Respiratory center
| Respiratory center | |
|---|---|
 Respiratory groups in the respiratory center and their influence | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D012125 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Therespiratory centeris located in themedulla oblongataandpons,in thebrainstem.The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups ofneurons,two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal respiratory group, and the ventral respiratory group. In the pons, the pontine respiratory group includes two areas known as the pneumotaxic center and the apneustic center.
The respiratory center is responsible for generating and maintaining the rhythm of respiration, and also of adjusting this inhomeostaticresponse to physiological changes. The respiratory center receives input fromchemoreceptors,mechanoreceptors,thecerebral cortex,and thehypothalamusin order to regulate the rate and depth of breathing. Input is stimulated by altered levels ofoxygen,carbon dioxide,andblood pH,byhormonal changes relating to stressand anxiety from the hypothalamus, and also by signals from the cerebral cortex to give aconscious controlof respiration.
Injury to respiratory groups can cause various breathing disorders that may requiremechanical ventilation,and is usually associated with a poor prognosis.
Respiratory groups
[edit]The respiratory center is divided into three major groups, two in the medulla and one in the pons. The two groups in the medulla are thedorsal respiratory groupand theventral respiratory group.In the pons, thepontine respiratory groupis made up of two areas – the pneumotaxic center and the apneustic center. The dorsal and ventral medullary groups control the basic rhythm of respiration.[1][2]The groups are paired with one on each side of the brainstem.[3]
Dorsal respiratory group
[edit]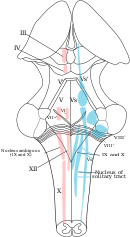
The dorsal respiratory group (DRG) has the most fundamental role in the control of respiration, initiating inspiration (inhalation). The DRG is a collection of neurons forming an elongated mass that extends most of the length of the dorsal medulla. They are near to thecentral canalof thespinal cord,and just behind the ventral group. They set and maintain therate of respiration.[4][5]
Most of the neurons are located in thenucleus of the solitary tract.Other important neurons are found in the adjacent areas including the reticular substance of the medulla. The solitary nucleus is the end-point for sensory information arriving from the pontine respiratory group, and from twocranial nerves– thevagus nerve,and theglossopharyngeal nerve.The solitary nucleus sends signals to the respiratory center fromperipheral chemoreceptors,baroreceptors,and other types of receptors in thelungsin particular thestretch receptors.Thus, the dorsal respiratory group is seen as an integrating center that gives the ventral respiratory group output to modify the breathing rhythm.[4][5]
Ventral respiratory group
[edit]The VRG maintains a constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration.[6]
In the medulla, the ventral respiratory group (VRG) consists of four groups of neurons that make up theexhalation(expiratory) area of respiratory control. This area is in the ventrolateral part of the medulla, about 5 mm anterior and lateral to the dorsal respiratory group. The neurons involved include those in thenucleus ambiguus,the nucleus retroambiguus, and theinterneuronsin thepre-Bötzinger complex.
The VRG contains both inspiratory and expiratory neurons.[7][4]The ventral respiratory group of neurons are active in forceful breathing and inactive during quiet, restful respirations.[1]The VRG sends inhibitory impulses to the apneustic center.
Pontine respiratory group
[edit]In thepontine tegmentumin the pons, the pontine respiratory group (PRG) includes the pneumotaxic and apneustic centers. These have connections between them, and from both to thesolitary nucleus.[8]
Pneumotaxic center
[edit]The pneumotaxic center is located in the upper part of the pons. Its nuclei are thesubparabrachial nucleusand themedial parabrachial nucleus.[9]The pneumotaxic center controls both the rate and the pattern of breathing. The pneumotaxic center is considered anantagonistto the apneustic center (which produces abnormal breathing during inhalation), cyclically inhibiting inhalation. The pneumotaxic center is responsible for limiting inspiration, providing aninspiratory off-switch(IOS).[10]It limits the burst ofaction potentialsin thephrenic nerve,effectively decreasing thetidal volumeand regulating therespiratory rate.Absence of the center results in an increase in depth of respiration and a decrease in respiratory rate.
