Antonio (SAS) using new train equipment".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024."Service Adjustment: As of 11:58 pm CT, due to previous weather events, Train 22, scheduled to depart Chicago (CHI) on 5/8, will have bus transportation provided between (TPL) and Fort Worth (FTW) at which operation will resume to Chicago (CHI) using new train equipment".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024.
- ^"Damage surveys continue across Osage County this afternoon. Currently, EF4 damage has been found southwest of Barnsdall. Still a long day of surveying with this storm and lots more to evaluate. #okwx".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on 7 May 2024.Retrieved7 May2024.
- ^"NEW VIDEO: Here's a first look at some of the damage left behind after a #tornado hit Barnsdall, OK on Monday evening. We'll have continued coverage on WeatherNation. #OKwx".twitter.X (formerly Twitter).Archivedfrom the original on 7 May 2024.Retrieved7 May2024.
- ^"LIVE UPDATES: 1 Killed After Tornado Hits Barnsdall; Heavy Rains Cause Flash Flood Warnings".newson6.May 7, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on May 7, 2024.RetrievedMay 7,2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Monday May 06, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 9 May 2024.Retrieved10 May2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Tuesday May 07, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 10 May 2024.Retrieved10 May2024.
- ^"One person dead in Maury County as severe storms continue through Middle Tennessee".News Channel 5 Nashville (WTVF).8 May 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 8 May 2024.Retrieved9 May2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Wednesday May 08, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 9 May 2024.Retrieved10 May2024.
- ^Farinacci, Alexis (May 8, 2024)."METS, CARDINALS SERIES FINALE POSTPONED, WILL BE MADE UP IN AUGUST".Mets Memorized Online.Archivedfrom the original on May 9, 2024.RetrievedMay 9,2024.
- ^ab"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Thursday May 09, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 14 May 2024.Retrieved14 May2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Tallahassee, Florida (May 12, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for the May 10, 2024 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 12, 2024.RetrievedMay 12,2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Friday May 10, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 14 May 2024.Retrieved14 May2024.
- ^https://x /sigtor2019/status/1790050762174636255?s=46&t=qS0n16XhYMOv-kF6m_Tg1g
- ^"Relief payments available, health warning in place after tornado tore through WA town".9news.au.May 12, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on May 13, 2024.RetrievedMay 13,2024.
- ^"Two hospitalised as tornado rips through WA's south-west, tearing off roofs and damaging property".ABC News.May 10, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-12.Retrieved2024-05-13– via abc.net.au.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Monday May 13, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 15 May 2024.Retrieved15 May2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Lake Charles, Louisiana (May 14, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/13/24 Tornado Event - Updated to Lower Wind Rating to an EF-2 of 120 mph(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 14, 2024.RetrievedMay 14,2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Lake Charles, Louisiana (May 14, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/13/24 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 14, 2024.RetrievedMay 14,2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Lake Charles, Louisiana (May 14, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/13/24 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 14, 2024.RetrievedMay 14,2024.
- ^Figliuolo, Miriam (2024-05-17)."Tromba d'aria su Santa Vittoria, al cimitero si spezzano le lapidi".Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-21.Retrieved2024-05-21.
- ^@PavanFederico00 (2024-05-19)."Thursday's tornadoes have been rated! Both were rainwrapped, but both managed to betray themselves by leaving long tracks across fields. Here are the main findings"(Tweet).Retrieved2024-05-21– viaTwitter.
- ^"EF-1 tornado confirmed near Cypress, another tornado strikes SW region of Waller Co., NWS says",abc13,KTRK-TVABC 13, May 17, 2024,archivedfrom the original on May 18, 2024,retrievedMay 18,2024
- ^National Weather Service in New Orleans, Louisiana (May 17, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/16/2024 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 18, 2024.RetrievedMay 17,2024.
- ^At least 7 dead after hurricane-force winds pound Houston as power outages persist amid rising temperatures,CNN, May 17, 2024,retrievedMay 18,2024[permanent dead link]
- ^"Storm Prediction Center 240519's Storm Reports".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 20 May 2024.Retrieved20 May2024.
- ^"National Weather Service Damage Surveys Ongoing".National Weather Service Norman, Oklahoma.20 May 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 20 May 2024.Retrieved20 May2024.
- ^"Storm Prediction Center May 21, 2024, 0600 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook".spc.noaa.gov.Storm Prediction Center. 2024-05-21.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-22.Retrieved2024-05-22.
- ^Guyer, Jared (2024-05-21)."Storm Prediction Center PDS Tornado Watch 277".spc.noaa.gov.Storm Prediction Center.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-22.Retrieved2024-05-22.