The pneumotaxic center regulates the amount of air that can be taken into the body in each breath. The dorsal respiratory group hasrhythmic bursts of activitythat are constant in duration and interval.[11]When a faster rate of breathing is needed the pneumotaxic center signals the dorsal respiratory group to speed up. When longer breaths are needed the bursts of activity are elongated. All the information that the body uses to help respiration happens in the pneumotaxic center. If this was damaged or in any way harmed it would make breathing almost impossible.
One study on this subject was on anaesthetized paralyzed cats before and after bilateralvagotomy.Ventilation was monitored in awake and anaesthetized cats breathing air or CO2.Ventilation was monitored both before and after lesions to the pneumatic center region and after subsequent bilateral vagotomy. Cats with pontine lesions had a prolonged inhalation duration.[12]In cats, after anaesthesia and vagotomy, pontine transaction has been described as evoking a long sustained inspiratory discharges interrupted by short expiratory pauses.[jargon]In rats on the other hand, after anaesthesia, vagotomy and pontine transaction, this breathing pattern was not observed, either in vivo or in vitro. These results suggest interspecies differences between rat and cat in the pontine influences on the medullary respiratory center.[13]
Apneustic center
[edit]The apneustic center of the lower pons appears to promote inhalation by constant stimulation of the neurons in the medulla oblongata. The apneustic center sends signals to the dorsal group in the medulla to delay the 'switch off, theinspiratory off switch(IOS) signal of the inspiratory ramp provided by the pneumotaxic center. It controls the intensity of breathing, giving positive impulses to the neurons involved with inhalation. The apneustic center is inhibited by pulmonary stretch receptors and also by the pneumotaxic center. It also discharges an inhibitory impulse to the pneumotaxic center.
Respiratory rhythm
[edit]Breathing is the repetitive process of bringing air into the lungs and taking waste products out. The oxygen brought in from the air is a constant, on-going need of an organism to maintain life. This need is still there during sleep so that the functioning of this process has to be automatic and be part of theautonomic nervous system.The in-breath is followed by the out-breath, giving the respiratory cycle of inhalation and exhalation. There are three phases of the respiratory cycle: inspiration, post-inspiration or passive expiration, and late or active expiration.[14][15]
The number of cycles per minute is therespiratory rate.The respiratory rate is set in the respiratory center by the dorsal respiratory group, in the medulla, and these neurons are mostly concentrated in thesolitary nucleusthat extends the length of the medulla.[4]
The basic rhythm of respiration is that of quiet, restful breathing known aseupnea.Quiet breathing only requires the activity of the dorsal group which activates thediaphragm,and theexternal intercostal muscles.Exhalation is passive and relies on theelastic recoil of the lungs.When the metabolic need for oxygen increases, inspiration becomes more forceful and the neurons in the ventral group are activated to bring aboutforceful exhalation.[1]Shortness of breathis termed dyspnea – the opposite of eupnea.
Clinical significance
[edit]Depression of the respiratory center can be caused by:brain trauma,brain damage,abrain tumour,orischemia.A depression can also be caused bydrugsincludingopioids,andsedatives.
The respiratory center can be stimulated byamphetamine,to produce faster and deeper breaths.[16]Normally at therapeutic doses, this effect is not noticeable, but may be evident when respiration is already compromised.[16]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^abcTortora, G; Derrickson, B (2011).Principles of anatomy & physiology(13th. ed.). Wiley. pp. 906–909.ISBN9780470646083.
- ^Pocock, Gillian; Richards, Christopher D. (2006).Human physiology: the basis of medicine(3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 332.ISBN978-0-19-856878-0.
- ^Saladin, Kenneth (2012).Anatomy Physiology The Unity of Form and Function.McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 868–871.ISBN9780073378251.
- ^abcdHall, John (2011).Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology(12th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 505–510.ISBN978-1-4160-4574-8.
- ^abSaladin, K (2011).Human anatomy(3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 646–647.ISBN9780071222075.
- ^Betts, J. Gordon; Young, Kelly A.; Wise, James A.; Johnson, Eddie; Poe, Brandon; Kruse, Dean H.; Korol, Oksana; Johnson, Jody E.; Womble, Mark (2022-04-20)."22.3 The Process of Breathing - Anatomy and Physiology 2e | OpenStax".openstax.org.Retrieved2024-03-20.
- ^Koeppen, Bruce M.; Stanton, Bruce A. (18 January 2017).Berne and Levy Physiology E-Book.Elsevier Health Sciences.ISBN9780323523400.
- ^Song, G; Poon, CS (15 November 2004). "Functional and structural models of pontine modulation of mechanoreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes".Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology.143(2–3): 281–92.doi:10.1016/j.resp.2004.05.009.PMID15519561.S2CID38265906.
- ^Song, Gang; Yu, Yunguo; Poon, Chi-Sang (2006)."Cytoarchitecture of Pneumotaxic Integration of Respiratory and Nonrespiratory Information in the Rat".Journal of Neuroscience.26(1): 300–10.doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3029-05.2006.PMC6674322.PMID16399700.
- ^Dutschmann, M; Dick, TE (October 2012)."Pontine mechanisms of respiratory control".Comprehensive Physiology.2(4): 2443–69.doi:10.1002/cphy.c100015.PMC4422496.PMID23720253.
- ^Dutschmann, Mathias (2011).Comprehensive Physiology.[Bethesda, Md.]: John Wiley and Sons.ISBN978-0-470-65071-4.
- ^Gautier, H; Bertrand, F (1975). "Respiratory effects of pneumatic center lesions and subsequent vagotomy in chronic cats".Respiration Physiology.23(1): 71–85.doi:10.1016/0034-5687(75)90073-0.PMID1129551.
- ^Monteau, R.; Errchidi, S.; Gauthier, P.; Hilaire, G.; Rega, P. (1989). "Pneumotaxic centre and apneustic breathing: Interspecies differences between rat and cat".Neuroscience Letters.99(3): 311–6.doi:10.1016/0304-3940(89)90465-5.PMID2725956.S2CID42790256.
- ^Mörschel, M; Dutschmann, M (12 September 2009)."Pontine respiratory activity involved in inspiratory/expiratory phase transition".Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences.364(1529): 2517–26.doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0074.PMC2865127.PMID19651653.
- ^Ramirez, JM; Dashevskiy, T; Marlin, IA; Baertsch, N (December 2016)."Microcircuits in respiratory rhythm generation: commonalities with other rhythm generating networks and evolutionary perspectives".Current Opinion in Neurobiology.41:53–61.doi:10.1016/j.conb.2016.08.003.PMC5495096.PMID27589601.
- ^abWestfall DP, Westfall TC (2010)."Miscellaneous Sympathomimetic Agonists".In Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC (eds.).Goodman & Gilman's Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics(12th ed.). New York, USA: McGraw-Hill.ISBN9780071624428.
Further reading
[edit]- Levitzky, Michael G. (2002).Pulmonary Physiology(6th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 193–4.ISBN978-0-07-138765-1.
- Costanzo, Linda S. (2006).Physiology(3rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA:Elsevier.p. 224.ISBN978-1-4160-2320-3.
- Shannon, Roger; Baekey, David M.; Morris, Kendall F.; Nuding, Sarah C.; Segers, Lauren S.; Lindsey, Bruce G. (2004). "Pontine respiratory group neuron discharge is altered during fictive cough in the decerebrate cat".Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology.142(1): 43–54.doi:10.1016/j.resp.2004.05.002.PMID15351303.S2CID8425115.