- ^Eller, Donnelle; Kealey, Kate."Watch: Drone video shows destructive tornado topple wind turbines near Greenfield, Iowa".Des Moines Register.RetrievedMay 23,2024.
- ^"Tornado warning update for Cass & other counties".KJAN.2024-05-21.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-21.Retrieved2024-05-21.
- ^National Weather Service in Des Moines, Iowa (May 23, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/21/2024 Tornado Event Update #2(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 23, 2024.RetrievedMay 23,2024.
- ^Harris, Tim; Wesner Childs, Jan."5 Dead, At Least 35 Hurt Following Iowa Tornadoes".The Weather Channel.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-23.RetrievedMay 23,2024.
- ^"Flexible Array of Radars and Mesonets (FARM) statement concerning preliminary peak wind speed determinations based on Doppler On Wheels (DOW) data obtained in the Greenfield, Iowa tornado of 21 May 2024"(PDF).Illinois edu.23 June 2024.Retrieved24 June2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Fort Worth, Texas (May 31, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for May 25th Tornado Event - Update #3(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.RetrievedMay 31,2024.
- ^"Seven dead, including two children, after tornado warning in Cooke and Denton counties".nbcdfw.26 May 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 26 May 2024.Retrieved26 May2024.
- ^"Texas Tornado Kills At Least 5 In Valley View - Videos from The Weather Channel".The Weather Channel.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-26.Retrieved2024-05-26.
- ^Kliewer, Addison (May 26, 2024)."2 confirmed dead this weekend in northeast Oklahoma tornadoes: What we know".KOCO.Archivedfrom the original on May 26, 2024.RetrievedMay 26,2024.
- ^abBrinkley, Rhett (May 26, 2024)."Storms kill at least 5 in north Arkansas overnight, more in Texas and Oklahoma".Arkansas Times.Archivedfrom the original on May 26, 2024.RetrievedMay 26,2024.
- ^"Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 26 May 2024.Retrieved26 May2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Little Rock, Arkansas (May 27, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/26/24 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on May 28, 2024.RetrievedMay 27,2024.
- ^"Mueren 2 personas en caída de barda tras tornado en Toluca".El Mañana(in Mexican Spanish). May 23, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-24.Retrieved2024-05-24.
- ^"Tornado in Toluca leaves 2 dead, one of them a US citizen".Mexico News Daily.2024-05-24.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-05-25.Retrieved2024-05-25.
- ^May 30, 2024 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook,Storm Prediction Center, May 30, 2024,archivedfrom the original on May 30, 2024,retrievedJune 5,2024
- ^National Weather Service in Midland, Texas (June 1, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for Midland and Upton County Tornadoes and Severe Wind Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on June 2, 2024.RetrievedJune 1,2024.
- ^Tornado talk with CBS7′s meteorologist Justin Lopez,KOSA-TV, May 31, 2024,archivedfrom the original on June 5, 2024,retrievedJune 5,2024
- ^National Weather Service in Shreveport, Louisiana (June 3, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 05/30/24 Severe Weather Event - Update # 1(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on June 4, 2024.RetrievedJune 4,2024.
- ^"Storm Prediction Center 240602's Storm Reports".spc.noaa.gov.Archivedfrom the original on 4 June 2024.Retrieved4 June2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Midland/Odessa, Texas (June 4, 2024).On June 3rd, the National Weather Service sent a survey team to investigate a tornado report from severe weather that impacted portions of Terrell County on June 2nd, including the town of Sanderson(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on June 4, 2024.RetrievedJune 4,2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Rapid City, South Dakota (June 3, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 06/02/2024 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on June 3, 2024.RetrievedJune 3,2024.
- ^National Weather Service in Amarillo, Texas (June 3, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 06/02/2024 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.Archivedfrom the original on June 3, 2024.RetrievedJune 3,2024.
- ^"Katastrofalne posljedice nevremena: Na 20 kuća uništen krov, mještani bez struje".
- ^"Dvadesetak kuća ostalo bez krova u Mišinom Hanu".
- ^"Nevrijeme u Banjaluci otkidalo krovove: Pogledajte štetu u Mišinom Hanu".
- ^"oThongathi tornado rated EF3 on the Enhanced Fujita scale"(PDF).Pretoria:South African Weather Service. 12 June 2024.Archived(PDF)from the original on 13 June 2024.Retrieved13 June2024.
- ^Rall, Se-Anne."eThekwini says estimated cost of damage from Tongaat tornado valued at R481.7 million".IOL.
- ^Rall, Se-Anne (June 4, 2024)."Tongaat residents pick up the pieces after Monday's tornado, death toll climbs to 11".IOL.Archivedfrom the original on June 4, 2024.RetrievedJune 4,2024.
- ^Marriah-Maharaj, Jolene (June 6, 2024)."Tongaat tornado: Death toll rises to 12, over 1,200 people are homeless".IOL.RetrievedJune 9,2024.
- ^South African Weather Service(June 12, 2024)."oThongathi tornado rated EF3 on the Enhanced Fujita Scale".Twitter.RetrievedJune 12,2024.
- ^"Tornado hits Michigan without warning, killing toddler, while twister in Maryland injures 5".Associated Press. June 6, 2024.Archivedfrom the original on June 6, 2024.RetrievedJune 6,2024.
- ^National Weather Serviceof Detroit/Pontiac MI (5 June 2024)."NWS Damage Survey for 06/05/24 for the Livonia Tornado".Iowa Environmental Mesonet(Public Information Statement).White Lake, Michigan:National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.Archivedfrom the original on 6 June 2024.Retrieved6 June2024.
- ^Joyce, Elijah (5 June 2024)."#BREAKING: 2024 Plymouth–Livonia Tornado Fatality Total: 1"(Post on𝕏).𝕏(FormerlyTwitter).@WXFatalities.Archivedfrom the original on 6 June 2024.Retrieved6 June2024.
- ^abc"Storm Prediction Center 20240605's Storm Reports".spc.noaa.gov.National Weather Service.Retrieved7 June2024.
- ^National Weather Service forecast office in Baltimore, Maryland/Washington DC (June 6, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 06/05/24 Tornado Even(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.RetrievedJune 7,2024.
- ^National Weather Service forecast office in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (June 6, 2024).NWS Damage Survey for 06/06/24 Tornado Event(Report). Iowa Environmental Mesonet.RetrievedJune 6,2024.
- ^https:// instagram /real_climate_news/reel/C8MjzKpN4an/
- ^https:// youtube /watch?v=aqXDXrRw2Js
- ^https://eswd.eu/
- ^"...NWS Damage Survey for Tuesday, June 25, 2024 Western Sandhills Tornado Event..."Iowa Environment Mesonet.National Weather Service North Platte NE.Retrieved28 June2024.
- ^Smith, Mike (2024-06-26)."Town Destroyed -- National Weather Service Misses Another Strong Tornado".Mike Smith Enterprises Blog.Archivedfrom the original on 2024-06-29.Retrieved2024-06-29.
- ^Mullen, Maureen (June 26, 2024)."Blue Jays-Red Sox series finale postponed due to weather, will be part of split DH in August".The Washington Post.Washington Post.RetrievedJune 30,2024.
{{cite news}}:CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^2 dead after severe weather tears across Northeast downing trees, knocking out power,Fox Weather, June 27, 2024
- ^https://std.stheadline /daily/article/2608342/%E6%97%A5%E5%A0%B1-%E4%B8%AD%E5%9C%8B-%E5%B1%B1%E6%9D%B1%E6%BE%A4%E9%BE%8D%E6%8D%B2%E9%A2%A85%E6%AD%BB83%E5%82%B7-2820%E6%88%BF%E5%B1%8B%E5%8F%97%E6%90%8D
- ^https://x /Ericwang1101/status/1809199010991010052
- ^https://x /Ericwang1101/status/1809132285700288949
- ^https:// telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2024/07/06/video-tornado-china-five-killed-dongming-shangdong/
- ^https://edition.cnn /2024/07/06/china/china-shandong-tornado-dead-injured-intl/index.html
- ^https://edition.cnn /2024/07/06/world/video/tornado-china-shandong-ldn-digvid
- ^https://x /Ericwang1101/status/1809174580675936466
- ^https://x /Ericwang1101/status/1809186552167444519
- ^https://x /Ericwang1101/status/1809202594843373944
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Sunday July 07, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Retrieved8 July2024.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Monday July 08, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Retrieved9 July2024.
- ^"1 person dies when Beryl leaves trail of damage across the ArkLaTex".KLSA.2024-07-08.Retrieved2024-07-08.
- ^"SPC Severe Weather Event Review for Tuesday July 09, 2024".spc.noaa.gov.Retrieved11 July2024.
- ^National Weather Service Paducah, KY (July 10, 2024)....NWS DAMAGE SURVEY FOR 07/09/2024 TORNADO EVENT...(Report). National Weather Service.RetrievedJuly 10,2024.
- ^"Storm Prediction Center Today's Storm Reports".spc.noaa.gov.Retrieved11 July2024.